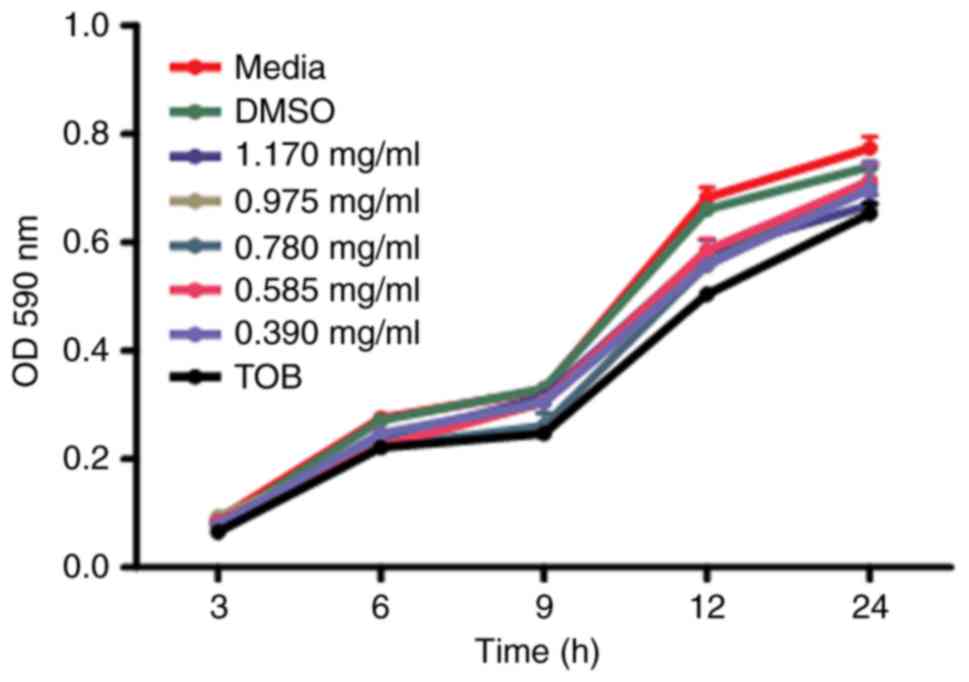
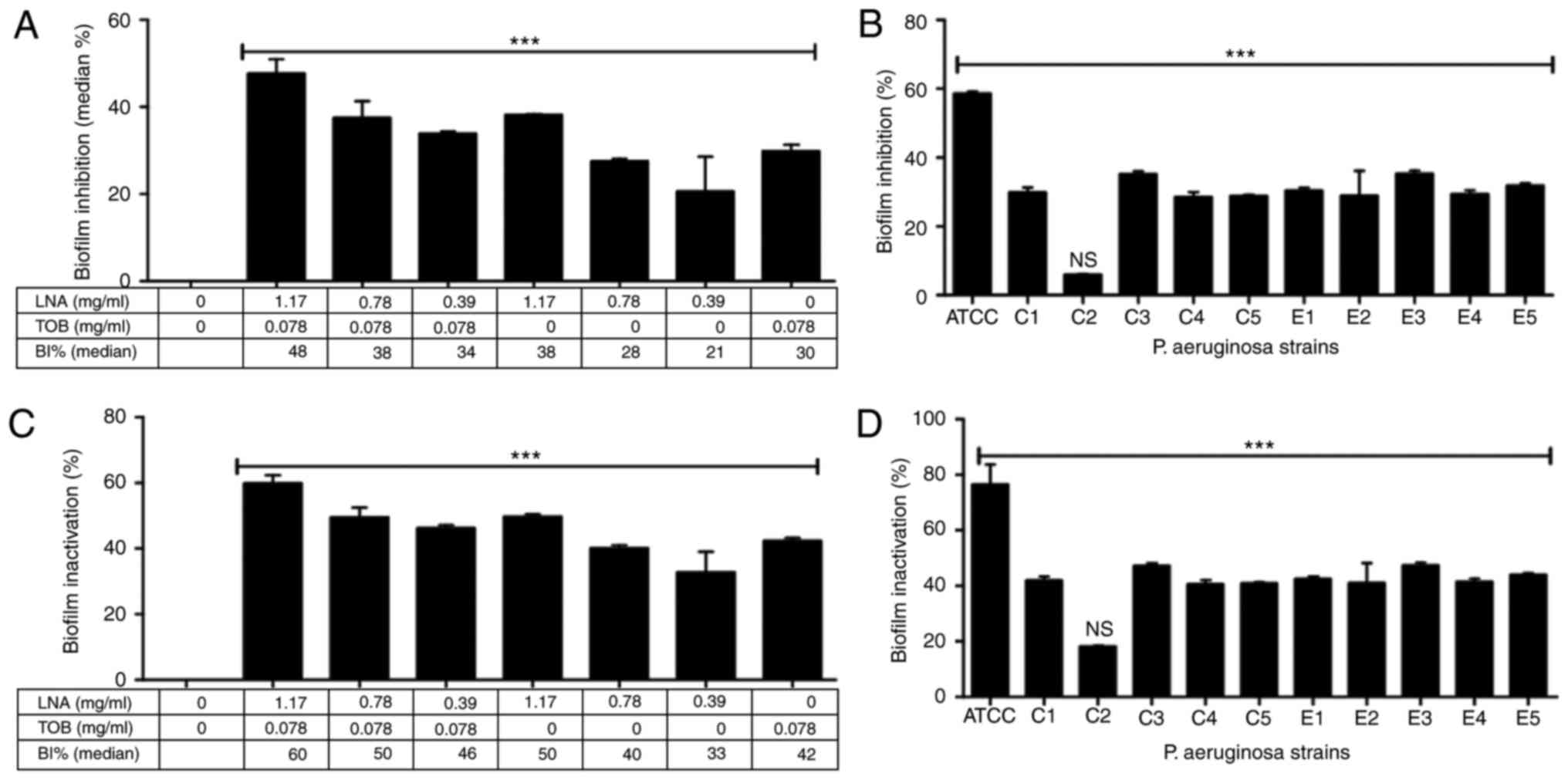
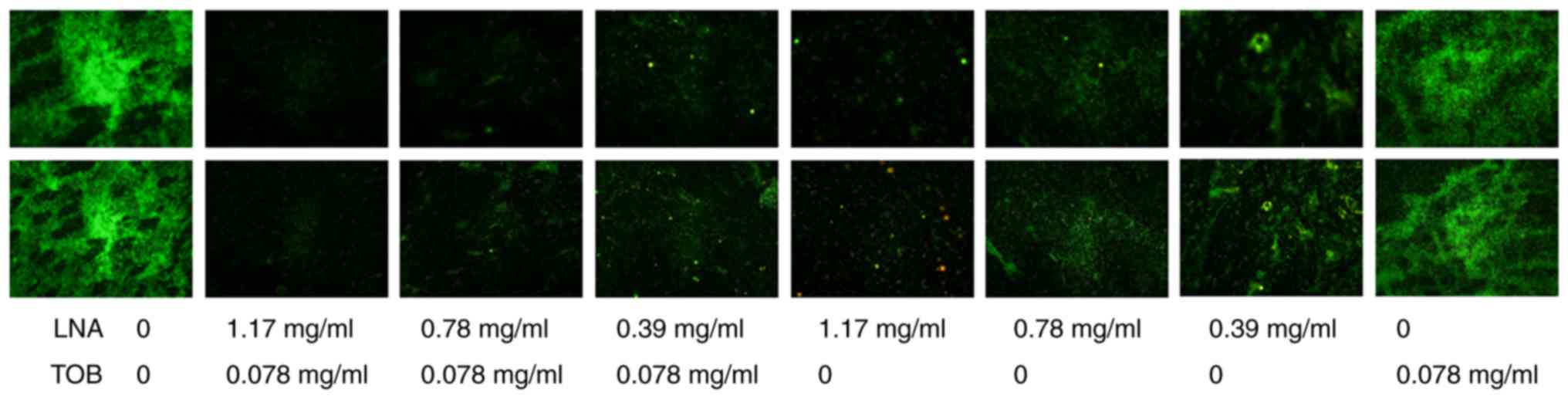
