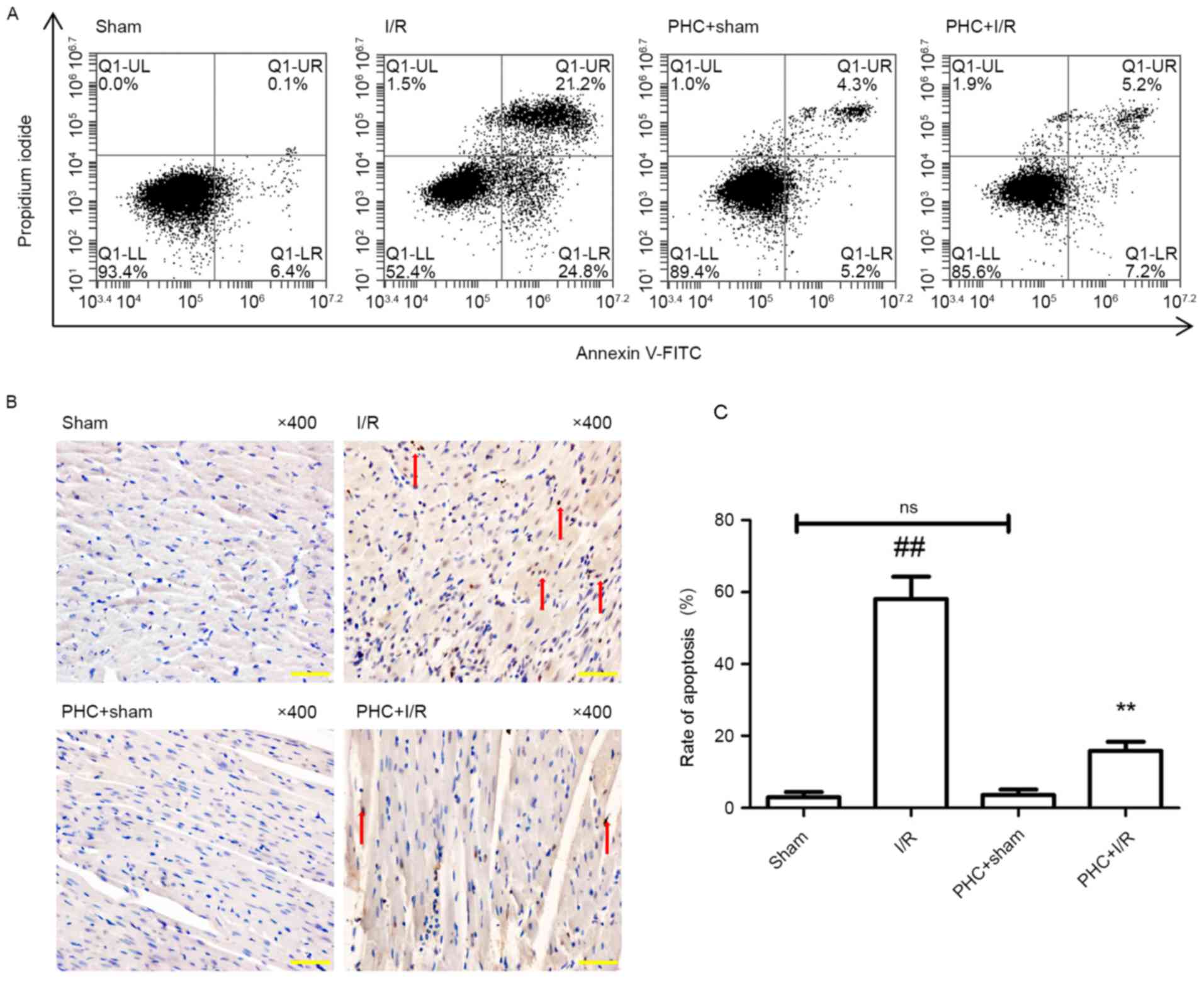
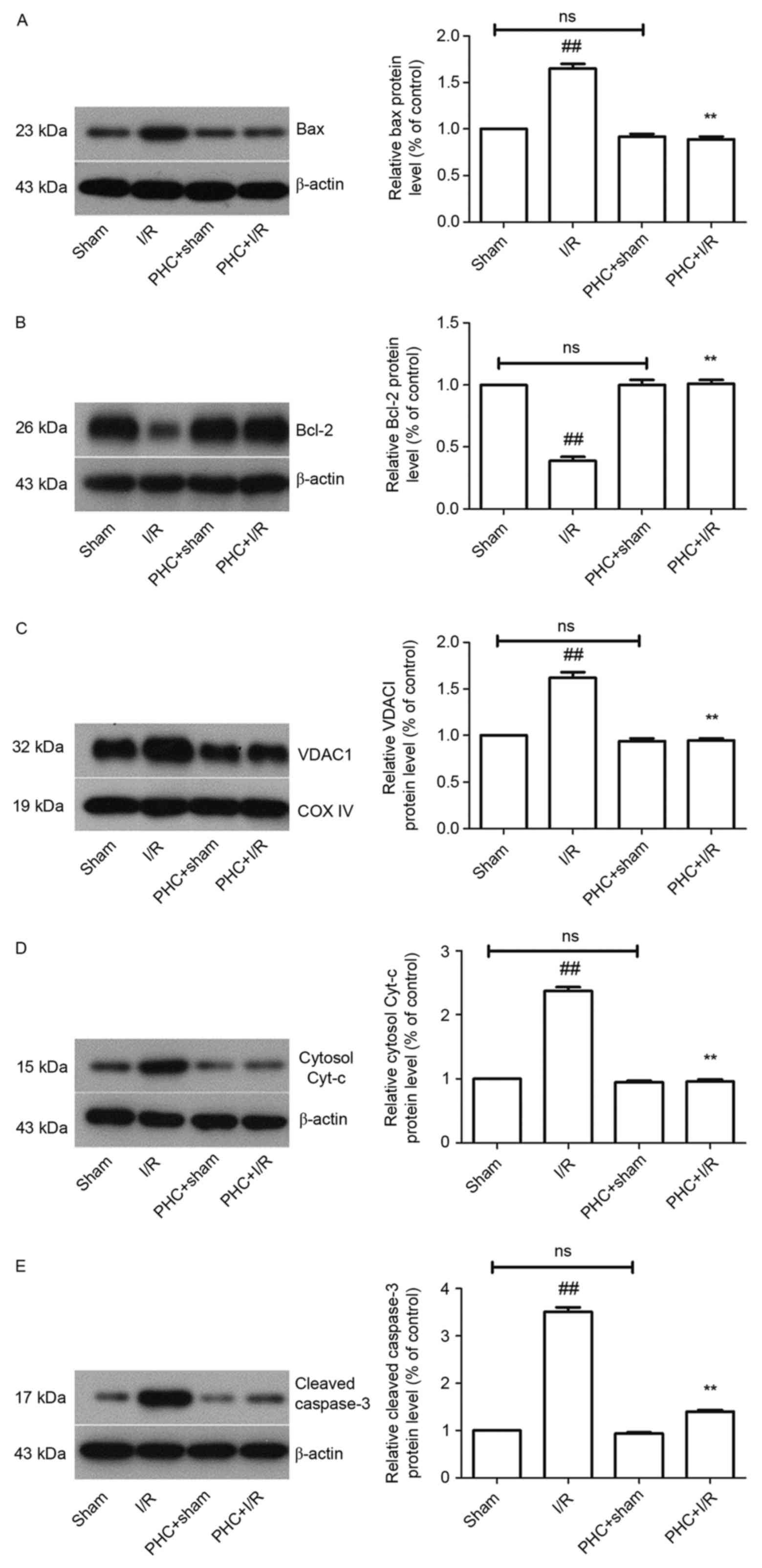
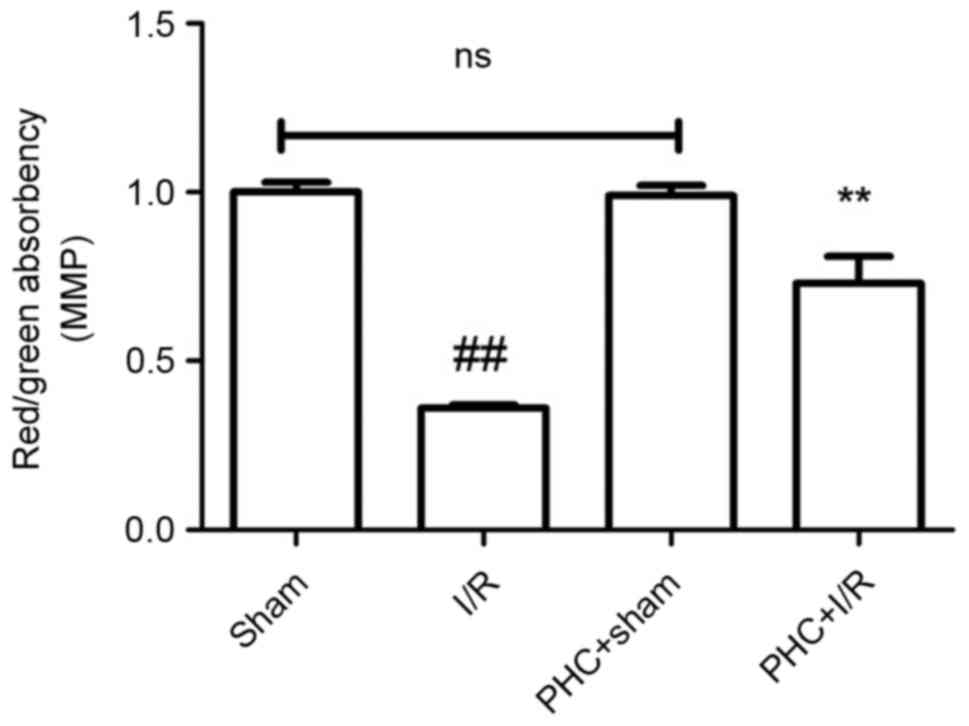
|
1
|
Ostadal B: The past, the present and the
future of experimental research on myocardial ischemia and
protection. Pharmacol Rep. 61:3–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pagidipati NJ and Gaziano TA: Estimating
deaths from cardiovascular disease: A review of global
methodologies of mortality measurement. Circulation. 127:749–756.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patel AV and Bangalore S: Challenges with
evidence-based management of stable ischemic heart disease. Curr
Cardiol Rep. 19:112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cordero A, Galve E, Bertomeu-Martinez V,
Bueno H, Fácila L, Alegria E, Cequier Á, Ruiz E and
González-Juanatey JR: Trends in risk factors and treatments in
patients with stable ischemic heart disease seen at cardiology
clinics between 2006 and 2014. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed).
69:401–407. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chi HJ, Chen ML, Yang XC, Lin XM, Sun H,
Zhao WS, Qi D, Cai J and Dong JL: Progress in therapies for
myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Curr Drug Targets. Apr
1–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barrere-Lemaire S, Nargeot J and Piot C:
Delayed postconditioning: Not too late? Trends Cardiovas Med.
22:173–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Qiao Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Ma N, Wang C, Zou
J, Liu Z, Zhou Z, Han D, He J, et al: miR-483-3p regulates
