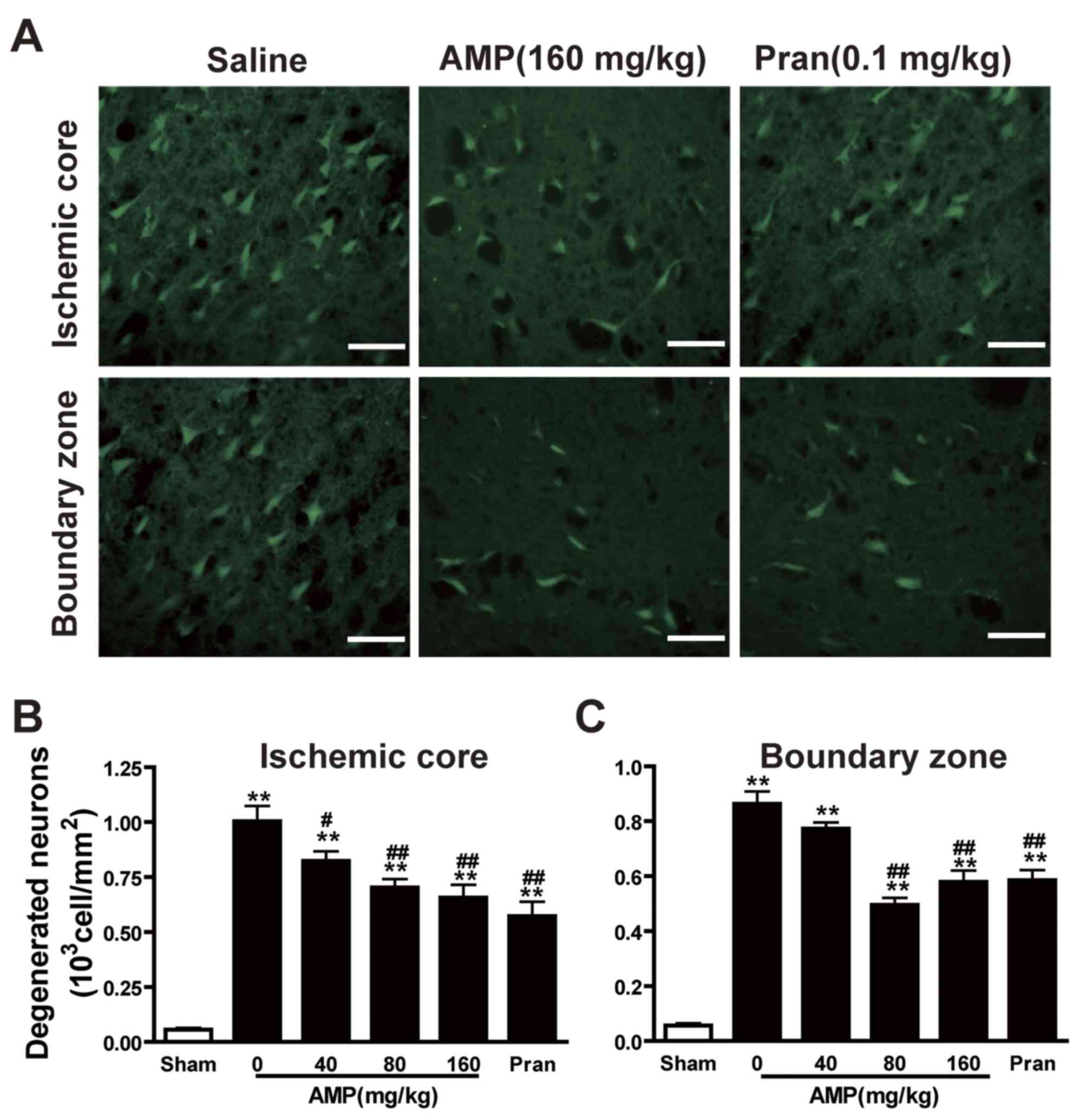
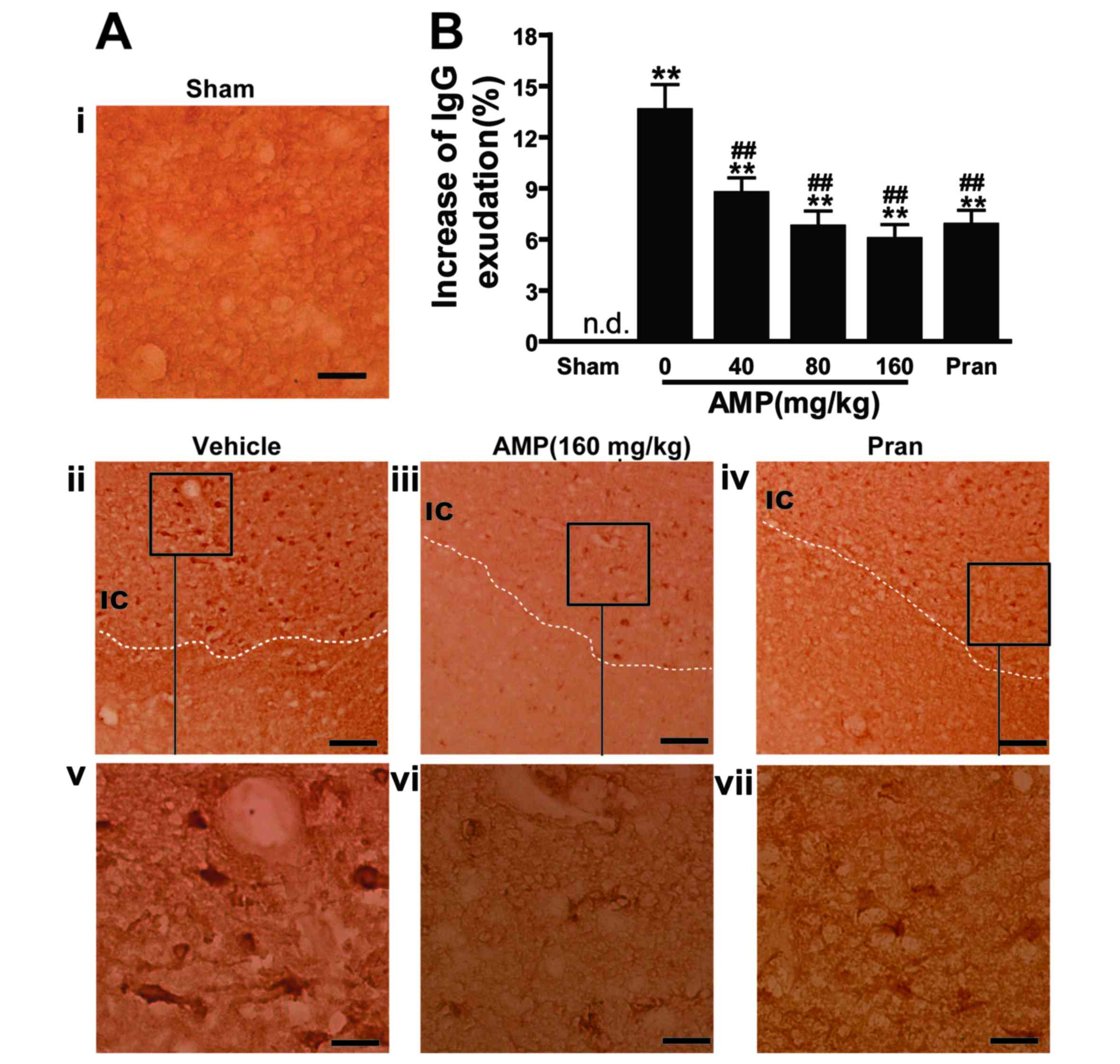
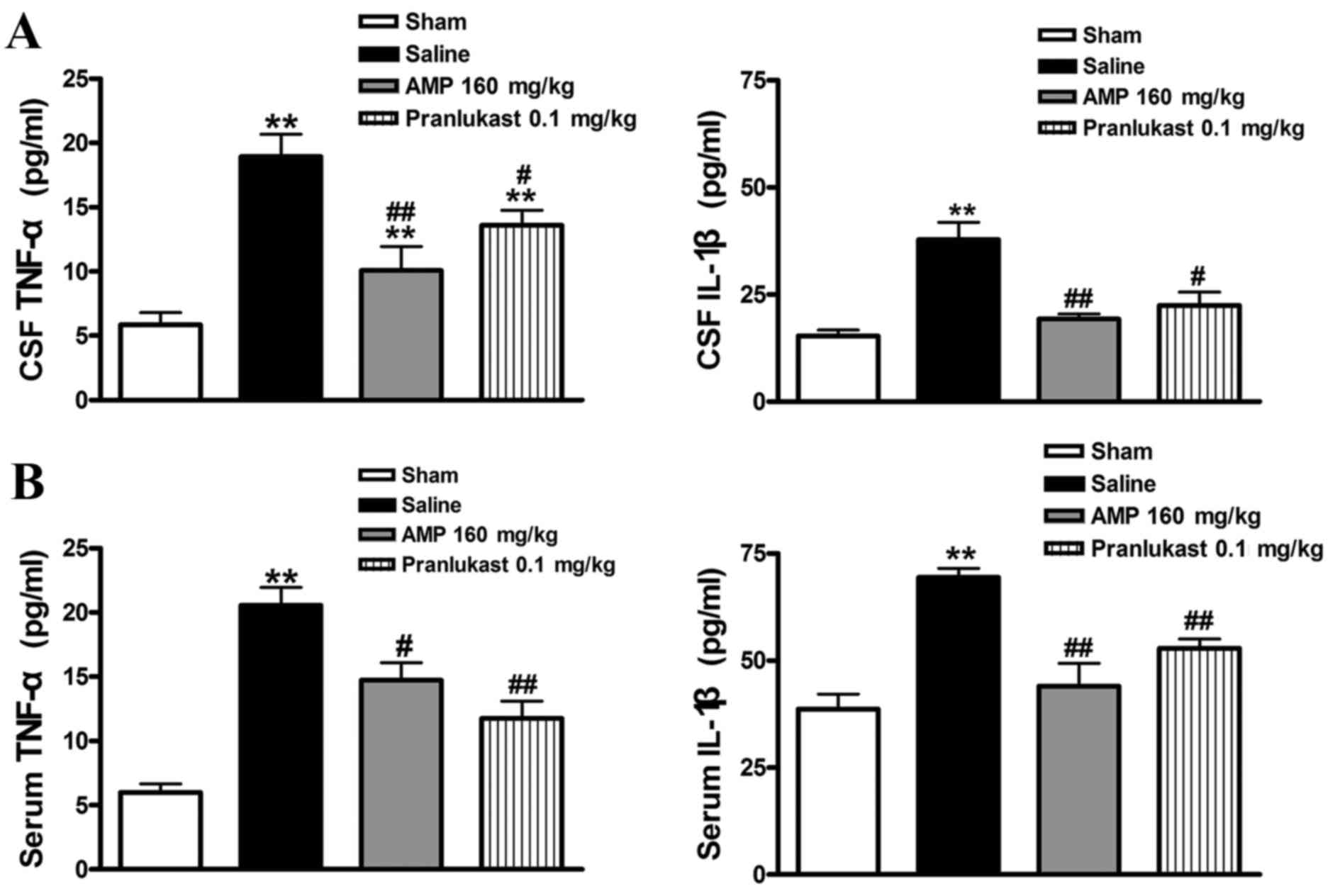
|
1
|
Tsai CF, Thomas B and Sudlow CL:
Epidemiology of stroke and its subtypes in Chinese vs white
populations: A systematic review. Neurology. 81:264–272. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pereira VM, Yilmaz H, Pellaton A, Slater
LA, Krings T and Lovblad KO: Current status of mechanical
thrombectomy for acute stroke treatment. J Neuroradiol. 42:12–20.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pierot L, Soize S, Benaissa A and Wakhloo
AK: Techniques for endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke:
From intra-arterial fibrinolytics to stent-retrievers. Stroke.