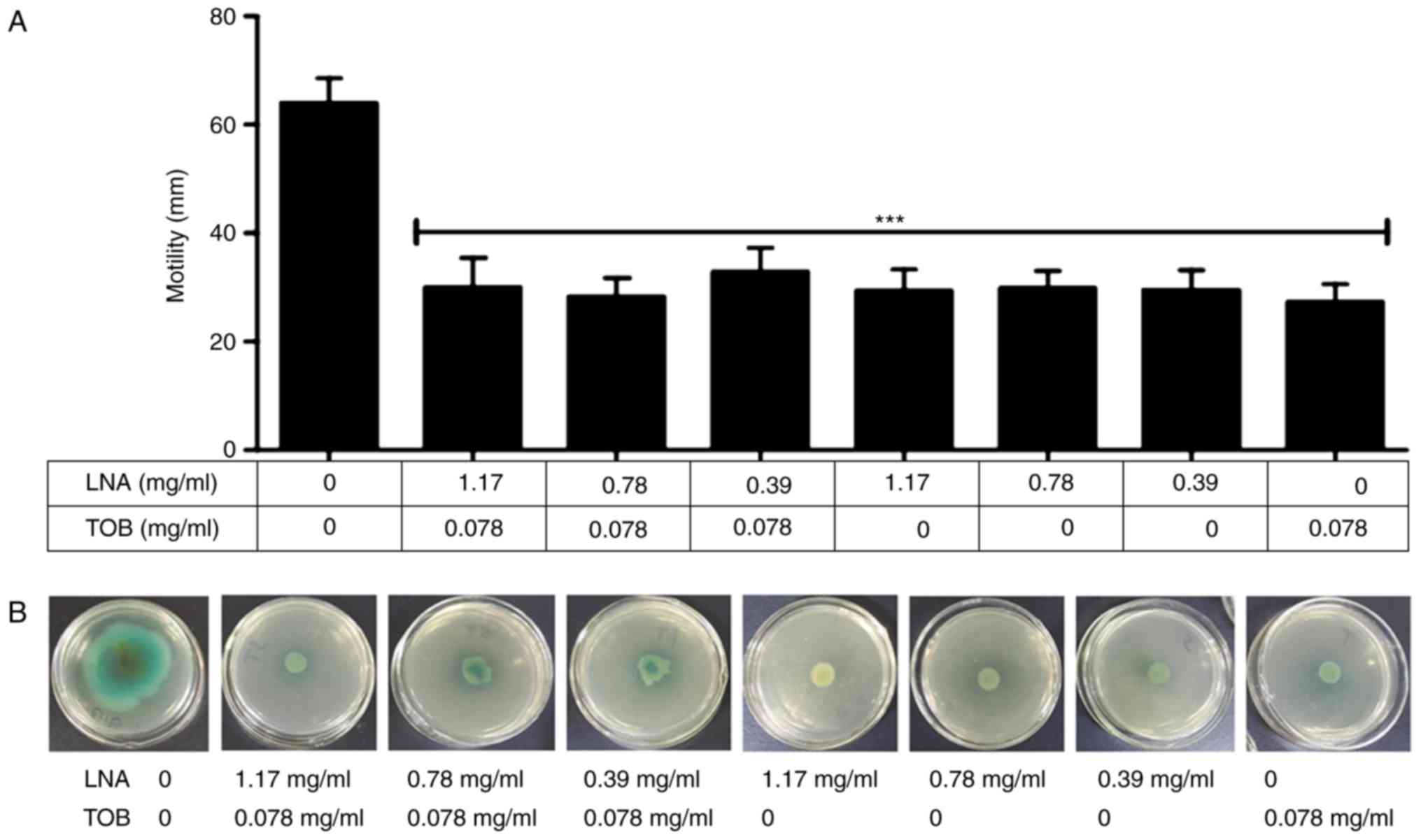
|
1
|
Bai AJ and Rai VR: Quorum-Sensing Systems
in PseudomonasQuorum Sensing vs Quorum Quenching: A Battle
with No End in Sight. Kalia VC: Springer; India: pp. 73–84.
