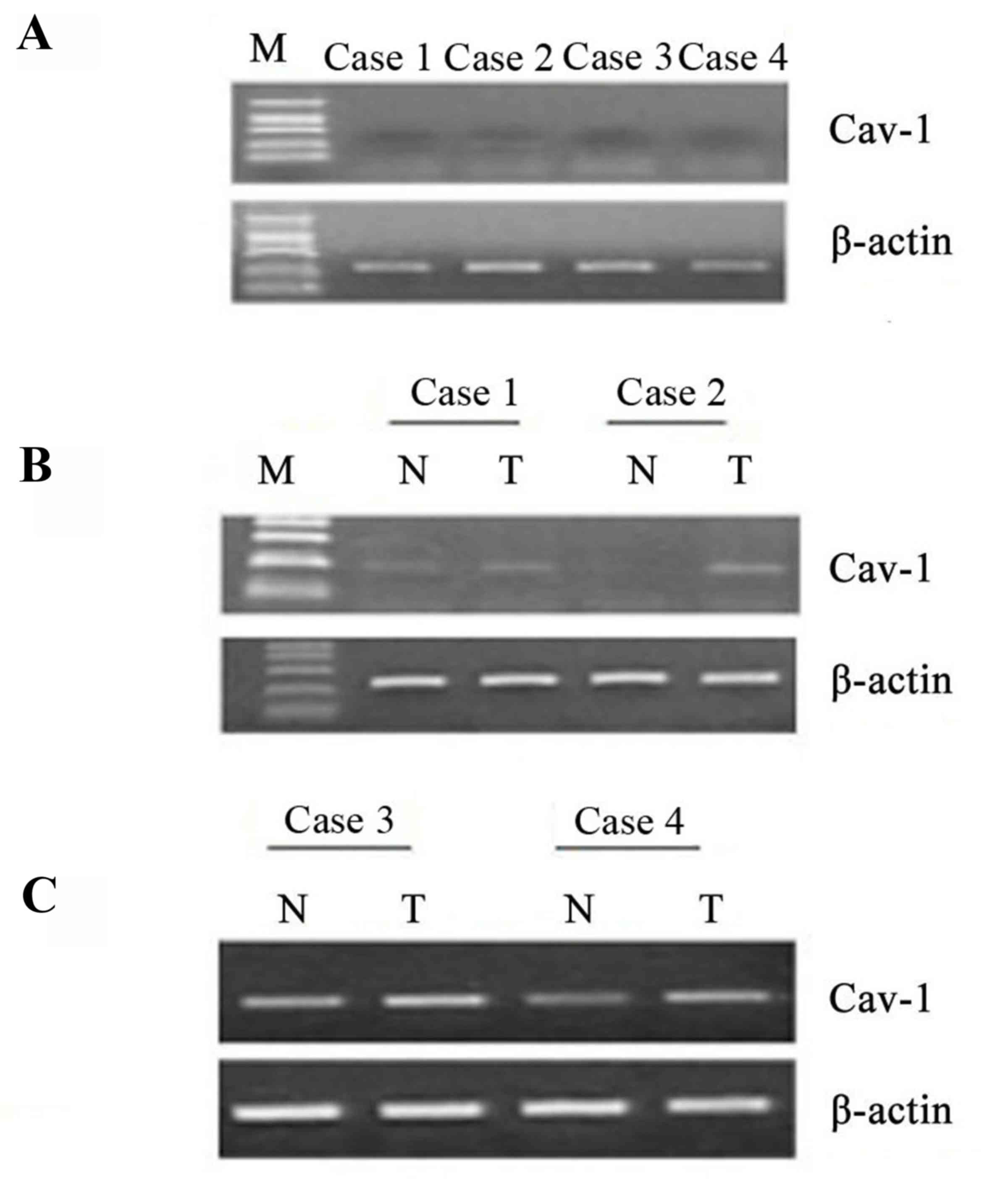
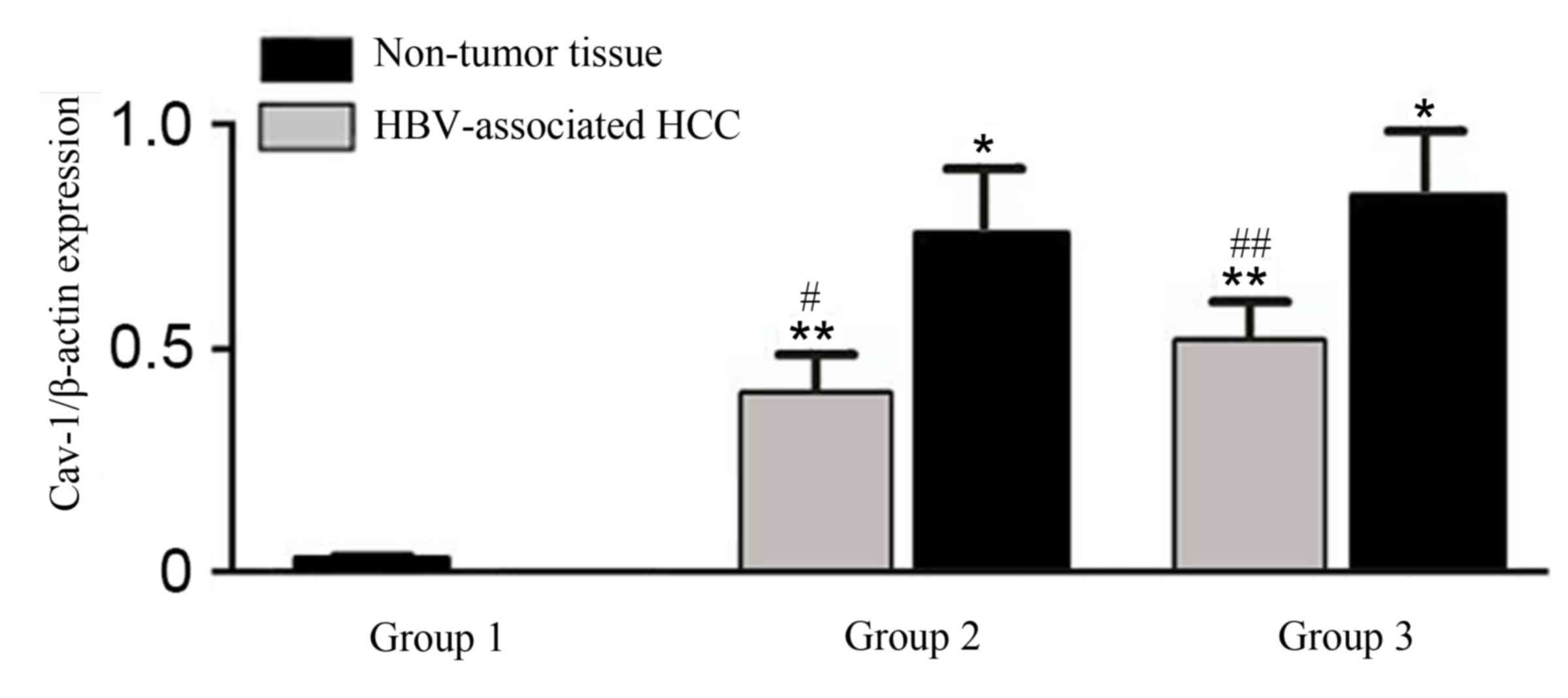
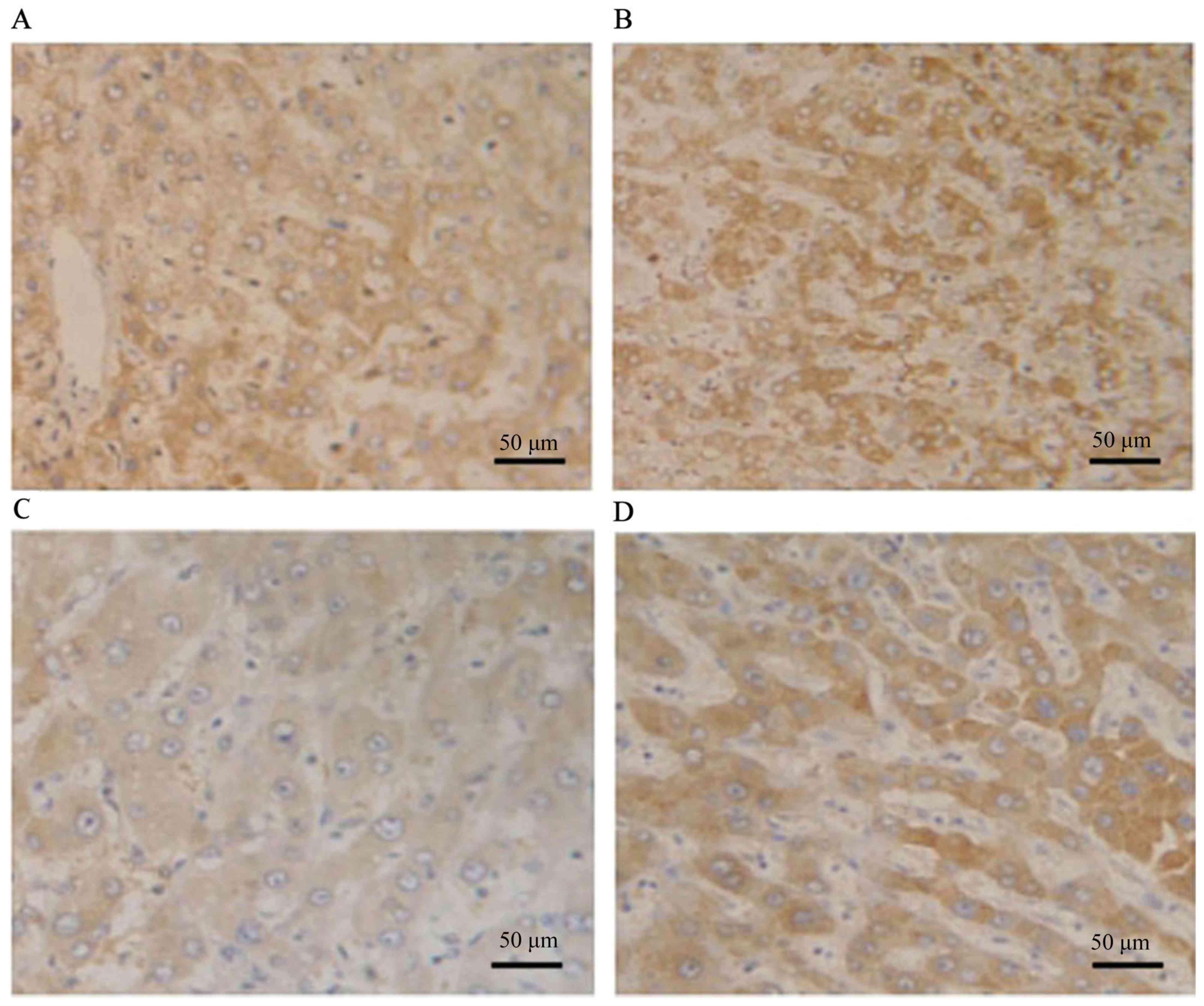
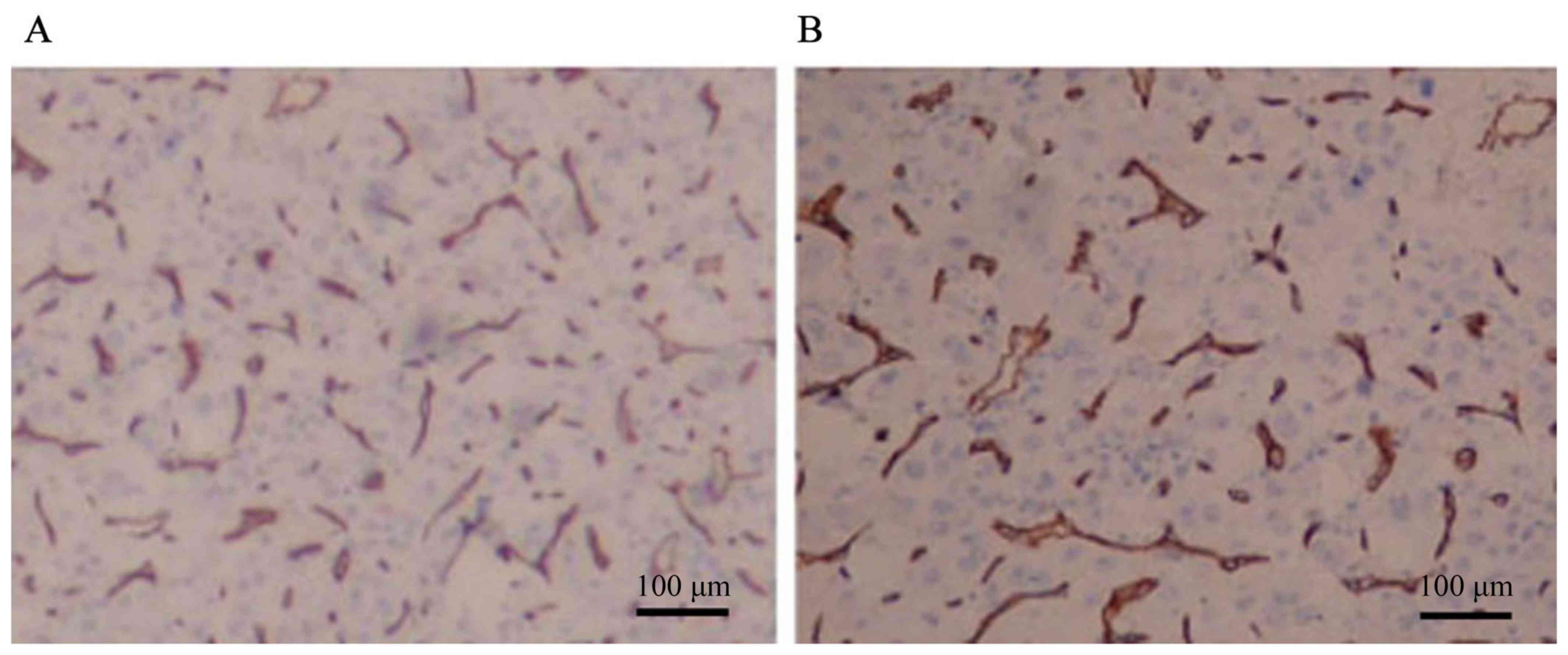
|
1
|
Cohen AW, Hnasko R, Schubert W and Lisanti
MP: Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease. Physiol
Rev. 84:1341–1379. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Busija AR, Patel HH and Insel PA:
Caveolins and cavins in the trafficking, maturation, and
degradation of caveolae: Implications for cell physiology. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 312:C459–C477. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE and
