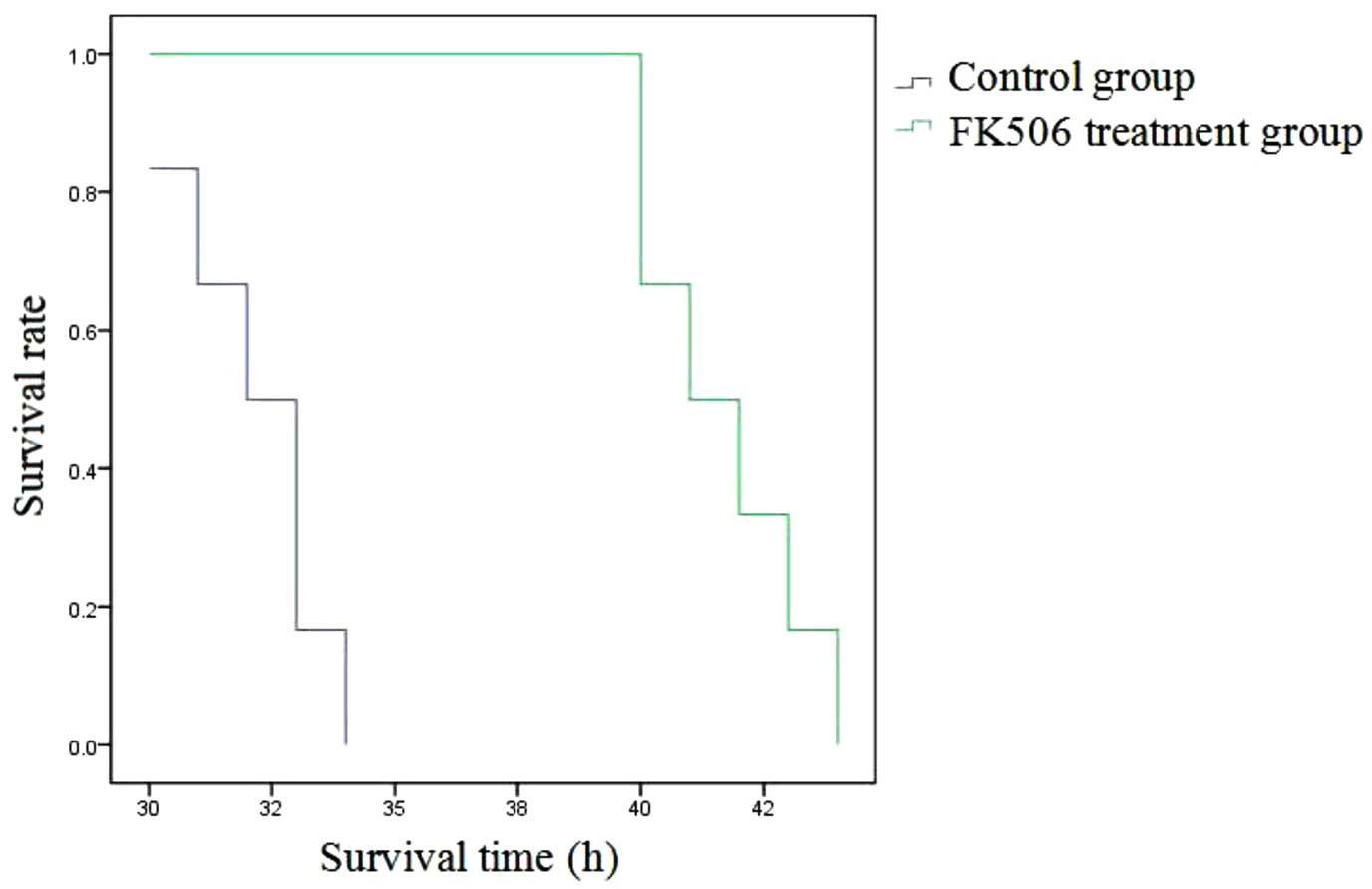
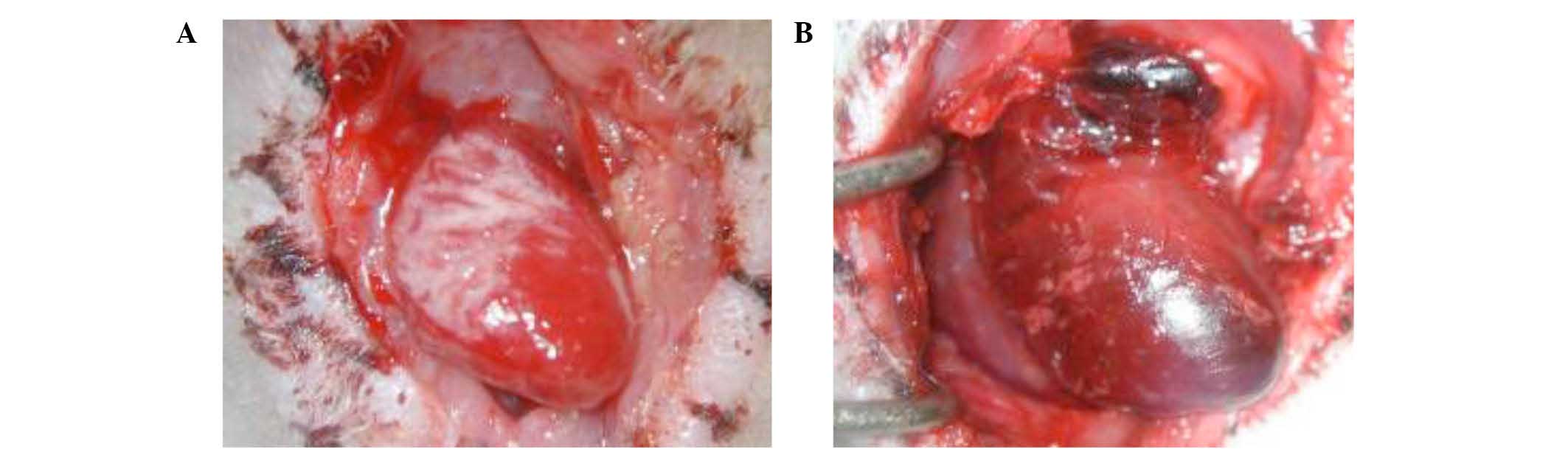
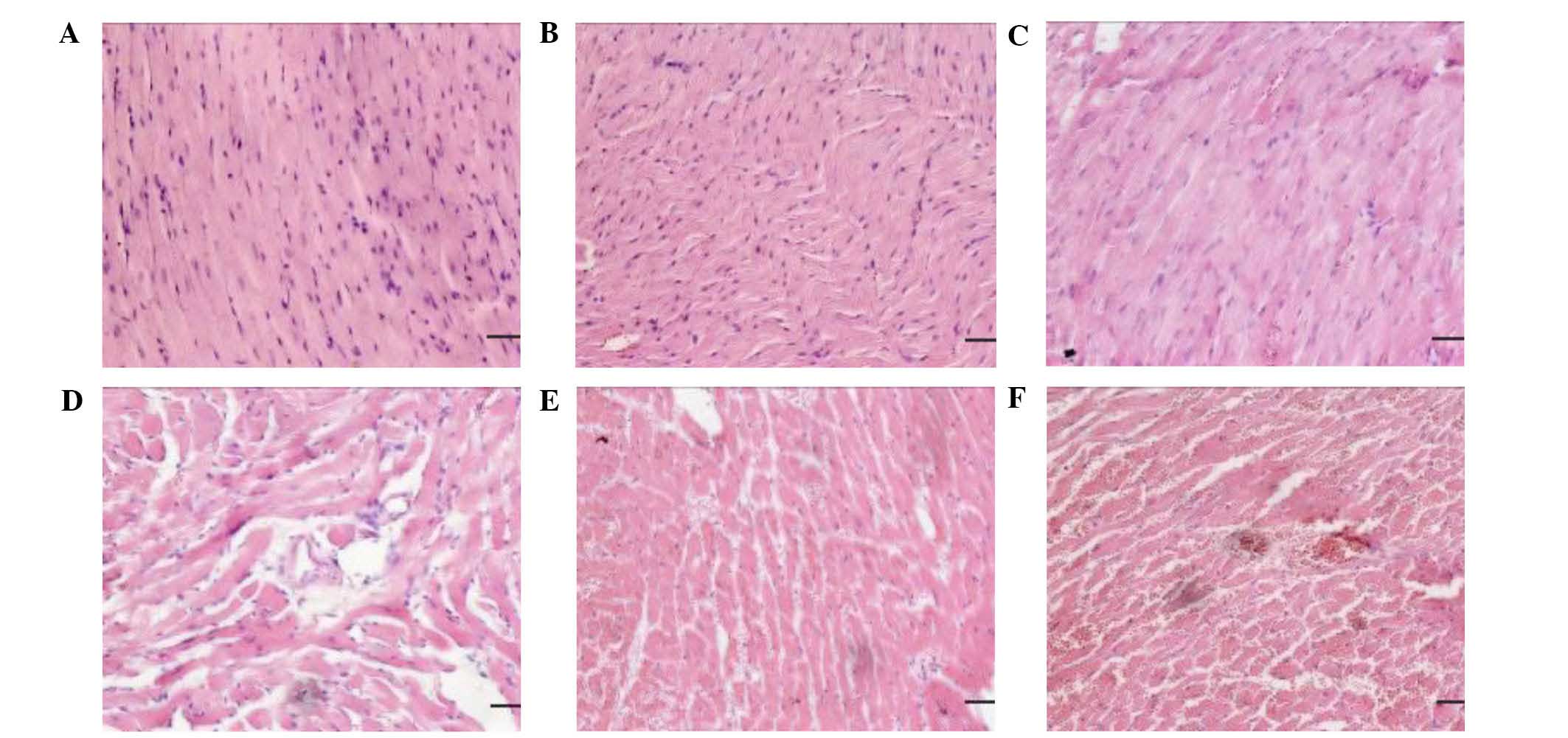
