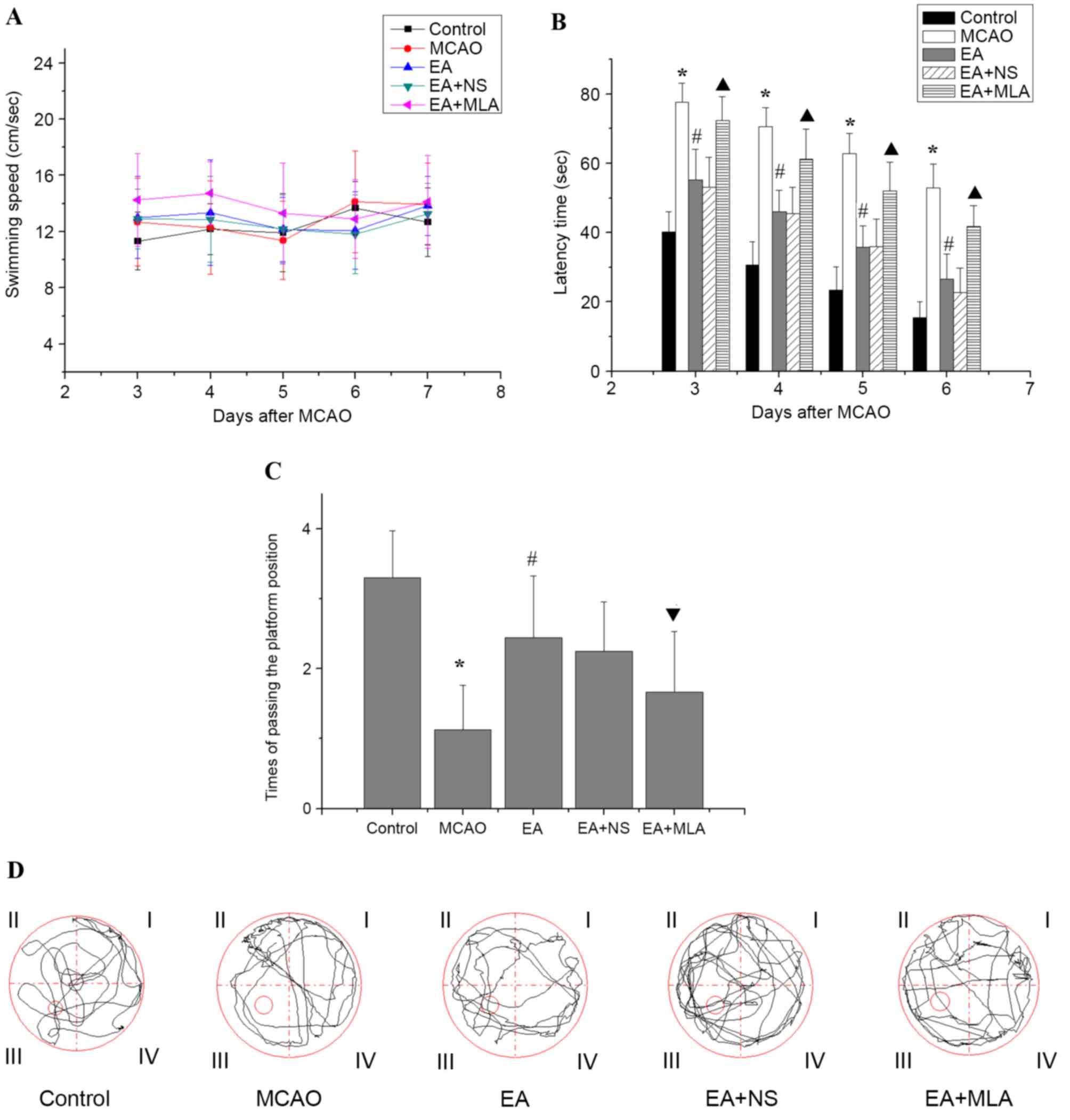
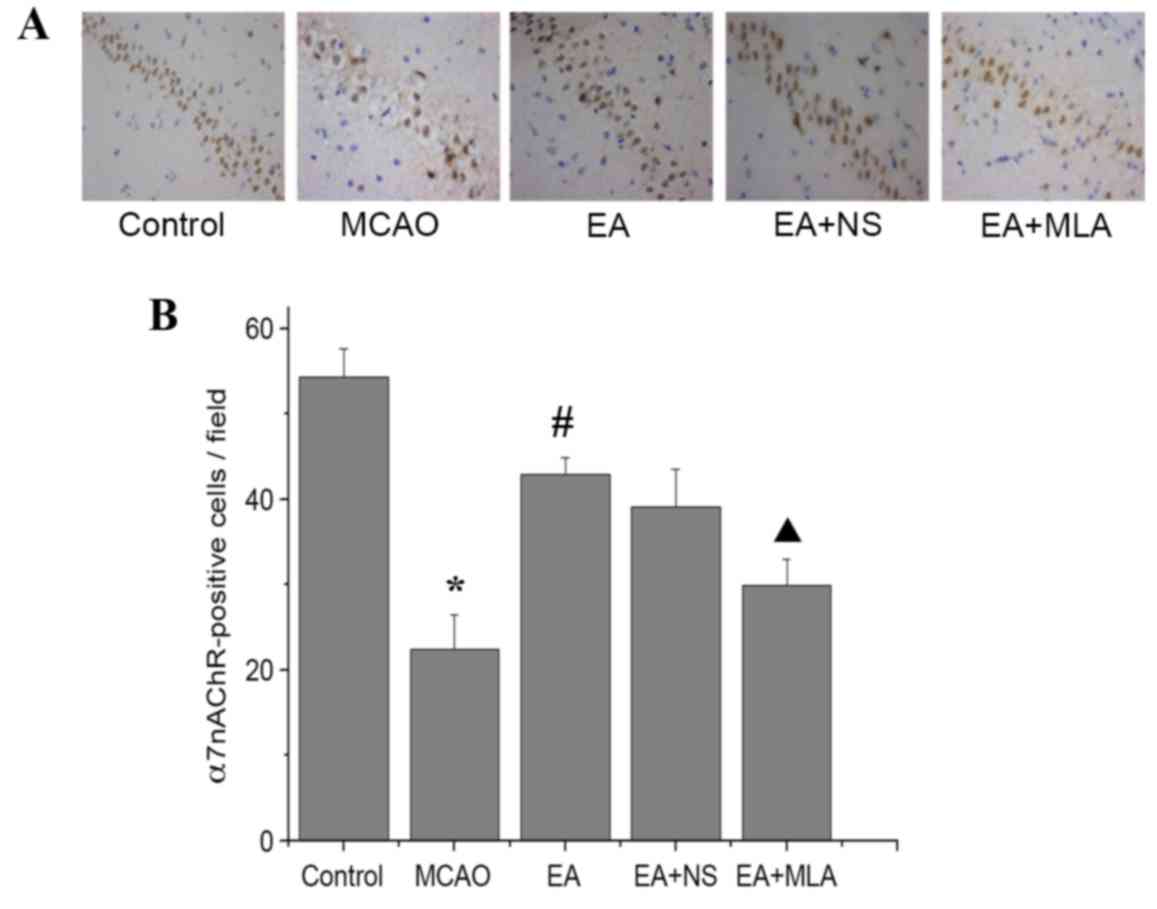
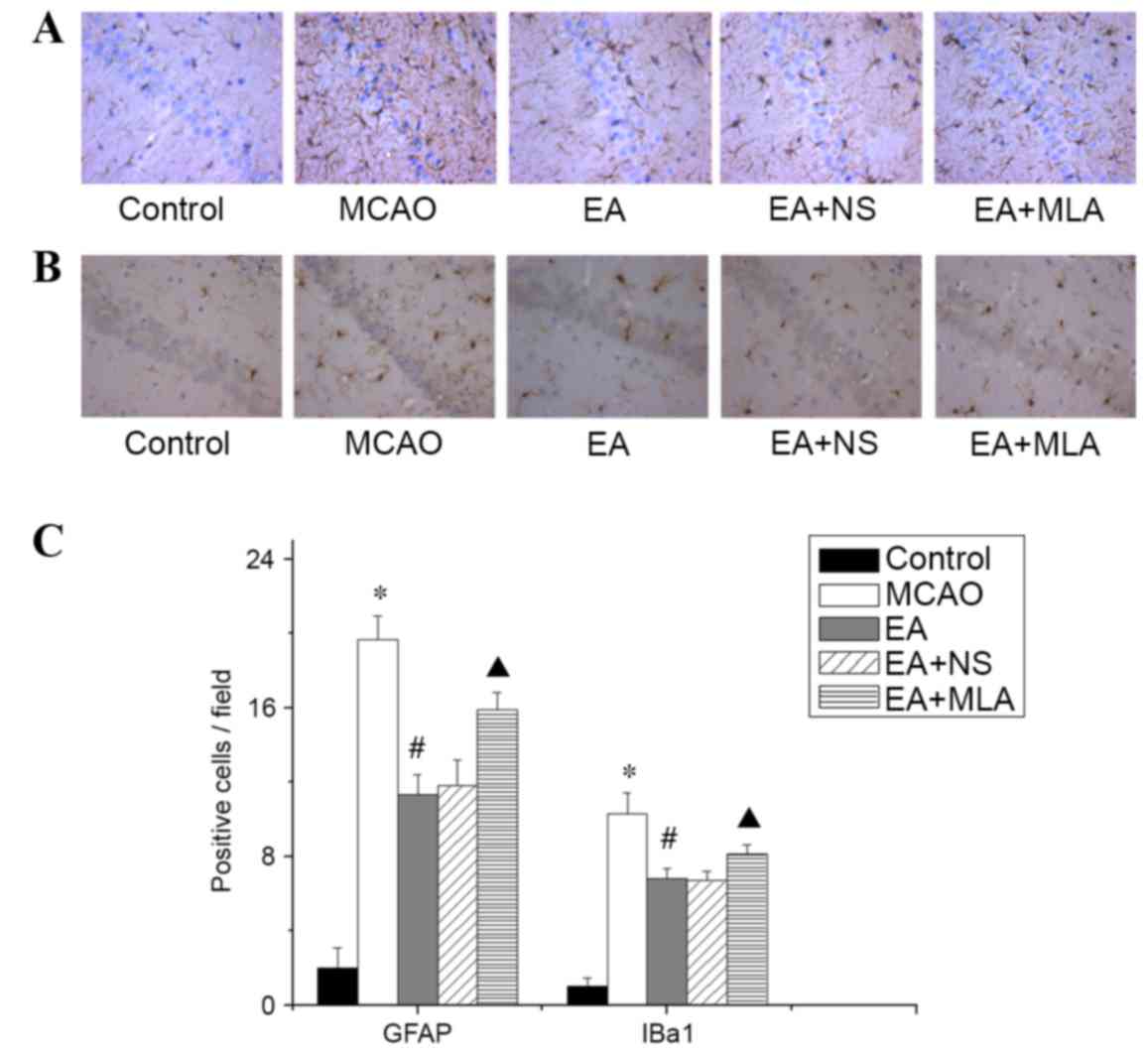
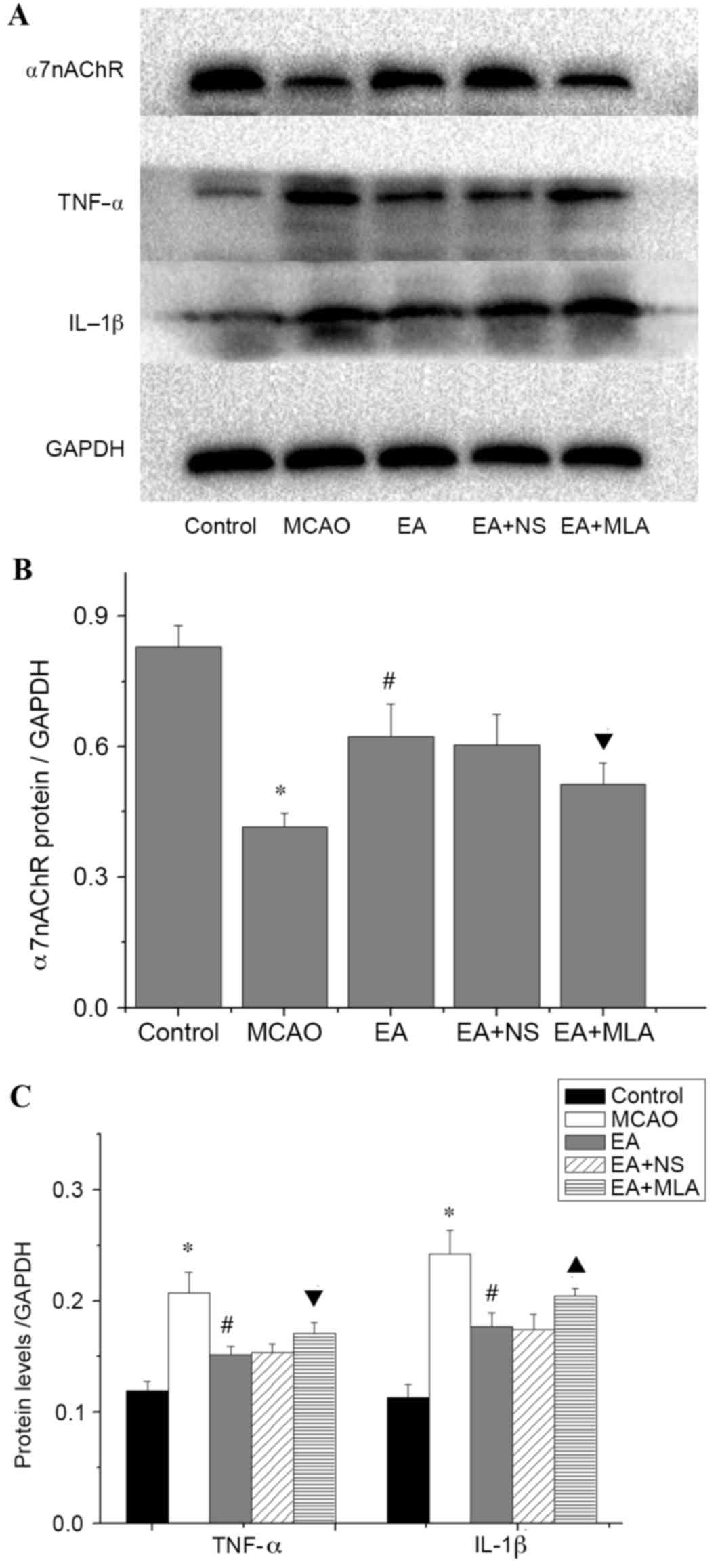
|
1
|
Bae CY and Sun HS: Current understanding
of TRPM7 pharmacology and drug development for stroke. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 34:10–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Niemi ML, Laaksonen R, Kotila M and
Waltimo O: Quality of life 4 years after stroke. Stroke.
19:1101–1107. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carey LM: Somatosensory loss after stroke.
Crit Rev Phys Rehabil Med. 7:51–91. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jin YP, Di Legge S, Ostbye T, Feightner JW
