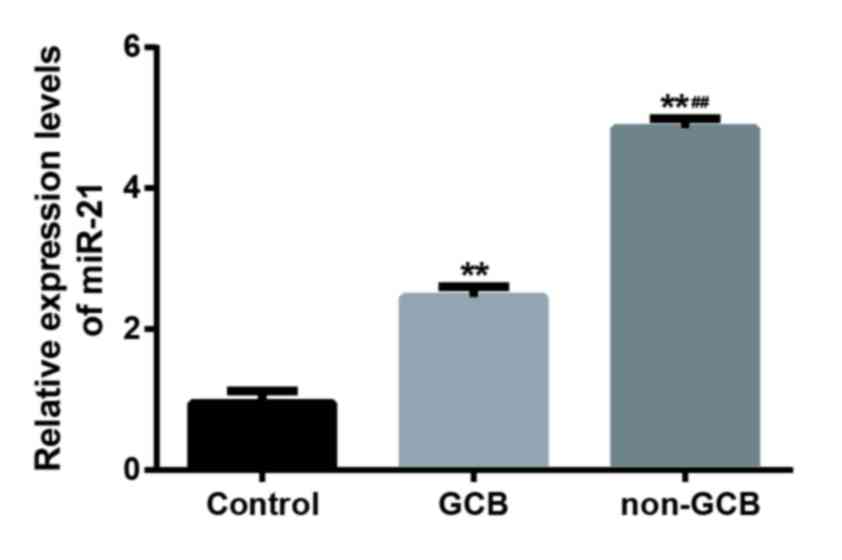
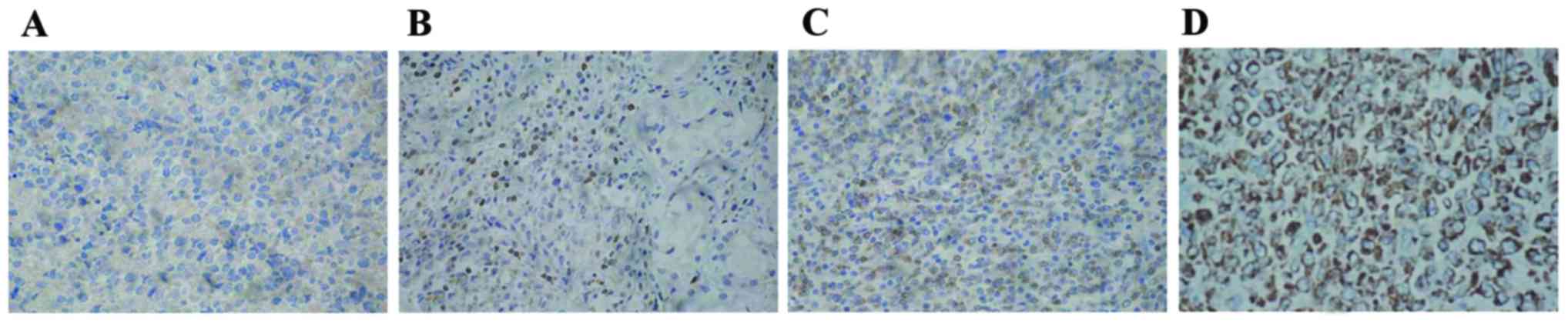
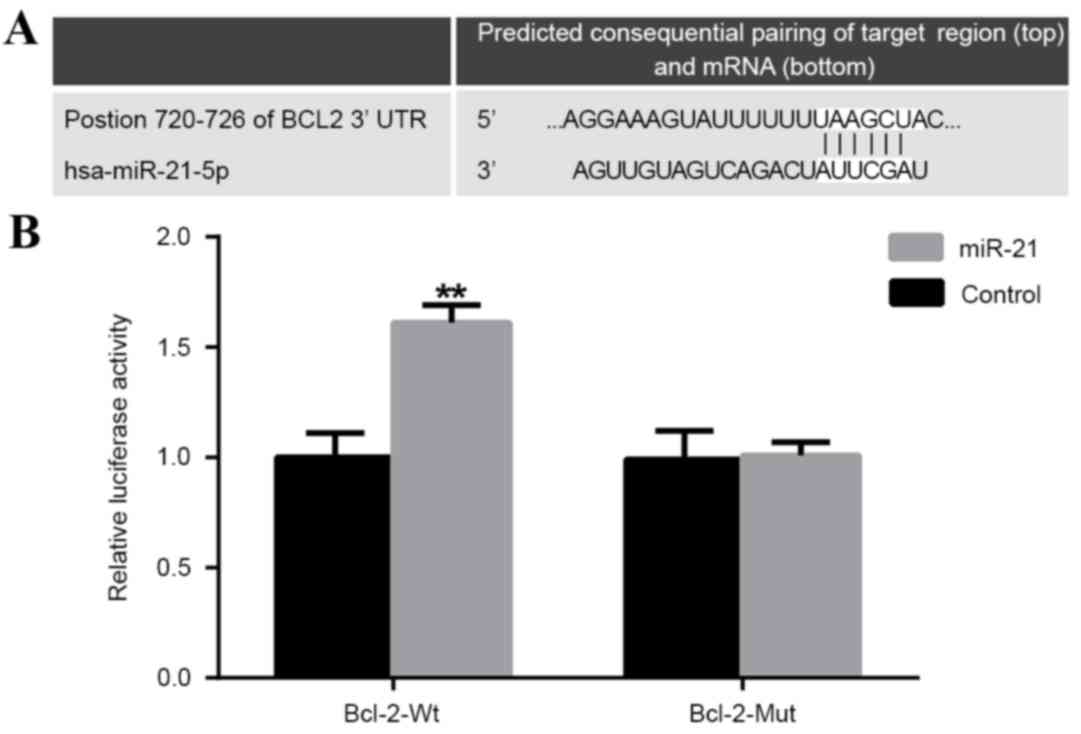
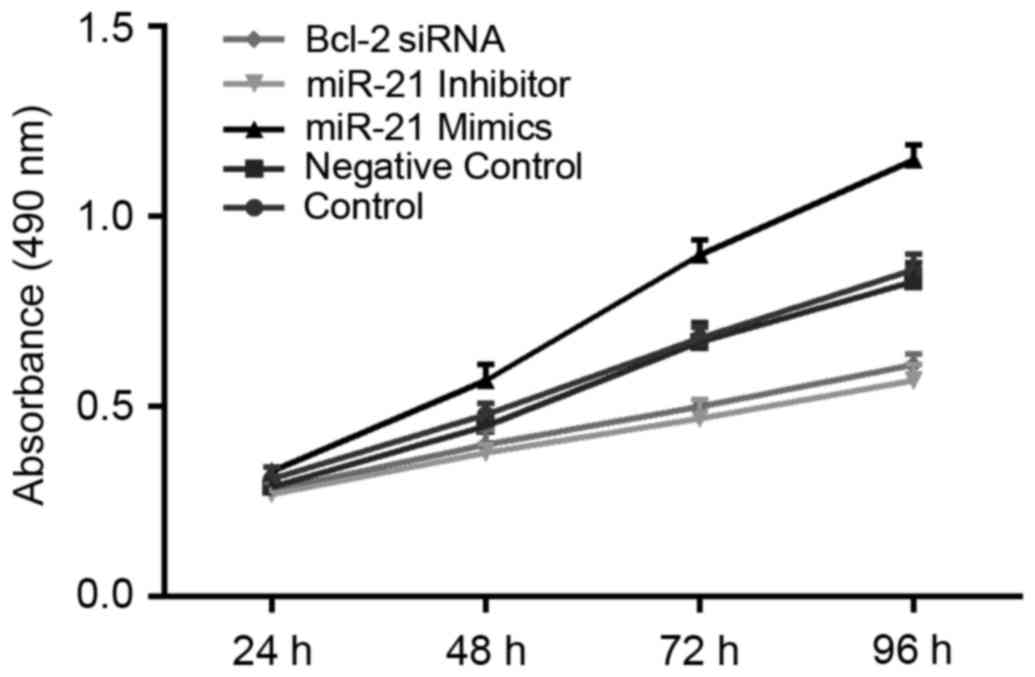
|
1
|
Flowers CR, Sinha R and Vose JM: Improving
outcomes for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. CA Cancer
J Clin. 60:393–408. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Roos AJ, Davis S, Colt JS, Blair A,
Airola M, Severson RK, Cozen W, Cerhan JR, Hartge P, Nuckols JR and
Ward MH: Residential proximity to industrial facilities and risk of
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Environ Res. 110:70–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang CM, Schroeder JC, Olshan AF, Dunphy
CH, Huang WY, Baric RS, Conway K, Cerhan JR, Lynch CF, Rothman N,
et al: A case-control study of tobacco use and other
non-occupational risk factors for lymphoma subtypes defined by
t(14; 18) translocations and bcl-2 expression. Cancer Causes
Control. 21:1147–1154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson CA, Habermann TM, Wang AH,
Vierkant RA, Folsom AR, Ross JA and Cerhan JR: Antioxidant intake
from fruits, vegetables and other sources and risk of non-Hodgkin's
lymphoma: The Iowa women's health study. Int J Cancer.
126:992–1003. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frankenfeld CL, Cerhan JR, Cozen W, Davis
S, Schenk M, Morton LM, Hartge P and Ward MH: Dietary flavonoid
intake and non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 87:1439–1445.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fisher SG and Fisher RI: The epidemiology
of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Oncogene. 23:6524–6534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang SS, Slager SL, Brennan P, Holly EA,
De Sanjose S, Bernstein L, Boffetta P, Cerhan JR, Maynadie M,
Spinelli JJ, et al: Family history of hematopoietic malignancies
and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL): A pooled analysis of 10 211
cases and 11 905 controls from the international lymphoma
epidemiology consortium (InterLymph). Blood. 109:3479–3488. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mazan-Mamczarz K and Gartenhaus RB: Role
of microRNA deregulation in the pathogenesis of diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Leuk Res. 37:1420–1428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Psathas JN, Doonan PJ, Raman P, Freedman
BD, Minn AJ and Thomas-Tikhonenko A: The Myc-miR-17-92 axis
amplifies B-cell receptor signaling via inhibition of ITIM
proteins: A novel lymphomagenic feed-forward loop. Blood.