Lisanti MP: Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for
organizing ‘preassembled signaling complexes’ at the plasma
membrane. J Biol Chem. 273:5419–5422. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gupta VK, You Y, Klistorner A and Graham
SL: Shp-2 regulates the TrkB receptor activity in the retinal
ganglion cells under glaucomatous stress. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1643–1649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Trane AE, Hiob MA, Uy T, Pavlov D and
Bernatchez P: Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain residue phenylalanine
92 modulates Akt signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 766:46–55. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen F, Barman S, Yu Y, Haigh S, Wang Y,
Black SM, Rafikov R, Dou H, Bagi Z, Han W, et al: Caveolin-1 is a
negative regulator of NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen
species. Free Radic Biol Med. 73:201–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sowa G: Regulation of cell signaling and
function by endothelial caveolins: Implications in disease. Transl
Med (Sunnyvale). (Suppl 8):pii: 001. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wiechen K, Sers C, Agoulnik AI, Arlt K,
Dietel M, Schlag PM and Schneider U: Down-regulation of caveolin-1,
a candidate tumor suppressor gene, in sarcomas. Am J Pathol.
158:833–839. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi L, Chen XM, Wang L, Zhang L and Chen
Z: Expression of caveolin-1 in mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the
salivary glands: Correlation with vascular endothelial growth
factor, microvessel density, and clinical outcome. Cancer.
