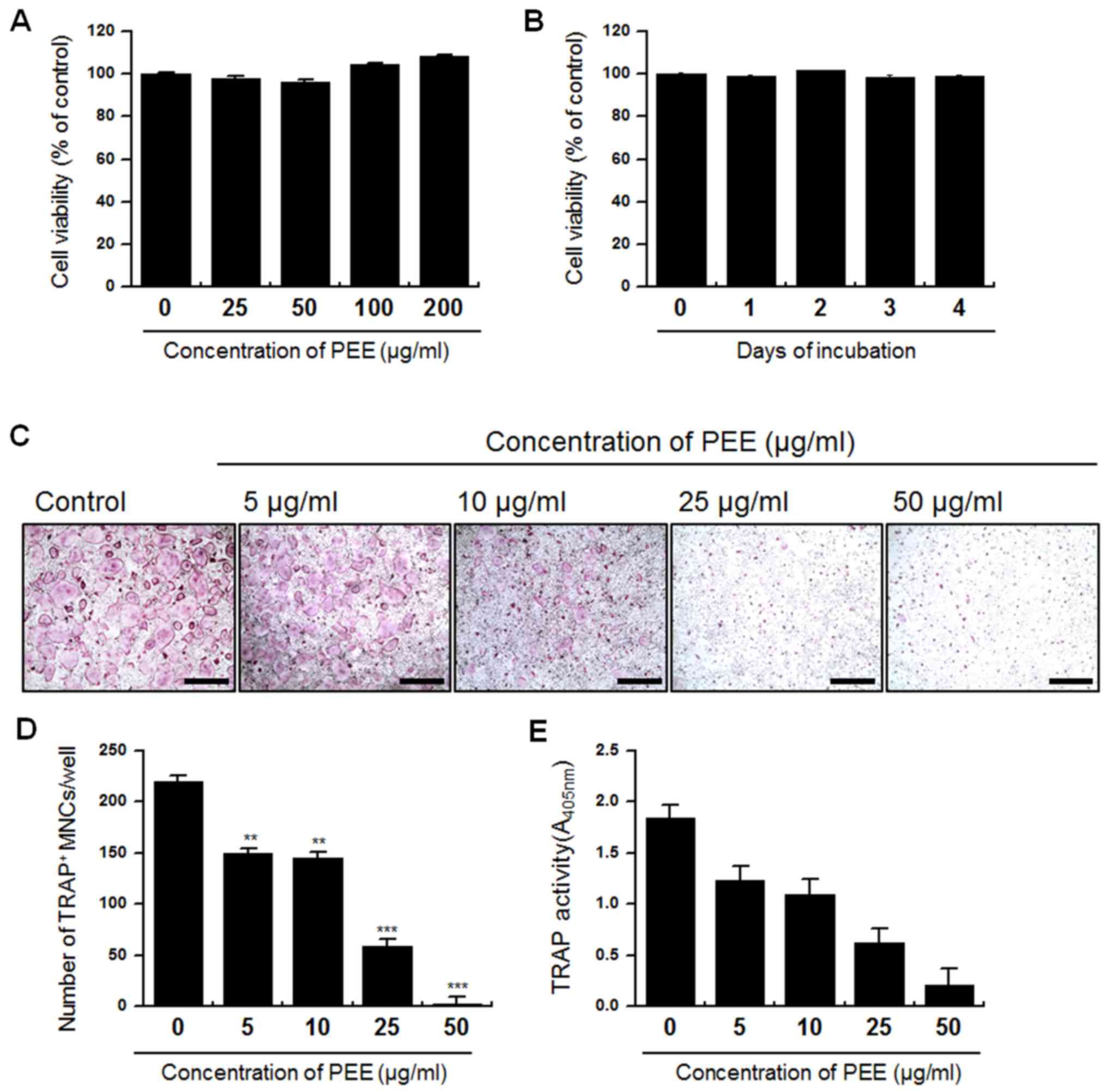
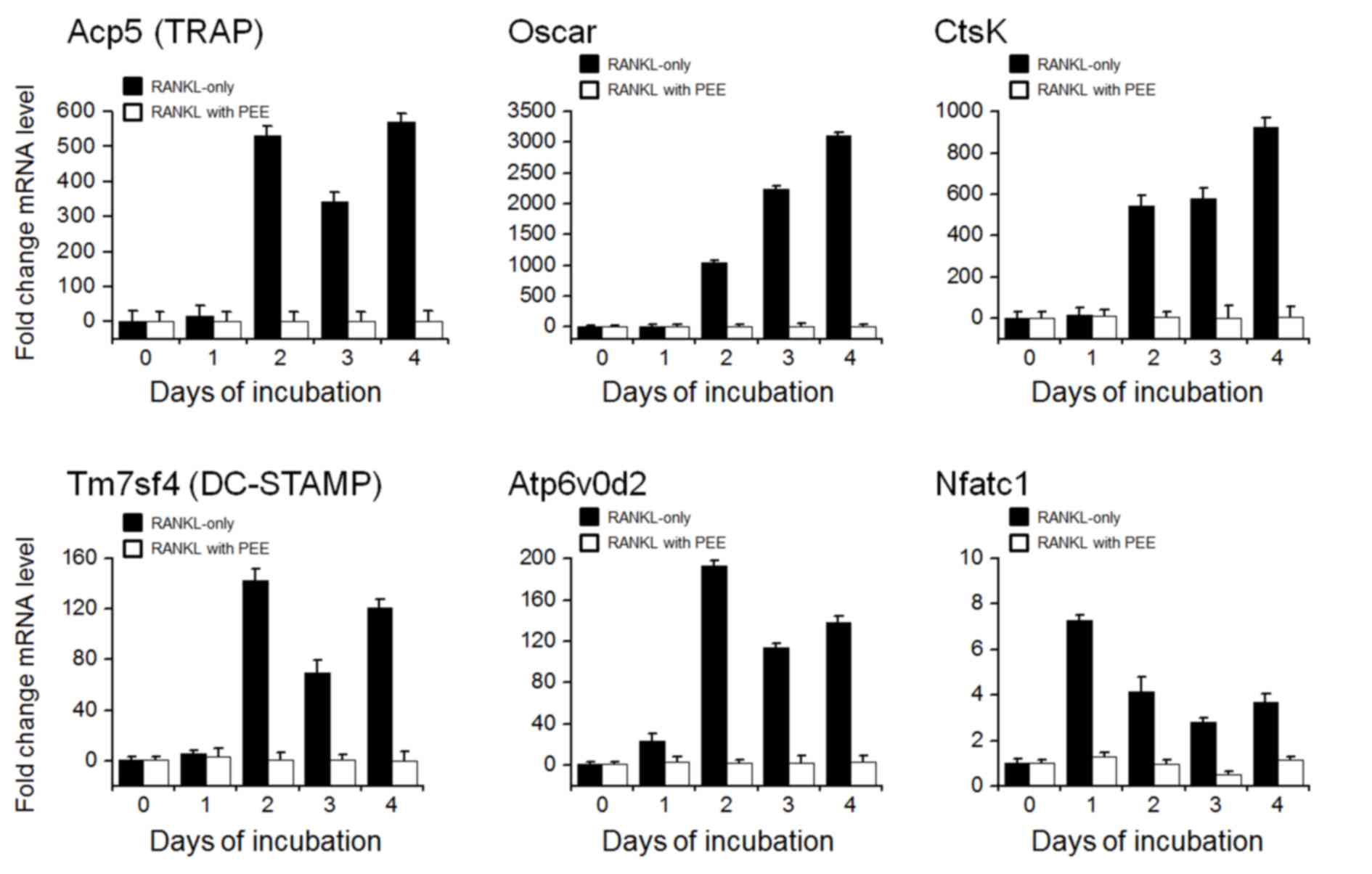
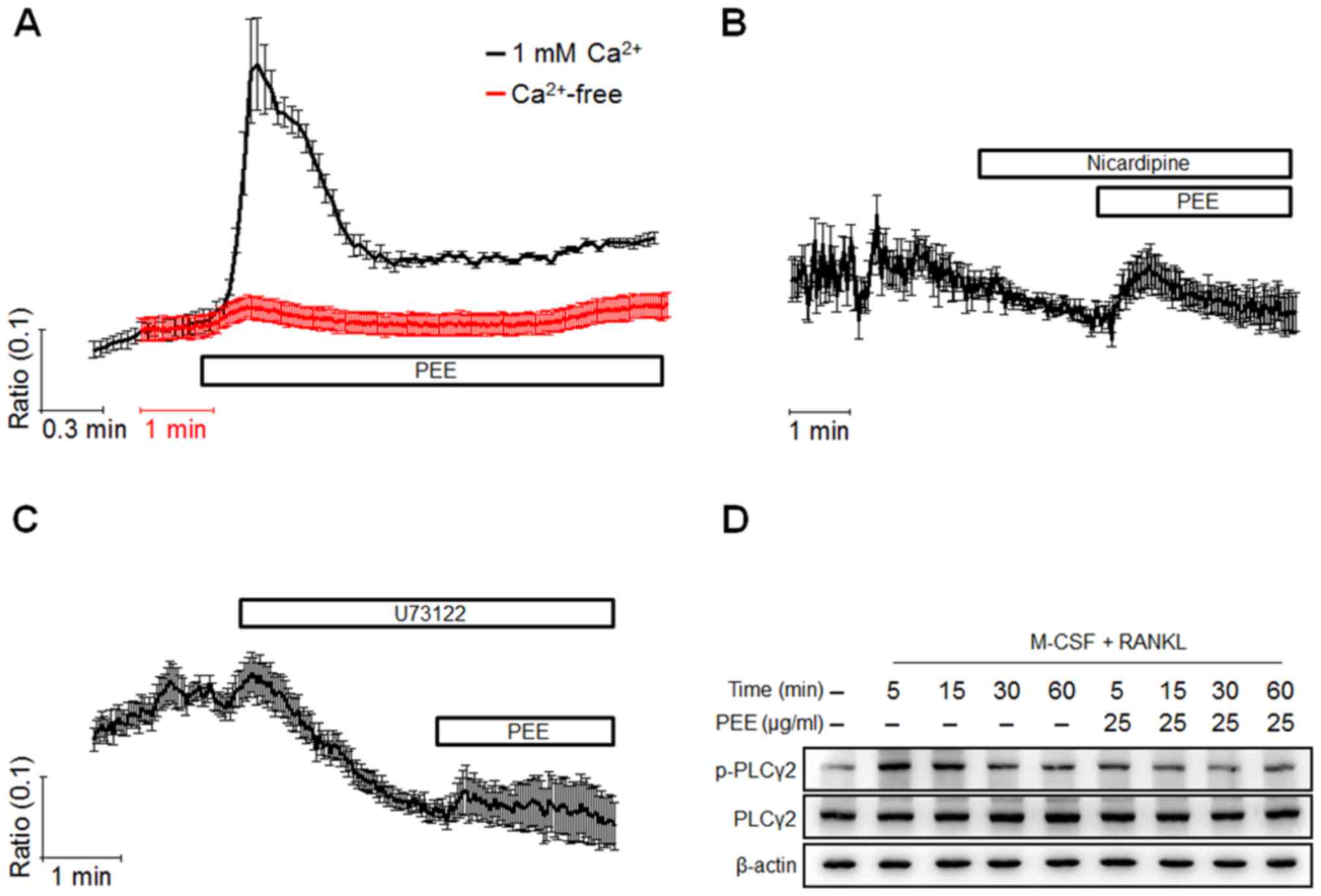
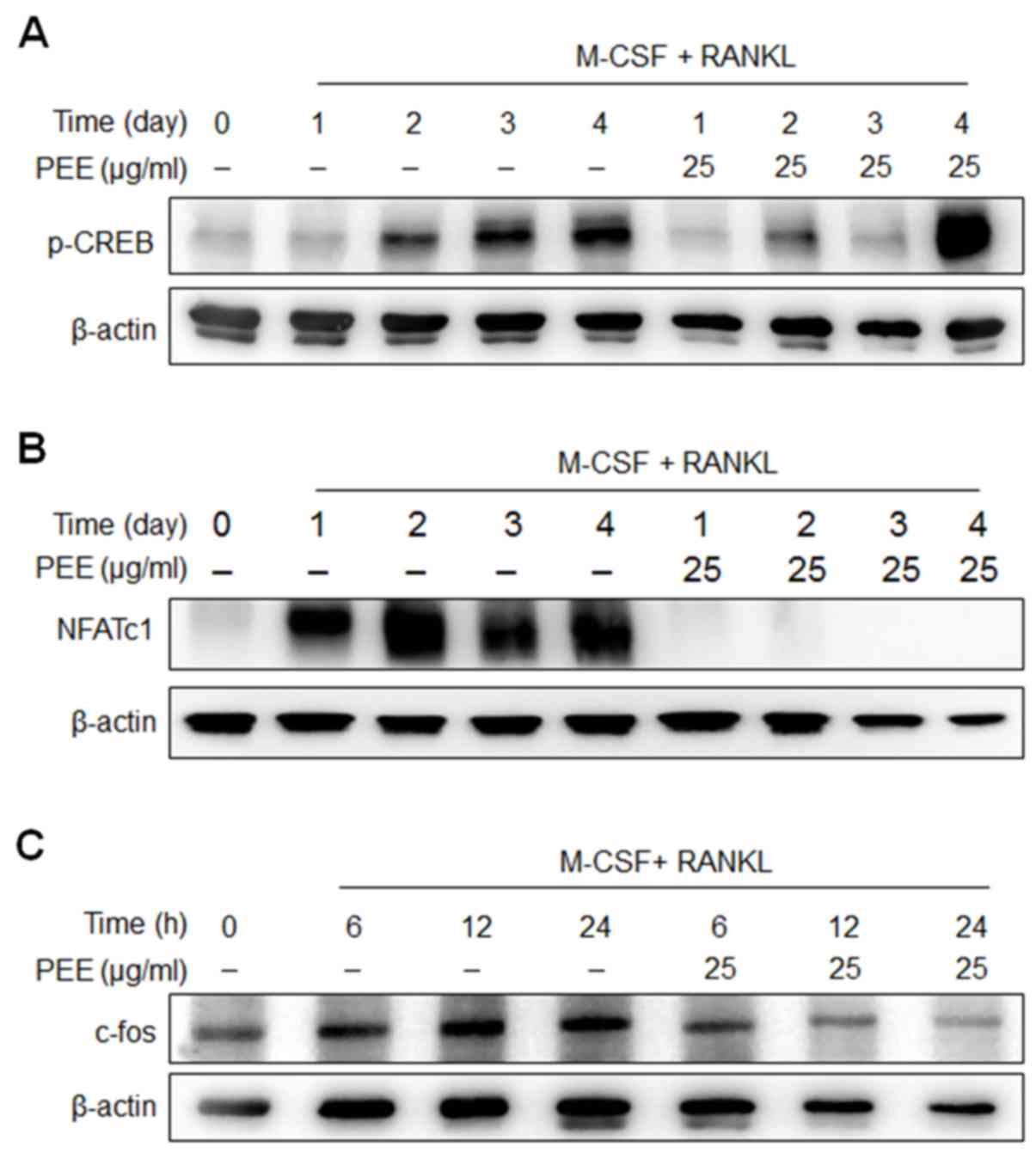
|
1
|
Hisamoto M, Kikuzaki H, Ohigashi H and
Nakatani N: Antioxidant compounds from the leaves of Peucedanum
japonicum Thunb. J Agric Food Chem. 51:5255–5261. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nukitrangsan N, Okabe T, Toda T, Inafuku
M, Iwasaki H and Oku H: Effect of Peucedanum japonicum Thunb
extract on high-fat diet-induced obesity and gene expression in
mice. J Oleo Sci. 61:89–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aida Y, Kasama T, Takeuchi N, Chiba M and
Tobinaga S: Pharmacological activities of khellactones, compounds
isolated from Peucedanum japonicum THUNB. and Peucedanum
praeruptorium DUNN. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 20:343–351.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim H, Kim T, Jeong BC, Cho IT, Han D,
Takegahara N, Negishi-Koga T, Takayanagi H, Lee JH, Sul JY, et al:
Tmem64 modulates calcium signaling during RANKL-mediated osteoclast
differentiation. Cell Metab. 17:249–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba
T, Murata S, Sato K, Takaoka A, Yokochi T, Oda H, Tanaka K, et al:
T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling
cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature. 408:600–605. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang YM, Jung HH, Lee SJ, Choi HJ, Kim MS
and Shin DM: TRPM7 is essential for RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 17:65–71. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Son A, Kim MS, Jo H, Byun HM and Shin DM:
Effects of Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate on osteoclast
differentiation in RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. Korean J
Physiol Pharmacol. 16:31–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang YM, Kim MS, Son A, Hong JH, Kim KH,
Seo JT, Lee SI and Shin DM: Alteration of RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis in primary cultured osteoclasts from SERCA2+/−
mice. J Bone Miner Res. 24:1763–1769. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HJ, Prasad V, Hyung SW, Lee ZH, Lee
SW, Bhargava A, Pearce D, Lee Y and Kim HH: Plasma membrane calcium
ATPase regulates bone mass by fine-tuning osteoclast
differentiation and survival. J Cell Biol. 199:1145–1158. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hwang JK, Erkhembaatar M, Gu DR, Lee SH,
Lee CH, Shin DM, Lee YR and Kim MS: Glechoma hederacea suppresses
RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis. J Dent Res. 93:685–690. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JW, Roh TC, Rho MC, Kim YK and Lee HS:
Mechanisms of relaxant action of a pyranocoumarin from Peucedanum
japonicum in isolated rat thoracic aorta. Planta Med. 68:891–895.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SH, Kim T, Jeong D, Kim N and Choi Y:
The Tec family tyrosine kinase Btk Regulates RANKL-induced
osteoclast maturation. J Biol Chem. 283:11526–11534. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu
A, Kobayashi E, Iwata T, Ohnishi H, Matozaki T, Kodama T, et al:
Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with
RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature. 428:758–763. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu M, Moreno JL, Stains JP and Keegan AD:
Complex regulation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)
expression by interleukin 4 (IL-4): IL-4 indirectly suppresses
receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-mediated TRAP
expression but modestly induces its expression directly. J Biol
Chem. 284:32968–32979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsumoto M, Kogawa M, Wada S, Takayanagi
H, Tsujimoto M, Katayama S, Hisatake K and Nogi Y: Essential role
