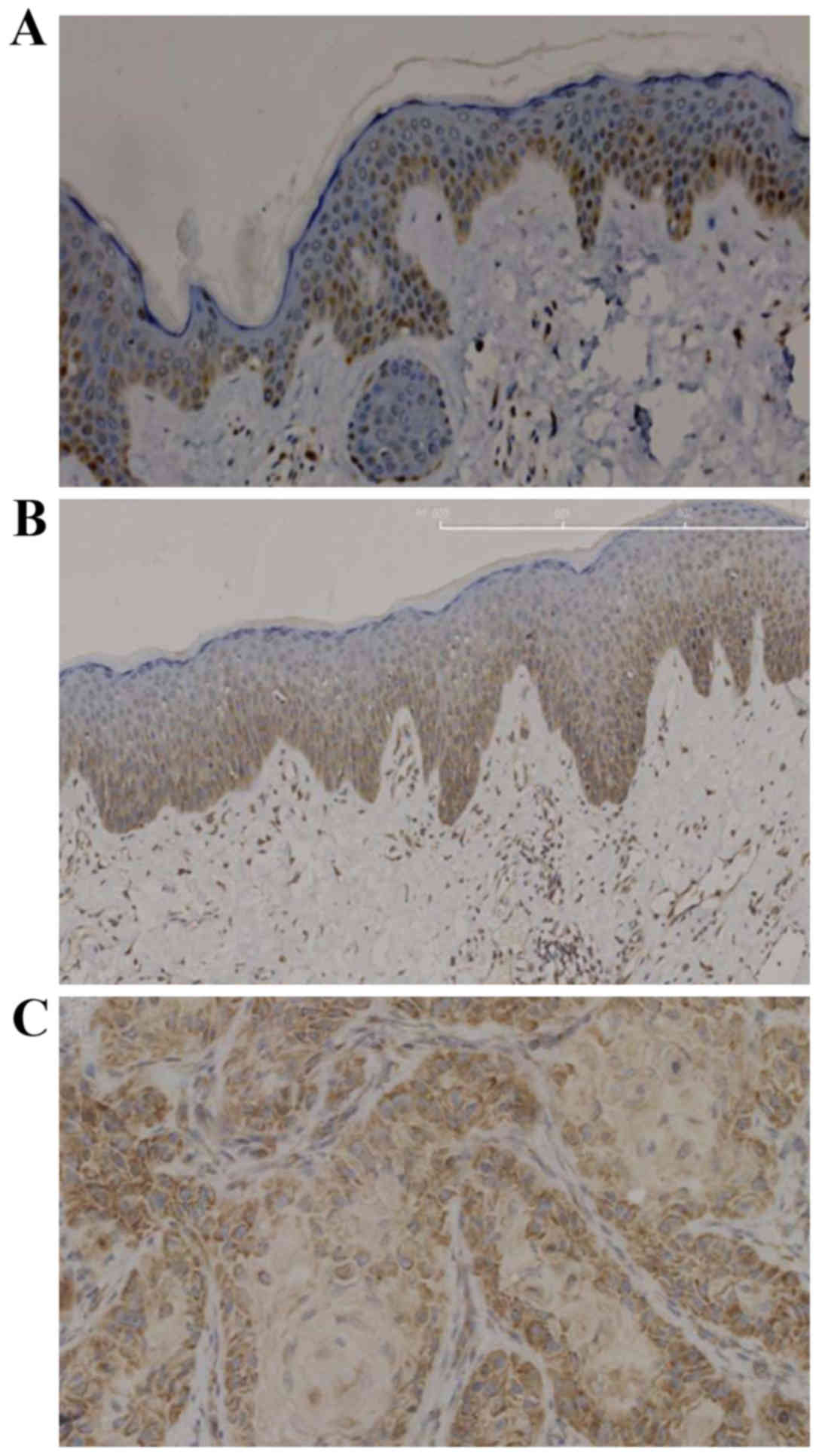
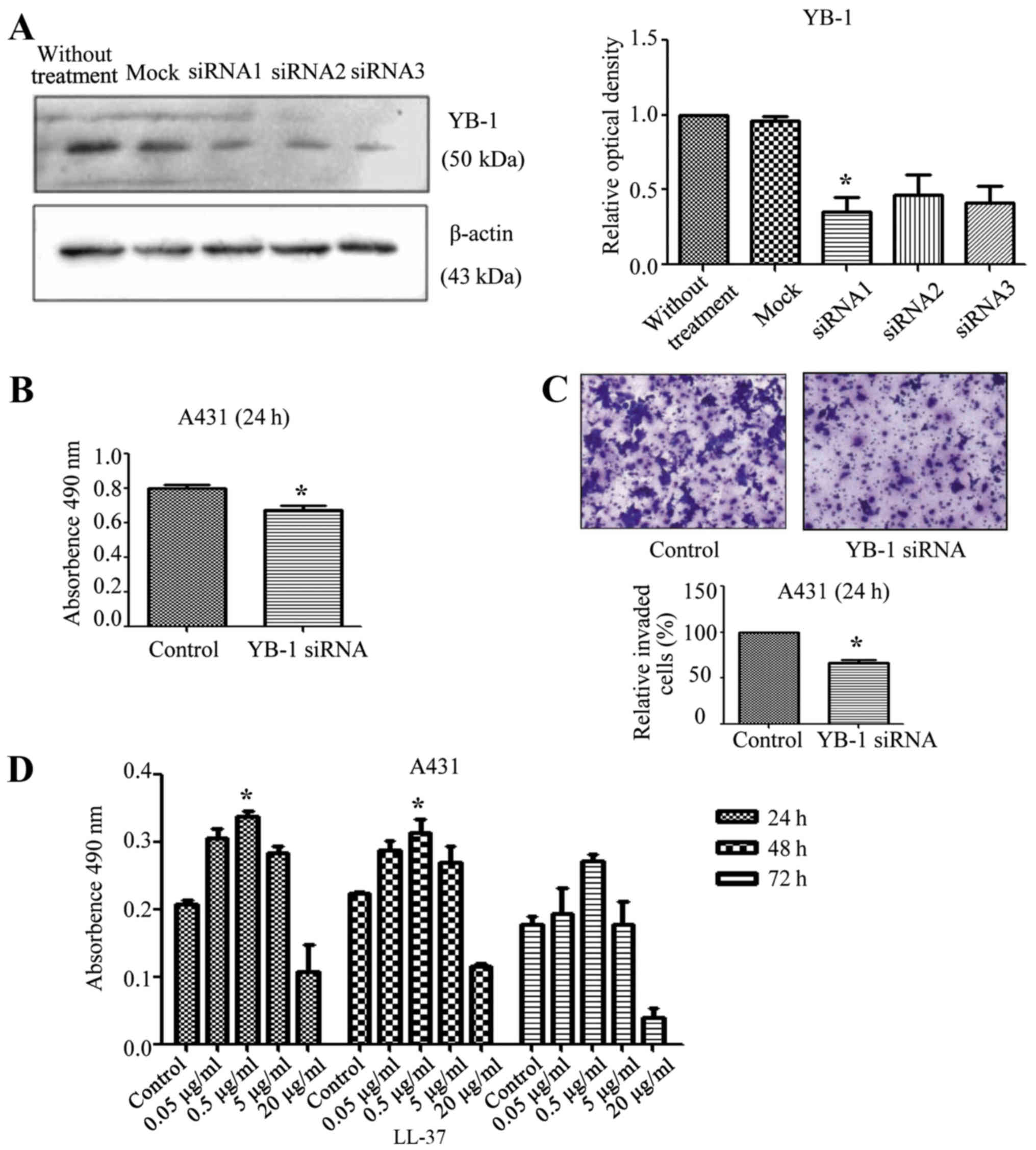
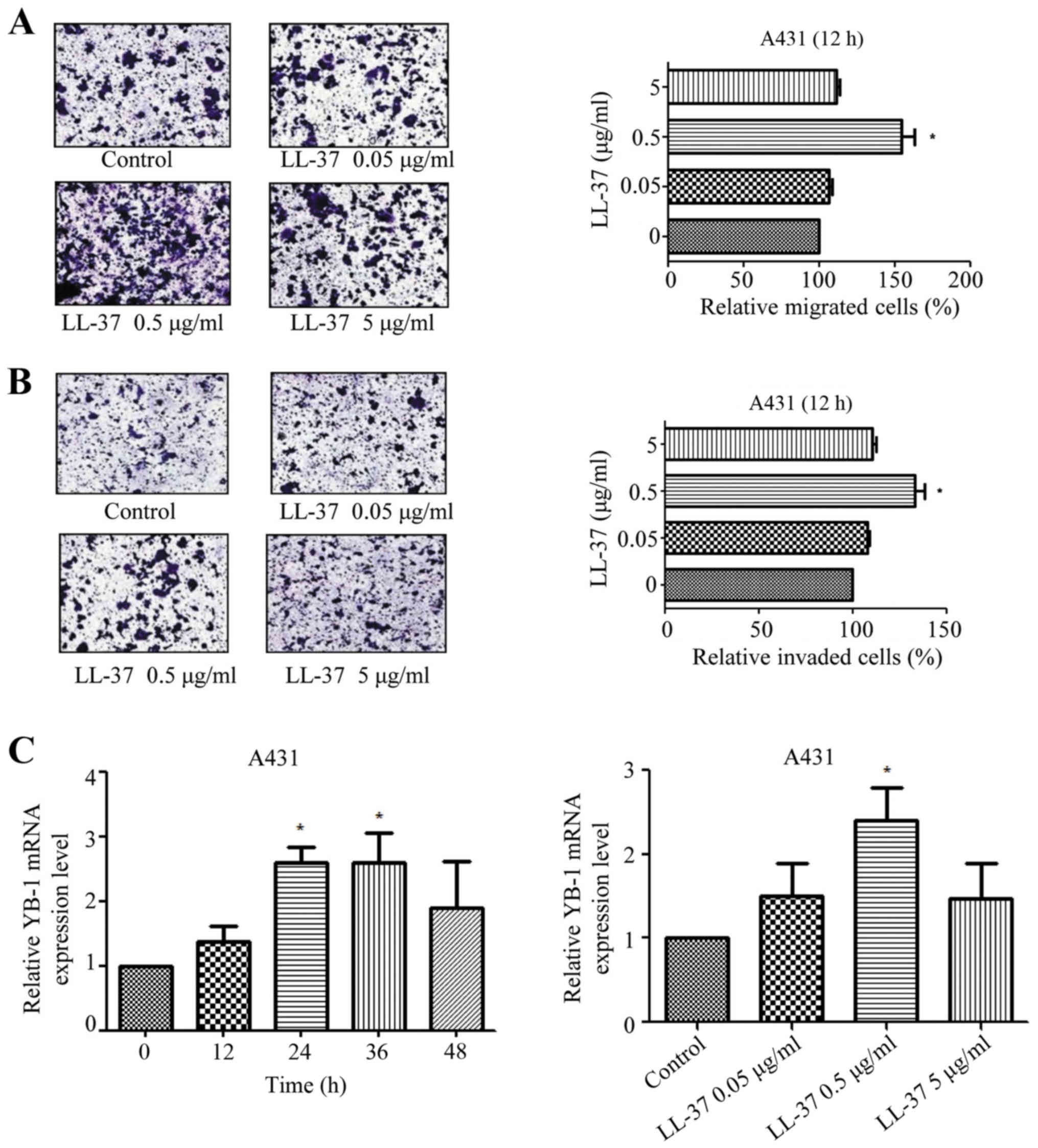
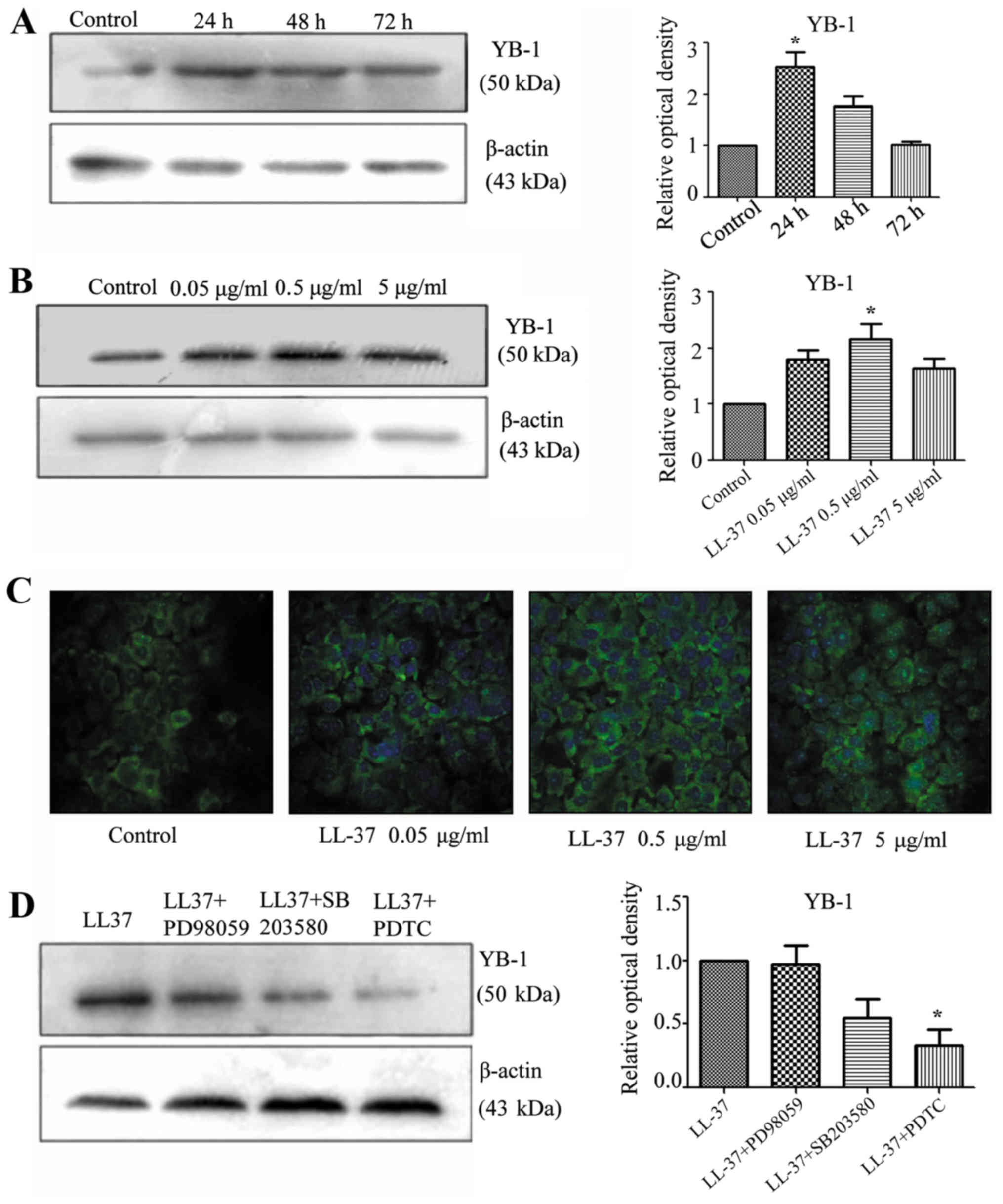
|
1
|
Knackstedt TJ, Brennick JB, Perry AE, Li
Z, Quatrano NA and Samie FH: Frequency of squamous cell carcinoma
(SCC) invasion in transected SCC in situ referred for Mohs surgery:
The dartmouth-hitchcock experience. Int J Dermatol. 54:830–833.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR and
Coldiron BM: Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer
(keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA
Dermatol. 151:1081–1086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sapijaszko M, Zloty D, Bourcier M, Poulin
Y, Janiszewski P and Ashkenas J; Canadian Non-melanoma Skin Cancer
Guidelines Committee, : Non-melanoma skin cancer in canada chapter
5: Management of squamous cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg.
19:249–259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakura H, Maekawa T, Imamoto F, Yasuda K
and Ishii S: Two human genes isolated by a novel method encode
DNA-binding proteins containing a common region of homology. Gene.
73:499–507. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eliseeva IA, Kim ER, Guryanov SG,
Ovchinnikov LP and Lyabin DN: Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) and
its functions. Biochemistry (Mosc). 76:1402–1433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shiota M, Izumi H, Onitsuka T, Miyamoto N,
Kashiwagi E, Kidani A, Yokomizo A, Naito S and Kohno K: Twist
promotes tumor cell growth through YB-1 expression. Cancer Res.