and Hachinski V: The reciprocal risks of stroke and cognitive
impairment in an elderly population. Alzheimers Dement. 2:171–178.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pendlebury ST and Rothwell PM: Risk of
recurrent stroke, other vascular events and dementia after
transient ischaemic attack and stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 27 Suppl
3:S1–S11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pohjasvaara T, Erkinjuntti T, Vataja R and
Kaste M: Dementia three months after stroke. Baseline frequency and
effect of different definitions of dementia in the Helsinki Stroke
Aging Memory Study (SAM) cohort. Stroke. 28:785–792. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pendlebury ST and Rothwell PM: Prevalence,
incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke
dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol.
8:1006–1018. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chan KY, Wang W, Wu JJ, Liu L, Theodoratou
E, Car J, Middleton L, Russ TC, Deary IJ, Campbell H, et al:
Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia in
China, 1990–2010: A systematic review and analysis. Lancet.
381:2016–2023. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aggarwal NT, Tripathi M, Dodge HH, Alladi
S and Anstey KJ: Trends in Alzheimer's disease and dementia in the
asian-pacific region. Int J Alzheimers Dis.
2012:1713272012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu JN: A short history of acupuncture. J
Altern Complement Med. 2:19–21. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu F, Li ZM, Jiang YJ and Chen LD: A
meta-analysis of acupuncture use in the treatment of cognitive
impairment after stroke. J Altern Complement Med. 20:535–544. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Y, Zhou J, Li J, Yang SB, Mo LQ, Hu
JH and Yuan WL: Electroacupuncture pretreatment prevents cognitive
impairment induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion via inhibition of
microglial activation and attenuation of oxidative stress in rats.
