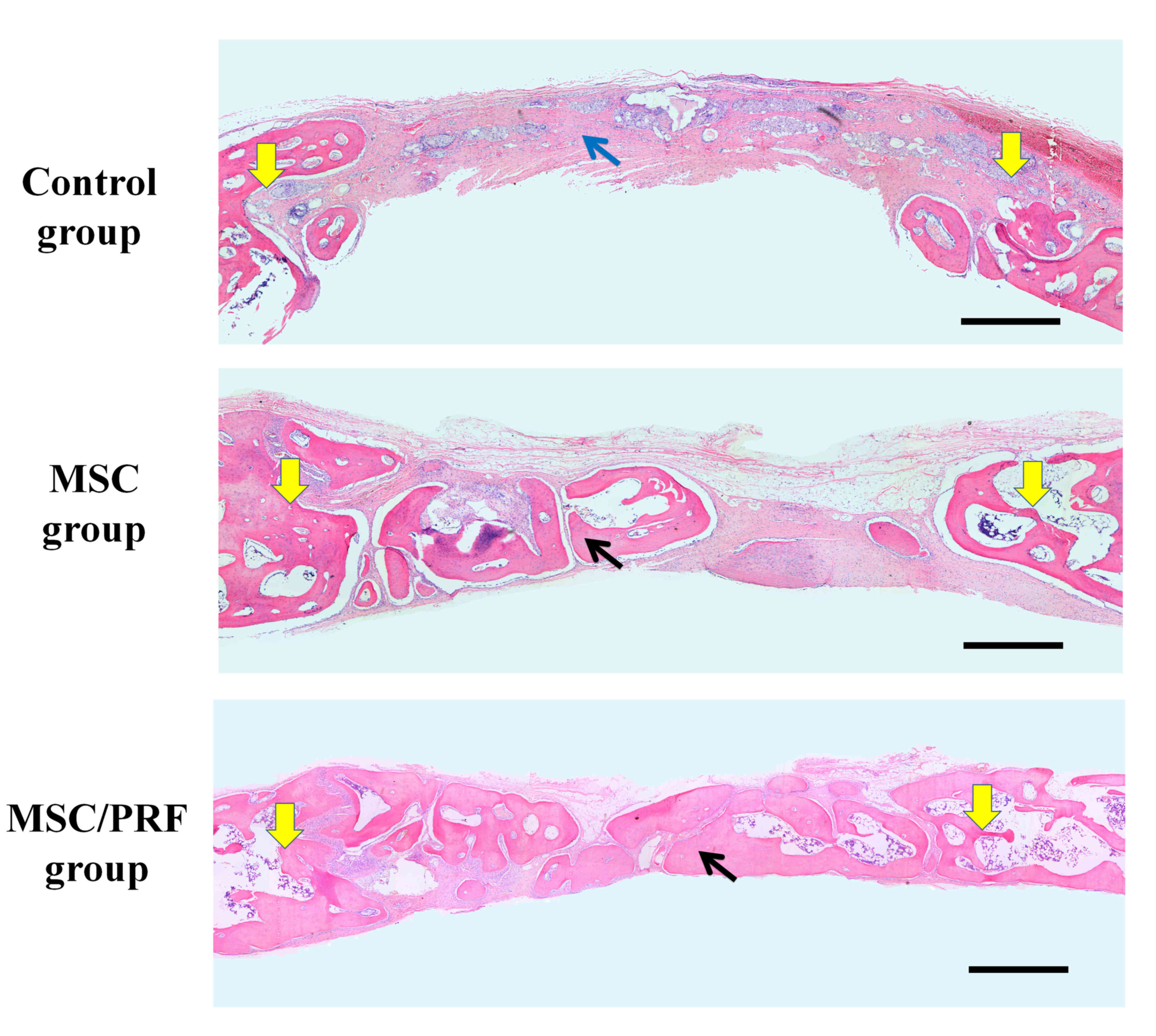
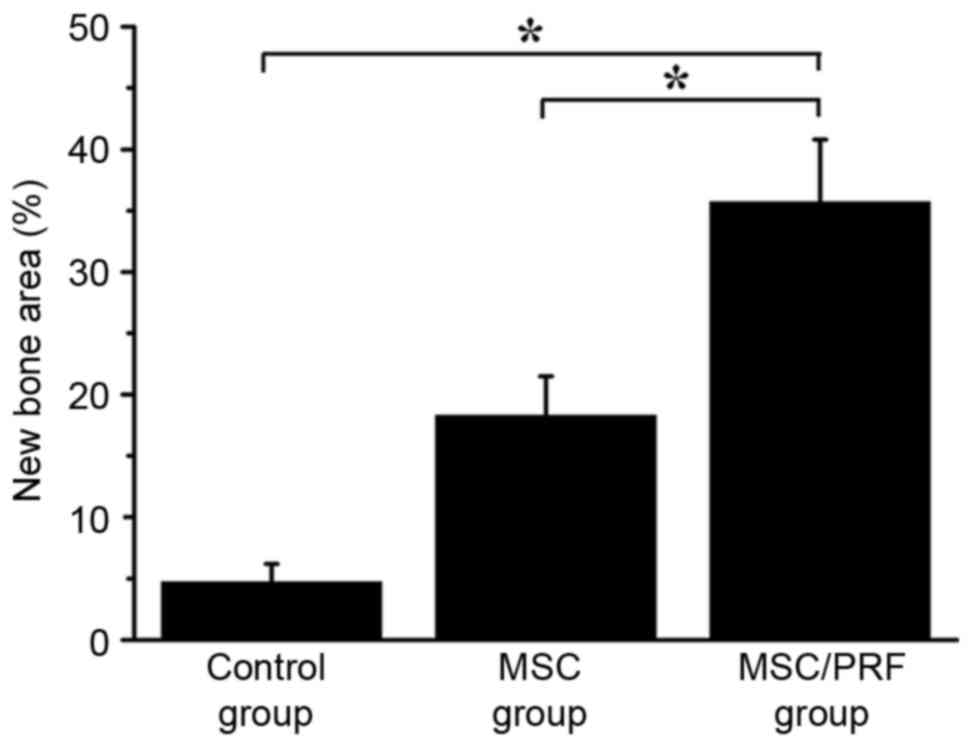
|
1
|
Uchiyama H, Yamato M, Sasaki R, Sekine H,
Yang J, Ogiuchi H, Ando T and Okano T: In vivo 3D analysis with
micro-computed tomography of rat calvaria bone regeneration using
periosteal cell sheets fabricated on temperature-responsive culture
dishes. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 5:483–490. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giovanini AF, Deliberador TM, Gonzaga CC,
de Oliveira Filho MA, Göhringer I, Kuczera J, Zielak JC and de
Andrade Urban C: Platelet-rich plasma diminishes calvarial bone
repair associated with alterations in collagen matrix composition
and elevated CD34+ cell prevalence. Bone. 46:1597–1603. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Intini G: The use of platelet-rich plasma
in bone reconstruction therapy. Biomaterials. 30:4956–4966. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burstein FD, Simms C, Cohen SR, Work F and
Paschal M: Iliac crest bone graft harvesting techniques: A
comparison. Plast Reconstr Surg. 105:34–39. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Monaco AP: The beginning of clinical
tolerance in solid organ allografts. Exp Clin Transplant.
2:153–161. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou Y, Chen F, Ho ST, Woodruff MA, Lim TM
and Hutmacher DW: Combined marrow stromal cell-sheet techniques and
high-strength biodegradable composite scaffolds for engineered
functional bone grafts. Biomaterials. 28:814–824. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kretlow JD, Spicer PP, Jansen JA, Vacanti
CA, Kasper FK and Mikos AG: Uncultured marrow mononuclear cells
delivered within fibrin glue hydrogels to porous scaffolds enhance
