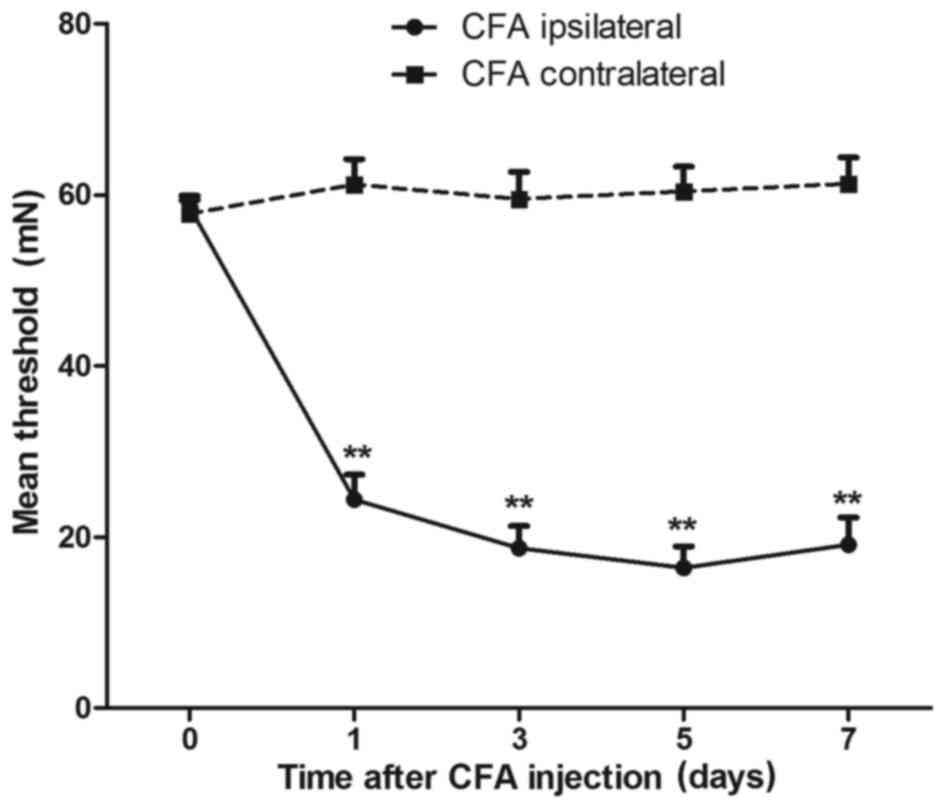
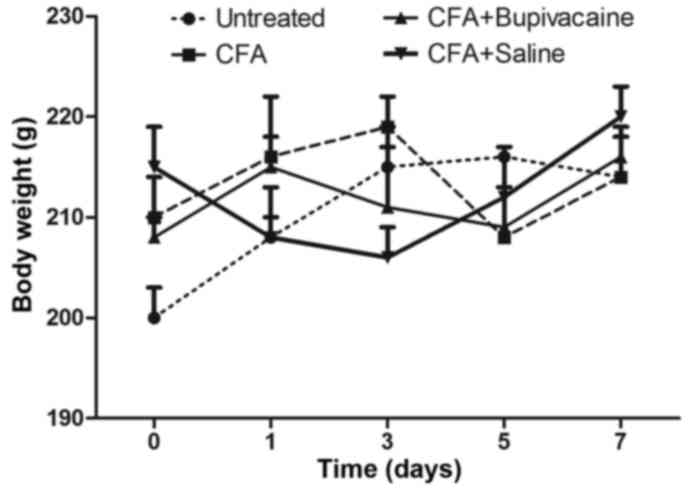
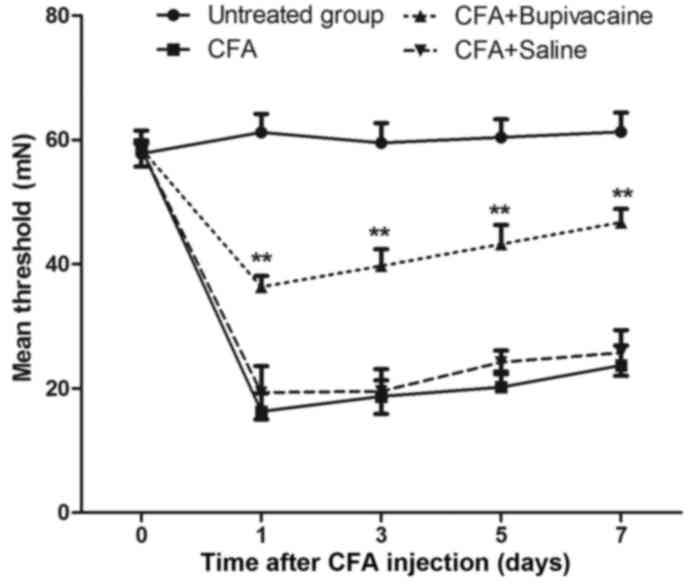
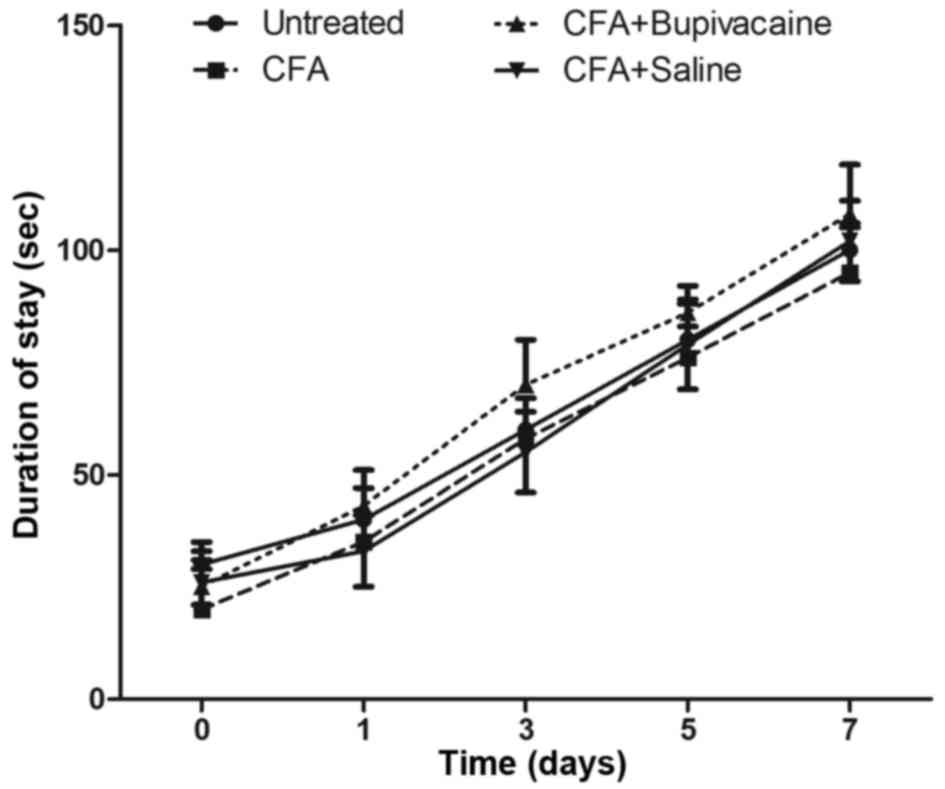
|
1
|
Hu Y, Yu SY, Zuo LJ, Cao CJ, Wang F, Chen
ZJ, Du Y, Lian TH, Wang YJ, Chan P, et al: Parkinson disease with
REM sleep behavior disorder: Features, α-synuclein, and
inflammation. Neurology. 84:888–894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Irwin MR, Olmstead RE, Ganz PA and Haque
R: Sleep disturbance, inflammation and depression risk in cancer
survivors. Brain Behav Immun. 30:(Suppl). S58–S67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Andersen HH, Duroux M and Gazerani P:
MicroRNAs as modulators and biomarkers of inflammatory and
neuropathic pain conditions. Neurobiol Dis. 71:159–168. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan J, Ramadan K, Korczeniewska O, Anwer
MM, Benoliel R and Eliav E: Interleukin-10 levels in rat models of
nerve damage and neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 592:99–106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ranoux D, Attal N, Morain F and Bouhassira
D: Botulinum toxin type A induces direct analgesic effects in
chronic neuropathic pain. Ann Neurol. 64:274–283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jaggi AS and Singh N: Exploring the
potential of telmisartan in chronic constriction injury-induced
neuropathic pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 667:215–221. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zollner C, Mousa SA, Fischer O, et al:
Chronic morphine use does not induce peripheral tolerance in a rat
model of inflammatory pain. J Clin Invest. 118:1065–1073.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Conrozier T, Mathieu P, Bonjean M, Marc
JF, Renevier JL and Balblanc JC: A complex of three natural
anti-inflammatory agents provides relief of osteoarthritis pain.
