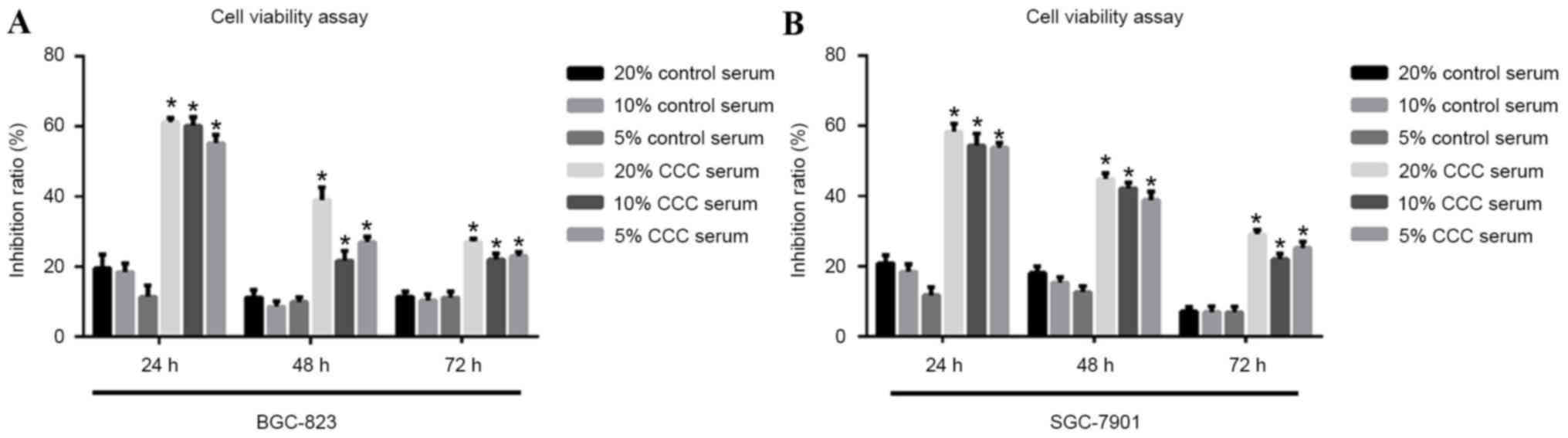
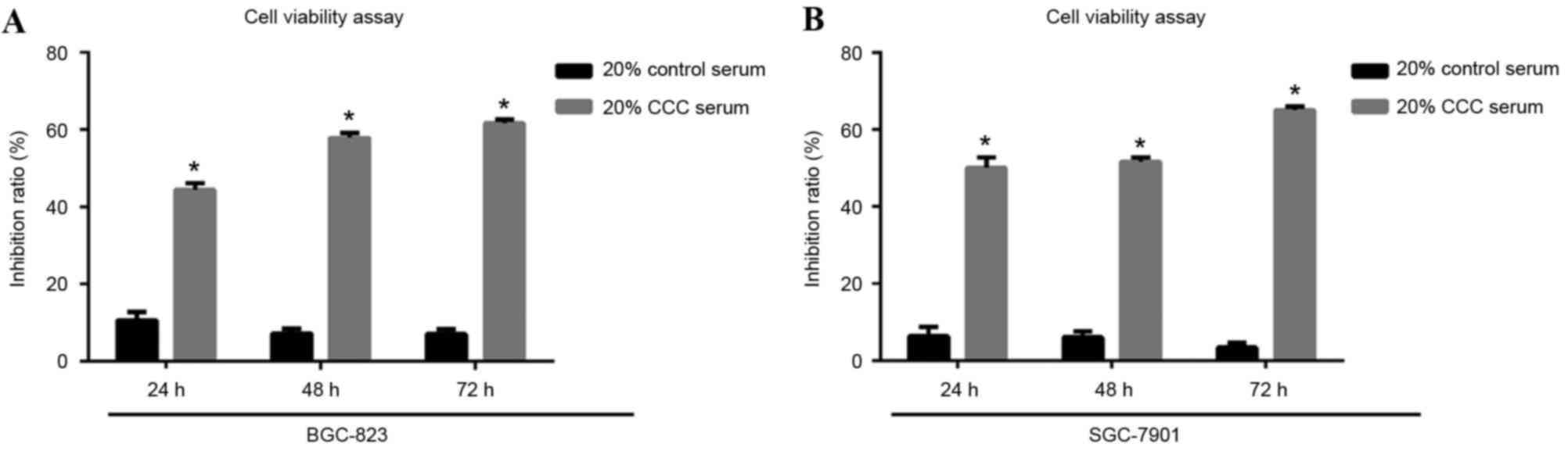
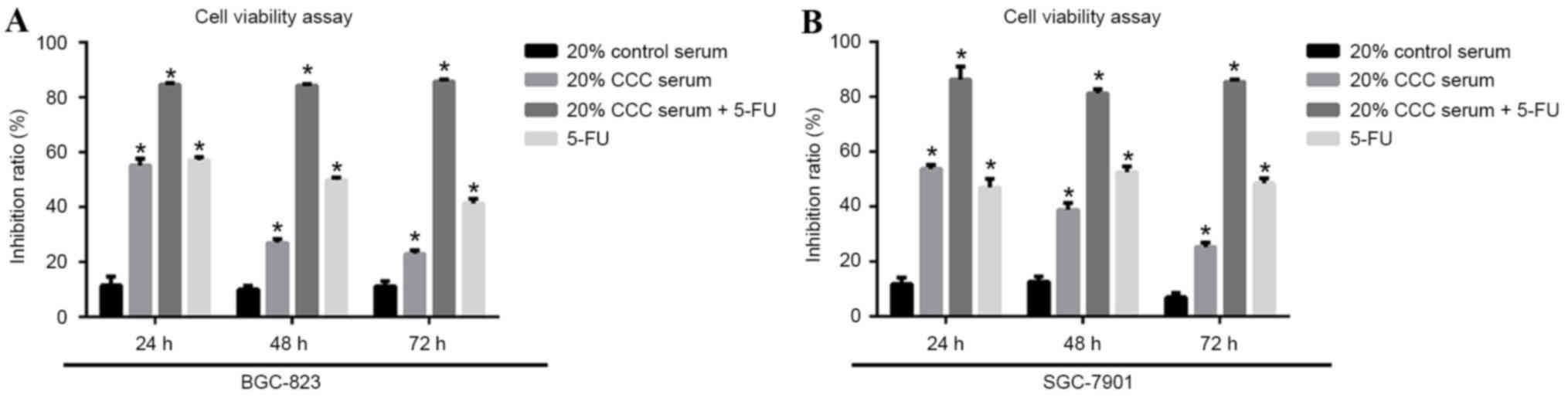
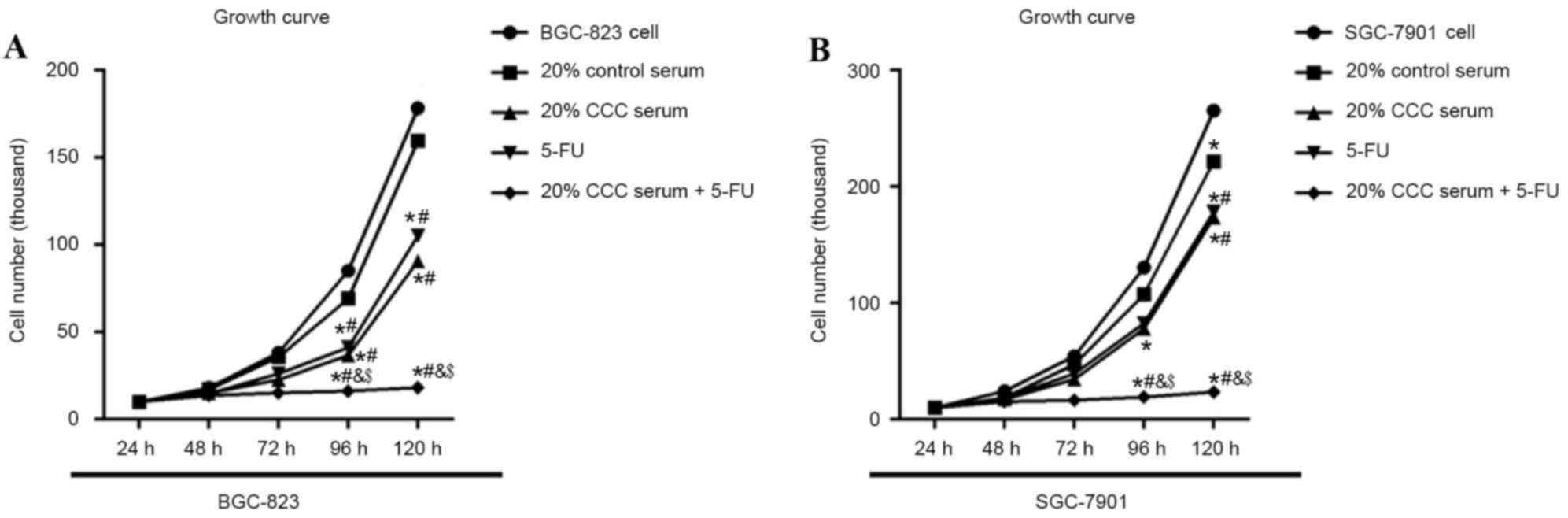
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. Ca Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang L: Incidence and mortality of gastric
cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 12:17–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ychou M, Boige V, Pignon JP, Conroy T,
Bouché O, Lebreton G, Ducourtieux M, Bedenne L, Fabre JM,
Saint-Aubert B, et al: Perioperative chemotherapy compared with
surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: An
FNCLCC and FFCD multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol.
