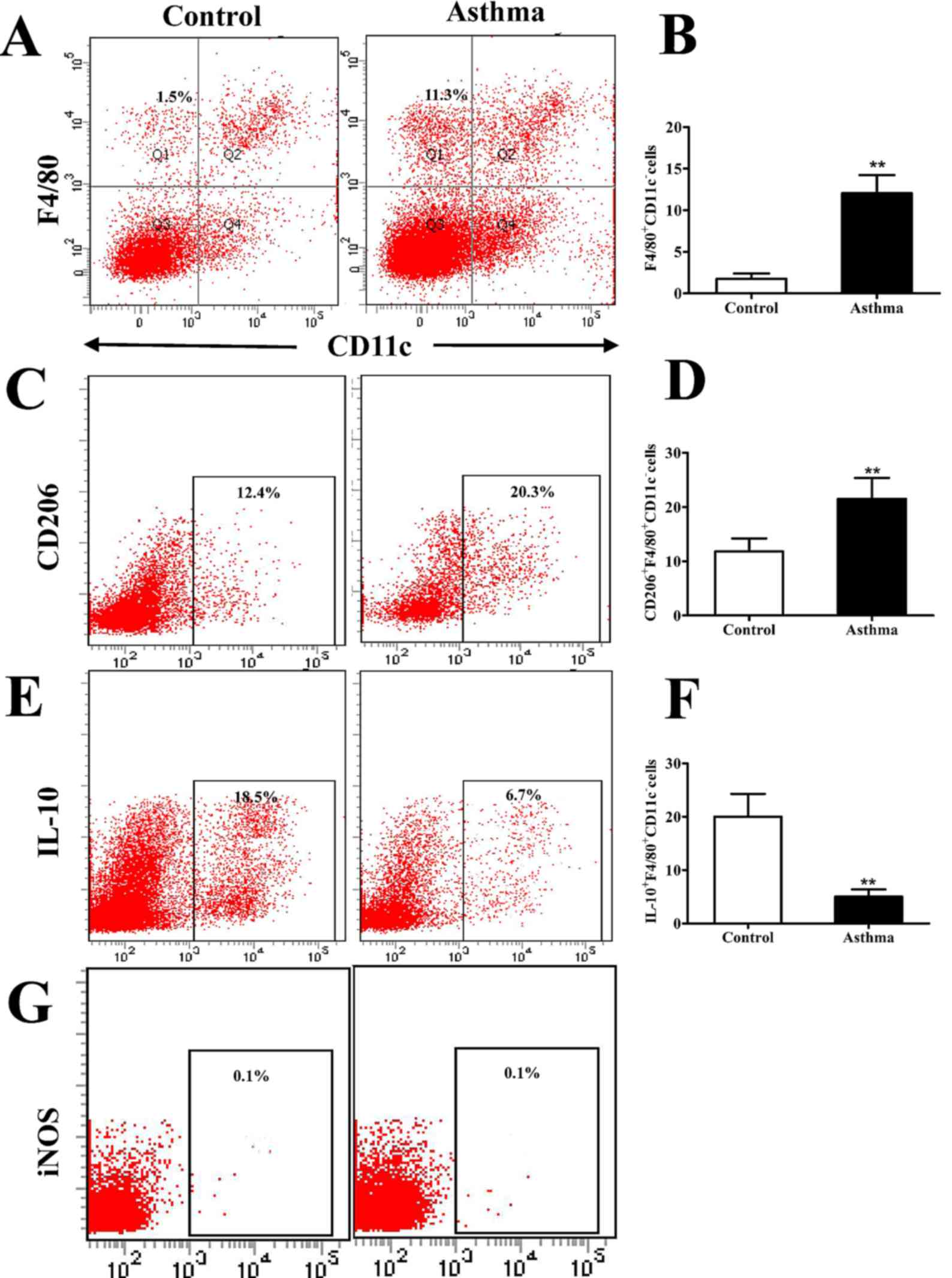
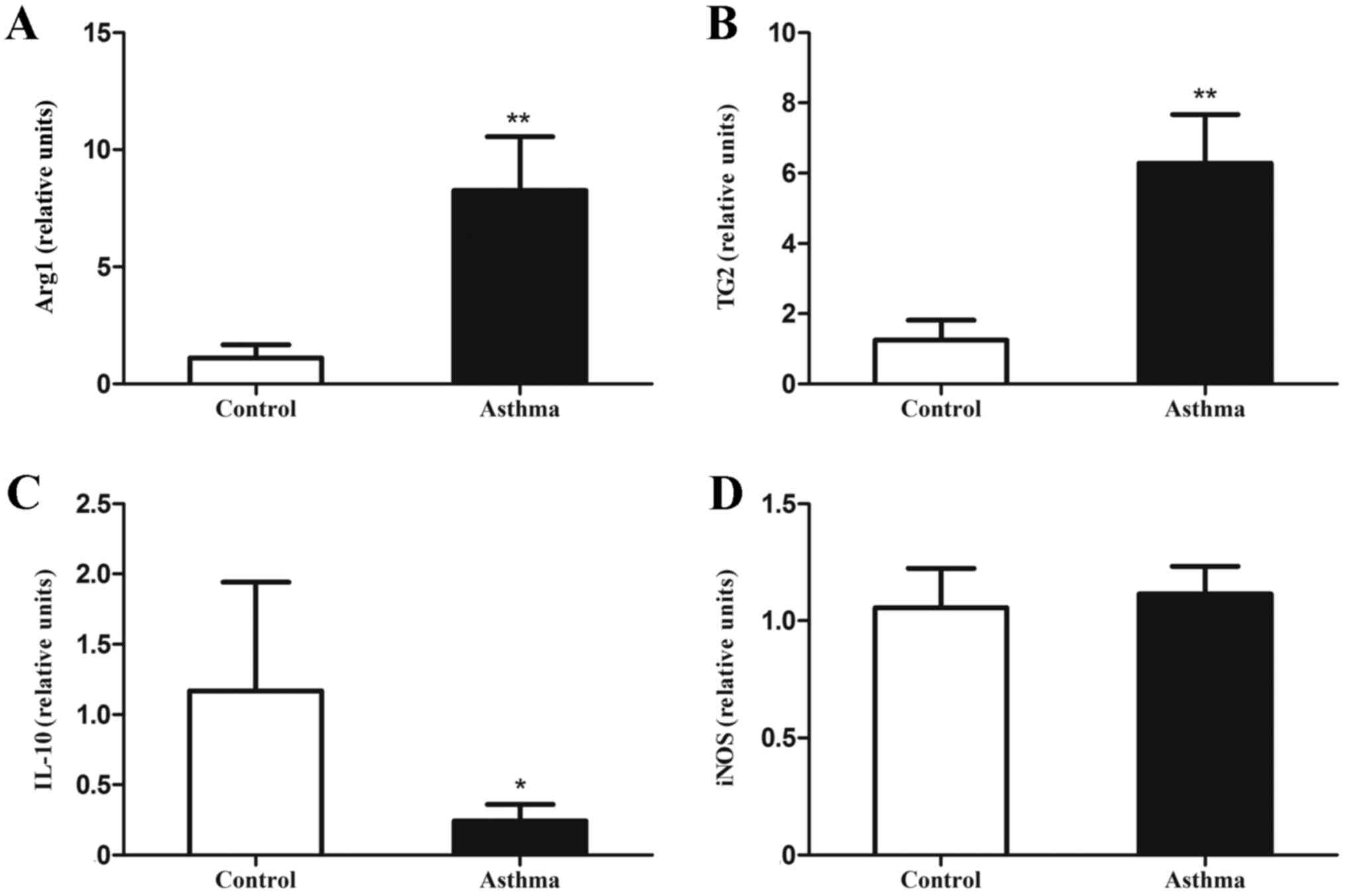
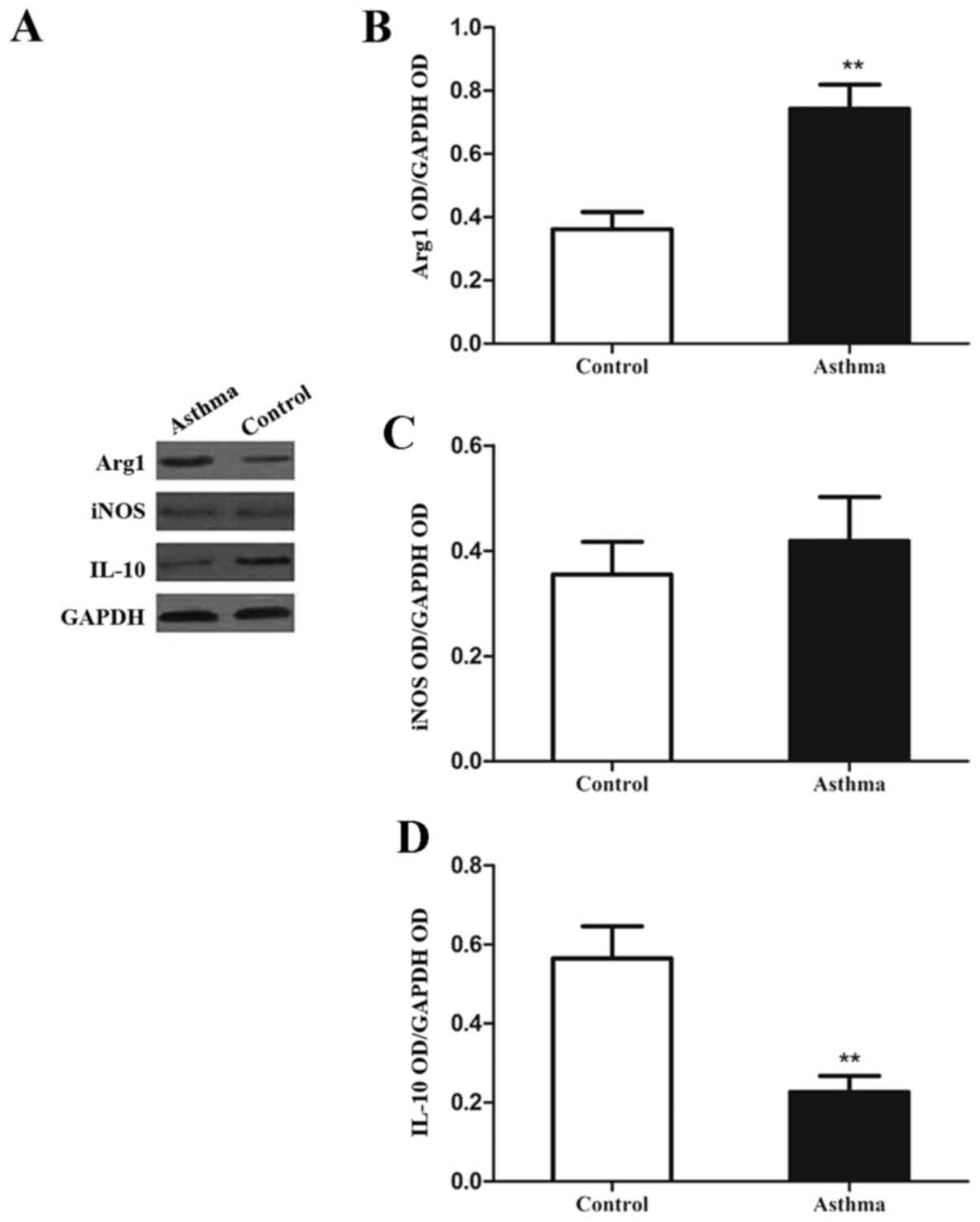
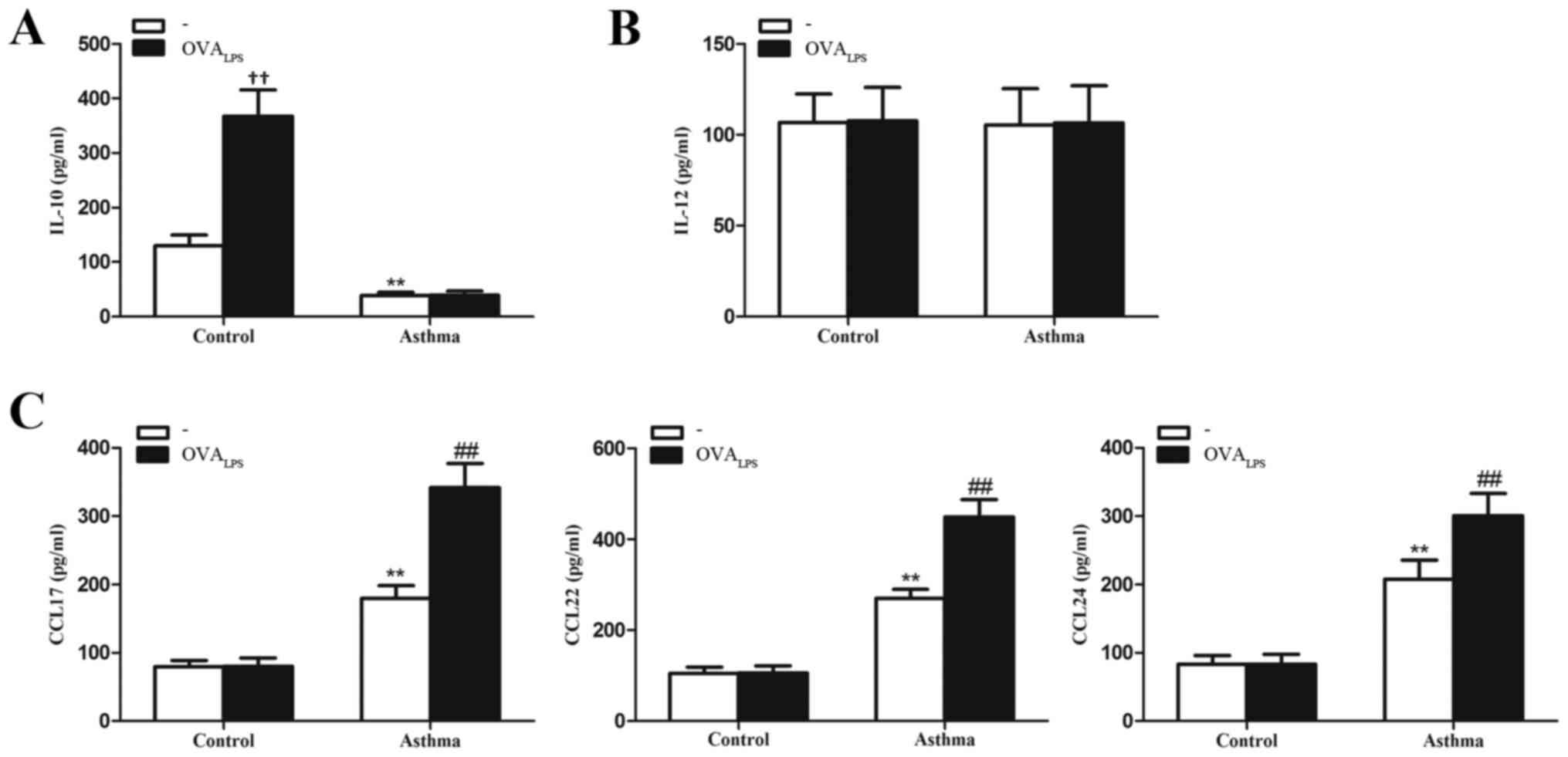
|
1
|
Barnes PJ: Immunology of asthma and
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:183–192.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anderson GP: Endotyping asthma: New
insights into key pathogenic mechanisms in a complex, heterogeneous
disease. Lancet. 372:1107–1119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martinez FO, Helming L and Gordon S:
Alternative activation of macrophages: An immunologic functional
perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:451–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Strauss-Ayali D, Conrad SM and Mosser DM:
