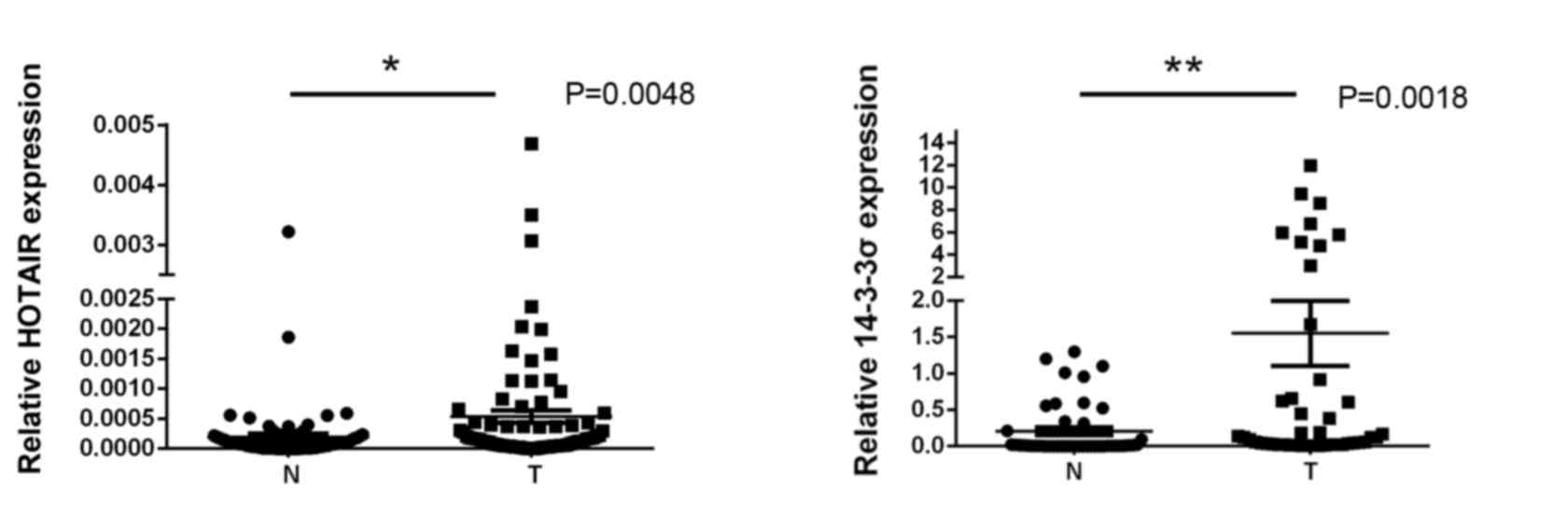
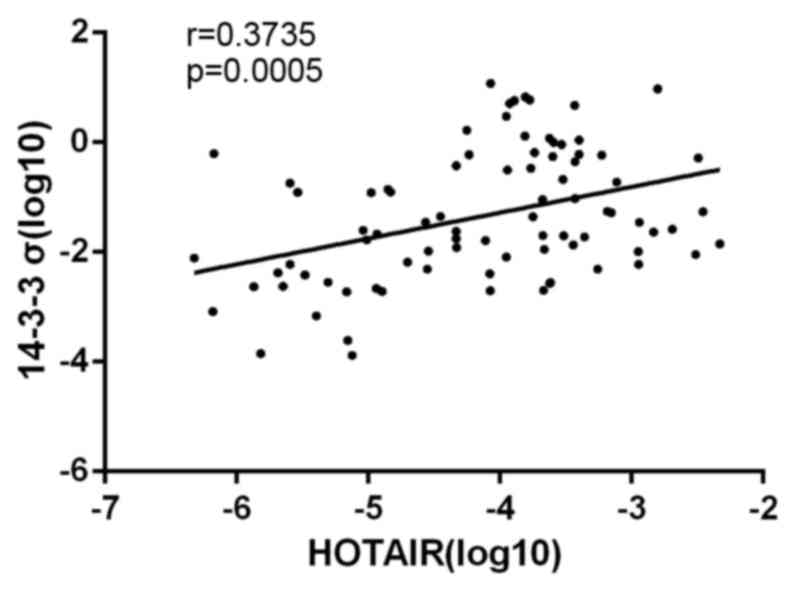
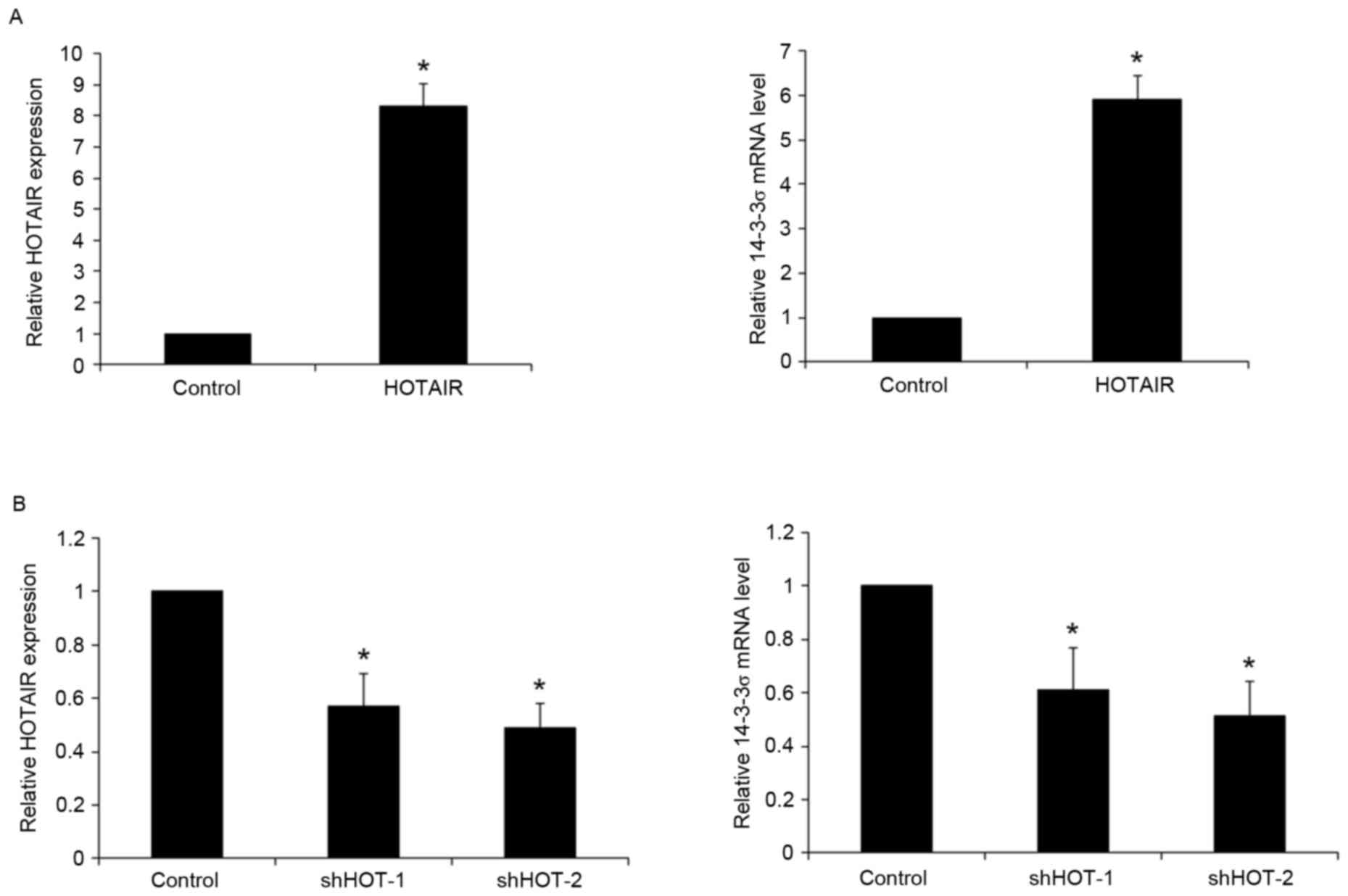
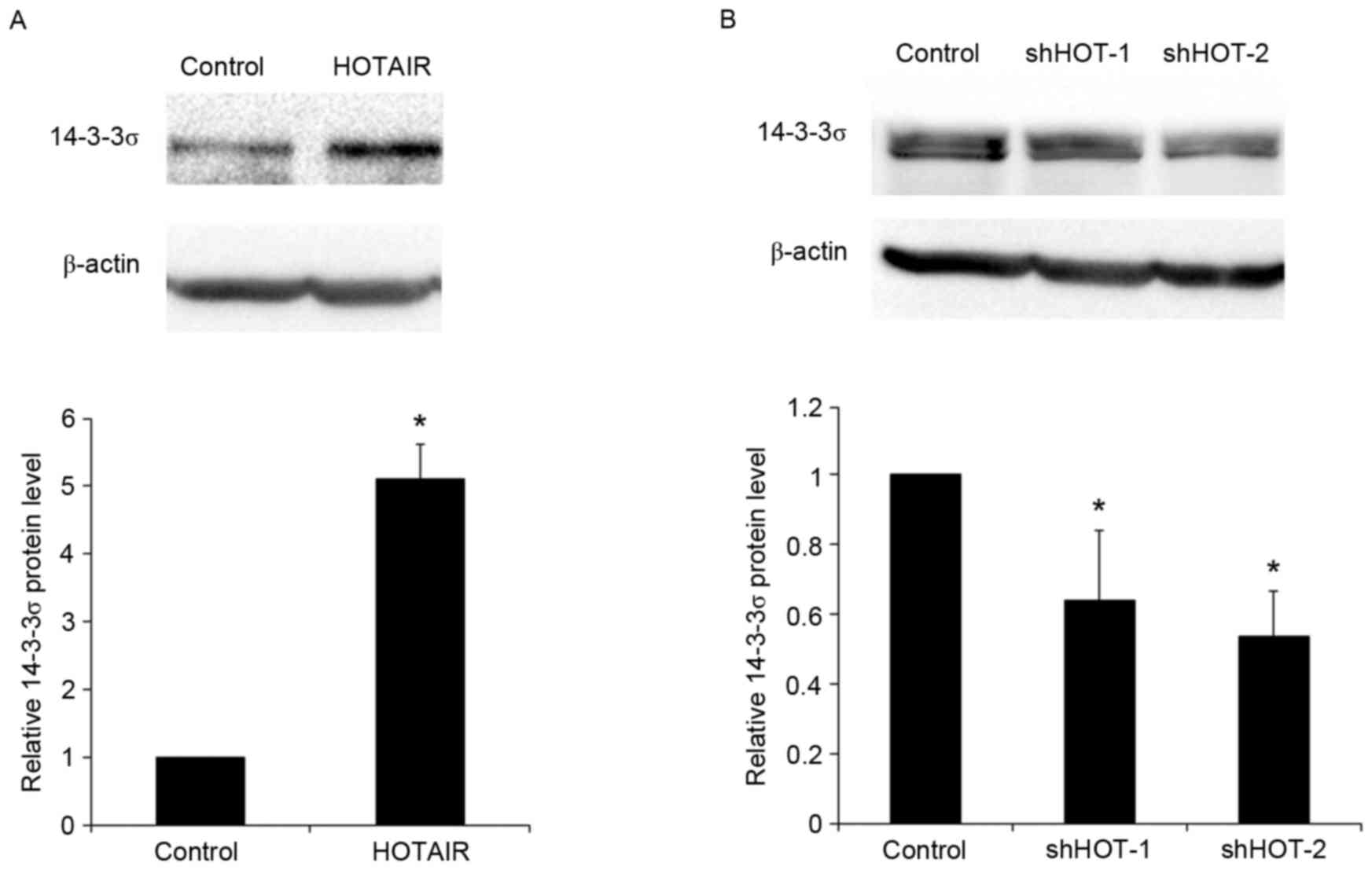
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chang A: Chemotherapy, chemoresistance and
the changing treatment landscape for NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 71:3–10.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Raungrut P, Wongkotsila A,
Lirdprapamongkol K, Svasti J, Geater SL, Phukaoloun M, Suwiwat S
and Thongsuksai P: Prognostic significance of 14-3-3γ
overexpression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3513–3518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Porter GW, Khuri FR and Fu H: Dynamic
14-3-3/client protein interactions integrate survival and apoptotic
pathways. Sem Cancer Biol. 16:193–202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Morrison D: The 14-3-3 proteins:
Integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and
cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 19:16–23. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okada T, Masuda N, Fukai Y, Shimura T,
Nishida Y, Hosouchi Y, Kashiwabara K, Nakajima T and Kuwano H:
