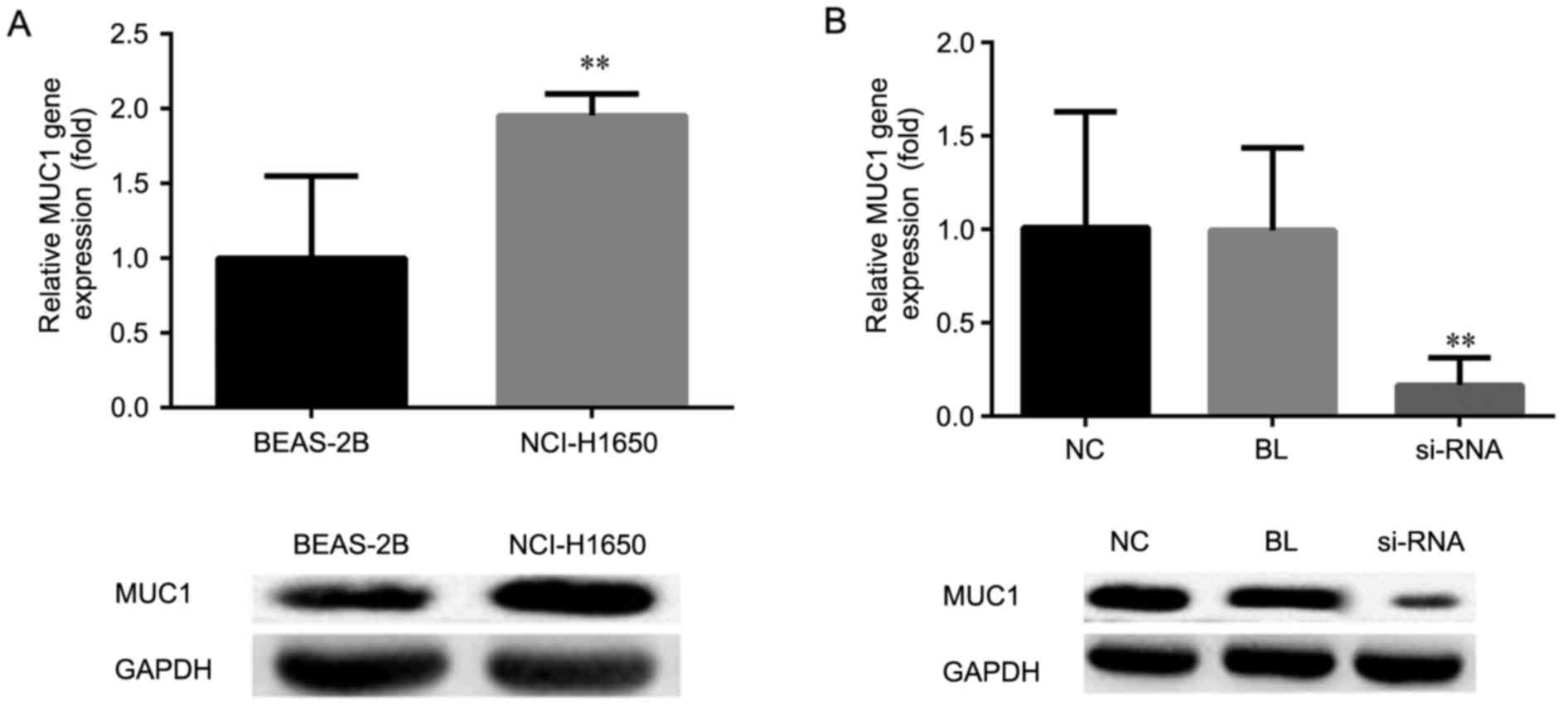
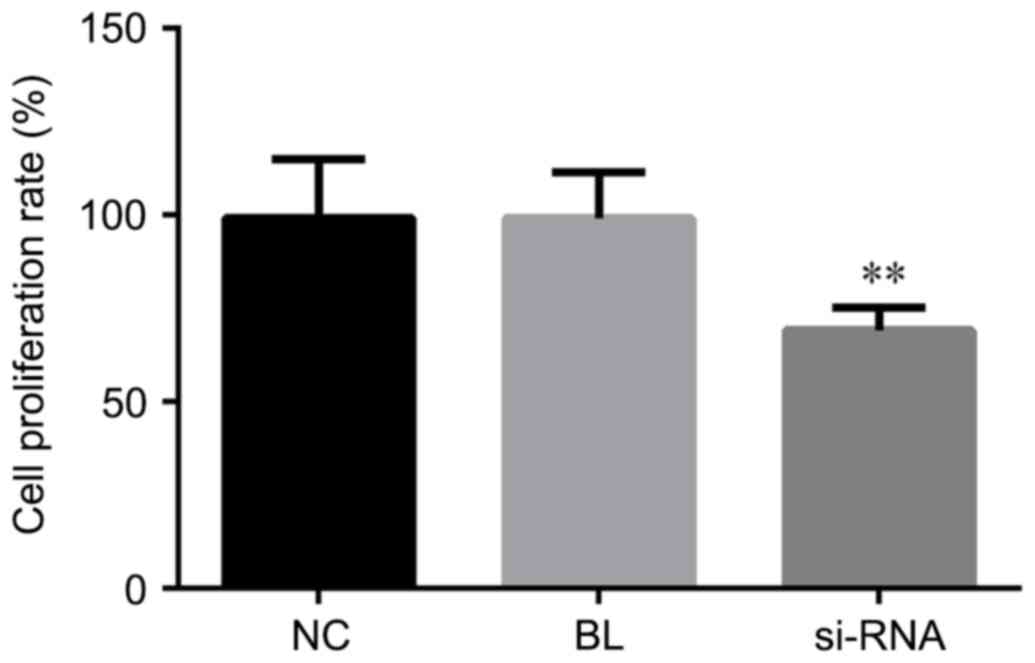
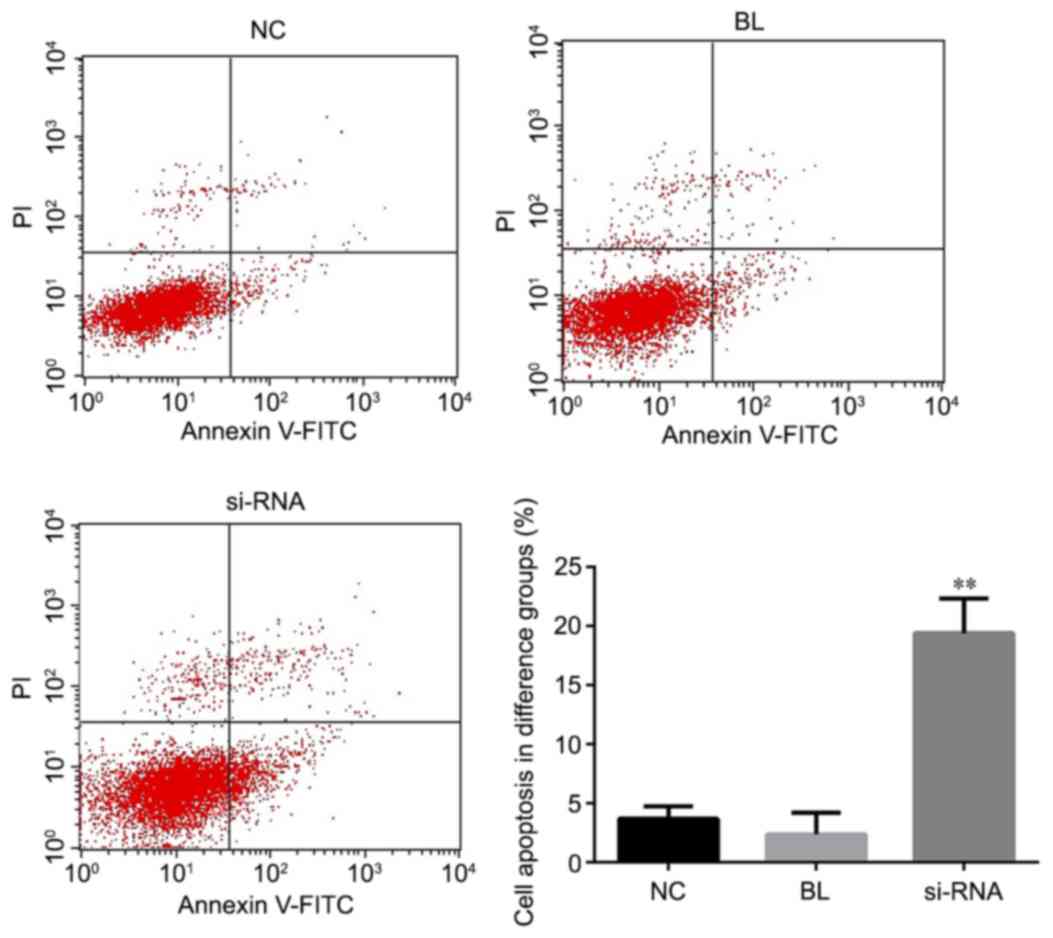
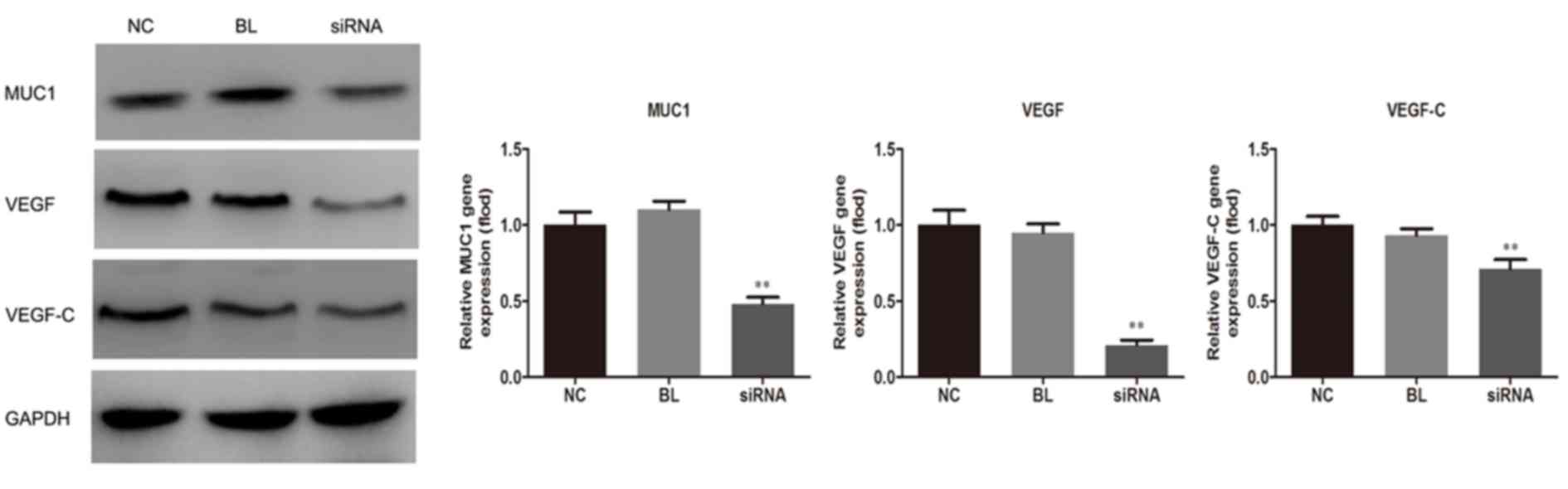
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Graham MV, Purdy JA, Emami B, Harms W,
Bosch W, Lockett MA and Perez CA: Clinical dose-volume histogram
analysis for pneumonitis after 3D treatment for non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 45:323–329. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou YY, Hu ZG, Zeng FJ and Han J:
Clinical profile of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in treating
non-small cell lung cancer: A Meta-Analysis of nine randomized
clinical trials. PLoS One. 11:e01519392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fenchel K, Sellmann L and Dempke WC:
Overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer-what is clinically
meaningful? Transl Lung Cancer Res. 5:115–119. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quéré G, Descourt R, Robinet G, Autret S,
Raguenes O, Fercot B, Alemany P, Uguen A, Férec C, Quintin-Roué I
and Le Gac G: Mutational status of synchronous and metachronous
tumor samples in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung
cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:2102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Thun MJ, Calle
EE, Krewski D, Ito K and Thurston GD: Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary
mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air
pollution. JAMA. 287:1132–1141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kufe D, Inghirami G, Abe M, Hayes D,
Justi-Wheeler H and Schlom J: Differential reactivity of a novel
monoclonal antibody (DF3) with human malignant versus benign breast
tumors. Hybridoma. 3:223–232. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim YS, Gum J Jr and Brockhausen I: Mucin
glycoproteins in neoplasia. Glycoconj J. 13:693–707. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Al Masri A and Gendler SJ: Muc1 affects
c-Src signaling in PyV MT-induced mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene.
