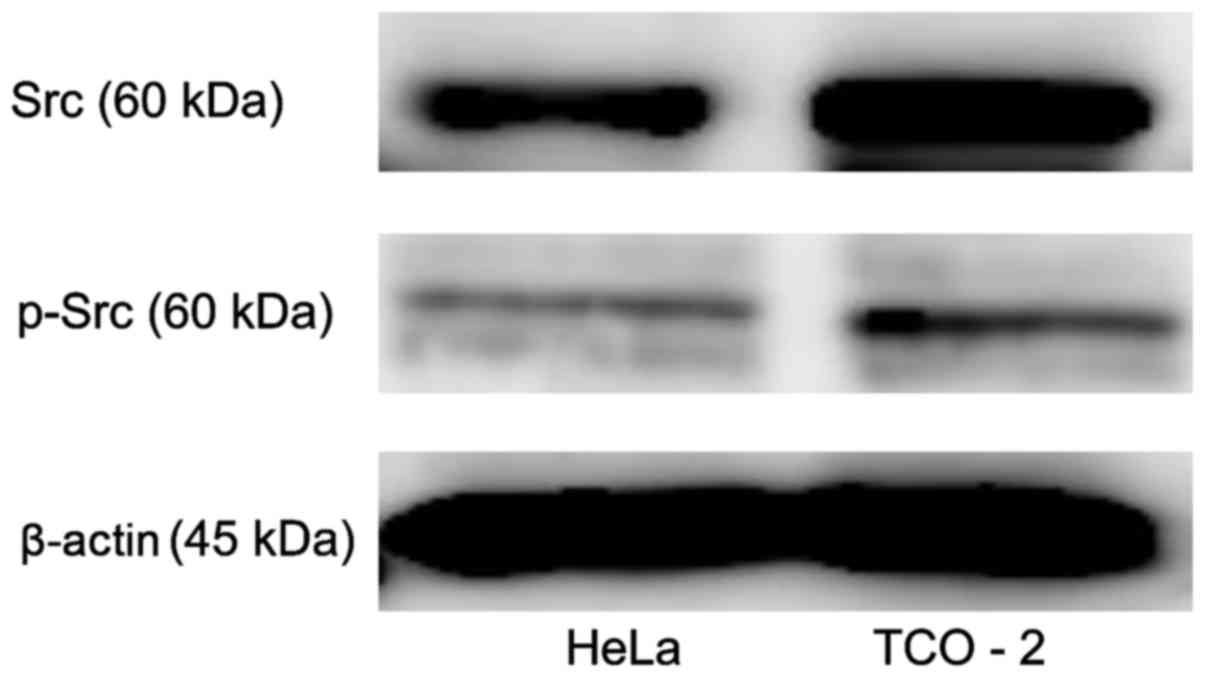
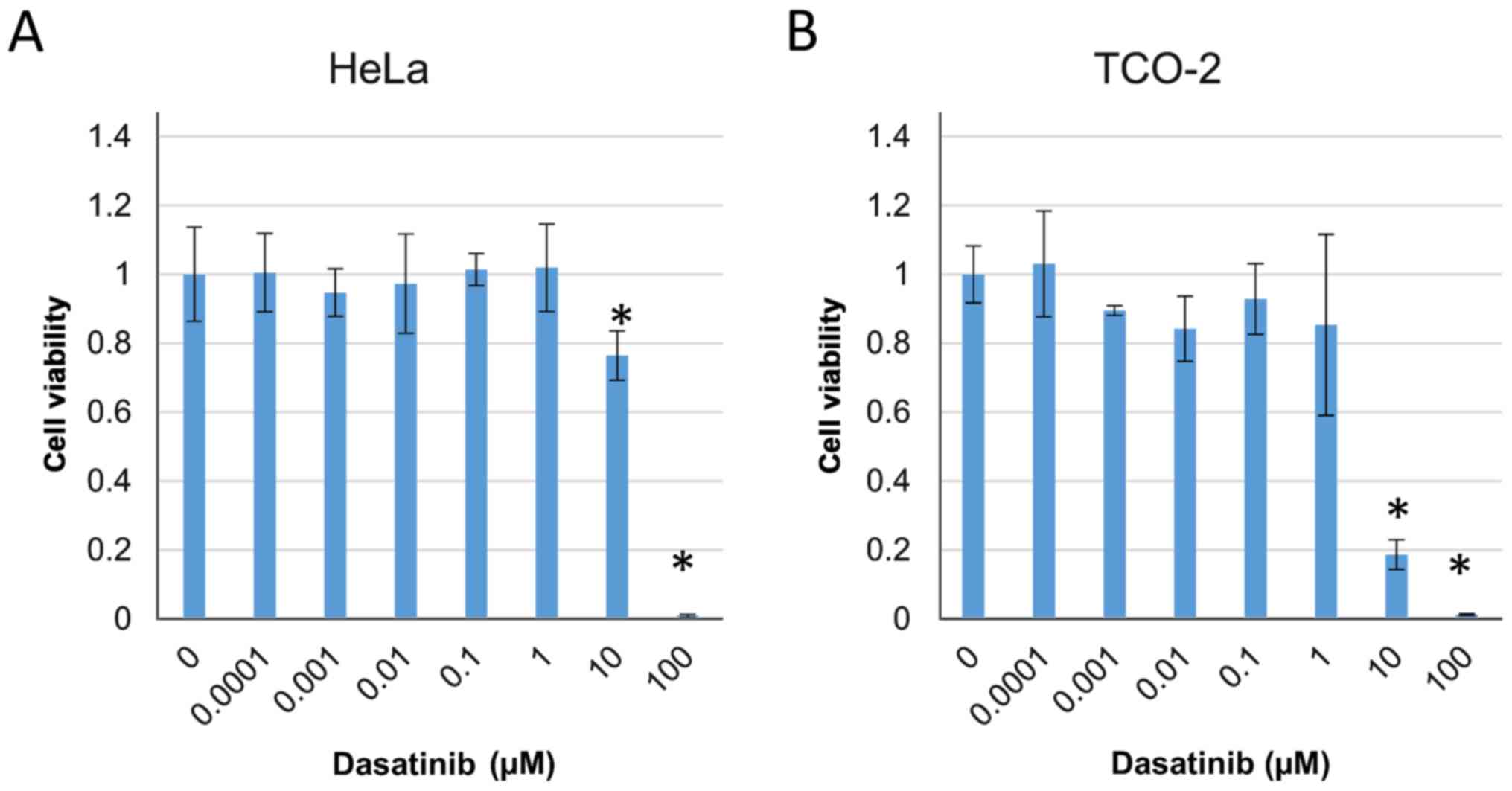
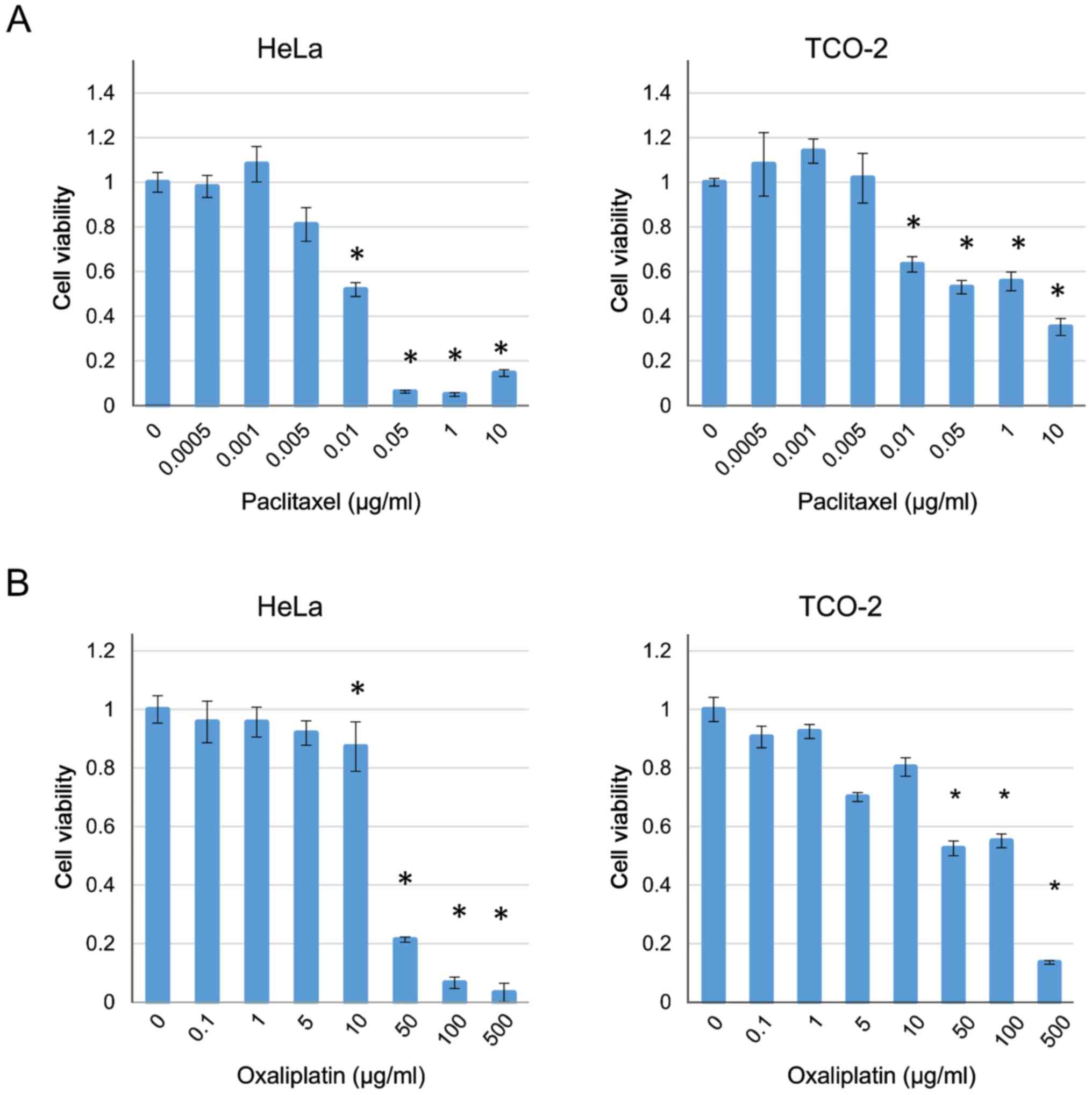
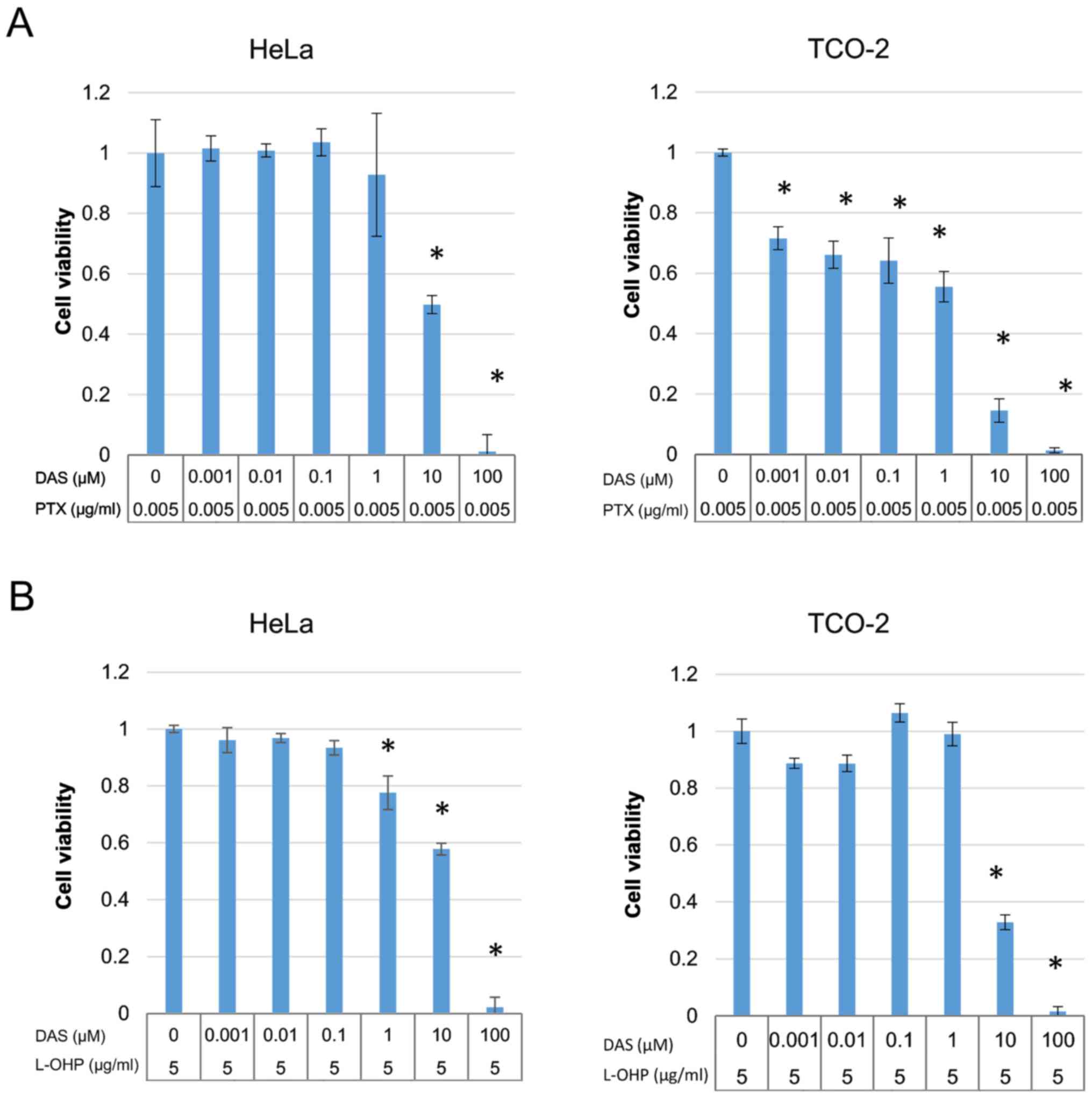
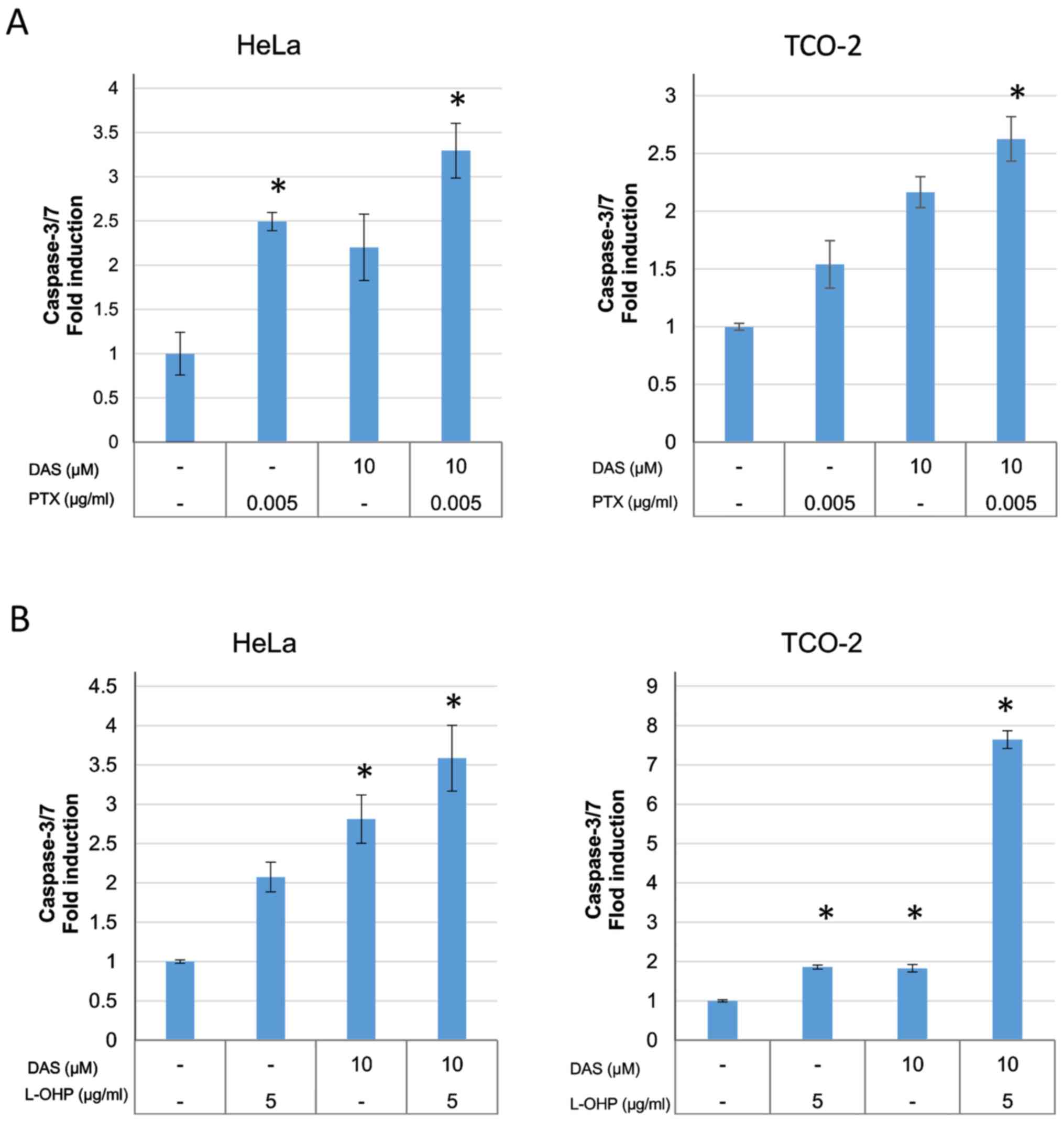
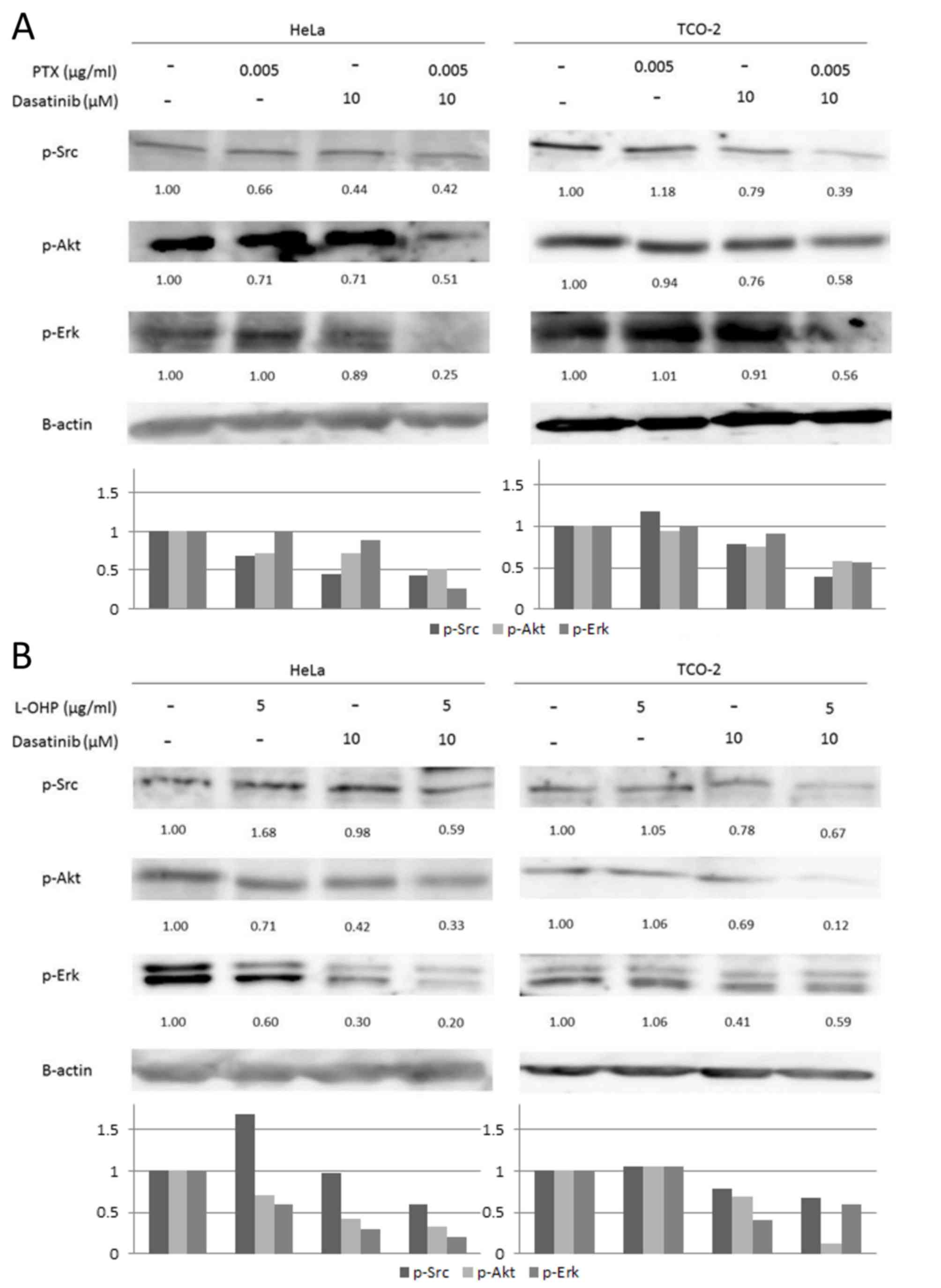
|
1
|
The Editorial Board of the Cancer
Statistics in Japan: Cancer Statistics in Japan. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Fujiwara K, Monk B and
Devouassoux-Shisheboran M: Adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix:
