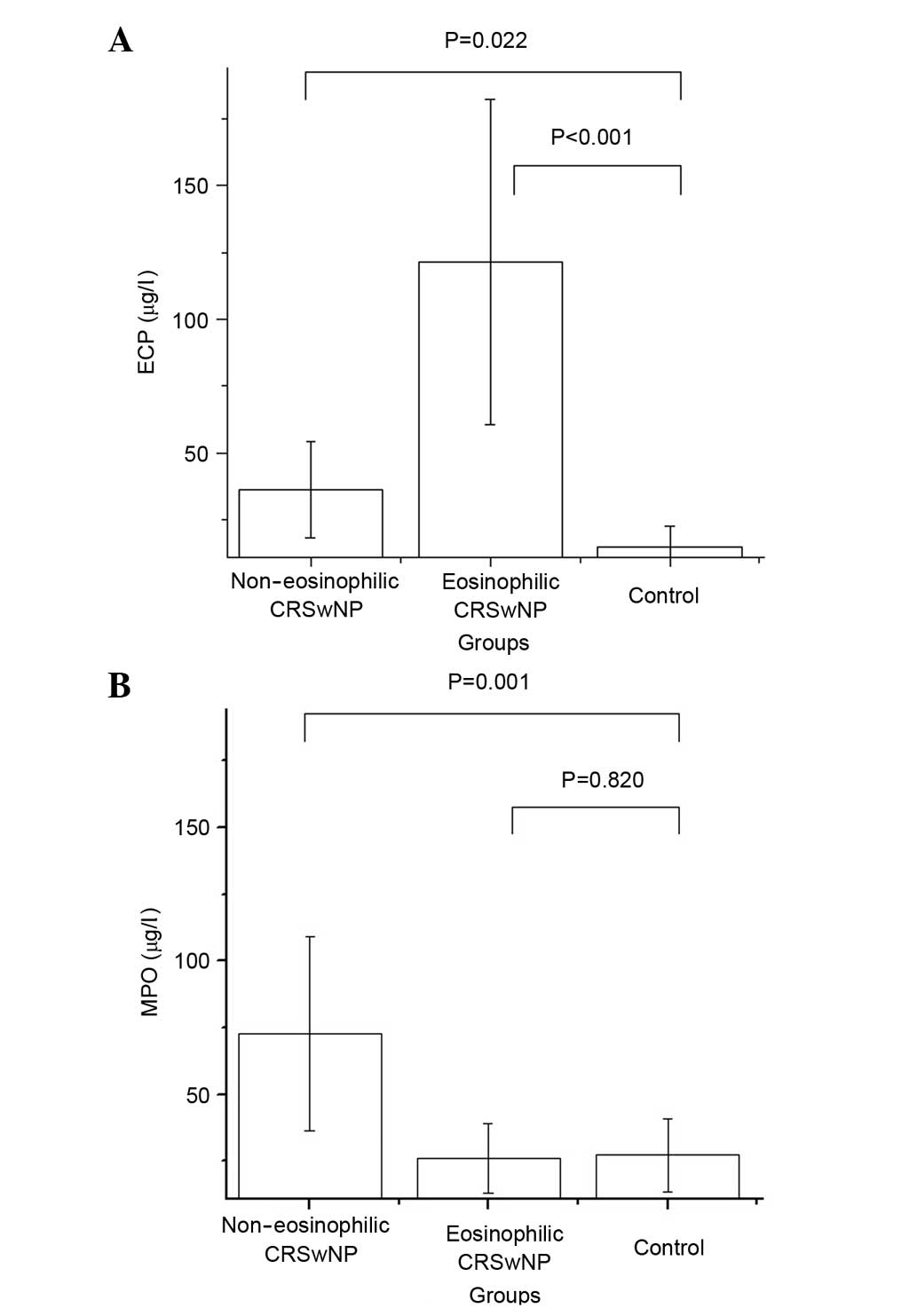
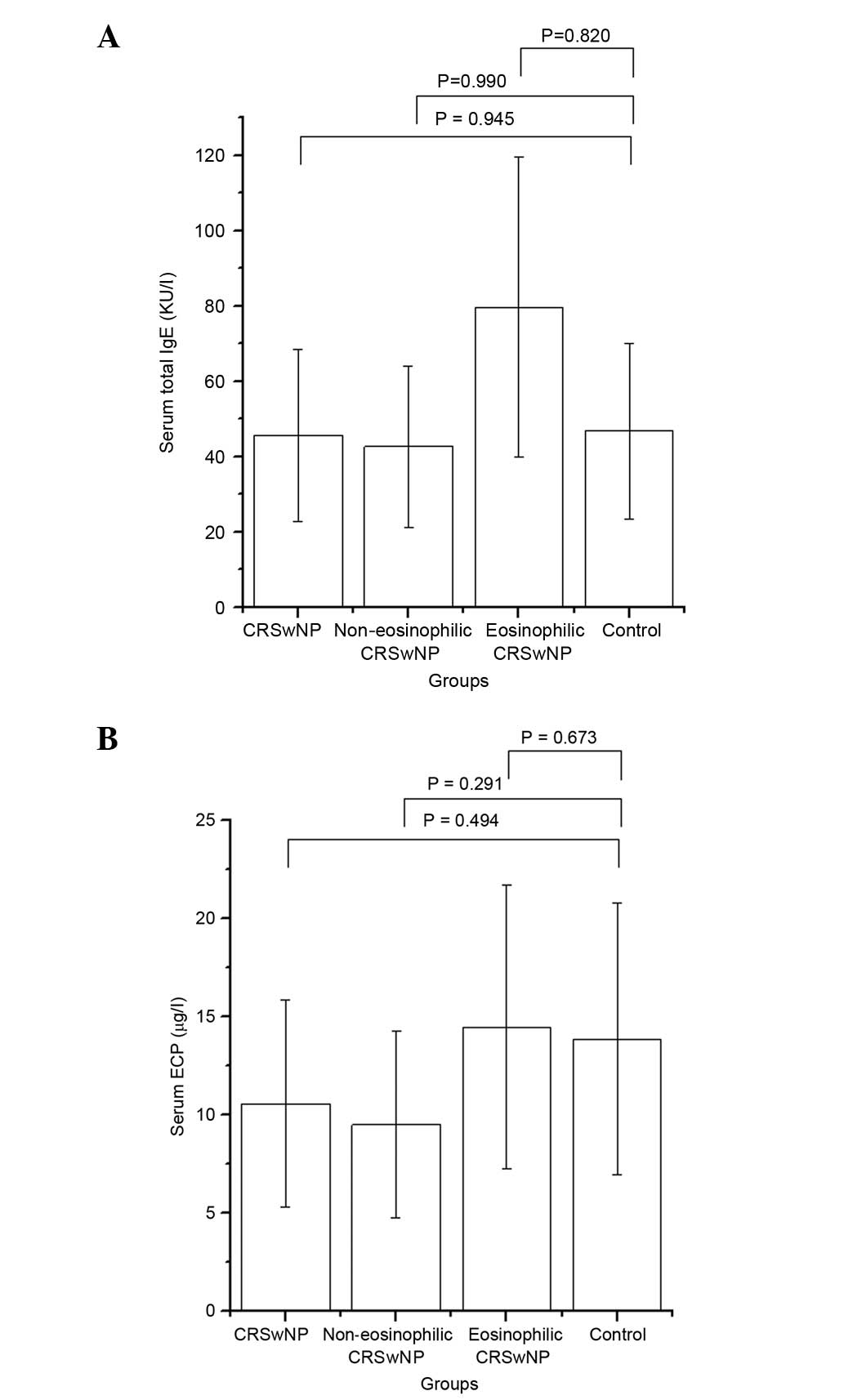
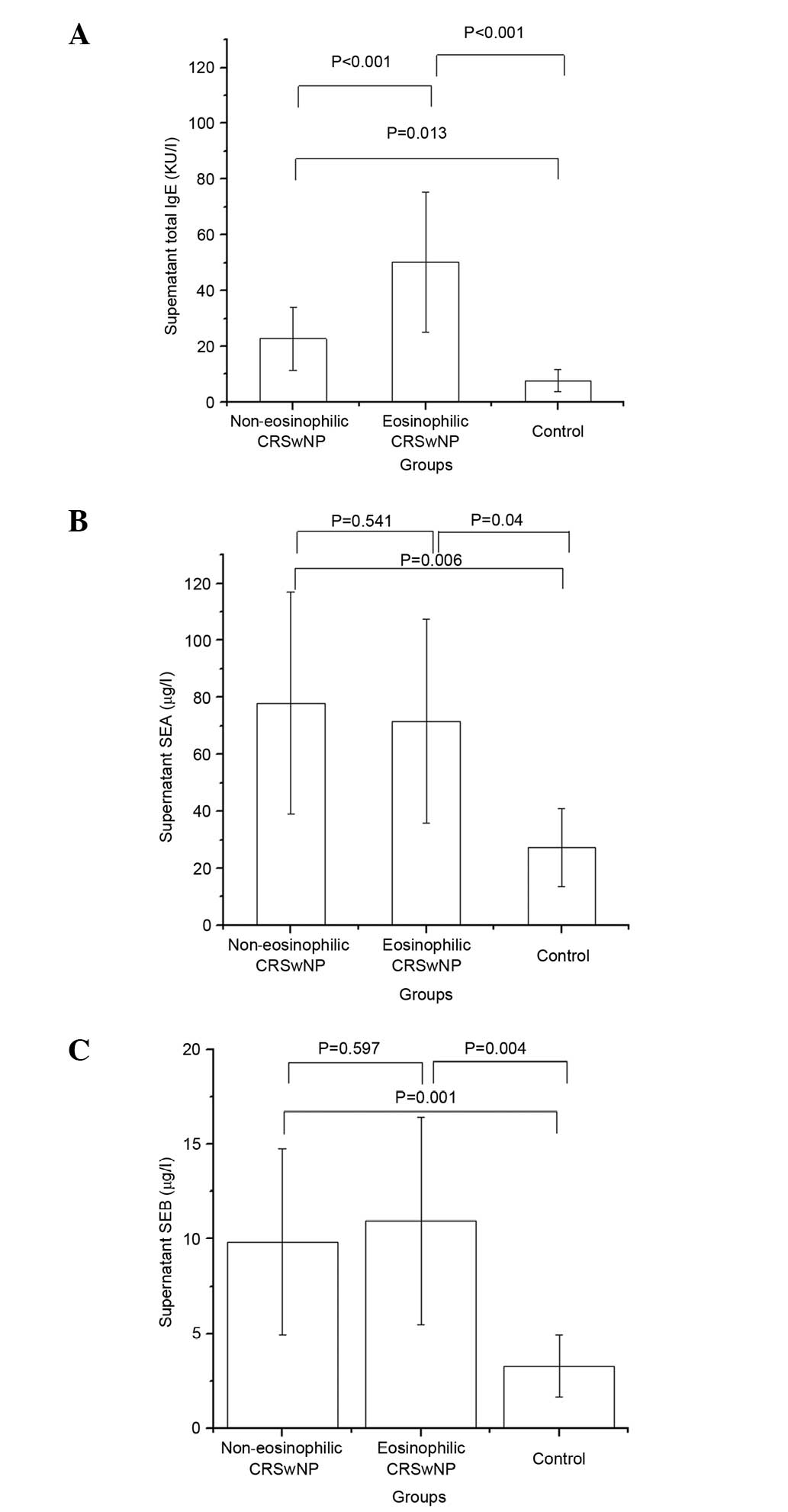
|
1
|
Bhattacharyya N and Lee LN: Evaluating the
diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis based on clinical guidelines
and endoscopy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 143:147–151. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Polzehl D, Moeller P, Riechelmann H and
Perner S: Distinct features of chronic rhinosinusitis with and
without nasal polyps. Allergy. 61:1275–1279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA,
Hamilos DL, Jacobs M, Kennedy DW, Lanza DC, Marple BF, Osguthorpe
JD, Stankiewicz JA, et al: Adult chronic rhinosinusitis:
Definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology.
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 129:(3 Suppl). S1–S32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tosun F, Arslan HH, Karslioglu Y, Deveci
MS and Durmaz A: Relationship between postoperative recurrence rate
and eosinophil density of nasal polyps. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.