29:1715–1721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu Y, Qi Y, Liu H, Wang X, Zhu H and Wang
Z: AMPK activator AICAR promotes 5-FU-induced apoptosis in gastric
cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 411:299–305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Camacho LH, Garcia S, Panchal AM, Lim J,
Hong DS, Ng C, Madoff DC, Fu S, Gayed I and Kurzrock R: Exploratory
study of hepatic arterial infusion oxaliplatin with systemic
5-fluorouracil/bevacizumab in patients with refractory solid tumor
and extensive liver metastases. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 9:311–314.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu MN, Liu AY, Pei FH, Ma X, Fan YJ, Du
YJ and Liu BR: Functional mechanism of the enhancement of
5-fluorouracil sensitivity by TUSC4 in colon cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 10:3682–3688. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He Q, Ma L, Li Y and Li G: A pilot study
of an individualized comprehensive treatment for advanced gastric
cancer with para-aortic lymph node metastasis. BMC Gastroenterol.
16:82016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xun L, Yang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Yang J,
Chang J, Sun X, Zhou X, Guo Y, Xu Y, et al: Traditional Chinese
medicine in cancer care: A review of controlled clinical studies
published in Chinese. PLoS One. 8:e603382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Éwe GE: Chinese cantharides (mylabris
Cichorii). A worthy candidate for admission to the u. s. p. J Pharm
Sci. 9:257–263. 1920.
|
|
11
|
Wang GS: Medical uses of mylabris in
ancient China and recent studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 26:147–162.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia JM, Wang ZQ, Wu LJ and Wu YL: Advance
of pharmacological study on ginsenoside Rb_1. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za
Zhi. 33:1371–1377. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Zhao H, Qian W, Li H, Zhang L, Ye Z,
Zhang G, Xia M, Li J, Gao J, et al: Chemotherapy for gastric cancer
by finely tailoring anti-Her2 anchored dual targeting
immunomicelles. Biomaterials. 33:5349–5462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han JJ, Yu JM, Wu HY, Liu JB, Song B and
Xue DW: Inhibitory effect of compound cantharides capsule on the
proliferation of xenografts of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG
(2)215 in mice. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 34:821–825. 2012.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tamura G: Alterations of tumor suppressor
and tumor-related genes in the development and progression of
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 12:192–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Otani K, Li X, Arakawa T, Chan FK and Yu
J: Epigenetic-mediated tumor suppressor genes as diagnostic or
prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn.
13:445–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee EY and Muller WJ: Oncogenes and tumor
suppressor genes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
10:a0032361997.
|
|
18
|
Krautheim A, Brechlin P, Becker K, Winkler
M and Steinfelder HJ: Hamster pancreatic beta cell lines with
altered sensitivity towards apoptotic signalling by phosphatase
inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 129:687–694. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Clarke PR, Hoffmann I, Draetta G and
Karsenti E: Dephosphorylation of cdc25-C by a type-2A protein
phosphatase: Specific regulation during the cell cycle in Xenopus
egg extracts. Mol Biol Cell. 4:397–411. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taylor BK, Stoops TD and Everett AD:
Protein phosphatase inhibitors arrest cell cycle and reduce
branching morphogenesis in fetal rat lung cultures. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 278:L1062–L1070. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shimizu S, Narita M and Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2
family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by
the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature. 399:483–487. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schuler M, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldstein JC,
Fitzgerald P and Green DR: p53 induces apoptosis by caspase
activation through mitochondrial cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem.
275:7337–7342. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marchenko ND, Zaika A and Moll UM: Death
Signal-induced localization of p53 protein to mitochondria a
potential role in apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem.