122:4220–4229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tagawa H, Ikeda S and Sawada K: Role of
microRNA in the pathogenesis of malignant lymphoma. Cancer Sci.
104:801–809. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jardin F and Figeac M: MicroRNAs in
lymphoma, from diagnosis to targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol.
25:480–486. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai H, Wei J, Deng C, Yang X, Wang C and
Xu R: MicroRNA-21 regulates the sensitivity of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma cells to the CHOP chemotherapy regimen. Int J Hematol.
97:223–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iqbal J, Neppalli VT, Wright G, Dave BJ,
Horsman DE, Rosenwald A, Lynch J, Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner
TC, et al: BCL2 expression is a prognostic marker for the activated
B-cell-like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol.
24:961–968. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Swerdllow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe
ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J and Vardiman JW: WHO
classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues.
4th. 2. IARC; 2008
|
|
16
|
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC,
Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E,
Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, et al: Confirmation of the molecular
classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by
immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 103:275–282.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi L, Chen J, Yang J, Pan T, Zhang S and
Wang Z: MiR-21 protected human glioblastoma U87MG cells from
chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide induced apoptosis by decreasing
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. Brain Res. 1352:255–264.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giovannetti E, Funel N, Peters GJ, Del
Chiaro M, Erozenci LA, Vasile E, Leon LG, Pollina LE, Groen A,
Falcone A, et al: MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: Correlation
with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role
in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res.
70:4528–4538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, Zhu QS, Hamidi S and
Navab R: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation,
invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and
Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One.
9:e1036982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Medina PP, Nolde M and Slack FJ: OncomiR
addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell
lymphoma. Nature. 467:86–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen L, Pei JH and Chen HM: Effects of
continuous positive airway pressure treatment on glycaemic control
and insulin sensitivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea
and type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci. 10:637–642.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao M, Guo L, Wang T, Zhu T, Jia L, Chen
L and Wen F: Interleukin-1B-31T/C promoter polymorphism and chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease risk: A meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci.
10:434–438. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lawrie CH, Soneji S, Marafioti T, Cooper
CD, Palazzo S, Paterson JC, Cattan H, Enver T, Mager R, Boultwood
J, et al: MicroRNA expression distinguishes between germinal center
B cell-like and activated B cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B
cell lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 121:1156–1161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu N, Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Xiong S and Chu Y:
Selective impairment of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by
paclitaxel is explained by Bcl-2/Bax mediated apoptosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:212–219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Q, Yang K and Li A: microRNA-21
protects against ischemia-reperfusion and
hypoxia-reperfusion-induced cardiocyte apoptosis via the
phosphatase and tensin homolog/Akt-dependent mechanism. Mol Med
Rep. 9:2213–2220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiong Y, Ma XY, Zhang Z, Shao ZJ, Zhang YY
and Zhou LM: Apoptosis induced by β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin is
associated with Bcl-2 and NF-κB in human breast carcinoma MCF-7
cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1789–1793. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Zhang S, Geng JX and Hu XY: Curcumin
inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell proliferation
through regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and cytochrome C. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:4599–4602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Yan L, Zhang W, Wang H, Chen W, Hu N
and Ou H: miR-21 inhibitor suppresses proliferation and migration
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through down-regulation of BCL2
expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3478–3487. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei B, Song Y, Zhang Y and Hu M:
microRNA-449a functions as a tumor-suppressor in gastric
adenocarcinoma by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Lett. 6:1713–1718.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F,
Richter JA, Siebert R, Climent J, Fresquet V, Beltran E, Agirre X,
Marugan I, Marín M, et al: Homozygous deletions localize novel
tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 109:271–280.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song B, Ji W, Guo S, Liu A, Jing W, Shao
C, Li G and Jin G: miR-545 inhibited Pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma growth by targeting RIG-I. FEBS Lett. 588:4375–4381.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thompson RC, Vardinogiannis I and Gilmore
TD: The sensitivity of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines to
histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis is modulated by
BCL-2 family protein activity. PLoS One. 8:e628222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pan X, Wang ZX and Wang R: MicroRNA-21: A
novel therapeutic target in human cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:1224–1232. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gu L, Song G, Chen L, Nie Z, He B, Pan Y,
Xu Y, Li R, Gao T, Cho WC and Wang S: Inhibition of miR-21 induces
biological and behavioral alterations in diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma. Acta Haematol. 130:87–94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tomek M, Akiyama T and Dass CR: Role of
Bcl-2 in tumour cell survival and implications for pharmacotherapy.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 64:1695–1702. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Snigdha S, Smith ED, Prieto GA and Cotman
CW: Caspase-3 activation as a bifurcation point between plasticity
and cell death. Neurosci Bull. 28:14–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|