Brain Res. 1432:36–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang C, Wen Y, Fan XN, Tian G, Zhou XY,
Deng SZ and Meng ZH: Therapeutic effects of different durations of
acupuncture on rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neural
Regen Res. 10:159–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan XW, Chen F, Chen Y, Chen GH, Liu HH,
Guan SK, Deng Y, Liu Y, Zhang SJ, Peng WJ, et al:
Electroacupuncture prevents cognitive impairments by regulating the
early changes after brain irradiation in rats. PLoS One.
10:e01220872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stoll G, Jander S and Schroeter M:
Inflammation and glial responses in ischemic brain lesions. Prog
Neurobiol. 56:149–171. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Q, Tang XN and Yenari MA: The
inflammatory response in stroke. J Neuroimmunol. 184:53–68. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Webster SJ, Van Eldik LJ, Watterson DM and
Bachstetter AD: Closed head injury in an age-related Alzheimer
mouse model leads to an altered neuroinflammatory response and
persistent cognitive impairment. J Neurosci. 35:6554–6569. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson VE, Stewart W and Smith DH:
Traumatic brain injury and amyloid-β pathology: A link to
Alzheimer's disease? Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:361–370. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramlackhansingh AF, Brooks DJ, Greenwood
RJ, Bose SK, Turkheimer FE, Kinnunen KM, Gentleman S, Heckemann RA,
Gunanayagam K, Gelosa G and Sharp DJ: Inflammation after trauma:
Microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol.
70:374–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Buchanan JB, Sparkman NL, Chen J and
Johnson RW: Cognitive and neuroinflammatory consequences of mild
repeated stress are exacerbated in aged mice.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 33:755–765. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chin Y, Kishi M, Sekino M, Nakajo F, Abe
Y, Terazono Y, Hiroyuki O, Kato F, Koizumi S, Gachet C and
Hisatsune T: Involvement of glial P2Y1 receptors in cognitive
deficit after focal cerebral stroke in a rodent model. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tweedie D, Ferguson RA, Fishman K,
Frankola KA, Van Praag H, Holloway HW, Luo W, Li Y, Caracciolo L,
Russo I, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-α synthesis inhibitor
3,6′-dithiothalidomide attenuates markers of inflammation,
Alzheimer pathology and behavioral deficits in animal models of
neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroinflammation.
9:1062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H,
Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW and Tracey
KJ: Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory
response to endotoxin. Nature. 405:458–462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boccia MM, Blake MG, Krawczyk MC and
Baratti CM: Hippocampal α7 nicotinic receptors modulate memory
reconsolidation of an inhibitory avoidance task in mice.
Neuroscience. 171:531–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Acheson DT, Twamley EW and Young JW:
Reward learning as a potential target for pharmacological
augmentation of cognitive remediation for schizophrenia: A roadmap
for preclinical development. Front Neurosci. 7:1032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kadir A, Almkvist O, Wall A, Langstrom B
and Nordberg A: PET imaging of cortical 11C-nicotine binding
correlates with the cognitive function of attention in Alzheimer's
disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 188:509–520. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Kang KM, Kim JH,
Bahn JJ, Jeon D, Kim M, Lee SK and Roh JK: Cholinergic
anti-inflammatory pathway in intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res.
1309:164–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu XY, Zhou HF, Pan YL, Liang XB, Niu DB,
Xue B, Li FQ, He QH, Wang XH and Wang XM: Electro-acupuncture
stimulation protects dopaminergic neurons from
inflammation-mediated damage in medial forebrain bundle-transected
rats. Exp Neurol. 189:189–196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Q, Wang F, Li X, Yang Q, Li X, Xu N,
Huang Y, Zhang Q, Gou X, Chen S and Xiong L: Electroacupuncture
pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury through α7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated inhibition of
high-mobility group box 1 release in rats. J Neuroinflammation.
