Article
Open Access
Clinical effect of hydrocolloid dressings in prevention and treatment of infant diaper rash
- Authors:
- Xiao‑Ping Qiao
- Yan‑Zhen Ge
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liaocheng People's Hospital, Liaocheng, Shandong 252000, P.R. China, Department of Pediatrics, Liaocheng People's Hospital, Liaocheng, Shandong 252000, P.R. China
-
Pages:
3665-3669
|
Published online on:
October 27, 2016
https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3848
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
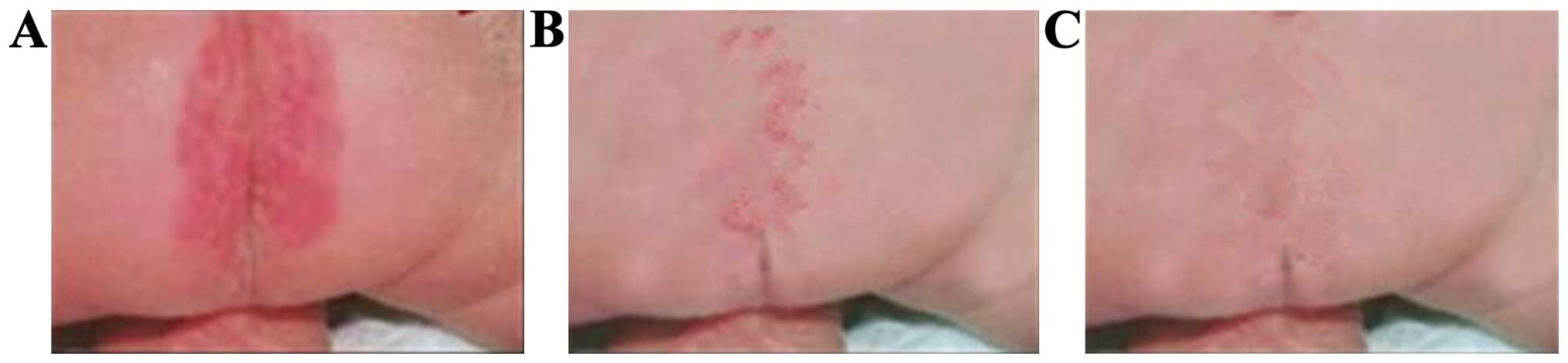
The aim of the study was to investigate the application of hydrocolloid dressings in the prevention and treatment of infant diaper rash. A total of 210 infants with diaper rash were included in the study and randomized into 3 groups of 70 infants. Infants in group A received hydrocolloid dressings and individualized nursing; infants in group B received mupirocin plaster and topical application of pearl powder as well as routine nursing; and infants in group C received zinc oxide plaster and routine nursing. The clinical efficacy, incidence of adverse events, time to resolution of diaper rash, hospitalization duration, mean cost and satisfaction of nursing were compared between the 3 groups. After 1 cycle of treatment and nursing, the difference in the healing rate of mild diaper rash between groups A, B and C was significant (P<0.05), with the best healing rate in group A. Differences in the healing rate of grade I and II diaper rash between groups A, B and C was significant (P<0.05), with the best healing rate in group A. The incidence of adverse events in infants between groups A, B and C were significantly different (P<0.05), with the lowest incidence in group A (2.9%). The time to resolution of diaper rash, hospitalization duration and cost in infants were not significantly different (P<0.05). The satisfaction rate of nursing for the parents of groups A, B and C was 98.6, 87.1 and 80.0%, respectively (P<0.05). Hydrocolloid dressings combined with individualized nursing may prevent and treat infant diaper rash effectively, decrease the incidence of adverse reactions significantly, shorten time to resolution of diaper rash and hospitalization duration, reduce mean hospitalization cost, improve parent satisfaction and promote nursing‑patient harmony. Thus, this method of treatment was worthy of clinical application.
View References
|
1
|
Adib-Hajbaghery M, Mahmoudi M and
Mashaiekhi M: Shampoo-clay heals diaper rash faster than calendula
officinalis. Nurs Midwifery Stud. 3:e14180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gaunder BN and Plummer E: Diaper rash:
Managing and controlling a common problem in infants and toddlers.
J Pediatr Health Care. 1:26–34. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shimizu M, Sakai S, Tatekawa Y, Ishikawa
S, Miyamoto M and Yachie A: An infant with PELVIS (perineal
hemangioma, external genital malformations, lipomyelomeningocele,
vesicorenal abnormalities, imperforate anus, and skin tag) syndrome
misdiagnosed as diaper rash. J Pediatr. 165:6342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Umachitra G: Disposable baby diaper - a
threat to the health and environment. J Environ Sci Eng.
54:447–452. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mohamadi J, Motaghi M, Panahi J, Havasian
MR, Delpisheh A, Azizian M and Pakzad I: Anti-fungal resistance in
candida isolated from oral and diaper rash candidiasis in neonates.
Bioinformation. 10:667–670. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shin HT: Diagnosis and management of
diaper dermatitis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 61:367–382. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li CH, Zhu ZH and Dai YH: Diaper
dermatitis: A survey of risk factors for children aged 1–24 months
in China. J Int Med Res. 40:1752–1760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ratliff C and Dixon M: Treatment of
incontinence-associated dermatitis (diaper rash) in a neonatal
unit. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 34:158–161; discussion
161–162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mak SS, Molassiotis A, Wan WM, Lee IY and
Chan ES: The effects of hydrocolloid dressing and gentian violet on
radiation- induced moist desquamation wound healing. Cancer Nurs.
23:220–229. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martin FT, O'Sullivan JB, Regan PJ, McCann
J and Kelly JL: Hydrocolloid dressing in pediatric burns may
decrease operative intervention rates. J Pediatr Surg. 45:600–605.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Block SL: Perianal dermatitis: Much more
than just a diaper rash. Pediatr Ann. 42:12–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Levy M: Diaper rash syndrome or
dermatitis. Cutis 67 (Suppl 5). 37–38. 2001.
|
|
13
|
Baldwin S, Odio MR, Haines SL, O'Connor
RJ, Englehart JS and Lane AT: Skin benefits from continuous topical
administration of a zinc oxide/petrolatum formulation by a novel
disposable diaper. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 15 (Suppl 1). 5–11.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y: Clinical application of Mupirocin
plaster in the treatment of pediatric diaper rash. Shanxi J Med.
42:2692013.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Tan F, Wang K and Huang Z: The application
of hydrocolloid dressings in the nursing of pressure sores. Nurs J
PLA. 28:41–42. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Michel JM, Couilliet D, Bleicher R, Bloch
B, Bochaton C and Groell S: Membres Du Groupe Plaies et
Cicatrisation Des Hôpitaux Civils de Colmar: Hydrocolloid
dressings. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 129:1326–1327. 2002.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lohmann I: Guidelines for treatment and
prevention of diaper rash. Kinderkrankenschwester. 24:481–482.
2005.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ying L: Sesame oil in the treatment of
infant diaper rash. Nurs Res. 24:5672010.
|
|
19
|
Jing L and Xia L: The treatment and
nursing of 136 cases of infant buttock erythema. Chinese J Misdiag.
10:72352010.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Lin R: Clinical nursing of neonatal
buttock erythema. Adv Med. 5:2732015.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Wan H: The efficacy of Kanghuier
transparent tape in severe neonatal buttock erythema. Chinese J
Prac Nurs. 31:662015.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Yuan Y and Li X: The effect of delicate
nursing in neonatal diaper rash. Chinese Contemp Med. 21:121–122.
2014.(In Chinese).
|