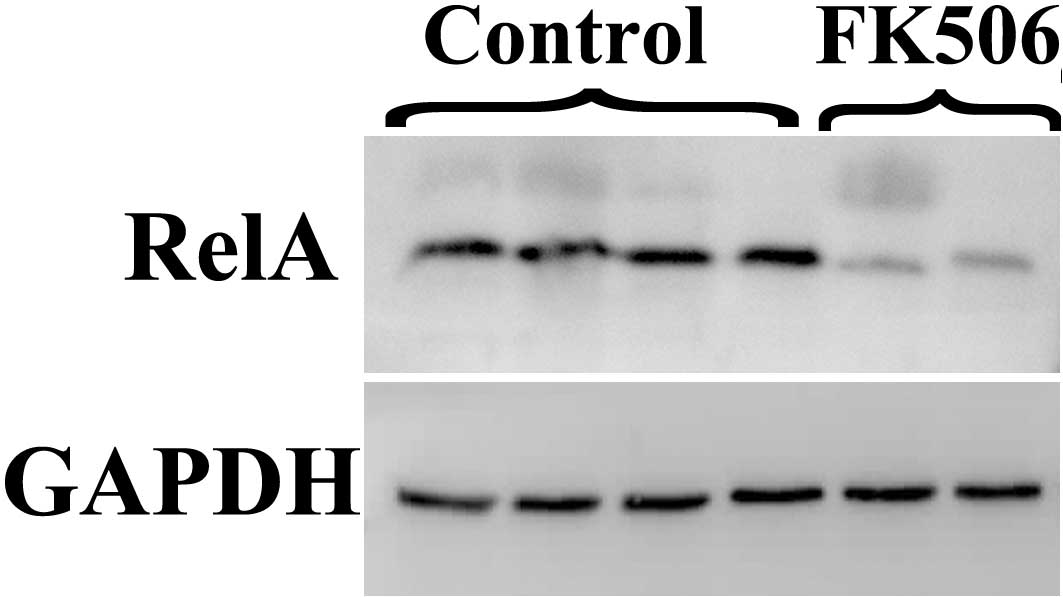
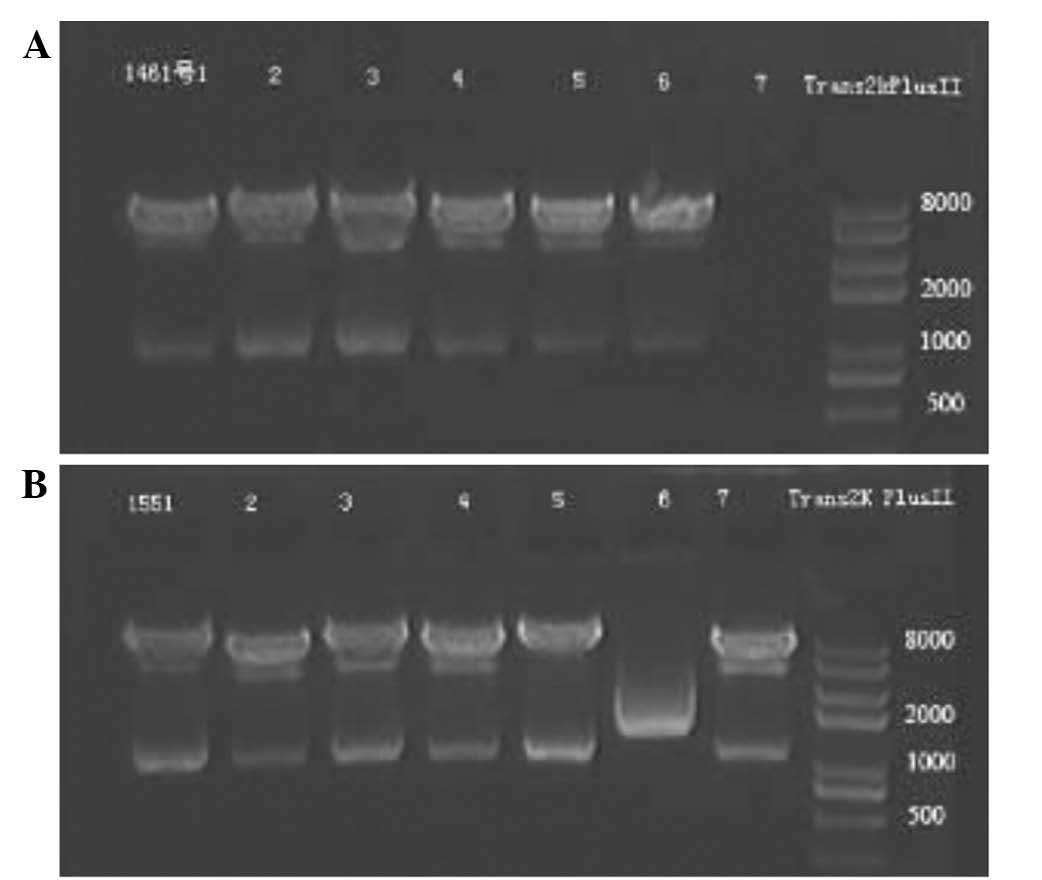
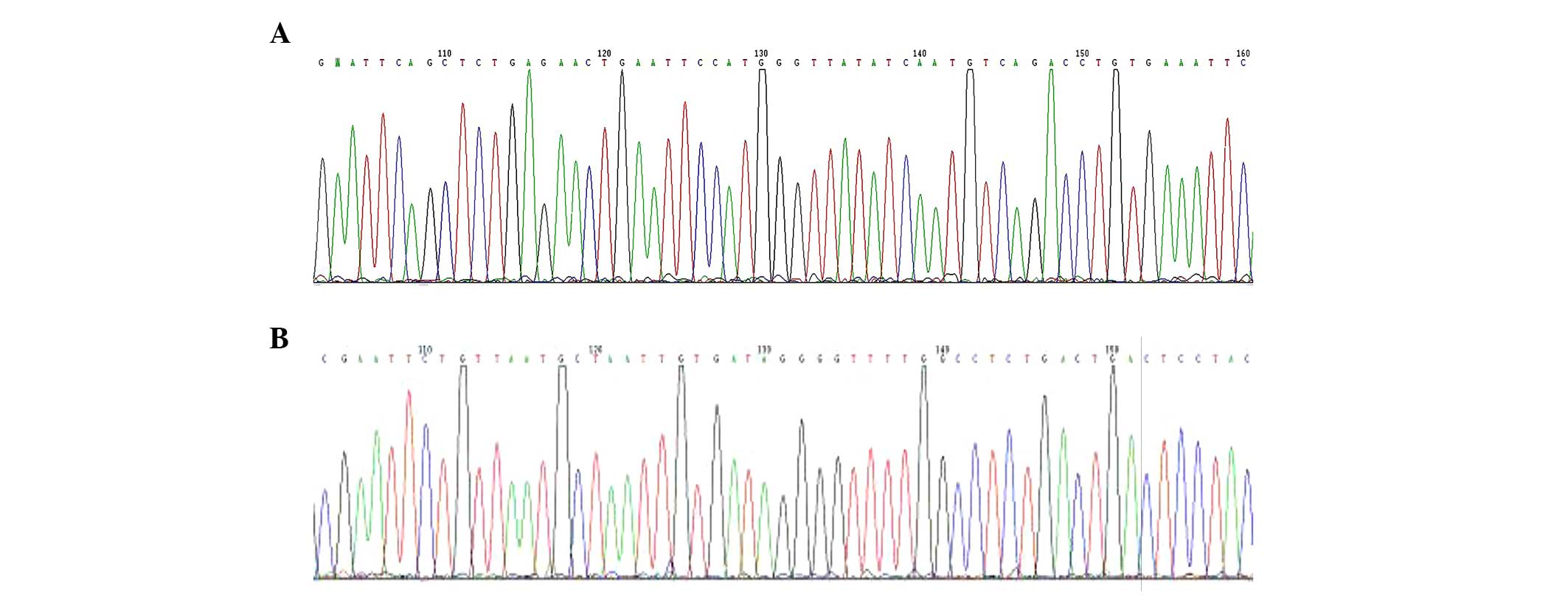