Why is it different? Curr Oncol Rep. 16:4162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
NCNN Guideline: NCCN Clinical Practice
Guidelines in Oncology, cervical cancer. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Gien LT, Beauchemin MC and Thomas G:
Adenocarcinoma: A unique cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
116:140–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wheeler DL, Iida M and Dunn EF: The role
of Src in solid tumors. Oncologist. 14:667–678. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Summy JM and Gallick GE: Treatment for
advanced tumors: SRC reclaims center stage. Clin Cancer Res.
12:1398–1401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le XF and Bast RC Jr: Src family kinases
and paclitaxel sensitivity. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:260–269. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schott AF, Barlow WE, Van Poznak CH, Hayes
DF, Moinpour CM, Lew DL, Dy PA, Keller ET, Keller JM and Hortobagyi
GN: Phase II studies of two different schedules of dasatinib in
bone metastasis predominant metastatic breast cancer: SWOG S0622.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 159:87–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fornier MN, Morris PG, Abbruzzi A,
D'Andrea G, Gilewski T, Bromberg J, Dang C, Dickler M, Modi S,
Seidman AG, et al: A phase I study of dasatinib and weekly
paclitaxel for metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 22:2575–2581.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Araujo JC, Mathew P, Armstrong AJ, Braud
EL, Posadas E, Lonberg M, Gallick GE, Trudel GC, Paliwal P, Agrawal
S and Logothetis CJ: Dasatinib combined with docetaxel for
castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results from a phase 1–2
study. Cancer. 118:63–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Araujo JC, Trudel GC, Saad F, Armstrong
AJ, Yu EY, Bellmunt J, Wilding G, McCaffrey J, Serrano SV, Matveev
VB, et al: Docetaxel and dasatinib or placebo in men with
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (READY): A
randomised, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:1307–1316.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chee CE, Krishnamurthi S, Nock CJ, Meropol
NJ, Gibbons J, Fu P, Bokar J, Teston L, O'Brien T, Gudena J, et al:
Phase II study of dasatinib (BMS-354825) in patients with
metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Oncologist.
