|
1
|
Hajarizadeh B, Grebely J and Dore GJ:
Epidemiology and natural history of HCV infection. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:553–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lavanchy D: Evolving epidemiology of
hepatitis C virus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 17:107–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartenschlager R: Hepatitis C virus: From
molecular virology to antiviral therapy. Current Topics in
Microbiology & Immunology. 369:V–VI. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alberti A and Benvegnù L: Management of
hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 38:Suppl 1. S104–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marcellin P, Asselah T and Boyer N:
Fibrosis and disease progression in hepatitis C. Hepatology. 36(5):
Suppl 1. S47–S56. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeuzem S, Alberti A, Rosenberg W,
Marcellin P, Diago M, Negro F, Prati D, Puoti C, Roberts SK and
Shiffman ML: Review article: Management of patients with chronic
hepatitis C virus infection and ‘normal’ alanine aminotransferase
activity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 24:1133–1149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adinolfi LE, Utili R, Andreana A, Tripodi
MF, Marracino M, Gambardella M, Giordano M and Ruggiero G: Serum
HCV RNA levels correlate with histological liver damage and concur
with steatosis in progression of chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci.
46:1677–1683. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petit JM, Benichou M, Duvillard L, Jooste
V, Bour JB, Minello A, Verges B, Brun JM, Gambert P and Hillon P:
Hepatitis C virus-associated hypobetalipoproteinemia is correlated
with plasma viral load, steatosis, and liver fibrosis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 98:1150–1154. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Durante-Mangoni E, Zampino R, Portella G,
Adinolfi LE, Utili R and Ruggiero G: Correlates and prognostic
value of the first-phase hepatitis C virus RNA kinetics during
treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 49:498–506. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsu CS, Liu CH, Liu CJ, Chen CL, Lai MY,
Chen PJ, Chen DS and Kao JH: Factors affecting early viral load
decline of Asian chronic hepatitis C patients receiving pegylated
interferon plus ribavirin therapy. Antivir Ther. 14:45–54.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
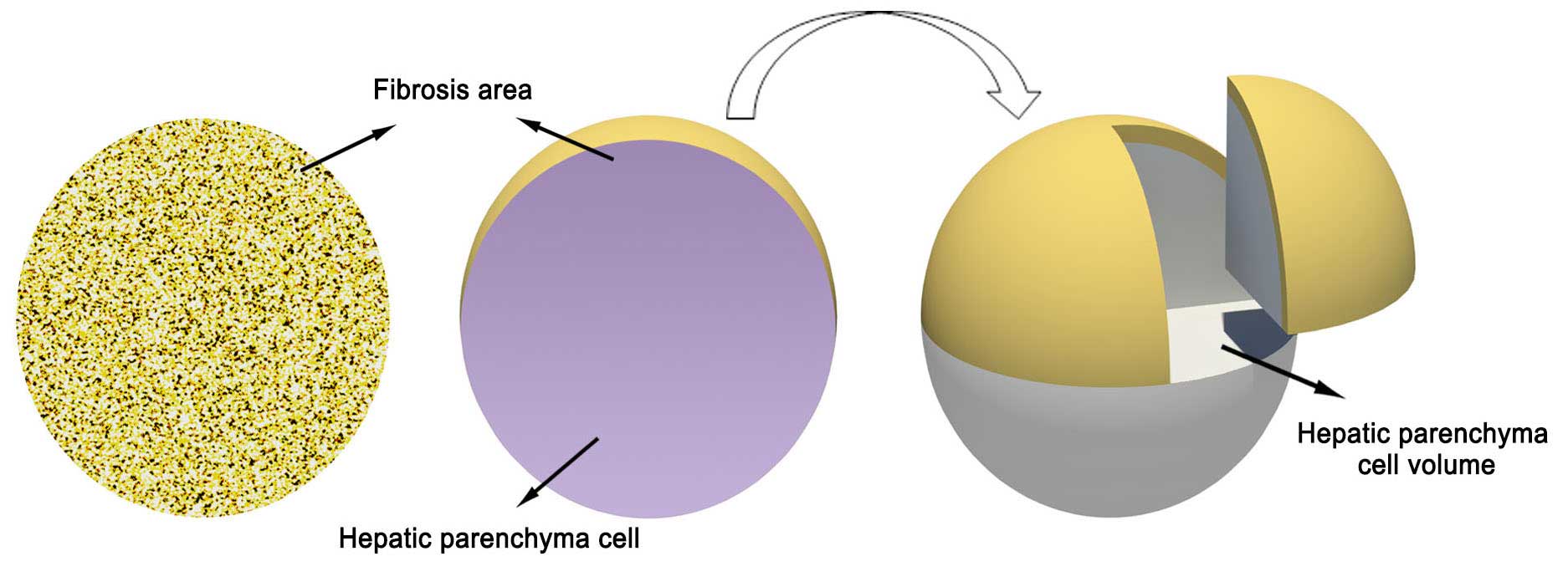
Ke WM, Xie SB, Yu LN, Liu T, Lai J, He DQ,
Li XH, Gao ZL, Ke Y and Chen PJ: Decline of serum HBV DNA and no
change apportioned by the same hepatic parenchyma cell volume from
hepatic fibrosis stage 1 to stage 4 during the natural history of
chronic hepatitis B. Intervirology. 51:235–240. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee YS, Yoon SK, Chung ES, Bae SH, Choi
JY, Han JY, Chung KW, Sun HS, Kim BS and Kim BK: The relationship
of histologic activity to serum ALT, HCV genotype and HCV RNA
titers in chronic hepatitis C. J Korean Med Sci. 16:585–591. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chinese Medical Association, . Viral
hepatitis prevention and treatment programs. Chuan Ran Bing Xin Xi.
13:141–150. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F,
De Groote J, Gudat F, Denk H, Desmet V, Korb G, MacSween RN, et al:
Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol.
22:696–699. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M
and Scheuer PJ: Classification of chronic hepatitis: Diagnosis,
grading and staging. Hepatology. 19:1513–1520. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie SB, Yao JL, Zheng SS, Yao CL and Zheng
RQ: The levels of serum fibrosis marks and morphometric
quantitative measurement of hepatic fibrosis. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 1:202–206. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ke WM, Xie SB, Li XJ, Zhang SQ, Lai J, Ye
YN, Gao ZL and Chen PJ: There were no differences in serum HBV DNA
level between HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B
with same liver histological necroinflammation grade but
differences among grades 1, 2, 3 and 4 apportioned by the same
hepatic parenchyma cell volume. J Viral Hepat. 18:637–645. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kar P: Risk factors for hepatocellular
carcinoma in India. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4:(Suppl 3). S34–S42. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cerny A and Chisari FV: Pathogenesis of
chronic hepatitis C: Immunological features of hepatic injury and
viral persistence. Hepatology. 30:595–601. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rehermann B: Interaction between the
hepatitis C virus and the immune system. Semin Liver Dis.
20:127–141. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anand BS and Velez M: Assessment of
correlation between serum titers of hepatitis C virus and severity
of liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2409–2411. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bacon BR: Treatment of patients with
hepatitis C and normal serum aminotransferase levels. Hepatology.
36:(Suppl 1). S179–S184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leone N and Rizzetto M: Natural history of
hepatitis C virus infection: from chronic hepatitis to cirrhosis,
to hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol.
51:31–46. 2005.(In English and Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Orellana NI, Poniachik TJ, Smok SG, Madrid
SAM, Menéndez AA, Tobar AE and Brahm BJ: Factors associated with
the severity of liver damage in chronic hepatitis C. Rev Med Chil.
133:1311–1316. 2005.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ramos Gómez M: Natural history of chronic
hepatitis C. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 67 Suppl. 2:S17–S20. 2002.(In
Spanish).
|
|
27
|
Zechini B, Pasquazzi C and Aceti A:
Correlation of serum aminotransferases with HCV RNA levels and
histological findings in patients with chronic hepatitis C: The
role of serum aspartate transaminase in the evaluation of disease
progression. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:891–896. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen L, Li JQ, Zeng MD, Fan ST, Lu LG, Bao
H and Cao AP: Evaluation of the value of ultrasonography in
diagnosis of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral
hepatitis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 13:117–120. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Umbetova KT, Volchkova EV, Kiselevskiĭ MV,
Lazareva AS and Pak SG: Lymphocyte subpopulation composition in
hepatic tissue and autoimmune manifestations in viral hepatitis.
Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 12:37–40. 2010.
|