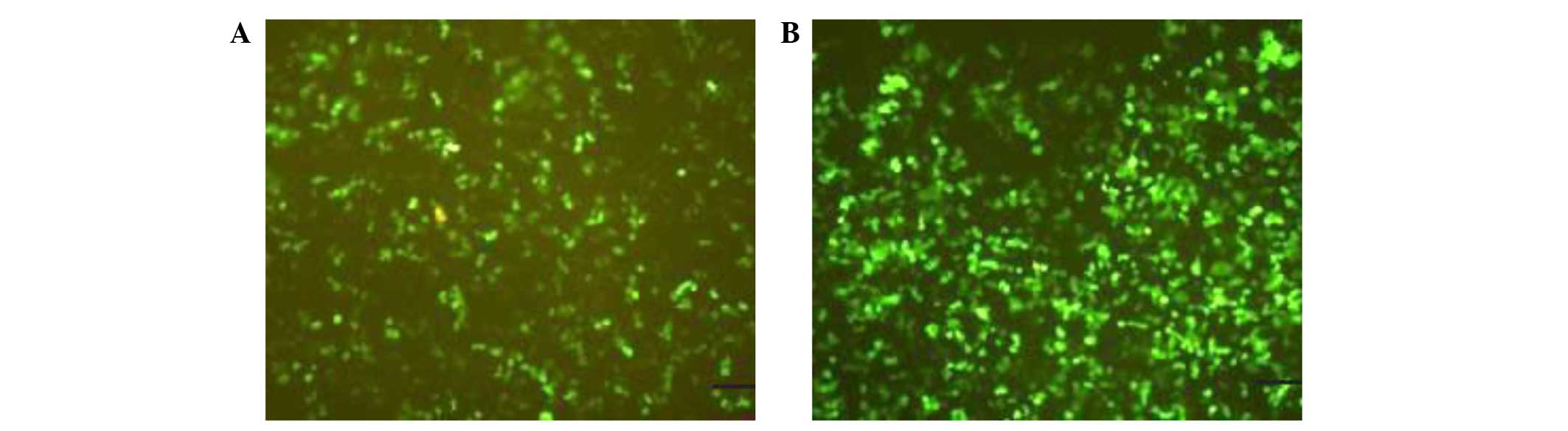
|
1
|
Cooper DKC and Lanza RP: Xeno: The promise
of transplanting animal organs into humans. Oxford University
Press; New York: pp. 1–274. 2000
|
|
2
|
Ekser B, Ezzelarab M, Hara H, van der
Windt DJ, Wijkstrom M, Bottino R, Trucco M and Cooper DK: Clinical
xenotransplantation: The next great medical revolution? Lancet.