275:16202–16212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pflaum J, Schlosser S and Müller M: p53
family and cellular stress responses in cancer. Front Oncol.
4:2852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Taylor CA, Zheng Q, Liu Z and Thompson JE:
Role of p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways and tumor suppressor
p53 on induction of apoptosis in response to Ad-eIF5A1 in A549 lung
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weilbacher A, Gutekunst M, Oren M,
Aulitzky WE and van der kuip H: RITA can induce cell death in
p53-defective cells independently of p53 function via activation of
JNK/SAPK and p38. Cell Death Dis. 5:e13182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda ÁR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huh JE, Kang KS, Chae C, Kim HM, Ahn KS
and Kim SH: Roles of p38 and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways during cantharidin-induced apoptosis in U937 cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 67:1811–1818. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shou LM, Zhang QY, Li W, Xie X, Chen K,
Lian L, Li ZY, Gong FR, Dai KS, Mao YX and Tao M: Cantharidin and
norcantharidin inhibit the ability of MCF-7 cells to adhere to
platelets via protein kinase C pathway-dependent downregulation of
α2 integrin. Oncol Rep. 30:1059–1066. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang K and Ma W: Clinical observation on
the patients with advanced esophageal cancer treated by
chemotherapy combined with compound cantharides capsule. Zhongliu
Jichu Yu Linchuang. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Poon M, Hwang J, Dennis K, DeAngelis C,
Zhang L, Chung H, Stinson J, Wong S, Pulenzas N and Chow E: A novel
prospective descriptive analysis of nausea and vomiting among
patients receiving gastrointestinal radiation therapy. Supportive
Care Cancer. 24:1545–1561. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang J, Zhao Y, Xu Y, Zhu Y, Huang J, Liu
Y, Zhao L, Li Z, Liu H, Wang QL and Qi X: Comparative effectiveness
and safety between oxaliplatin-based and cisplatin-based therapy in
advanced gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. Oncotarget. 7:34824–34831. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mann J: Natural products in cancer
chemotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:143–148.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ledermann DW: Simon Bolivar and the
cantharides. Rev Chilena Infectol. 24:409–412. 2007.(In Spanish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Efferth T, Rauh R, Kahl S, Tomicic M,
Böchzelt H, Tome ME, Briehl MM, Bauer R and Kaina B: Molecular
modes of action of cantharidin in tumor cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
69:811–818. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu D and Chen Z: The effects of
cantharidin and cantharidin derivates on tumour cells. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 9:392–396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Efferth T, Li PC, Konkimalla VS and Kaina
B: From traditional Chinese medicine to rational cancer therapy.
Trends Mol Med. 13:353–361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kadioglu O, Kermani NS, Kelter G,
Schumacher U, Fiebig HH, Greten HJ and Efferth T: Pharmacogenomics
of cantharidin in tumor cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 87:399–409. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang H and Yan X: Cantharidin modulates
the E2F1/MCM7-miR-106b-93/p21-PTEN signaling axis in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 10:2849–2855. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sagawa M, Nakazato T, Uchida H, Ikeda Y
and Kizaki M: Cantharidin induces apoptosis of human multiple
myeloma cells via inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway. Cancer Sci.
99:1820–1826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kok SH, Chui CH, Lam WS, Chen J, Lau FY,
Cheng GY, Wong RS, Lai PP, Leung TW, Tang JC and Chan AS: Apoptotic
activity of a novel synthetic cantharidin analogue on hepatoma cell
lines. Int J Mol Med. 17:945–949. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen YN, Chen JC, Yin SC, Wang GS, Tsauer
W, Hsu SF and Hsu SL: Effector mechanisms of norcantharidin-induced
mitotic arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer.
100:158–165. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kok SH, Cheng SJ, Hong CY, Lee JJ, Lin SK,
Kuo YS, Chiang CP and Kuo MY: Norcantharidin-induced apoptosis in
oral cancer cells is associated with an increase of proapoptotic to
antiapoptotic protein ratio. Cancer Lett. 217:43–52. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li W, Xie L, Chen Z, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Miao Y,
Xu Z and Han X: Cantharidin, a potent and selective PP2A inhibitor,
induces an oxidative stress-independent growth inhibition of
pancreatic cancer cells through G2/M cell-cycle arrest and
apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 101:1226–1233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Amaral JD, Xavier JM, Steer CJ and
Rodrigues CM: The role of p53 in apoptosis. Discov Med. 9:145–152.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|