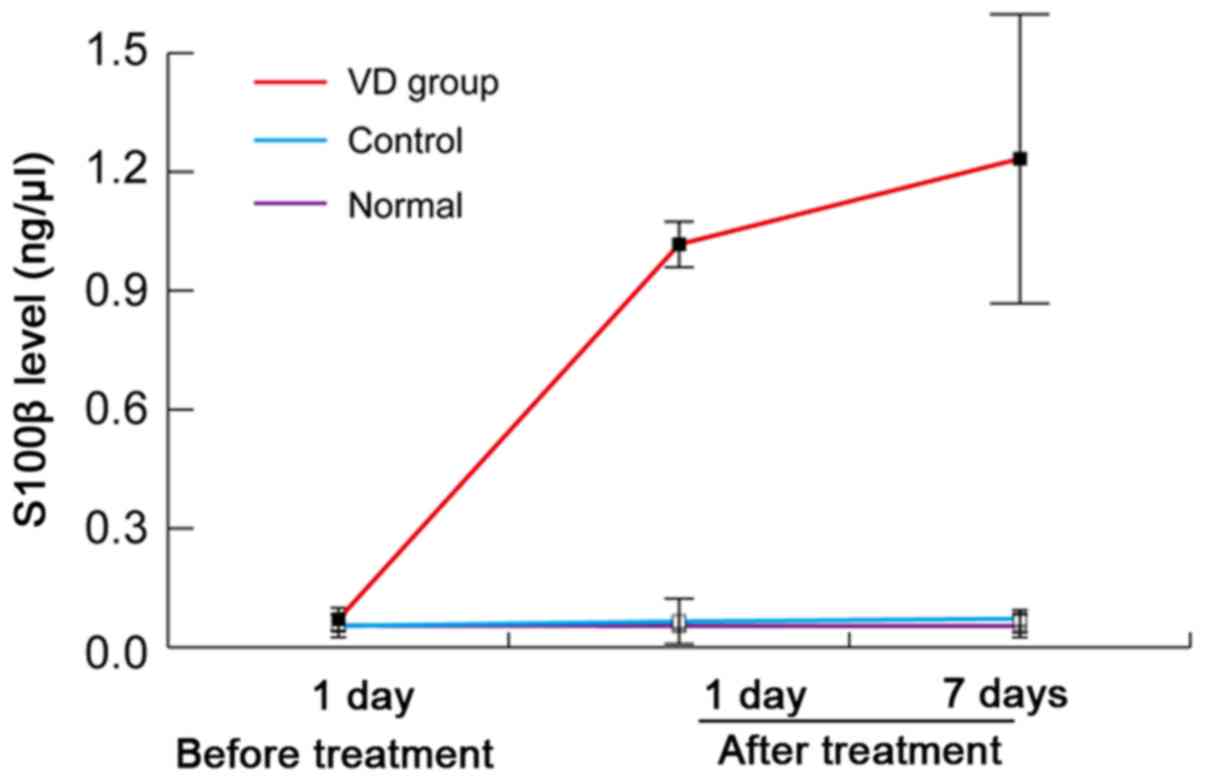
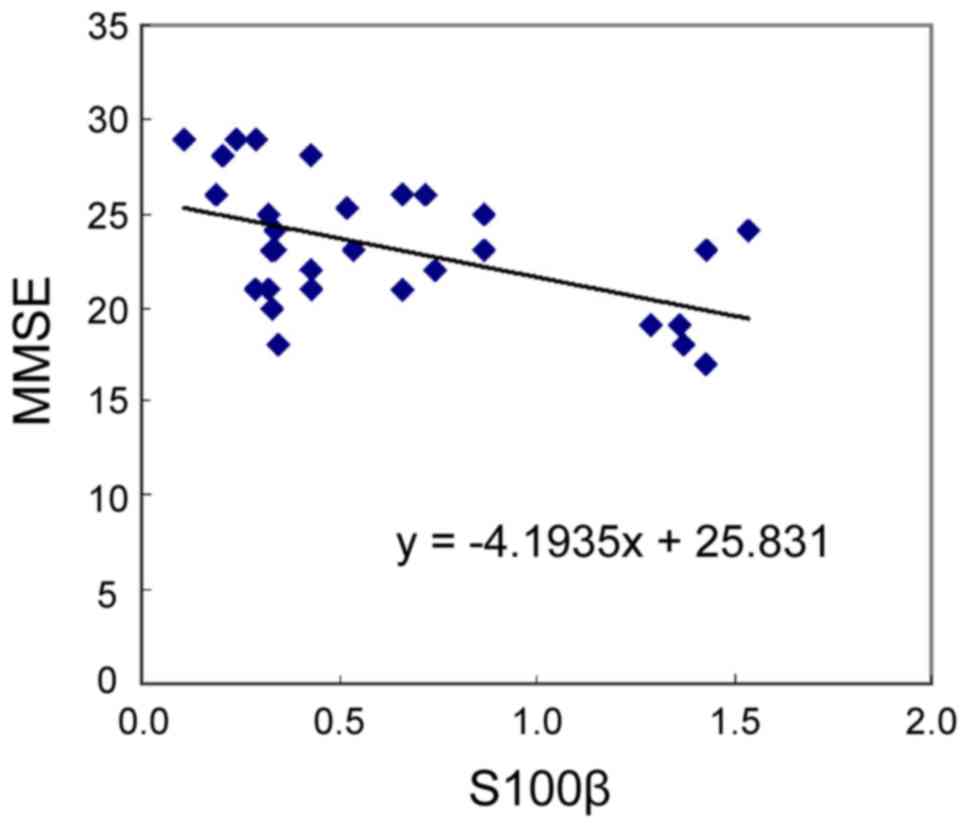
|
1
|
Black SE: Vascular cognitive impairment:
epidemiology, subtypes, diagnosis and management. J R Coll
Physicians Edinb. 41:49–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo J, Yang CX, Yang J and Yao Y:
Glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates cognitive impairment on vascular
dementia model rats associated with oxidative damage and inhibition
of voltage-gated sodium channels. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
May 27–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhi XL, Li CY, Xue M, Hu Y and Ji Y:
Changes in cognitive function due to combined propofol and
remifentanil treatment are associated with phosphorylation of Tau
in the hippocampus, abnormal total water and calcium contents of
the brain, and elevated serum S100β levels. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 20:2156–2162. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iemolo F, Sanzaro E, Duro G, Giordano A
and Paciaroni M: The prognostic value of biomarkers in stroke.
Immun Ageing. 13:192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Román GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T,
Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH, Amaducci L, Orgogozo JM, Brun A,
Hofman A, et al: Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for
research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop.
Neurology. 43:250–260. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ong HL, Subramaniam M, Abdin E, Wang P,
Vaingankar JA, Lee SP, Shafie S, Seow E and Chong SA: Performance
of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in long-stay patients with
schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders in a psychiatric
institute. Psychiatry Res. 241:256–262. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marceau EM, Lunn J, Berry J, Kelly PJ and
Solowij N: The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is sensitive to
head injury and cognitive impairment in a residential alcohol and
other drug therapeutic community. J Subst Abuse Treat. 66:30–36.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wen YH, Wu SS, Lin CH, Tsai JH, Yang P,
Chang YP and Tseng KH: A bayesian approach to identifying new risk
factors for dementia: a nationwide population-based study. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e36582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du SQ, Wang XR, Xiao LY, Tu JF, Zhu W, He
T and Liu CZ: Molecular mechanisms of vascular dementia: what can
be learned from animal models of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion?
Mol Neurobiol. May 20–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhou S, Bao J, Wang Y and Pan S: S100β as