109:1523–1531. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Riwaldt S, Bauer J, Pietsch J, Braun M,
Segerer J, Schwarzwälder A, Corydon TJ, Infanger M and Grimm D: The
importance of caveolin-1 as key-regulator of three-dimensional
growth in thyroid cancer cells cultured under real and simulated
microgravity conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 16:28296–28310. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang CF, Yu GT, Wang WM, Liu B and Sun
ZJ: Prognostic and predictive values of SPP1, PAI and caveolin-1 in
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:6032–6039. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Auzair LB, Vincent-Chong VK, Ghani WM,
Kallarakkal TG, Ramanathan A, Lee CE, Rahman ZA, Ismail SM, Abraham
MT and Zain RB: Caveolin 1 (Cav-1) and actin-related protein 2/3
complex, subunit 1B (ARPC1B) expressions as prognostic indicators
for oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.
273:1885–1893. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Profirovic J, Strekalova E, Urao N,
Krbanjevic A, Andreeva AV, Varadarajan S, Fukai T, Hen R,
Ushio-Fukai M and Voyno-Yasenetskaya TA: A novel regulator of
angiogenesis in endothelial cells: 5-hydroxytriptamine 4 receptor.
Angiogenesis. 16:15–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nassar ZD, Hill MM, Parton RG, Francois M
and Parat MO: Non-caveolar caveolin-1 expression in prostate cancer
cells promotes lymphangiogenesis. Oncoscience. 2:635–645. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo JD and Chen AF: Nitric oxide: A newly
discovered function on wound healing. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
26:259–264. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Phillips PG and Birnby LM: Nitric oxide
modulates caveolin-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and
distribution at the endothelial cell/tumor cell interface. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 286:L1055–L1065. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan YM, Yao YZ, Zhu ZH, Sun XT, Qiu YD and
Ding YT: Caveolin-1 is important for nitric-oxide angiogenesis in
fibrin gels with human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 27:1567–1574. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Niu ZS, Niu XJ and Wang WH: Genetic
alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:9069–9095. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Riccardo Lencioni, Adrian M and Di
Bisceglie EASL: An update of angiogenesis in endothelial cells:
5-hypatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatology. 56:9082012.
|
|
20
|
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan
HL, Chen CJ, Chen DS, Chen HL, Chen PJ, Chien RN, et al:
Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of
hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 10:1–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Marone M, Mozzetti S, De Ritis D, Pierelli
L and Scambia G: Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis to assess the
expression levels of multiple transcripts from the same sample.
Biol Proced Onlin. 3:19–25. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Friedrichs K, Gluba S, Eidtmann H and
Jonat W: Overexpression of p53 and prognosis in breast cancer.
Cancer. 72:3641–3647. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Weidner N, Carroll PR, Flax J, Blumenfeld
W and Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in
invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 143:401–409.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koleske AJ, Baltimore D and Lisanti MP:
Reduction of caveolin and caveolae in oncogenically transformed
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:1381–1385. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hayashi K, Matsuda S, Machida K, Yamamoto
T, Fukuda Y, Nimura Y, Hayakawa T and Hamaguchi M: Invasion
activating caveolin-1 mutation in human scirrhous breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 61:2361–2364. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fu P, Chen F, Pan Q, Zhao X, Zhao C, Cho
WC and Chen H: The different functions and clinical significances
of caveolin-1 in human adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 10:819–835. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trimmer C, Sotgia F, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Balliet RM, Eaton G, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pavlides S, Howell A,
Iozzo RV, Pestell RG, et al: Caveolin-1 and mitochondrial SOD2
(MnSOD) function as tumor suppressors in the stromal
microenvironment: A new genetically tractable model for human
cancer associated fibroblasts. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:383–394. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang R, He W, Li Z, Chang W, Xin Y and
Huang T: Caveolin-1 functions as a key regulator of
17β-estradiol-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in BT474 breast
cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 34:822–827. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sugie S, Mukai S, Yamasaki K, Kamibeppu T,
Tsukino H and Kamoto T: Significant association of caveolin-1 and
caveolin-2 with prostate cancer progression. Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 12:391–396. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Williams TM, Medina F, Badano I, Hazan RB,
Hutchinson J, Muller WJ, Chopra NG, Scherer PE, Pestell RG and
Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 gene disruption promotes mammary
tumorigenesis and dramatically enhances lung metastasis in vivo.