hyperglycaemia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in transgenic mice.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 477:541–547. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek
WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips DJ and Doevendans PA: Role of apoptosis
in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 61:414–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Desagher S and Martinou JC: Mitochondria
as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol.
10:369–377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Teringova E and Tousek P: Apoptosis in
ischemic heart disease. J Transl Med. 15:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhan J, Xiao F, Li JJ, Zhang ZZ, Chen K,
Wang YP and Wang YL: Penehyclidine hydrochloride decreases
pulmonary microvascular permeability by upregulating beta arrestins
in a murine cecal ligation and puncture model. J Surg Res.
193:391–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang YA, Zhou WX, Li JX, Liu YQ, Yue YJ,
Zheng JQ, Liu KL and Ruan JX: Anticonvulsant effects of
phencynonate hydrochloride and other anticholinergic drugs in soman
poisoning: Neurochemical mechanisms. Life Sci. 78:210–223. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma TF, Zhou L, Wang Y, Qin SJ, Zhang Y, Hu
B, Yan JZ, Ma X, Zhou CH and Gu SL: A selective M1 and M3 receptor
antagonist, penehyclidine hydrochloride, prevents postischemic LTP:
Involvement of NMDA receptors. Synapse. 67:865–874. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu XB, Pan S, Yang XG, Li ZW, Sun QS,
Zhao Z, Ma HC and Cui CR: Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on
heart rate variability in hysteroscopy. Exp Ther Med. 10:181–186.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin D, Ma J, Xue Y and Wang Z:
Penehyclidine hydrochloride preconditioning provides
cardioprotection in a rat model of myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion
injury. PLoS One. 10:e1380512015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Research NRCU: Guide for the Care and Use
of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press (US); Washington
(DC): 1996
|
|
18
|
Li T, Xu XH, Tang ZH, Wang YF, Leung CH,
Ma DL, Chen XP, Wang YT, Chen Y and Lu JJ: Platycodin D induces
apoptosis and triggers ERK- and JNK-mediated autophagy in human
hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
36:1503–1513. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koka S, Das A, Salloum FN and Kukreja RC:
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil attenuates oxidative stress
and protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type
2 diabetic mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 60:80–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reifschneider NH, Goto S, Nakamoto H,
Takahashi R, Sugawa M, Dencher NA and Krause F: Defining the
mitochondrial proteomes from five rat organs in a physiologically
significant context using 2D blue-native/SDS-PAGE. J Proteome Res.
5:1117–1132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sharma V, Bell RM and Yellon DM: Targeting
reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction: A review of
reperfusion injury pharmacotherapy. Expert Opin Pharmaco.