46:909–914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
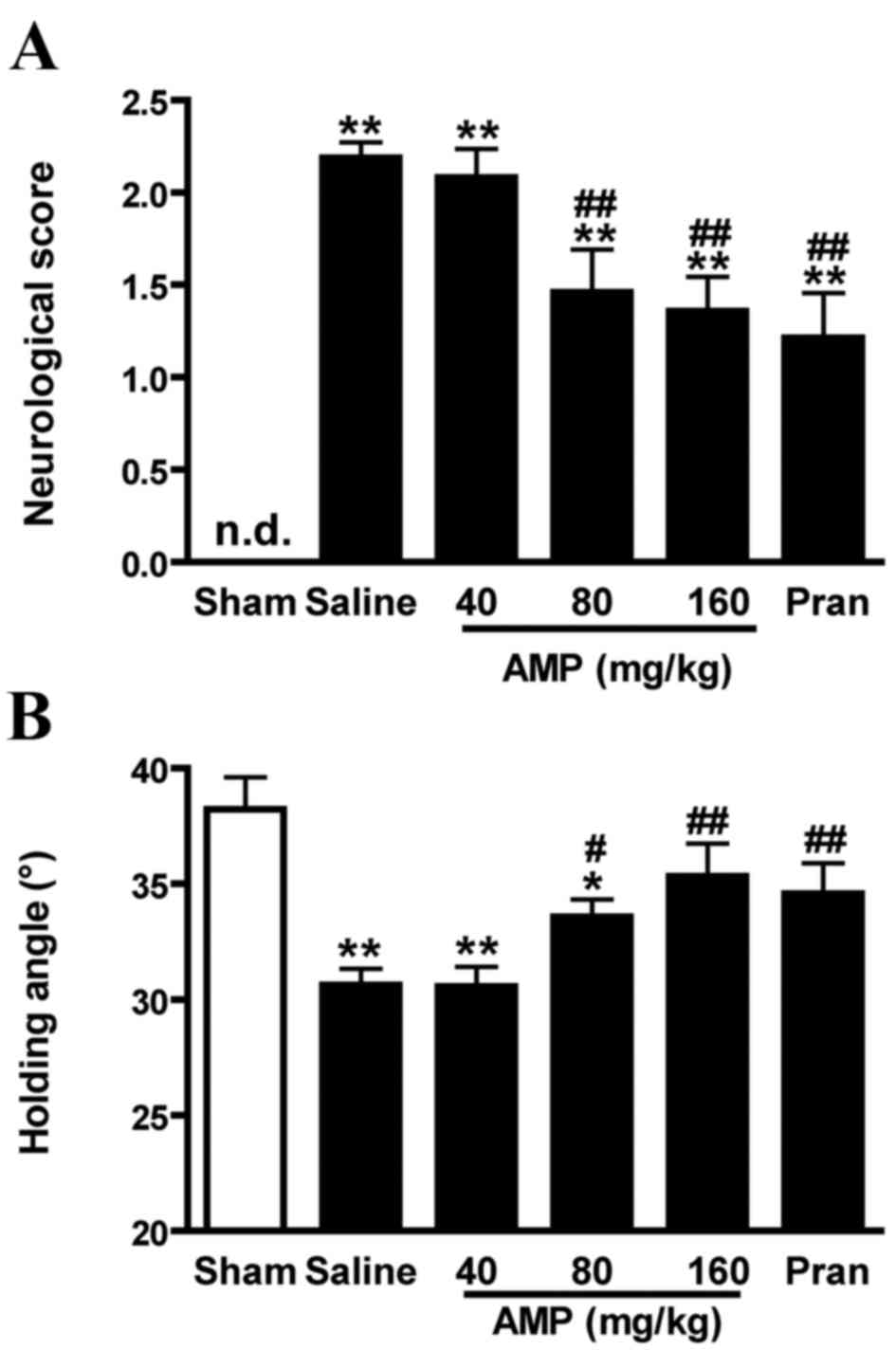
|
|
4
|
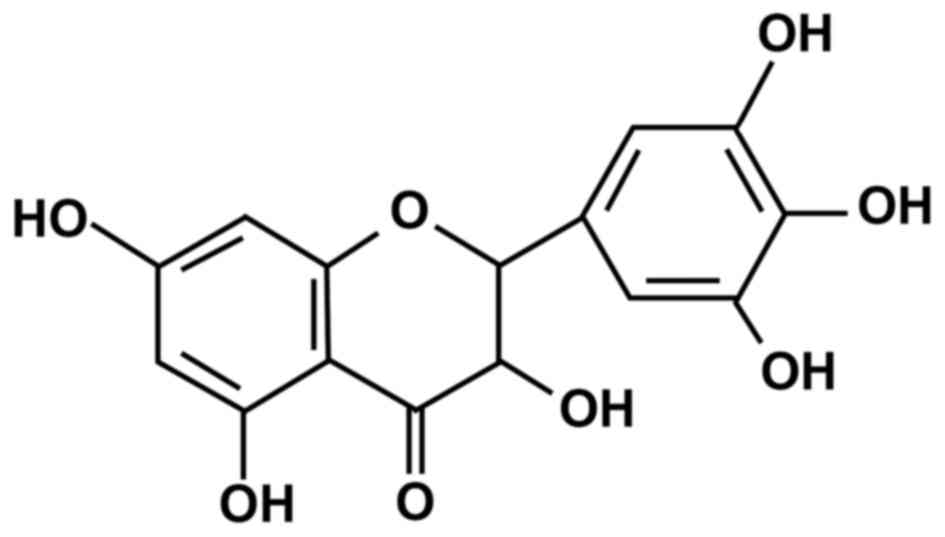
Kou X and Chen N: Pharmacological
potential of ampelopsin in Rattan tea. Food Sci Human Wellness.