Monocyte subpopulations and their differentiation patterns during
infection. J Leukoc Biol. 82:244–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, Elain G,
Join-Lambert O, Kayal S, Sarnacki S, Cumano A, Lauvau G and
Geissmann F: Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a
population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science.
317:666–670. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gordon S and Taylor PR: Monocyte and
macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:953–964. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A and
Locati M: Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci.
13:453–461. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gorden S and Martinez FO: Alternative
activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity.
32:593–604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loke P, Nair MG, Parkinson J, Guiliano D,
Blaxter M and Allen JE: IL-4 dependent alternative activated
macrophages have a distinct in vivo gene expression phenotype. BMC
Immunol. 3:72002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nair MG, Cochrane DW and Allen JE:
Macrophages in chronic type 2 inflammation have a novel phenotype
characterized by the abundant expression of Ym1 and Fizzl that can
be partly replicated in vivo. Immunol Lett. 85:173–180. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sandler NG, Mentink-Kane MM, Cheever AW
and Wynn TA: Global gene expression profiles during acute
pathogen-induced pulmonary inflammation reveal divergent roles for
Th1 and Th2 responses in tissue repair. J Immunol. 171:3655–3667.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sutterwala FS, Noel GJ, Salgame P and
Mosser DM: Reversal of proinflammatory responses by ligating the
macrophage Fcgamma receptor type I. J Exp Med. 188:217–222. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gerber JS and Mosser DM: Reversing
lipopolysaccharide toxicity by ligating the macrophage Fc gamma
receptors. J Immunol. 166:6861–6868. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fleming BD and Mosser DM: Regulatory
macrophages: Setting the threshold for therapy. Eur J Immunol.