Altern Ther Health Med. 20:(Suppl 1). 32–37. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moalem G and Tracey DJ: Immune and
inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res Rev.
51:240–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lorenzini L, Giuliani A, Giardino L and
Calza L: Laser acupuncture for acute inflammatory, visceral and
neuropathic pain relief: An experimental study in the laboratory
rat. Res Vet Sci. 88:159–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McHugh JM and McHugh WB: Pain:
Neuroanatomy, chemical mediators, and clinical implications. AACN
Clin Issues. 11:168–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schaible HG, Ebersberger A and Von Banchet
GS: Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 966:343–354.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gabriel AF, Marcus MA, Honig WM, Helgers N
and Joosten EA: Environmental housing affects the duration of
mechanical allodynia and the spinal astroglial activation in a rat
model of chronic inflammatory pain. Brain Res. 1276:83–90. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu XN, Zhang T, Qian NS, Guo XD, Yang HJ,
Huang KB, Luo GQ, Xiang W, Deng WT, Dai GH, et al: Antinociceptive
effects of endomorphin-2: Suppression of substance P release in the
inflammatory pain model rat. Neurochem Int. 82:1–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao X, Zhao XT, Xu LC, Yue LP, Liu FY,
Cai J, Liao FF, Kong JG, Xing GG, Yi M and Wan Y: Shp-1
dephosphorylates TRPV1 in dorsal root ganglion neurons and
alleviates CFA-induced inflammatory pain in rats. Pain.
156:597–608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Q and Yaksh TL: A brief comparison of
the pathophysiology of inflammatory versus neuropathic pain. Curr
Opin Anaesthesiol. 24:400–407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aoki Y, Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Ino H,
Takahashi Y, Chiba T and Moriya H: Innervation of the lumbar
intervertebral disc by nerve growth factor-dependent neurons
related to inflammatory pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 29:1077–1081.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao J, Yuan G, Cendan CM, Nassar MA,
Lagerström MC, Kullander K, Gavazzi I and Wood JN:
Nociceptor-expressed ephrin-B2 regulates inflammatory and
neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 6:772010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Silva GD, Lopes PS, Fonoff ET and Pagano
RL: The spinal anti-inflammatory mechanism of motor cortex
stimulation: Cause of success and refractoriness in neuropathic
pain? J Neuroinflammation. 12:102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burke NN, Geoghegan E, Kerr DM, Moriarty
O, Finn DP and Roche M: Altered neuropathic pain behaviour in a rat
model of depression is associated with changes in inflammatory gene
expression in the amygdala. Genes Brain Behav. 12:705–713.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ikeda H, Kiritoshi T and Murase K:
Contribution of microglia and astrocytes to the central
sensitization, inflammatory and neuropathic pain in the juvenile
rat. Mol Pain. 8:432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Puszynski K, Bertolusso R and Lipniacki T:
Crosstalk between p53 and nuclear factor-B systems: Pro- and
anti-apoptotic functions of NF-B. IET Syst Biol. 3:356–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Acquisto F, May MJ and Ghosh S:
Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B): An emerging theme in
anti-inflammatory therapies. Mol Interv. 2:22–35. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vincenzi F, Targa M, Corciulo C, Tabrizi
MA, Merighi S, Gessi S, Saponaro G, Baraldi PG, Borea PA and Varani
K: Antinociceptive effects of the selective CB2 agonist MT178 in
inflammatory and chronic rodent pain models. Pain. 154:864–873.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chiechio S, Zammataro M, Morales ME,
Busceti CL, Drago F, Gereau RW, Copani A and Nicoletti F:
Epigenetic modulation of mGlu2 receptors by histone deacetylase
inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory pain. Mol Pharmacol.