1:14–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
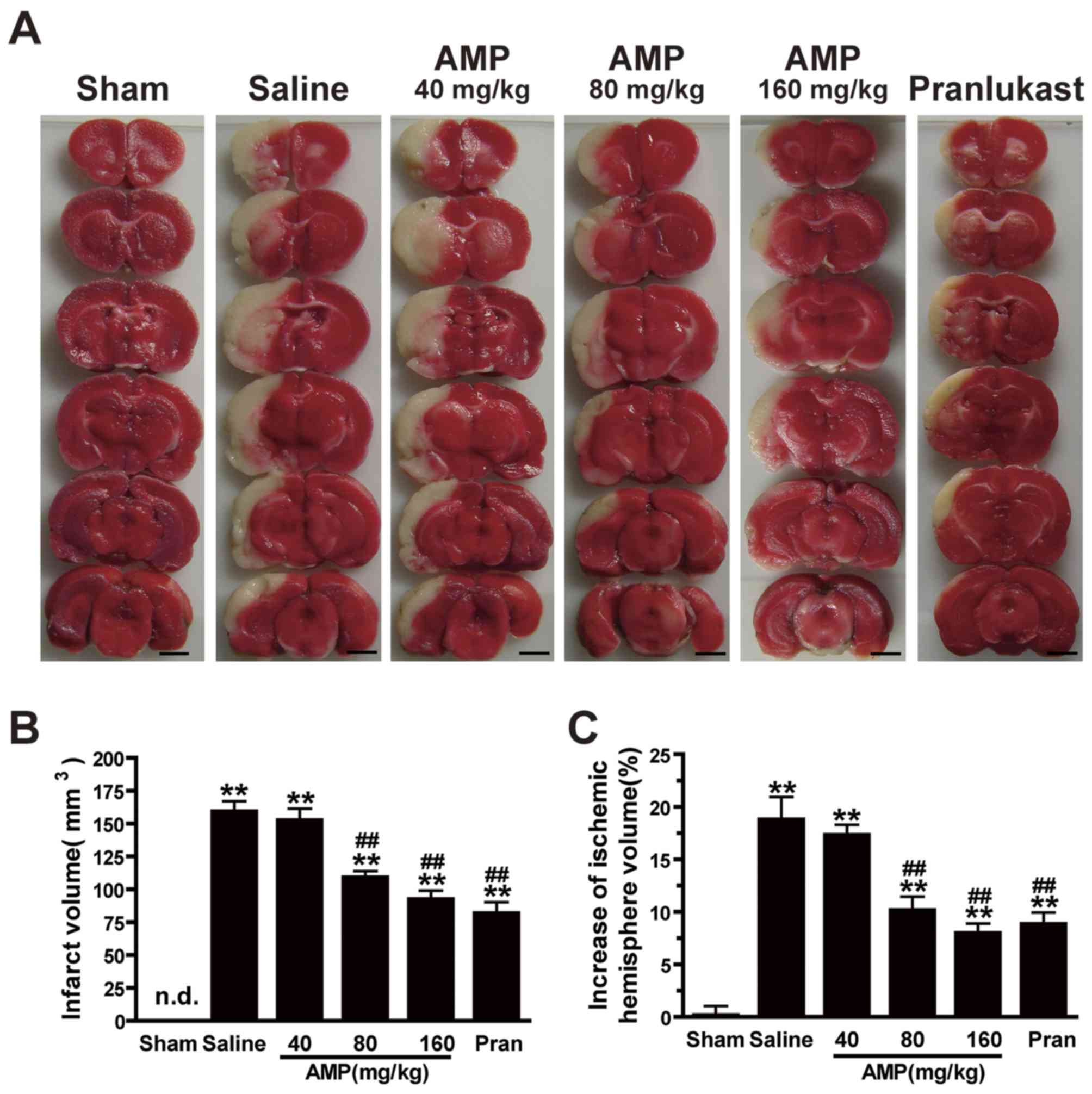
|
|
5
|
Murakami T, Miyakoshi M, Araho D, Mizutani
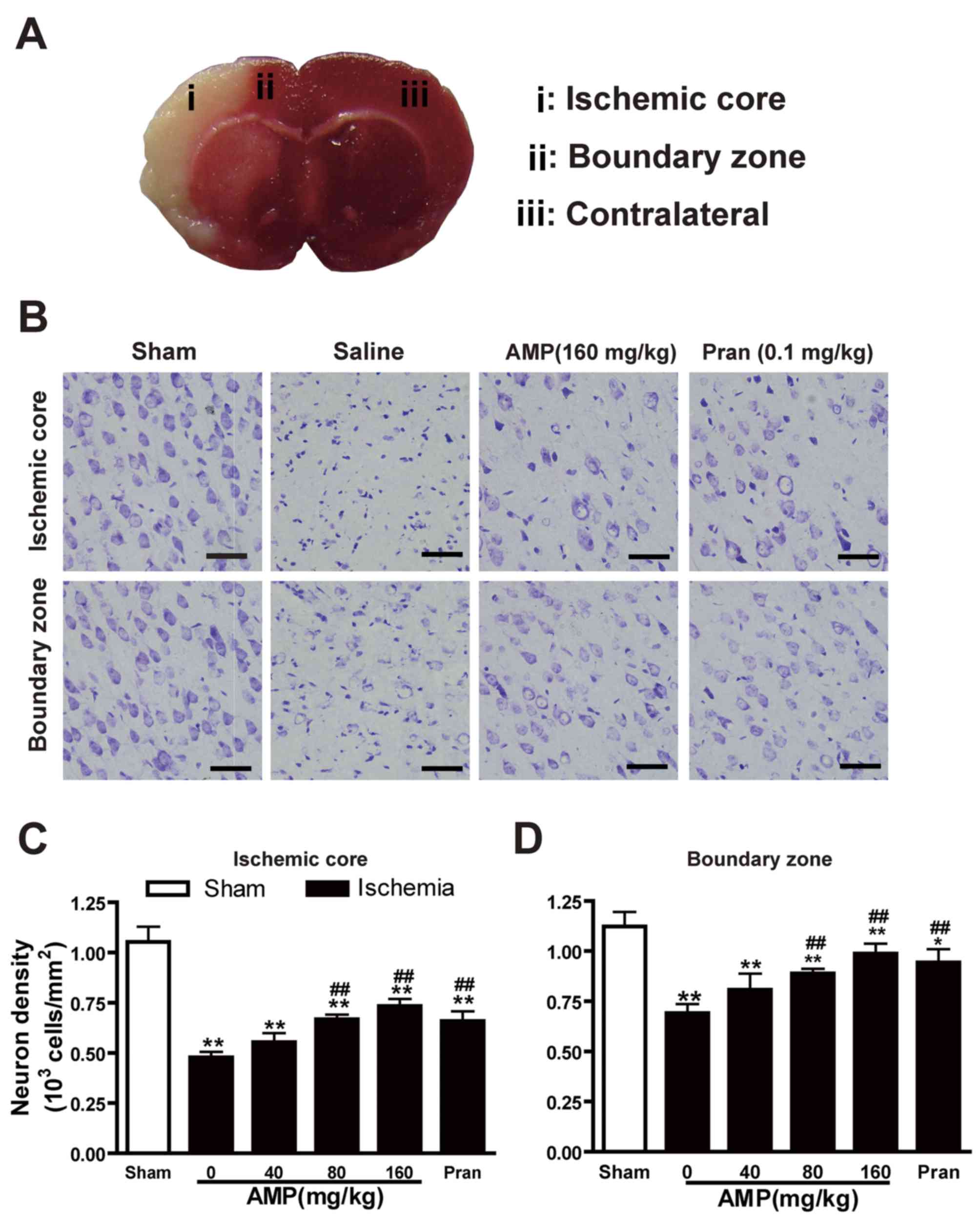
K, Kambara T, Ikeda T, Chou WH, Inukai M, Takenaka A and Igarashi
K: Hepatoprotective activity of tocha, the stems and leaves of
Ampelopsis grossedentata, and ampelopsin. Biofactors.