of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cathepsin K gene
expression during osteoclastogenesis through association of NFATc1
and PU.1. J Biol Chem. 279:45969–45979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim K, Lee SH, Ha Kim J, Choi Y and Kim N:
NFATc1 induces osteoclast fusion via up-regulation of Atp6v0d2 and
the dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). Mol
Endocrinol. 22:176–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee SH, Rho J, Jeong D, Sul JY, Kim T, Kim
N, Kang JS, Miyamoto T, Suda T, Lee SK, et al: v-ATPase V0 subunit
d2-deficient mice exhibit impaired osteoclast fusion and increased
bone formation. Nat Med. 12:1403–1409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barrow AD, Raynal N, Andersen TL, Slatter
DA, Bihan D, Pugh N, Cella M, Kim T, Rho J, Negishi-Koga T, et al:
OSCAR is a collagen receptor that costimulates osteoclastogenesis
in DAP12-deficient humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:3505–3516.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sato K, Suematsu A, Nakashima T,
Takemoto-Kimura S, Aoki K, Morishita Y, Asahara H, Ohya K,
Yamaguchi A, Takai T, et al: Regulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the CaMK-CREB pathway. Nat Med.
12:1410–1416. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen J, Xu X, Cheng F, Liu H, Luo X, Shen
J, Chen K, Zhao W, Shen X and Jiang H: Virtual screening on natural
products for discovering active compounds and target information.
Curr Med Chem. 10:2327–2342. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McChesney JD: Natural products in drug
discovery-organizing for success. P R Health Sci J. 21:91–95.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nguta JM, Appiah-Opong R, Nyarko AK,
Yeboah-Manu D, Addo PG, Otchere I and Kissi-Twum A:
Antimycobacterial and cytotoxic activity of selected medicinal
plant extracts. J Ethnopharmacol. 182:10–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Joray MB, Trucco LD, González ML, Napal
GN, Palacios SM, Bocco JL and Carpinella MC: Antibacterial and
Cytotoxic Activity of Compounds Isolated from Flourensia oolepis.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:9124842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim MS, Yang YM, Son A, Tian YS, Lee SI,
Kang SW, Muallem S and Shin DM: RANKL-mediated reactive oxygen
species pathway that induces long lasting Ca2+ oscillations
essential for osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 285:6913–6921. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|