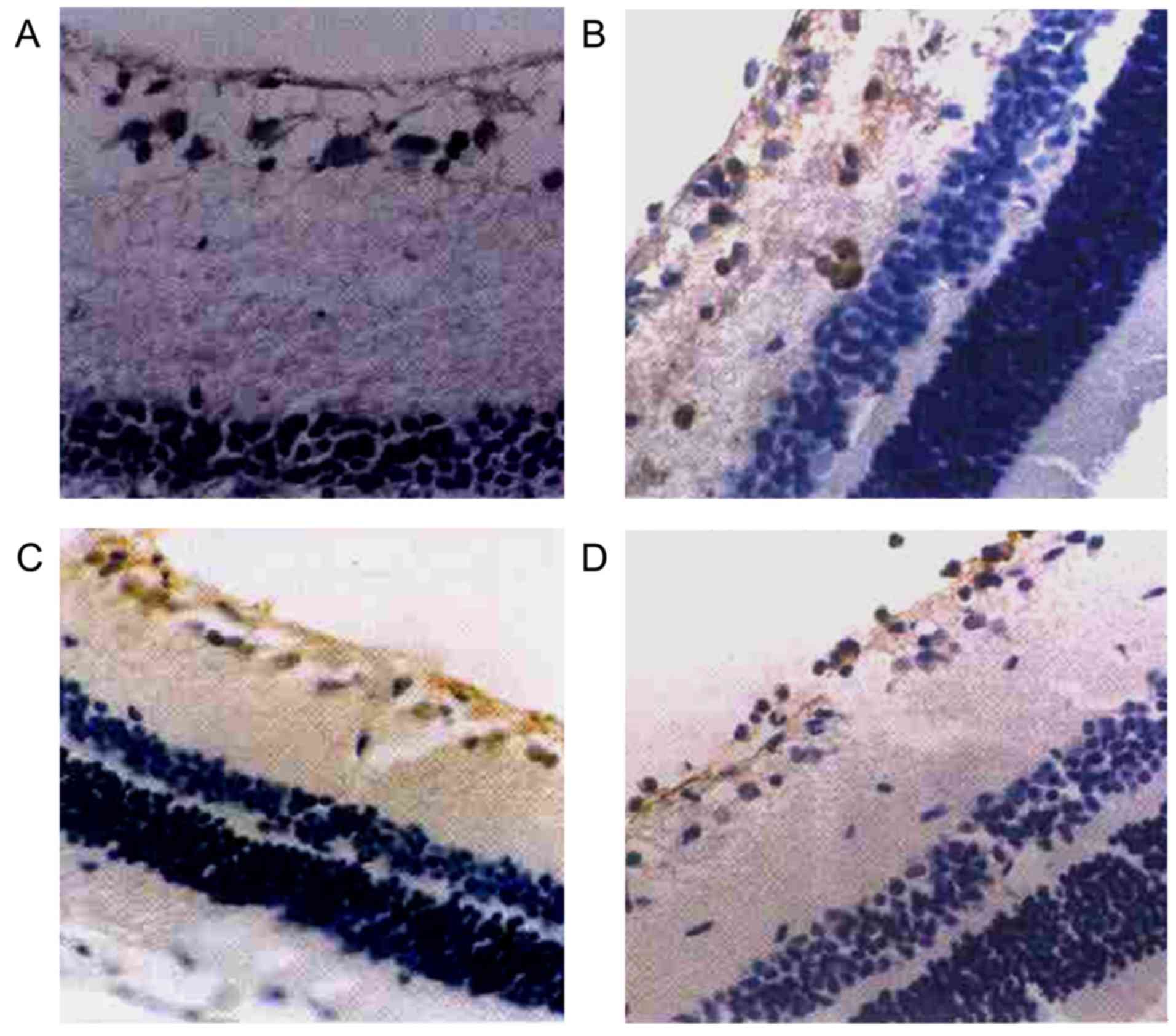
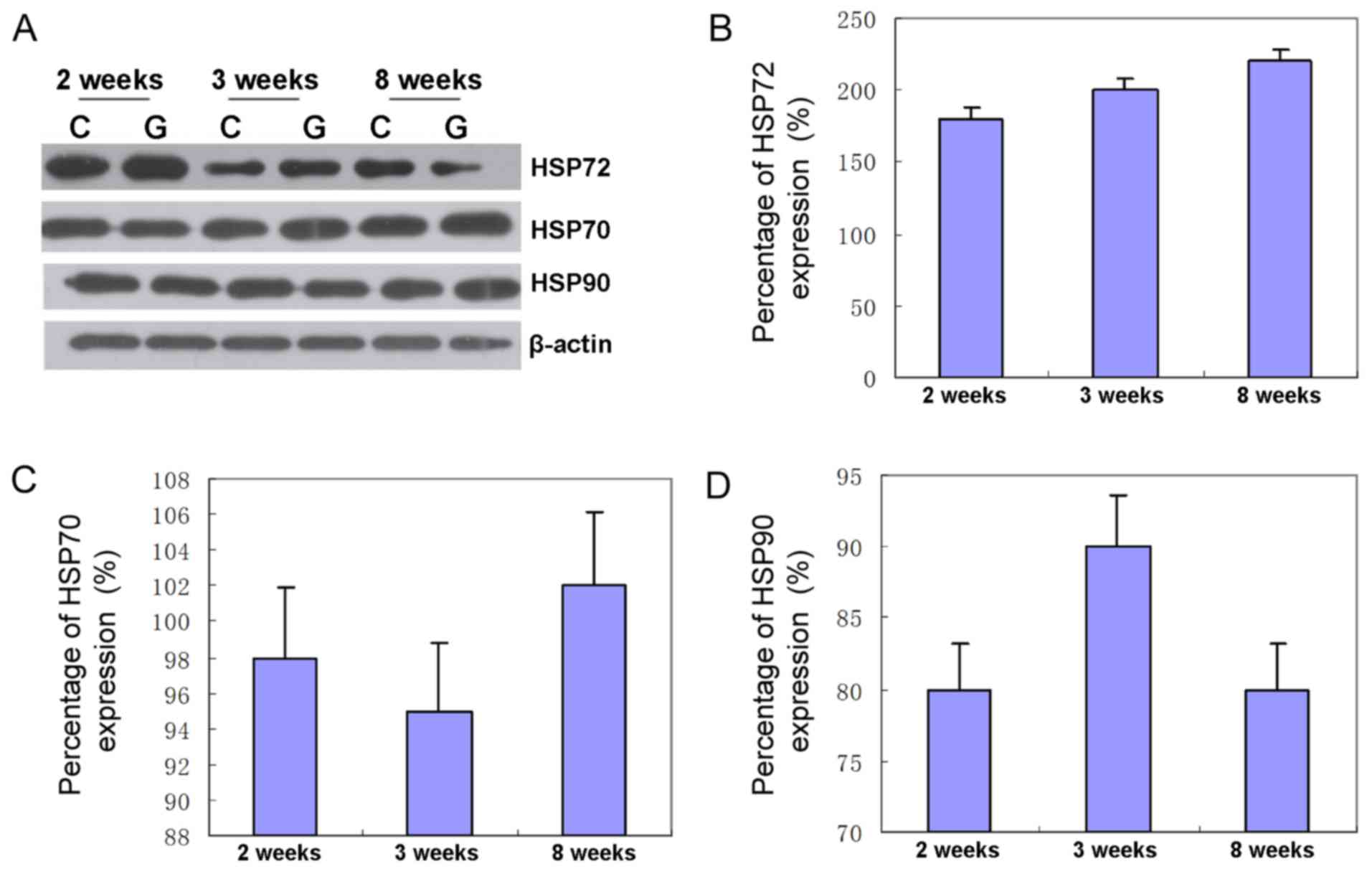
|
1
|
Sleath B, Sayner R, Vitko M, Carpenter DM,
Blalock SJ, Muir KW, Giangiacomo AL, Hartnett ME and Robin AL:
Glaucoma patient-provider communication about vision
quality-of-life. Patient Educ Couns. Nov 22–2016.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
2
|
Shim MS, Kim KY and Ju WK: Role of cyclic
AMP in the eye of glaucoma. BMB Rep. 50:60–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giannaccare G, Vagge A, Gizzi C, Bagnis A,
Sebastiani S, Del Noce C, Fresina M, Traverso CE and Campos EC:
High-intensity focused ultrasound treatment in patients with
refractory glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 255:599–605.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tosaka K, Mashima Y, Funayama T, Ohtake Y
and Kimura I; Glaucoma Gene Research Group, : Association between
open-angle glaucoma and gene polymorphism for heat-shock protein
70–1. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 51:417–423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nowak A, Szaflik JP, Gacek M,
Przybylowska-Sygut K, Kamińska A, Szaflik J and Majsterek I: BDNF
and HSP gene polymorphisms and their influence on the progression
of primary open-angle glaucoma in a Polish population. Arch Med
Sci. 10:1206–1213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Urbak L and Vorum H: Heat shock proteins
in the human eye. Int J Proteomics. 2010:4795712010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yokoyama A, Oshitari T, Negishi H, Dezawa
M, Mizota A and Adachi-Usami E: Protection of retinal ganglion
cells from ischemia-reperfusion injury by electrically applied
Hsp27. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 42:3283–3286. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Birnbaum G: Stress proteins: Their role in
the normal central nervous system and in disease states, especially
multiple sclerosis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 17:107–118. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mehlen P, Schulze-Osthoff K and Arrigo AP:
Small stress proteins as novel regulators of apoptosis. Heat shock
protein 27 blocks Fas/APO-1- and staurosporine-induced cell death.
J Biol Chem. 271:16510–16514. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yenari MA, Giffard RG, Sapolsky RM and
Steinberg GK: The neuroprotective potential of heat shock protein
70 (HSP70). Mol Med Today. 5:525–531. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
WoldeMussie E, Ruiz G, Wijono M and
Wheeler LA: Neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells by
brimonidine in rats with laser-induced chronic ocular hypertension.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 42:2849–2855. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamashima T: Hsp70.1 and related lysosomal
factors for necrotic neuronal death. J Neurochem. 120:477–494.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sohn S, Im JE, Kim TE and Kee C: Effect of
heat shock protein 72 expression on etoposide-induced cell death of
rat retinal ganglion cells. Korean J Ophthalmol. 27:48–51. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li N, Li Y and Duan X: Heat shock protein
72 confers protection in retinal ganglion cells and lateral
geniculate nucleus neurons via blockade of the SAPK/JNK pathway in
a chronic ocular-hypertensive rat model. Neural Regen Res.
9:1395–1401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tezel G, Hernandez R and Wax MB:
Immunostaining of heat shock proteins in the retina and optic nerve
head of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 118:511–518.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nickells RW: Retinal ganglion cell death
in glaucoma: The how, the why, and the maybe. J Glaucoma.
5:345–356. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qing G, Duan X and Jiang Y: Induction of
heat shock protein 72 in RGCs of rat acute glaucoma model after
heat stress or zinc administration. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 20:30–3.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|