21:175–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tahara S: A journey of twenty-five years
through the ecological biochemistry of flavonoids. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 71:1387–1404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klotter F and Studer A: Total synthesis of
resveratrol-based natural products using a palladium-catalyzed
decarboxylative arylation and an oxidative Heck reaction. Angew
Chem Int Ed Engl. 53:2473–2476. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pflieger A, Teguo Waffo P, Papastamoulis
Y, Chaignepain S, Subra F, Munir S, Delelis O, Lesbats P, Calmels
C, Andreola ML, et al: Natural stilbenoids isolated from grapevine
exhibiting inhibitory effects against HIV-1 integrase and eukaryote
MOS1 transposase in vitro activities. PLoS One. 8:e811842013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi S, Xin Y, Guo Y, Diao Y, Kou X, Luo L
and Yin Z: Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing
ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-kB signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JY, Jeong HY, Lee HK, Kim S, Hwang BY,
Bae K and Seong YH: Neuroprotection of the leaf and stem of
Vitis amurensis and their active compounds against ischemic
brain damage in rats and excitotoxicity in cultured neurons.
Phytomedicine. 19:150–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou Y, Shu F, Liang X, Chang H, Shi L,
Peng X, Zhu J and Mi M: Ampelopsin induces cell growth inhibition
and apoptosis in breast cancer cells through ROS generation and
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. PLoS One. 9:e890212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kou X, Shen K, An Y, Qi S, Dai WX and Yin
Z: Ampelopsin inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis
by ERK and Akt signaling pathways and up-regulation of heme
oxygenase-1. Phytother Res. 26:988–994. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang B, Dong S, Cen X, Wang X, Liu X,
Zhang H, Zhao X and Wu Y: Ampelopsin sodium exhibits antitumor
effects against bladder carcinoma in orthotopic xenograft models.
Anticancer Drugs. 23:590–596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dung HV, Cuong TD, Chinh NM, Quyen D, Kim
JA, Byeon JS, Woo MH, Choi JS and Min BS: Compounds from the aerial
parts of Piper bavinum and their anti-cholinesterase
activity. Arch Pharm Res. 38:677–682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Papastamoulis Y, Richard T, Nassra M,
Badoc A, Krisa S, Harakat D, Monti JP, Mérillon JM and Waffo-Teguo
P: Viniphenol A, a complex resveratrol hexamer from Vitis
vinifera stalks: Structural elucidation and protective effects
against amyloid-β-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. J Nat Prod.
77:213–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lambertsen KL, Biber K and Finsen B:
Inflammatory cytokines in experimental and human stroke. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 32:1677–1698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi QJ, Wang H, Liu ZX, Fang SH, Song XM,
Lu YB, Zhang WP, Sa XY, Ying HZ and Wei EQ: HAMI 3379, a CysLT2R
antagonist, dose- and time-dependently attenuates brain injury and
inhibits microglial inflammation after focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. Neuroscience. 291:53–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xing C, Arai K, Lo EH and Hommel M:
Pathophysiologic cascades in ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke.
7:378–385. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Turner RC, Dodson SC, Rosen CL and Huber
JD: The science of cerebral ischemia and the quest for
neuroprotection: Navigating past failure to future success. J
Neurosurg. 118:1072–1085. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HH, Oh MH, Park KJ, Heo JH and Lee MW:
Anti-inflammatory activity of sulfate-containing phenolic compounds
isolated from the leaves of Myrica rubra. Fitoterapia.
92:188–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ku KT, Huang YL, Huang YJ and Chiou WF:
Miyabenol A inhibits LPS-induced NO production via IKK/IkappaB
inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the
p38 and PI3K pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 56:8911–8918. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi QJ, Xiao L, Zhao B, Zhang XY, Wang XR,
Xu DM, Yu SY, Fang SH, Lu YB, Zhang WP, et al:
Intracerebroventricular injection of HAMI 3379, a selective
cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 antagonist, protects against acute
brain injury after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res.