119:455–459. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hirotsu M, Kikuchi K, Kusunoki T, Kase K,
Ono N and Ikeda K: Comparison of bacterial examinations between
eosinophilic and neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyps. Acta Otolaryngol. 131:997–1001. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ba L, Zhang N, Meng J, Zhang J, Lin P,
Zhou P, Liu S and Bachert C: The association between bacterial
colonization and inflammatory pattern in Chinese chronic
rhinosinusitis patients with nasal polyps. Allergy. 66:1296–303.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fokkens W, Lund V and Mullol J: European
Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps Group: EP3OS
2007: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps
2007. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 45:97–101.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, Lanza
DC, Marple BF, Nicklas RA, Adinoff AD, Bachert C, Borish L,
Chinchilli M, et al: Rhinosinusitis Initiative: Rhinosinusitis:
Developing guidance for clinical trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
118:(5 Suppl). S17–S61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bachert C, Zhang N, van Zele T and Gevaert
P: Chronic rhinosinusitis: From one disease to different
phenotypes. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 23:(Suppl 22). S2–S4. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Patou J, Gevaert P, Van Zele T, Holtappels
G, van Cauwenberge P and Bachert C: Staphylococcus aureus
enterotoxin B, protein A, and lipoteichoic acid stimulations in
nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 121:110–115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bernstein JM and Kansal R: Superantigen
hypothesis for the early development of chronic hyperplastic
sinusitis with massive nasal polyposis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 13:39–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, van
Cauwenberge P and Bachert C: Local immunoglobulin production in
nasal polyposis is modulated by superantigens. Clin Exp Allergy.