24:5799–5808. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Liu D, Chen D, Kharbanda S and Kufe
D: Human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated protein functions as an
oncogene. Oncogene. 22:6107–6110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu M and Wang X: Critical roles of mucin-1
in sensitivity of lung cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-alpha
and dexamethasone. Cell Biol Toxicol. 33:361–371. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) methods. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cook KM and Figg WD: Angiogenesis
inhibitors: Current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J
Clin. 60:222–243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arsham AM, Plas DR, Thompson CB and Simon
MC: Akt and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 independently enhance tumor
growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:3500–3507. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Jiang X, Qin X, Ye D, Yi Z, Liu
M, Bai O, Liu W, Xie X, Wang Z, et al: RKTG inhibits angiogenesis
by suppressing MAPK-mediated autocrine VEGF signaling and is
downregulated in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene.
29:5404–5415. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khodarev N, Ahmad R, Rajabi H, Pitroda S,
Kufe T, McClary C, Joshi MD, MacDermed D, Weichselbaum R and Kufe
D: Cooperativity of the MUC1 oncoprotein and STAT1 pathway in poor
prognosis human breast cancer. Oncogene. 29:920–929. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Retterspitz MF, Monig SP, Schreckenberg S,
Schneider PM, Hölscher AH, Dienes HP and Baldus SE: Expression of
{beta}-catenin, MUC1 and c-met in diffuse-type gastric carcinomas:
Correlations with tumour progression and prognosis. Anticancer Res.
30:4635–4641. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaira K, Murakami H, Serizawa M, Koh Y,
Abe M, Ohde Y, Takahashi T, Kondo H, Nakajima T and Yamamoto N:
MUC1 expression in thymic epithelial tumors: MUC1 may be useful
marker as differential diagnosis between type B3 thymoma and thymic
carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 458:615–620. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohgami A, Tsuda T, Osaki T, Mitsudomi T,
Morimoto Y, Higashi T and Yasumoto K: MUC1 mucin mRNA expression in
stage I lung adenocarcinoma and its association with early
recurrence. Ann Thorac Surg. 67:810–814. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren J, Agata N, Chen D, Li Y, Yu WH, Huang
L, Raina D, Chen W, Kharbanda S and Kufe D: Human MUC1
carcinoma-associated protein confers resistance to genotoxic
anticancer agents. Cancer Cell. 5:163–175. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao J, McConnell MJ, Yu B, Li J, Balko JM,
Black EP, Johnson JO, Lloyd MC, Altiok S and Haura EB: MUC1 is a
downstream target of STAT3 and regulates lung cancer cell survival
and invasion. Int J Oncol. 35:337–345. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ferrara N: Molecular and biological
properties of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Mol Med (Berl).
77:527–543. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kajita T, Ohta Y, Kinura K, Tamura M,
Tanaka Y, Tsunezuka Y, Oda M, Sasaki T and Watanabe G: The
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C and its
receptors in non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 85:255–260.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karkkainen MJ and Petrova TV: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptors in the regulation of
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Oncogene. 19:5598–5605. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roberts N, Kloos B, Cassella M,
Podgrabinska S, Persaud K, Wu Y, Pytowski B and Skobe M: Inhibition
of VEGFR-3 activation with the antagonistic antibody more potently
suppresses lymph node and distant metastases than inactivation of
VEGFR-2. Cancer. 66:2650–2657. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Kawano T, Ahmad R, Nogi H, Agata N,
Anderson K and Kufe D: MUC1 oncoprotein promotes growth and
survival of human multiple myeloma cells. Int J Oncol. 33:153–159.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|