68:98–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lasham A, Samuel W, Cao H, Patel R, Mehta
R, Stern JL, Reid G, Woolley AG, Miller LD, Black MA, et al: YB-1,
the E2F pathway, and regulation of tumor cell growth. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 104:133–146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lasham A, Print CG, Woolley AG, Dunn SE
and Braithwaite AW: YB-1: Oncoprotein, prognostic marker and
therapeutic target? Biochem J. 449:11–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takahashi M, Shimajiri S, Izumi H, Hirano
G, Kashiwagi E, Yasuniwa Y, Wu Y, Han B, Akiyama M, Nishizawa S, et
al: Y-box binding protein-1 is a novel molecular target for tumor
vessels. Cancer Sci. 101:1367–1373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stratford AL, Habibi G, Astanehe A, Jiang
H, Hu K, Park E, Shadeo A, Buys TP, Lam W, Pugh T, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR) is transcriptionally induced by the
Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) and can be inhibited with Iressa in
basal-like breast cancer, providing a potential target for therapy.
Breast Cancer Res. 9:R612007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schittek B, Psenner K, Sauer B, Meier F,
Iftner T and Garbe C: The increased expression of Y box-binding
protein 1 in melanoma stimulates proliferation and tumor invasion,
antagonizes apoptosis and enhances chemoresistance. Int J Cancer.
120:2110–2118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Durr UH, Sudheendra US and Ramamoorthy A:
LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of
antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1758:1408–1425. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bucki R, Leszczyńska K, Namiot A and
Sokolowski W: Cathelicidin LL-37: A multitask antimicrobial
peptide. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 58:15–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu WK, Wang G, Coffelt SB, Betancourt AM,
Lee CW, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J, Sung JJ and Cho CH: Emerging roles of
the host defense peptide LL-37 in human cancer and its potential
therapeutic applications. Int J Cancer. 127:1741–1747. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Coffelt SB and Scandurro AB: Tumors sound
the alarmin(s). Cancer Res. 68:6482–6485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hensel JA, Chanda D, Kumar S, Sawant A,
Grizzle WE, Siegal GP and Ponnazhagan S: LL-37 as a therapeutic
target for late stage prostate cancer. Prostate. 71:659–670. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gill K, Mohanti BK, Singh AK, Mishra B and
Dey S: The over expression of cathelicidin peptide LL37 in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma: The peptide marker for the prognosis
of cancer. Cancer Biomark. 10:125–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim JE, Kim HJ, Choi JM, Lee KH, Kim TY,
Cho BK, Jung JY, Chung KY, Cho D and Park HJ: The antimicrobial
peptide human cationic antimicrobial protein-18/cathelicidin LL-37
as a putative growth factor for malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol.
163:959–967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heilborn JD, Nilsson MF, Jimenez CI,
Sandstedt B, Borregaard N, Tham E, Sørensen OE, Weber G and Ståhle
M: Antimicrobial protein hCAP18/LL-37 is highly expressed in breast
cancer and is a putative growth factor for epithelial cells. Int J
Cancer. 114:713–719. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Coffelt SB, Waterman RS, Florez L, Höner
zu Bentrup K, Zwezdaryk KJ, Tomchuck SL, LaMarca HL, Danka ES,
Morris CA and Scandurro AB: Ovarian cancers overexpress the
antimicrobial protein hCAP-18 and its derivative LL-37 increases
ovarian cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Int J Cancer.
122:1030–1039. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
von Haussen J, Koczulla R, Shaykhiev R,
Herr C, Pinkenburg O, Reimer D, Wiewrodt R, Biesterfeld S, Aigner
A, Czubayko F and Bals R: The host defence peptide LL-37/hCAP-18 is
a growth factor for lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 59:12–23. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coffelt SB, Tomchuck SL, Zwezdaryk KJ,
Danka ES and Scandurro AB: Leucine leucine-37 uses formyl peptide
receptor-like 1 to activate signal transduction pathways, stimulate
oncogenic gene expression, and enhance the invasiveness of ovarian
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:907–915. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coffelt SB, Marini FC, Watson K, Zwezdaryk
KJ, Dembinski JL, LaMarca HL, Tomchuck SL, zu Bentrup K Honer,
Danka ES, Henkle SL and Scandurro AB: The pro-inflammatory peptide
LL-37 promotes ovarian tumor progression through recruitment of
multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:pp. 3806–3811. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Girnita A, Zheng H, Grönberg A, Girnita L
and Ståhle M: Identification of the cathelicidin peptide LL-37 as
agonist for the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor.