bone regeneration within critical-sized rat cranial defects. Tissue
Eng Part A. 16:3555–3568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Porada CD, Zanjani ED and Almeida-Porad G:
Adult mesenchymal stem cells: A pluripotent population with
multiple applications. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 1:365–369. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gazit D, Turgeman G, Kelley P, Wang E,
Jalenak M, Zilberman Y and Moutsatsos I: Engineered pluripotent
mesenchymal cells integrate and differentiate in regenerating bone:
A novel cell-mediated gene therapy. J Gene Med. 1:121–133. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kon E, Muraglia A, Corsi A, Bianco P,
Marcacci M, Martin I, Boyde A, Ruspantini I, Chistolini P, Rocca M,
et al: Autologous bone marrow stromal cells loaded onto porous
hydroxyapatite ceramic accelerate bone repair in critical-size
defects of sheep long bones. J Biomed Mater Res. 49:328–337. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bianco P, Riminucci M, Gronthos S and
Robey PG: Bone marrow stromal stem cells: Nature, biology, and
potential applications. Stem Cells. 19:180–192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quarto R, Mastrogiacomo M, Cancedda R,
Kutepov SM, Mukhachev V, Lavroukov A, Kon E and Marcacci M: Repair
of large bone defects with the use of autologous bone marrow
stromal cells. N Engl J Med. 344:385–386. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamada Y, Ueda M, Hibi H and Nagasaka T:
Translational research for injectable tissue-engineered bone
regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma:
From basic research to clinical case study. Cell Transplant.