18:1091–1092. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sharma MR, Wroblewski K, Polite BN, Knost
JA, Wallace JA, Modi S, Sleckman BG, Taber D, Vokes EE, Stadler WM
and Kindler HL: Dasatinib in previously treated metastatic
colorectal cancer: A phase II trial of the University of Chicago
Phase II Consortium. Invest New Drugs. 30:1211–1215. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gold K, Lee J, Harun N, Tang X, Price J,
Kawedia JD, Tran HT, Erasmus JJ, Blumenschein GR and William WN: A
phase I/II study combining erlotinib and dasatinib for non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 19:1040–1041. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schilder RJ, Brady WE, Lankes HA, Fiorica
JV, Shahin MS, Zhou XC, Mannel R, Pathak HB, Hu W, Alpaugh K, et
al: Phase II evaluation of dasatinib in the treatment of recurrent
or persistent epithelial ovarian or primary peritoneal carcinoma: A
gynecologic oncology group study. Gynecol Oncol. 127:70–74. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Secord AA, Teoh DK, Barry WT, Yu M,
Broadwater G, Havrilesky LJ, Lee PS, Berchuck A, Lancaster J and
Wenham RM: A phase I trial of dasatinib, a Src-family kinase
inhibitor, in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in
patients with advanced or recurrent ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:5489–5498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hong DS, Choe DH, Naing A, Wheler JJ,
Falchook GS, Piha-Paul S, Moulder SL, George GC, Choe JM, Strauss
LC, et al: A phase 1 study of gemcitabine combined with dasatinib
in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
31:918–926. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matsuo K, Nishimura M, Bottsford-Miller
JN, Huang J, Komurov K, Armaiz-Pena GN, Shahzad MM, Stone RL, Roh
JW, Sanguino AM, et al: Targeting Src in mucinous ovarian
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 17:5367–5378. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pengetnze Y, Steed M, Roby KF, Terranova
PF and Taylor CC: Src tyrosine kinase promotes survival and
resistance to chemotherapeutics in a mouse ovarian cancer cell
line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 309:377–383. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao J, Xu M, Hou T, Huang Y, Yang C and
Li J: Dasatinib enhances antitumor activity of paclitaxel in
ovarian cancer through Src signaling. Mol Med Rep. 12:3249–3256.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Teoh D, Ayeni TA, Rubatt JM, Adams DJ,
Grace L, Starr MD, Barry WT, Berchuck A, Murphy SK and Secord AA:
Dasatinib (BMS-35482) has synergistic activity with paclitaxel and
carboplatin in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 121:187–192.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu T, Hu W, Dalton HJ, Choi HJ, Huang J,
Kang Y, Pradeep S, Miyake T, Song JH, Wen Y, et al: Targeting Src
and tubulin in mucinous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
19:6532–6543. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kong L, Deng Z, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Sarkar FH
and Zhan Y: Down-regulation of phospho-non-receptor Src tyrosine
kinases contributes to growth inhibition of cervical cancer cells.
Med Oncol. 28:1495–1506. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kong L, Deng Z, Shen H and Zhang Y: Src
family kinase inhibitor PP2 efficiently inhibits cervical cancer
cell proliferation through down-regulating phospho-Src-Y416 and
phospho-EGFR-Y1173. Mol Cell Biochem. 348:11–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|