Oncogene. 31:352–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chuang CM, Monie A, Wu A, Mao CP and Hung
CF: Treatment with LL-37 peptide enhances antitumor effects induced
by CpG oligodeoxynucleotides against ovarian cancer. Hum Gene Ther.
20:303–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li D, Wang X, Wu JL, Quan WQ, Ma L, Yang
F, Wu KY and Wan HY: Tumor-produced versican V1 enhances
hCAP18/LL-37 expression in macrophages through activation of TLR2
and vitamin D3 signaling to promote ovarian cancer progression in
vitro. PLoS One. 8:e566162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kittaka M, Shiba H, Kajiya M, Ouhara K,
Takeda K, Kanbara K, Fujita T, Kawaguchi H, Komatsuzawa H and
Kurihara H: Antimicrobial peptide LL37 promotes vascular
endothelial growth factor-A expression in human periodontal
ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 48:228–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yasen M, Kajino K, Kano S, Tobita H,
Yamamoto J, Uchiumi T, Kon S, Maeda M, Obulhasim G, Arii S and Hino
O: The up-regulation of Y-box binding proteins (DNA binding protein
A and Y-box binding protein-1) as prognostic markers of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7354–7361. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang LL, He DL, Li X, Li L, Zhu GD, Zhang
D and Wang XY: Overexpression of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor
inhibit growth of human bladder cancer cell in vitro and in vivo.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:895–900. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guay D, Garand C, Reddy S, Schmutte C and
Lebel M: The human endonuclease III enzyme is a relevant target to
potentiate cisplatin cytotoxicity in Y-box-binding protein-1
overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 99:762–769. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shiota M, Yokomizo A, Tada Y, Uchiumi T,
Inokuchi J, Tatsugami K, Kuroiwa K, Yamamoto K, Seki N and Naito S:
P300/CBP-associated factor regulates Y-box binding protein-1
expression and promotes cancer cell growth, cancer invasion and
drug resistance. Cancer Sci. 101:1797–1806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koike K, Uchiumi T, Ohga T, Toh S, Wada M,
Kohno K and Kuwano M: Nuclear translocation of the Y-box binding
protein by ultraviolet irradiation. FEBS Lett. 417:390–394. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oda Y, Ohishi Y, Basaki Y, Kobayashi H,
Hirakawa T, Wake N, Ono M, Nishio K, Kuwano M and Tsuneyoshi M:
Prognostic implications of the nuclear localization of
Y-box-binding protein-1 and CXCR4 expression in ovarian cancer:
Their correlation with activated Akt, LRP/MVP and P-glycoprotein
expression. Cancer Sci. 98:1020–1026. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sasaki Y and Iwai K: Roles of the NF-κB
pathway in B-lymphocyte biology. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
393:177–209. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang L, Liu Q, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Hu L, Li
C, Wang S, Li J, Zhang Y, Yu H, et al: Encephalomyocarditis virus
3C protease relieves TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator
(TANK) inhibitory effect on TRAF6-mediated NF-κB signaling through
cleavage of TANK. J Biol Chem. 290:27618–27632. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Quaglio AE, Castilho AC and Di Stasi LC:
Experimental evidence of heparanase, Hsp70 and NF-κB gene
expression on the response of anti-inflammatory drugs in
TNBS-induced colonic inflammation. Life Sci. 141:179–187. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tomás A, Lery L, Regueiro V,
Pérez-Gutiérrez C, Martínez V, Moranta D, Llobet E,
González-Nicolau M, Insua JL, Tomas JM, et al: Functional genomic
screen identifies klebsiella pneumoniae factors implicated in
blocking nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling. J Biol Chem.
290:16678–16697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|