9:242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen LP, Wang FW, Zuo F, Jia JJ and Jiao
WG: Clinical research on comprehensive treatment of senile vascular
dementia. J Tradit Chin Med. 31:178–181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tyagi E, Agrawal R, Nath C and Shukla R:
Cholinergic protection via alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
and PI3K-Akt pathway in LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Neurochem
Int. 56:135–142. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng X, Yang S, Liu J, Huang J, Peng J,
Lin J, Tao J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive
impairment through inhibition of NF-κB-mediated neuronal cell
apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med
Rep. 7:1516–1522. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han X, Zhao X, Lu M, Liu F, Guo F, Zhang J
and Huang X: Electroacupuncture ameliorates learning and memory via
activation of the CREB signaling pathway in the hippocampus to
attenuate apoptosis after cerebral hypoperfusion. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:1564892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic
M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, et al: Nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of
inflammation. Nature. 421:384–388. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yoshikawa H, Kurokawa M, Ozaki N, Nara K,
Atou K, Takada E, Kamochi H and Suzuki N: Nicotine inhibits the
production of proinflammatory mediators in human monocytes by
suppression of I-kappaB phosphorylation and nuclear factor-kappaB
transcriptional activity through nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
alpha7. Clin Exp Immunol. 146:116–123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saeed RW, Varma S, Peng-Nemeroff T, Sherry
B, Balakhaneh D, Huston J, Tracey KJ, Al-Abed Y and Metz CN:
Cholinergic stimulation blocks endothelial cell activation and
leukocyte recruitment during inflammation. J Exp Med.
201:1113–1123. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
de Jonge WJ, van der Zanden EP, The FO,
Bijlsma MF, van Westerloo DJ, Bennink RJ, Berthoud HR, Uematsu S,
Akira S, van den Wijngaard RM and Boeckxstaens GE: Stimulation of
the vagus nerve attenuates macrophage activation by activating the
Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 6:844–851. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu F, Fang J, Shao X, Liang Y, Wu Y and
Jin Y: Electroacupuncture exerts an anti-inflammatory effect in a
rat tissue chamber model of inflammation via suppression of NF-κB
activation. Acupunct Med. 32:340–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou H, Zhang Z, Wei H, Wang F, Guo F, Gao
Z, Marsicano G, Wang Q and Xiong L: Activation of STAT3 is involved
in neuroprotection by electroacupuncture pretreatment via
cannabinoid CB1 receptors in rats. Brain Res. 1529:154–164. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Norman GJ, Morris JS, Karelina K, Weil ZM,
Zhang N, Al-Abed Y, Brothers HM, Wenk GL, Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ and
Devries AC: Cardiopulmonary arrest and resuscitation disrupts
cholinergic anti-inflammatory processes: A role for cholinergic α7
nicotinic receptors. J Neurosci. 31:3446–3452. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guan YZ, Jin XD, Guan LX, Yan HC, Wang P,
Gong Z, Li SJ, Cao X, Xing YL and Gao TM: Nicotine inhibits
microglial proliferation and is neuroprotective in global ischemia
rats. Mol Neurobiol. 51:1480–1488. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu Y, Hu J, Wu J, Zhu C, Hui Y, Han Y,
Huang Z, Ellsworth K and Fan W: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor-mediated neuroprotection against dopaminergic neuron loss
in an MPTP mouse model via inhibition of astrocyte activation. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bellinger FP, Madamba S and Siggins GR:
Interleukin 1 beta inhibits synaptic strength and long-term
potentiation in the rat CA1 hippocampus. Brain Res. 628:227–234.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kelly A, Vereker E, Nolan Y, Brady M,
Barry C, Loscher CE, Mills KH and Lynch MA: Activation of p38 plays
a pivotal role in the inhibitory effect of lipopolysaccharide and
interleukin-1 beta on long term potentiation in rat dentate gyrus.
J Biol Chem. 278:19453–19462. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tong L, Prieto GA, Kramér EA, Smith ED,
Cribbs DH, Lynch G and Cotman CW: Brain-derived neurotrophic
factor-dependent synaptic plasticity is suppressed by
interleukin-1β via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J
Neurosci. 32:17714–17724. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ondrejcak T, Wang Q, Kew JN, Virley DJ,
Upton N, Anwyl R and Rowan MJ: Activation of α7 nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors persistently enhances hippocampal synaptic
transmission and prevents Ass-mediated inhibition of LTP in the rat
hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 677:63–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang M, Felix AR, Kwon S, Lowe D, Wallace
T, Santarelli L and Meltzer HY: The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor
partial agonist/5-HT3 antagonist RG3487 enhances cortical and
hippocampal dopamine and acetylcholine release. Psychopharmacology
(Berl). 231:2199–2210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|