13:343–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meijer GJ, de Bruijn JD, Koole R and van
Blitterswijk CA: Cell based bone tissue engineering in jaw defects.
Biomaterials. 29:3053–3061. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou H and Lee J: Nanoscale hydroxyapatite
particles for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 7:2769–2781.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin H, Zhang K, Qiao C, Yuan A, Li D, Zhao
L, Shi C, Xu X, Ni S, Zheng C, et al: Efficiently engineered cell
sheet using a complex of polyethylenimine-alginate nanocomposites
plus bone morphogenetic protein 2 gene to promote new bone
formation. Int J Nanomedicine. 9:2179–2190. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang J, Yamato M, Shimizu T, Sekine H,
Ohashi K, Kanzaki M, Ohki T, Nishida K and Okano T: Reconstruction
of functional tissues with cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials.
28:5033–5043. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma D, Ren L, Liu Y, Chen F, Zhang J, Xue Z
and Mao T: Engineering scaffold-free bone tissue using bone marrow
stromal cell sheets. J Orthop Res. 28:697–702. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakamura A, Akahane M, Shigematsu H,
Tadokoro M, Morita Y, Ohgushi H, Dohi Y, Imamura T and Tanaka Y:
Cell sheet transplantation of cultured mesenchymal stem cells
enhances bone formation in a rat nonunion model. Bone. 46:418–424.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bohner M: Calcium orthophosphates in
medicine: From ceramics to calcium phosphate cements. Injury.
31:(Suppl 4). S37–S47. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Johnson Wagoner AJ and Herschler BA: A
review of the mechanical behavior of CaP and CaP/polymer composites
for applications in bone replacement and repair. Acta Biomater.
7:16–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
LeGeros RZ: Biodegradation and
bioresorption of calcium phosphate ceramics. Clin Mater. 14:65–88.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dorozhkin SV: Nanosized and
nanocrystalline calcium orthophosphates. Acta Biomater. 6:715–734.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim ES, Park EJ and Choung PH: Platelet
concentration and its effect on bone formation in calvarial
defects: An experimental study in rabbits. J Prosthet Dent.
86:428–433. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito K, Yamada Y, Naiki T and Ueda M:
Simultaneous implant placement and bone regeneration around dental
implants using tissue-engineered bone with fibrin glue, mesenchymal
stem cells and platelet-rich plasma. Clin Oral Implants Res.