41:2498–2502. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schneberger D, Aharonson-Raz K and Singh
B: Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity and Toll-like receptors in
the lung. Cell Tissue Res. 343:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Holt PG, Strickland DH, Wikström ME and
Jahnsen FL: Regulation of immunological homeostasis in the
respiratory tract. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:142–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Martinez FO, Helming L, Milde R, Varin A,
Melgert BN, Draijer C, Thomas B, Fabbri M, Crawshaw A, Ho LP, et
al: Genetic programs expressed in resting and IL-4 alternatively
activated mouse and human macrophages: Similarities and
differences. Blood. 121:e57–e69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Melgert BN, ten Hacken NH, Rutgers B,
Timens W, Postma DS and Hylkema MN: More alternative activation of
macrophages in lungs of asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
127:831–833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim EY, Battaile JT, Patel AC, You Y,
Agapov E, Grayson MH, Benoit LA, Byers DE, Alevy Y, Tucker J, et
al: Persistent activation of an innate immune response translates
respiratory viral infection into chronic lung disease. Nat Med.
14:633–640. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chupp GL, Lee CG, Jarjour N, Shim YM, Holm
CT, He S, Dziura JD, Reed J, Coyle AJ, Kiener P, et al: A
chitinase-like protein in the lung and circulation of patients with
severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 357:2016–2027. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Draijer C, Robbe P, Boorsma CE, Hylkema MN
and Melgert BN: Characterization of macrophage phenotypes in three
murine models of house-dust-mite-induced asthma. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:6320492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maneechotesuwan K, Supawita S,
Kasetsinsombat K, Wongkajornsilp A and Barnes PJ: Sputum
indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase activity is increased in asthmatic
airways by using inhaled corticosteroids. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
121:43–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fitzpatrick AM, Higgins M, Holguin F,
Brown LA and Teague WG: National Institutes of Health/National
Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Severe Asthma Research Program:
The molecular phenotype of severe asthma in children. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 125:851–857.e18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bedoret D, Wallemacq H, Marichal T, Desmet
C, Calvo F Quesada, Henry E, Closset R, Dewals B, Thielen C, Gustin
P, et al: Lung interstitial macrophages alter dendritic cell
functions to prevent airway allergy in mice. J Clin Invest.
119:3723–3738. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lagranderie M, Nahori MA, Balazuc AM,
Kiefer-Biasizzo H, e Silva JR Lapa, Milon G, Marchal G and
Vargaftig BB: Dendritic cells recruited to the lung shortly after
intranasal delivery of Mycobacterium bovis BCG drive the primary
immune response towards a type 1 cytokine production. Immunology.
108:352–364. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Larionov A, Krause A and Miller W: A
standard curve based method for relative real time PCR data
processing. BMC Bioinformatics. 6:622005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gordon S: Alternative activation of
macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:23–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu Z, Zheng T, Homer RJ, Kim YK, Chen NY,
Cohn L, Hamid Q and Elias JA: Acidic mammalian chitinase in
asthmatic Th2 inflammation and IL-13 pathway activation. Science.
304:1678–1682. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Porcheray F, Viaud S, Rimaniol AC, Léone
C, Samah B, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Dormont D and Gras G: Macrophage
activation switching: An asset for the resolution of inflammation.
Clin Exp Immunol. 142:481–489. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Laskin DL, Sunil VR, Gardner CR and Laskin
JD: Macrophages and tissue injury: Agents of defense or
destruction? Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 51:267–288. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stout RD and Suttles J: Functional
plasticity of macrophages: Reversible adaptation to changing
microenvironments. J Leukoc Biol. 76:509–513. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bronte V and Zanovello P: Regulation of
immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol.
5:641–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Melgert BN, Oriss TB, Qi Z, Dixon-McCarthy
B, Geerlings M, Hylkema MN and Ray A: Macrophages: Regulators of
sex differences in asthma? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 42:595–603.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ford AQ, Dasgupta P, Mikhailenko I, Smith
EM, Noben-Trauth N and Keegan AD: Adoptive transfer of IL-4Rα+
macrophages is sufficient to enhance eosinophilic inflammation in a
mouse model of allergic lung inflammation. BMC Immunol. 13:62012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nieuwenhuizen NE, Kirstein F, Jayakumar J,
Emedi B, Hurdayal R, Horsnell WG, Lopata AL and Brombacher F:
Allergic airway disease is unaffected by the absence of
IL-4Rα-dependent alternatively activated macrophages. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 130:743–750.e8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|