75:1014–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Toulme E, Tsuda M, Khakh BS and Inoue K:
On the Role of ATP-Gated P2X Receptors in Acute, Inflammatory and
Neuropathic PainTranslational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man.
Kruger L and Light AR: Boca Raton, FL: 2010
|
|
28
|
Zhang J, Echeverry S, Lim TK, Lee SH, Shi
XQ and Huang H: Can modulating inflammatory response be a good
strategy to treat neuropathic pain? Curr Pharm Des. 21:831–839.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
HuangFu WC, Matsumoto K and Ninomiya-Tsuji
J: Osmotic stress blocks NF-kappaB-dependent inflammatory responses
by inhibiting ubiquitination of IkappaB. FEBS Lett. 581:5549–5554.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang ED, Wang CY, Xiong Y and Guan KL: A
role for NF-kappaB essential modifier/IkappaB kinase-gamma
(NEMO/IKKgamma) ubiquitination in the activation of the IkappaB
kinase complex by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem.
278:37297–37305. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Starokadomskyy P and Burstein E: Detection
of IkB Degradation dynamics and IkB-α ubiquitination. Methods Mol
Biol. 1280:15–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shambharkar PB, Blonska M, Pappu BP, Li H,
You Y, Sakurai H, Darnay BG, Hara H, Penninger J and Lin X:
Phosphorylation and ubiquitination of the IkappaB kinase complex by
two distinct signaling pathways. EMBO J. 26:1794–1805. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alebouyeh MR, Imani F, Rahimzadeh P and
Faiz SH: Evaluation of the efficacy of intrathecal injection of
amitriptyline and doxepin in spinal anesthesia in comparison with
bupivacaine in rats. Anesth Pain Med. 1:15–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schwoerer AP, Scheel H and Friederich P: A
comparative analysis of bupivacaine and ropivacaine effects on
human cardiac SCN5A channels. Anesth Analg. 120:1226–1234. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mohamed SA and Abdel-Ghaffar HS: Effect of
the addition of clonidine to locally administered bupivacaine on
acute and chronic postmastectomy pain. J Clin Anesth. 25:20–27.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Deruddre S, Combettes E, Estebe JP,
Duranteau J, Benhamou D, Beloeil H and Mazoit JX: Effects of a
bupivacaine nerve block on the axonal transport of Tumor Necrosis
Factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in a rat model of carrageenan-induced
inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 24:652–659. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tanaka T, Kai S, Matsuyama T, Adachi T,
Fukuda K and Hirota K: General anesthetics inhibit LPS-induced
IL-1beta expression in glial cells. PloS One. 8:e829302013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miyazaki H, Nakamura Y, Arai T and Kataoka
K: Increase of glutamate uptake in astrocytes: a possible mechanism
of action of volatile anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 86:1359–1366;
discussion 1358A. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shin JW, Pancaro C, Wang CF and Gerner P:
Low-dose systemic bupivacaine prevents the development of allodynia
after thoracotomy in rats. Anesth Analg. 107:1587–1591. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suter MR, Berta T, Gao YJ, Decosterd I and
Ji RR: Large A-fiber activity is required for microglial
proliferation and p38 MAPK activation in the spinal cord: Different
effects of resiniferatoxin and bupivacaine on spinal microglial
changes after spared nerve injury. Mol Pain. 5:532009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|