17:579–586. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liao HT, Chen CT, Chen CH, Chen JP and
Tsai JC: Combination of guided osteogenesis with autologous
platelet-rich fibrin glue and mesenchymal stem cell for mandibular
reconstruction. J Trauma. 70:228–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anitua E, Sanchez M, Nurden AT, Nurden P,
Orive G and Andía I: New insights into and novel applications for
platelet-rich fibrin therapies. Trends Biotechnol. 24:227–234.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ehrenfest Dohan DM, Rasmusson L and
Albrektsson T: Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure
platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin
(L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 27:158–167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eppley BL, Woodell JE and Higgins J:
Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from
platelet-rich plasma: Implications for wound healing. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 114:1502–1508. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tong W, Glimcher MJ, Katz JL, Kuhn L and
Eppell SJ: Size and shape of mineralites in young bovine bone
measured by atomic force microscopy. Calcif Tissue Int. 72:592–598.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL,
Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J and Gogly B: Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A
second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: Leucocyte
activation: A new feature for platelet concentrates? Oral Surg Oral
Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 101:e51–e55. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ehrenfest Dohan DM, Doglioli P, de Peppo
GM, Del Corso M and Charrier JB: Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin
(PRF) stimulates in vitro proliferation and differentiation of
human oral bone mesenchymal stem cell in a dose-dependent way. Arch
Oral Biol. 55:185–194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shimizu T, Yamato M, Isoi Y, Akutsu T,
Setomaru T, Abe K, Kikuchi A, Umezu M and Okano T: Fabrication of
pulsatile cardiac tissue grafts using a novel 3-dimensional cell
sheet manipulation technique and temperature-responsive cell
culture surfaces. Circ Res. 90:e402002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL,
Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J and Gogly B: Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A
second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: Technological
concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Endod. 101:e37–e44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao YH, Zhang M, Liu NX, Lv X, Zhang J,
Chen FM and Chen YJ: The combined use of cell sheet fragments of
periodontal ligament stem cells and platelet-rich fibrin granules
for avulsed tooth reimplantation. Biomaterials. 34:5506–5520. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hollinger JO and Kleinschmidt JC: The
critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair
materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1:60–68. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ehrenfest Dohan DM, Lemo N, Jimbo R and
Sammartino G: Selecting a relevant animal model for testing the in
vivo effects of Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): Rabbit
tricks and traps. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
110:413–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Langer R and Vacanti JP: Tissue
engineering. Science. 260:920–926. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mattar P and Bieback K: Comparing the
immunomodulatory properties of bone marrow, adipose tissue and
birth-associated tissue mesenchymal stromal cells. Front Immunol.
6:5602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu X, Tang X, Gohil SV and Laurencin CT:
Biomaterials for bone regenerative engineering. Adv Healthc Mater.
4:1268–1285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Latsinik
NV, Panasyuk AF and Keiliss-Borok IV: Stromal cells responsible for
transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues.
Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation.
17:331–340. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bronckaers A, Hilkens P, Martens W,
Gervois P, Ratajczak J, Struys T and Lambrichts I: Mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells as a pharmacological and therapeutic approach to
accelerate angiogenesis. Pharmacol Ther. 143:181–196. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Satija NK, Singh VK, Verma YK, Gupta P,
Sharma S, Afrin F, Sharma M, Sharma P, Tripathi RP and Gurudutta
GU: Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: A new paradigm in
regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med. 13:4385–4402. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kagami H, Agata H and Tojo A: Bone marrow
stromal cells (bone marrow-derived multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells) for bone tissue engineering: Basic science to clinical
translation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:286–289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Caplan AI and Correa D: The MSC: An injury
drugstore. Cell Stem Cell. 9:11–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, Lee CW,
Barr S, Fuchs S and Epstein SE: Marrow-derived stromal cells
express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines
and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine
mechanisms. Circ Res. 94:678–685. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG and Tredget EE:
Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through
differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 25:2648–2659. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen L, Tredget EE, Wu PY and Wu Y:
Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and
endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One.
3:e18862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Del Papa N, Quirici N, Soligo D, Scavullo
C, Cortiana M, Borsotti C, Maglione W, Comina DP, Vitali C,
Fraticelli P, et al: Bone marrow endothelial progenitors are
defective in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 54:2605–2615.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nauta AJ and Fibbe WE: Immunomodulatory
properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood. 110:3499–3506.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Holtorf HL, Jansen JA and Mikos AG:
Ectopic bone formation in rat marrow stromal cell/titanium fiber
mesh scaffold constructs: Effect of initial cell phenotype.
Biomaterials. 26:6208–6216. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang J, Yamato M, Kohno C, Nishimoto A,
Sekine H, Fukai F and Okano T: Cell sheet engineering: Recreating
tissues without biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials.
26:6415–6422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Sha XJ, Li GH, Yang FS, Ji K, Wen
LY, Liu SY, Chen L, Ding Y and Xuan K: Comparative characterization
of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp
stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 57:1231–1240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen F, Zhou Y, Barnabas ST, Woodruff MA
and Hutmacher DW: Engineering tubular bone constructs. J Biomech.