13:1153–1175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhu T, Yao Q, Wang W, Yao H and Chao J:
iNOS induces vascular endothelial cell migration and apoptosis via
autophagy in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:1575–1588. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Cao Y, Shen M, Wang B, Zhang W,
Liu Y, He X, Wang L, Xia Y, Ding M, et al: DIDS reduces
ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in rats. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:676–688. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sima N, Lü W and Xie X: Early proteins E6
and E7 of human papillomavirus may attenuate ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Med Hypotheses. 76:607–609. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang S, Li G, Fu X, Qi Y, Li M, Lu G, Hu
J, Wang N, Chen Y, Bai Y and Cui M: PDCD5 protects against cardiac
remodeling by regulating autophagy and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 461:321–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fliss H and Gattinger D: Apoptosis in
ischemic and reperfused rat myocardium. Circ Res. 79:949–956. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park YJ, Choi C, Chung KH and Kim KH:
Pharbilignan C induces apoptosis through a mitochondria-mediated
intrinsic pathway in human breast cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 26:4645–4649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Wang QL, Nong XH, Zhang XY, Xu XY,
Qi SH and Wang YF: Oxalicumone A, a new dihydrothiophene-condensed
sulfur chromone induces apoptosis in leukemia cells through
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 783:47–55.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee HP, Li TM, Tsao JY, Fong YC and Tang
CH: Curcumin induces cell apoptosis in human chondrosarcoma through
extrinsic death receptor pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:163–169.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu C and Wang J: Neuroprotective effect of
penehyclidine hydrochloride on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Neural Regen Res. 8:622–632. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Palchaudhuri R, Lambrecht MJ, Botham RC,
Partlow KC, van Ham TJ, Putt KS, Nguyen LT, Kim SH, Peterson RT,
Fan TM and Hergenrother PJ: A small molecule that induces intrinsic
pathway apoptosis with unparalleled speed. Cell Rep. 13:2027–2036.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weintraub WS and Boden WE: Reexamining the
efficacy and value of percutaneous coronary intervention for
patients with stable ischemic heart disease. JAMA Intern Med.
176:1190–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brenner D and Mak TW: Mitochondrial cell
death effectors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:871–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xia A, Xue Z, Li Y, Wang W, Xia J, Wei T,
Cao J and Zhou W: Cardioprotective effect of betulinic Acid on
myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2014:5737452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lindsay J, Esposti MD and Gilmore AP:
Bcl-2 proteins and mitochondria-specificity in membrane targeting
for death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:532–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lyon AR, Joudrey PJ, Jin D, Nass RD, Aon
MA, O'Rourke B and Akar FG: Optical imaging of mitochondrial
function uncovers actively propagating waves of mitochondrial
membrane potential collapse across intact heart. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 49:565–575. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kadenbach B, Ramzan R, Moosdorf R and Vogt
S: The role of mitochondrial membrane potential in ischemic heart
failure. Mitochondrion. 11:700–706. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiao-Feng L, Wen-Ting Z, Yuan-Yuan X,
Chong-Fa L, Lu Z, Jin-Jun R and Wen-Ya W: Protective role of
6-Hydroxy-1-H-Indazole in an MPTP-induced mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:348–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shoshan-Barmatz V and Ben-Hail D: VDAC, a
multi-functional mitochondrial protein as a pharmacological target.
Mitochondrion. 12:24–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shoshan-Barmatz V, De Pinto V,
Zweckstetter M, Raviv Z, Keinan N and Arbel N: VDAC, a
multi-functional mitochondrial protein regulating cell life and
death. Mol Aspects Med. 31:227–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marenzi G, Giorgio M, Trinei M, Moltrasio
M, Ravagnani P, Cardinale D, Ciceri F, Cavallero A, Veglia F,
Fiorentini C, et al: Circulating cytochrome c as potential
biomarker of impaired reperfusion in ST-segment elevation acute
myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 106:1443–1449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Ko SG, Bae HS, Kim
CH, Ahn KS, Lu J and Kim SH: Mitochondria-cytochrome
c-caspase-9 cascade mediates isorhamnetin-induced apoptosis.
Cancer Lett. 270:342–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Demon D, Van Damme P, Vanden Berghe T,
Deceuninck A, Van Durme J, Verspurten J, Helsens K, Impens F, Wejda
M, Schymkowitz J, et al: Proteome-wide substrate analysis indicates
substrate exclusion as a mechanism to generate caspase-7 versus
caspase-3 specificity. Mol Cell Proteomics. 8:2700–2714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cao L, Duanmu W, Yin Y, Zhou Z, Ge H, Chen
T, Tan L, Yu A, Hu R, Fei L and Feng H: Dihydroartemisinin exhibits
anti-glioma stem cell activity through inhibiting p-AKT and
activating caspase-3. Pharmazie. 69:752–758. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|