Immunohistochemical expression of 14-3-3 sigma protein in
intraductal papillary-mucinous tumor and invasive ductal carcinoma
of the pancreas. Anticancer Res. 26:3105–3110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shiba-Ishii A, Kano J, Morishita Y, Sato
Y, Minami Y and Noguchi M: High expression of stratifin is a
universal abnormality during the course of malignant progression of
early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 129:2445–2453. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boudreau A, Tanner K, Wang D, Geyer FC,
Reis-Filho JS and Bissell MJ: 14-3-3σ stabilizes a complex of
soluble actin and intermediate filament to enable breast tumor
invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E3937–E3944. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Neal CL and Yu D: 14-3-3ζ as a prognostic
marker and therapeutic target for cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:1343–1354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qi W, Liu X, Qiao D and Martinez JD:
Isoform-specific expression of 14-3-3 proteins in human lung cancer
tissues. Int J Cancer. 113:359–363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Radhakrishnan VM, Jensen TJ, Cui H,
Futscher BW and Martinez JD: Hypomethylation of the 14-3-3σ
promoter leads to increased expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 50:830–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cetintas VB, Tetik A, Cok G, Kucukaslan
AS, Kosova B, Gunduz C, Veral A and Eroglu Z: Role of 14-3-3σ in
resistance to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell
Biol Int. 37:78–86. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao W, An Y, Liang Y and Xie XW: Role of
HOTAIR long noncoding RNA in metastatic progression of lung cancer.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:1930–1936. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu XH, Liu ZL, Sun M, Liu J, Wang ZX and
De W: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
13:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Greene FL and Sobin LH: The staging of
cancer: A retrospective and prospective appraisal. CA Cancer J
Clin. 58:180–190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gospodarowicz MK, Miller D, Groome PA,
Greene FL, Logan PA and Sobin LH: The process for continuous
improvement of the TNM classification. Cancer. 100:1–5. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang R, Shi Y, Chen L, Jiang Y, Mao C, Yan
B, Liu S, Shan B, Tao Y and Wang X: The ratio of FoxA1 to FoxA2 in
lung adenocarcinoma is regulated by LncRNA HOTAIR andchromatin
remodeling factor LSH. Sci Rep. 5:178262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhuang Y, Wang X, Nguyen HT, Zhuo Y, Cui
X, Fewell C, Flemington EK and Shan B: Induction of long intergenic
non-coding RNA HOTAIR in lung cancer cells by type I collagen. J
Hematol Oncol. 6:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E and
Chang HY: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin
domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson
G, Frank J, Burghardt R, Kim S and Safe S: HOTAIR is a negative
prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic
cancer. Oncogene. 32:1616–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Niinuma T, Suzuki H, Nojima M, Nosho K,
Yamamoto H, Takamaru H, Yamamoto E, Maruyama R, Nobuoka T, Miyazaki
Y, et al: Upregulation of miR-196a and HOTAIR drive malignant
character in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Res.
72:1126–1136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|