40:(Suppl 1). S73–S79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Stupp SI and Ciegler GW: Organoapatites:
Materials for artificial bone. I. Synthesis and microstructure. J
Biomed Mater Res. 26:169–183. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Appleford MR, Oh S, Oh N and Ong JL: In
vivo study on hydroxyapatite scaffolds with trabecular architecture
for bone repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 89:1019–1027. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cai Y, Liu Y, Yan W, Hu Q, Tao J, Zhang M,
Shi Z and Tang R: Role of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle size in bone
cell proliferation. J Mater Chem. 17:3780–3787. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Granchi D, Devescovi V, Baglio SR, Magnani
M, Donzelli O and Baldini N: A regenerative approach for bone
repair in congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia associated or not
associated with type 1 neurofibromatosis: Correlation between
laboratory findings and clinical outcome. Cytotherapy. 14:306–314.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pripatnanont P, Nuntanaranont T,
Vongvatcharanon S and Phurisat K: The primacy of platelet-rich
fibrin on bone regeneration of various grafts in rabbit's calvarial
defects. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 41:e191–e200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xuan F, Lee CU, Son JS, Jeong SM and Choi
BH: A comparative study of the regenerative effect of sinus bone
grafting with platelet-rich fibrin-mixed Bio-Oss® and
commercial fibrin-mixed Bio-Oss®: An experimental study.
J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 42:e47–e50. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tunali M, Özdemir H, Küçükodaci Z, Akman S
and Firatlı E: In vivo evaluation of titanium-prepared
platelet-rich fibrin (T-PRF): A new platelet concentrate. Br J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 51:438–443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL,
Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J and Gogly B: Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A
second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: Platelet-related
biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Endod. 101:e45–e50. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ehrenfest Dohan DM, de Peppo GM, Doglioli
P and Sammartino G: Slow release of growth factors and
thrombospondin-1 in Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A gold
standard to achieve for all surgical platelet concentrates
technologies. Growth Factors. 27:63–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
He L, Lin Y, Hu X, Zhang Y and Wu H: A
comparative study of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich
plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of
rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol Endod. 108:707–713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu B, Tan XY, Liu YP, Xu XF, Li L, Xu HY,
An R and Chen FM: The adjuvant use of stromal vascular fraction and
platelet-rich fibrin for autologous adipose tissue transplantation.
Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 19:1–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Schmitz JP and Hollinger JO: The critical
size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial
nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 299–308. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ade Costa M, Kobayashi GS, Bueno DF,
Martins MT, Mde Ferreira C, Passos-Bueno MR and Alonso N: An
experimental model for the study of craniofacial deformities. Acta
Cir Bras. 25:264–268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Djasim UM, Wolvius EB, van Neck JW,
Weinans H and van der Wal KGH: Recommendations for optimal
distraction protocols for various animal models on the basis of a
systematic review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
36:877–883. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lee EH, Kim JY, Kweon HY, Jo YY, Min SK,
Park YW, Choi JY and Kim SG: A combination graft of
low-molecular-weight silk fibroin with Choukroun platelet-rich
fibrin for rabbit calvarial defect. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Oral Radiol Endod. 109:e33–e38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang Y, Tangl S, Huber CD, Lin Y, Qiu L
and Rausch-Fan X: Effects of Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin on
bone regeneration in combination with deproteinized bovine bone
mineral in maxillary sinus augmentation: A histological and
histomorphometric study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 40:321–328. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li Q, Pan S, Dangaria SJ, Gopinathan G,
Kolokythas A, Chu S, Geng Y, Zhou Y and Luan X: Platelet-rich
fibrin promotes periodontal regeneration and enhances alveolar bone
augmentation. Biomed Res Int. 2013:6380432013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Boquest AC, Shahdadfar A, Frønsdal K,
Sigurjonsson O, Tunheim SH, Collas P and Brinchmann JE: Isolation
and transcription profiling of purified uncultured human stromal
stem cells: Alteration of gene expression after in vitro cell
culture. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1131–1141. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lepperdinger G, Brunauer R, Jamnig A,
Laschober G and Kassem M: Controversial issue: Is it safe to employ
mesenchymal stem cells in cell-based therapies? Exp Gerontol.
43:1018–1023. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lawson JH: The clinical use and
immunologic impact of thrombin in surgery. Semin Thromb Hemost.
32:(Suppl 1). S98–S110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|