37:1840–1847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C,
Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin A, Douglas R, Gevaert P, et
al: EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal
polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology.
50:1–12. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van
Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, Van Cauwenberge P and Bachert
C: Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal
inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
122:961–968. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sheahan P, Ahn CN, Harvey RJ, Wise SK,
Mulligan RM, Lathers DM and Schlosser RJ: Local IgE production in
nonatopic nasal polyposis. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 39:45–51.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bonfils P, Badoual C, Bonfils NA, Gallas D
and Malinvaud D: Eosinophil infiltration of nasal polyps in
patients with nasal polyposis Role in clinical evolution after
medical and surgical treatment. J Laryngol Otol. 123:509–516. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Asero R and Bottazzi G: Nasal polyposis: A
study of its association with airborne allergen hypersensitivity.
Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 86:283–285. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kirtsreesakul V and Atchariyasathian V:
Nasal polyposis: Role of allergy on therapeutic response of
eosinophil- and noneosinophil-dominated inflammation. Am J Rhinol.
20:95–100. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Collins MM, Loughran S, Davidson P and
Wilson JA: Nasal polyposis: Prevalence of positive food and
inhalant skin tests. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 135:680–683. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kennedy JL and Borish L: Chronic sinusitis
pathophysiology: The role of allergy. Am J Rhinol Allergy.
27:367–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Erbek SS, Erbek S, Topal O and Cakmak O:
The role of allergy in the severity of nasal polyposis. Am J
Rhinol. 21:686–690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nguyen LH, Fakhri S, Frenkiel S and Hamid
QA: Molecular immunology and immunotherapy for chronic sinusitis.
Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 3:505–512. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS,
Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, Schleimer RP and Ledford D: Endotypes and
phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: A PRACTALL document of the
European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the
American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. JAllergy Clin
Immunol. 131:1479–1490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ouyang Y, Fan E, Li Y, Wang X and Zhang L:
Clinical characteristics and expression of thymic stromal
lymphopoetin in eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic
rhinosinusitis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 75:37–45. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu Y, Cao PP, Liang GT, Cui YH and Liu Z:
Diagnostic significance of blood eosinophil count in eosinophilic
chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Chinese adults.
Laryngoscope. 122:498–503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suzuki H and Ikeda K: Mode of action of
long-term low-dose macrolide therapy for chronic sinusitis in the
light of neutrophil recruitment. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy.
1:117–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ikeda K, Shiozawa A, Ono N, Kusunoki T,
Hirotsu M, Homma H, Saitoh T and Murata J: Subclassification of
chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp based on eosinophil and
neutrophil. Laryngoscope. 123:E1–E9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bachert C, Zhang N, Holtappels G, De Lobel
L, van Cauwenberge P, Liu S, Lin P, Bousquet J and Van Steen K:
Presence of IL-5 protein and IgE antibodies to staphylococcal
enterotoxins in nasal polyps is associated with comorbid asthma. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 126:962–968, 968.e1-e6. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sejima T, Holtappels G, Kikuchi H,
Imayoshi S, Ichimura K and Bachert C: Cytokine profiles in Japanese
patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int. 61:115–122.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ,
Cui YH, Wang DY, Desrosiers M and Liu Z: Distinct immunopathologic
characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult
Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 124:478–484, 484.e1-e2. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao PP, Zhang YN, Liao B, Ma J, Wang BF,
Wang H, Zeng M, Liu WH, Schleimer RP and Liu Z: Increased local IgE
production induced by common aeroallergens and phenotypic
alteration of mast cells in Chinese eosinophilic, but not
non-eosinophilic, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Clin
Exp Allergy. 44:690–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tripathi A, Conley DB, Grammes LC, Ditto
AM, Lowery MM, Seiberling KA, Yarnold PA, Zeifer B and Kern RC:
Immunoglobulin E to staphylococcal and streptococcal toxins in
patients with chronic sinusitis/nasal polyposis. Laryngoscope.
114:1822–1826. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang N, Holtappels G, Claeys C, Huang G,
van Cauwenberge P and Bachert C: Pattern of inflammation and impact
of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in nasal polyps from southern
China. Am J Rhinol. 20:445–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tripathi A, Kern R, Conley DB, Seiberling
K, Klemens JC, Harris KE, Suh L, Huang J and Grammer LC:
Staphylococcal exotoxins and nasal polyposis: Analysis of systemic
and local responses. Am J Rhinol. 19:327–333. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|