379:672–683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nahid MA, Pauley KM, Satoh M and Chan EK:
MiR-146a is critical for endotoxin-induced tolerance: Implication
in innate immunity. J Biol Chem. 284:34590–34599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hou J, Wang P, Lin L, Liu X, Ma F, An H,
Wang Z and Cao X: MicroRNA-146a feedback inhibits RIG-I-dependent
type I IFN production in macrophages by targeting TRAF6, IRAK1, and
IRAK2. J Immunol. 183:2150–2158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng
G and Baltimore D: MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage
inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:1604–1609. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruggiero T, Trabucchi M, De-Santa F, Zupo
S, Harfe BD, McManus MT, Rosenfeld MG, Briata P and Gherzi R: LPS
induces KH-type splicing regulatory protein-dependent processing of
microRNA-155 precursors in macrophages. FASEB J. 23:2898–2908.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jones-Hughes T, Snowsill T, Haasova M,
Coelho H, Crathorne L, Cooper C, Mujica-Mota R and Peters J:
Immunosuppressive therapy for kidney transplantation in adults: A
systematic review and economic model. Health Technol Assess.
20:1–594. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Heron I: A technique for accessory
cervical heart transplantation in rabbits and rats. Acta Pathol
Microbiol Scand A. 79:366–372. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stewart S, Winters GL, Fishbein MC,
Tazelaar HD, Kobashigawa J, Abrams J, Andersen CB, Angelini A,
Berry GJ, Burke MM, et al: Revision of the 1990 working formulation
for the standardization of nomenclature in the diagnosis of heart
rejection. J Heart Lung Transplant. 24:1710–1720. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang QL, Wang JM, Jiang S, Wen LM and
Zhou H: Large-scale real-time titration of
green-fluorescence-protein-marked recombinant retrovirus:
comparison with standard titration method. J First Mil Med Univ.
23:1101–1103. 2003.
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qi F, Zhu LW, He XH, et al: Research on
function of combined drugs of immune rejection in mouse to rat
cardiac xenotransplantation. Shangdong Med J. 50:12–14. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Zou XM, Li XL, Li F, et al: Effect of
immunosuppressant FK506 on syrian hamster to rat small bowel
xenotransplantation. Zhong Hua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 6:251–254.
2003.
|
|
17
|
Sui WG, Dai Y, Huang Y, Lan H, Yan Q and
Huang H: Microarray analysis of MicroRNA expression in acute
rejection after renal transplantation. Transpl Immunol. 19:81–85.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sotolongo B, Asaoka T, Island E, Carreno
M, Delacruz V, Cova D, Russo C, Tryphonopoulos P, Moon J, Weppler
D, et al: Gene expression profiling of MicroRNAs in small-bowel
transplantation paraffin-embedded mucosal biopsy tissue. Transplant
Proc. 42:62–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jelencsics K and Oberbauer R: microRNA and
kidney transplantation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 888:271–290. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vitalone MJ, Wei L, Fujiki M, Lau AH,
Littau E, Esquivel C, Martinez OM and Krams SM: Liver microRNA
profile of induced allograft tolerance. Transplantation.
100:781–790. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Orjalo AV, Rodier F, Lithgow GJ and Campisi J: MicroRNA
miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated
inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8. Aging (Albany NY). 1:402–411.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stahl HF, Fauti T, Ullch N, Bopp T, Kubach
J, Rust W, Labhart P, Alexiadis V, Becker C, Hafner M, et al:
MiRNA-155 inhibition sensitizes CD4+ Th cells for TREG mediated
suppression. PLoS One. 4:e71582009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vigorito E, Perks KL, Abreu-Goodger C,
Bunting S, Xiang Z, Kohlhaas S, Das PP, Miska EA, Rodriguez A,
Bradley A, et al: MicroRNA-155 regulates the generation of
immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity. 27:847–859.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li M, Liu ZX, Liu T, Cheng W, Gao Y and
Wang H: The built eukaryotic expression vector of microRNA-101 and
the expression in the human placenta carcinoma cells. Zhong Guo Lin
Chuang Yi Xue. 17:627–630. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumor invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|