a biomarker for differential diagnosis of intracerebral hemorrhage
and ischemic stroke. Neurol Res. 38:327–332. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prohl J, Bodenburg S and Rustenbach SJ:
Early prediction of long-term cognitive impairment after cardiac
arrest. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 15:344–353. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Scott DA, Evered LA and Silbert BS:
Cardiac surgery, the brain, and inflammation. J Extra Corpor
Technol. 46:15–22. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Quintard H, Leduc S, Ferrari P, Petit I
and Ichai C: Early and persistent high level of PS 100β is
associated with increased poor neurological outcome in patients
with SAH: is there a PS 100β threshold for SAH prognosis? Crit
Care. 20:332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chou RH, Chiu CC, Huang CC, Chan WL, Huang
PH, Chen YC, Chen TJ, Chung CM, Lin SJ, Chen JW, et al: Prediction
of vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease in patients with
atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter using CHADS2
score. J Chin Med Assoc. 79:470–476. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee C: Best linear unbiased prediction of
individual polygenic susceptibility to sporadic vascular dementia.
J Alzheimers Dis. 53:1115–1119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Min D and Xu-Feng W: An updated
meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of acupuncture treatment
for vascular cognitive impairment without dementia. Curr Neurovasc
Res. 13:230–238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Jin X, Yan J, Jin Y, Yu W, Wu H
and Xu S: Prevalence of dementia, cognitive status and associated
risk factors among elderly of Zhejiang province, China in 2014. Age
Ageing. May 21–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Czuriga-Kovács KR, Czuriga D and Csiba L:
Influence of hypertension, alone and in combination with other
vascular risk factors on cognition. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
15:690–698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lane EM, Paul RH, Moser DJ, Fletcher TD
and Cohen RA: Influence of education on subcortical
hyperintensities and global cognitive status in vascular dementia.
J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 17:531–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Plassman BL, Langa KM, Fisher GG, Heeringa
SG, Weir DR, Ofstedal MB, Burke JR, Hurd MD, Potter GG, Rodgers WL,
et al: Prevalence of dementia in the United States: the aging,
demographics, and memory study. Neuroepidemiology. 29:125–132.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|