1484:57–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chu LS, Wei EQ, Yu GL, Fang SH, Zhou Y,
Wang ML and Zhang WP: Pranlukast reduces neutrophil but not
macrophage/microglial accumulation in brain after focal cerebral
ischemia in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:282–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu GL, Wei EQ, Wang ML, Zhang WP, Zhang
SH, Weng JQ, Chu LS, Fang SH, Zhou Y, Chen Z, et al: Pranlukast, a
cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-1 antagonist, protects against
chronic ischemic brain injury and inhibits the glial scar formation
in mice. Brain Res. 1053:116–125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang LH and Wei EQ: Neuroprotective
effect of ONO-1078, a leukotriene receptor antagonist, on transient
global cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 24:1241–1247.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nirogi R, Kandikere V, Mudigonda K,
Bhyrapuneni G, Muddana N, Saralaya R and Benade V: A simple and
rapid method to collect the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and its
application for the assessment of drug penetration into the central
nervous system. J Neurosci Methods. 178:116–119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pegg CC, He C, Stroink AR, Kattner KA and
Wang CX: Technique for collection of cerebrospinal fluid from the
cisterna magna in rat. J Neurosci Methods. 187:8–12. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yonemori F, Yamaguchi T, Yamada H and
Tamura A: Evaluation of a motor deficit after chronic focal
cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 18:1099–1106.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin TN, He YY, Wu G, Khan M and Hsu CY:
Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral
ischemia model in rats. Stroke. 24:117–121. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schmued LC and Hopkins KJ: Fluoro-Jade B:
A high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal
degeneration. Brain Res. 874:123–130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schmidt-Kastner R, Meller D, Bellander BM,
Strömberg I, Olson L and Ingvar M: A one-step immunohistochemical
method for detection of blood-brain barrier disturbances for
immunoglobulins in lesioned rat brain with special reference to
false-positive labelling in immunohistochemistry. J Neurosci
Methods. 46:121–132. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tominaga T and Ohnishi ST:
Interrelationship of brain edema, motor deficits, and memory
impairment in rats exposed to focal ischemia. Stroke. 20:513–518.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fang SH, Wei EQ, Zhou Y, Wang ML, Zhang
WP, Yu GL, Chu LS and Chen Z: Increased expression of cysteinyl
leukotriene receptor-1 in the brain mediates neuronal damage and
astrogliosis after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neuroscience.
140:969–979. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gürer G, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Erdemli E, Can
A and Dalkara T: Astrocytes are more resistant to focal cerebral
ischemia than neurons and die by a delayed necrosis. Brain Pathol.
19:630–641. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jia F, Yin YH, Gao GY, Wang Y, Cen L and
Jiang JY: MMP-9 inhibitor SB-3CT attenuates behavioral impairments
and hippocampal loss after traumatic brain injury in rat. J
Neurotrauma. 31:1225–1234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang Z, Watts LT, Huang S, Shen Q,
Rodriguez P, Chen C, Zhou C and Duong TQ: The effects of methylene
blue on autophagy and apoptosis in MRI-defined normal tissue,
ischemic penumbra and ischemic core. PLoS One. 10:e01319292015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gotoh O, Asano T, Koide T and Takakura K:
Ischemic brain edema following occlusion of the middle cerebral
artery in the rat. I: The time courses of the brain water, sodium
and potassium contents and blood-brain barrier permeability to
125I-albumin. Stroke. 16:101–109. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lv S, Song HL, Zhou Y, Li LX, Cui W, Wang
W and Liu P: Tumour necrosis factor-alpha affects blood-brain
barrier permeability and tight junction-associated occludin in
acute liver failure. Liver Int. 30:1198–1210. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rodrigues SF and Granger DN: Blood cells
and endothelial barrier function. Tissue Barriers. 3:e9787202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Willis CL, Brooks TA and Davis TP: Chronic
inflammatory pain and the neurovascular unit: A central role for
glia in maintaining BBB integrity? Curr Pharm Des. 14:1625–1643.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Candelario-Jalil E: Injury and repair
mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Considerations for the development
of novel neurotherapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 10:644–654.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kriz J: Inflammation in ischemic brain
injury: Timing is important. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 18:145–157. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jørgensen HS, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO and
Olsen TS: Progressive apoplexy. Incidence, risk factors and
prognosis-the Copenhagen stroke study. Ugeskr Laeger.
157:3619–3622. 1995.(In Danish). PubMed/NCBI
|