Role of Cav-1 in cell invasiveness and matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP-2/9) secretion. J Biol Chem. 279:51630–51646. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gai X, Lu Z, Tu K, Liang Z and Zheng X:
Caveolin-1 Is up-regulated by GLI1 and contributes to GLI1-driven
EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e845512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu WR, Jin L, Tian MX, Jiang XF, Yang LX,
Ding ZB, Shen YH, Peng YF, Gao DM, Zhou J, et al: Caveolin-1
promotes tumor growth and metastasis via autophagy inhibition in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
40:169–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang W, Feng X, Zhang S, Ren Z, Liu Y,
Yang B, Lv B, Cai Y, Xia J and Ge N: Caveolin-1 confers resistance
of hepatoma cells to anoikis by activating IGF-1 pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:1223–1236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yokomori H, Oda M, Yoshimura K, Nomura M,
Wakabayashi G, Kitajima M and Ishii H: Elevated expression of
caveolin-1 at protein and mRNA level in human cirrhotic liver:
Relation with nitric oxide. J Gastroenterol. 38:854–860. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pan YM, Yao YZ, Zhu ZH, Sun XT, Qiu YD and
Ding YT: Caveolin-1 is important for nitric oxide-mediated
angiogenesis in fibrin gels with human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:1567–1574. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yerian LM, Anders RA, Tretiakova M and
Hart J: Caveolin and thrombospondin expression during
hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 28:357–364. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang WS, Wang RJ, Ding JL, Liu CY and
Wang JH: Caveolin-1: A novel biomarker for prostate cancer.
Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 18:635–638. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Williams TM, Hassan GS, Li J, Cohen AW,
Medina F, Frank PG, Pestell RG, Di Vizio D, Loda M and Lisanti MP:
Caveolin-1 promotes tumor progression in an autochthonous mouse
model of prostate cancer: Genetic ablation of Cav-1 delays advanced
prostate tumor development in tramp mice. J Biol Chem.
280:25134–25145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bocci G, Fioravanti A, Orlandi P, Di
Desidero T, Natale G, Fanelli G, Viacava P, Naccarato AG, Francia G
and Danesi R: Metronomic ceramide analogs inhibit angiogenesis in
pancreatic cancer through up-regulation of caveolin-1 and
thrombospondin-1 and down-regulation of cyclin D1. Neoplasia.
14:833–845. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bauer PM, Yu J, Chen Y, Hickey R,
Bernatchez PN, Looft-Wilson R, Huang Y, Giordano F, Stan RV and
Sessa WC: Endothelial-specific expression of caveolin-1 impairs
microvascular permeability and angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:204–209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu J, Razani B, Tang S, Terman BI, Ware
JA and Lisanti MP: Angiogenesis activators and inhibitors
differentially regulate caveolin-1 expression and caveolae
formation in vascular endothelial cells. Angiogenesis inhibitors
block vascular endothelial growth factor-induced down-regulation of
caveolin-1. J Biol Chem. 274:15781–15785. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mazzanti R, Messerini L, Monsacchi L,
Buzzelli G, Zignego AL, Foschi M, Monti M, Laffi G, Morbidelli L,
Fantappié O, et al: Chronic viral hepatitis induced by hepatitis C
but not hepatitis B virus infection correlates with increased liver
angiogenesis. Hepatology. 25:229–234. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sonveau X, Martinive P, DeWever J, Batova
Z, Daneau G, Pelat M, Ghisdal P, Grégoire V, Dessy C, Balligand JL
and Feron O: Caveolin-1 expression is critical for vascular
endothelial growth factor-induced ischemic hindlimb
collateralization and nitric oxide-mediated angiogenesis. Circ Res.
95:154–161. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Joo HJ, Oh DK, Kim YS, Lee KB and Kim SJ:
Increased expression of caveolin-1 and microvessel density
correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 93:291–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|