2015
|
|
2
|
Sharma G, Rao S, Bansal A, Dang S, Gupta S
and Gabrani R: Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm: Potential
therapeutic targets. Biologicals. 42:1–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takajo D, Iwaya K, Katsurada Y, Miyai K,
Takasu A, Matsubara O, Sakamoto T, Tamai S and Tsuda H:
Community-acquired lobar pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas
aeruginosa infection in Japan: A case report with histological
and immunohistochemical examination. Pathol Int. 64:224–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gharabaghi MA, Abdollahi SM, Safavi E and
Abtahi SH: Community acquired Pseudomonas pneumonia in an
immune competent host. BMJ Case Rep. 2012:pii: bcr0120125673. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Stryjewski M and Sexton D: Pseudomonas
aeruginosa infections in specific types of patients and
clinical settingsSevere infections caused by Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Hauser AR and Rello J: Kluwer Academic Publishers;
Boston: pp. 1–15. 2003, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Caron E, Desseyn JL, Sergent L, Bartke N,
Husson MO, Duhamel A and Gottrand F: Impact of fish oils on the
outcomes of a mouse model of acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa
pulmonary infection. Br J Nutr. 113:191–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kollef MH, Chastre J, Fagon JY, François
B, Niederman MS, Rello J, Torres A, Vincent JL, Wunderink RG, Go KW
and Rehm C: Global prospective epidemiologic and surveillance study
of ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Crit Care Med. 42:2178–2187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bodey GP, Bolivar R, Fainstein V and
Jadeja L: Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev
Infect Dis. 5:279–313. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
CDC: Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the
United States, 2013. Journal. 69–70. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Breidenstein EB, de la Fuente-Núñez C and
Hancock RE: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: All roads lead to
resistance. Trends Microbiol. 19:419–426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Das MC, Sandhu P, Gupta P, Rudrapaul P, De
UC, Tribedi P, Akhter Y and Bhattacharjee S: Attenuation of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by Vitexin: A
combinatorial study with azithromycin and gentamicin. Sci Rep.
6:233472016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Antunes LC, Ferreira RB, Buckner MM and
Finlay BB: Quorum sensing in bacterial virulence. Microbiology.
156:2271–2282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Juhas M, Eberl L and Tümmler B: Quorum
sensing: The power of cooperation in the world of
Pseudomonas. Environ Microbiol. 7:459–471. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Winzer K, Falconer C, Garber NC, Diggle
SP, Camara M and Williams P: The Pseudomonas aeruginosa
lectins PA-IL and PA-IIL are controlled by quorum sensing and by
RpoS. J Bacteriol. 182:6401–6411. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lyczak JB, Cannon CL and Pier GB:
Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: Lessons
from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect. 2:1051–1060. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hancock RE and Speert DP: Antibiotic
resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mechanisms and impact
on treatment. Drug Resist Updat. 3:247–255. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Desbois AP and Smith VJ: Antibacterial
free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and
biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
85:1629–1642. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Desbois AP: Potential applications of
antimicrobial fatty acids in medicine, agriculture and other
industries. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 7:111–122. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Olveira G, Olveira C, Acosta E, Espíldora
F, Garrido-Sánchez L, García-Escobar E, Rojo-Martínez G, Gonzalo M
and Soriguer F: Fatty acid supplements improve respiratory,
inflammatory and nutritional parameters in adults with cystic
fibrosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 46:70–77. 2010.(In English, Spanish).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nieuwenhove CPV, Terán V and González
SN: Conjugated Linoleic and Linolenic Acid Production by Bacteria:
Development of Functional FoodsProbiotics. Rigobelo EC: INTECH;
2012
|
|
21
|
WHO and FAO joint consultation: fats and
oils in human nutrition. Nutr Rev. 53:202–205. 1995.
|
|
22
|
Sun M, Zhou Z, Dong J, Zhang J, Xia Y and
Shu R: Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of docosahexaenoic
acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) against periodontopathic
bacteria. Microb Pathog. 99:196–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Correia M, Michel V, Matos AA, Carvalho P,
Oliveira MJ, Ferreira RM, Dillies MA, Huerre M, Seruca R,
Figueiredo C, et al: Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits Helicobacter
pylori growth in vitro and mice gastric mucosa colonization.
PLoS One. 7:e350722012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huang CB, George B and Ebersole JL:
Antimicrobial activity of n-6, n-7 and n-9 fatty acids and their
esters for oral microorganisms. Arch Oral Biol. 55:555–560. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Desbois AP and Lawlor KC: Antibacterial
activity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids against
Propionibacterium acnes Staphylococcus aureus. Mar Drugs.
11:4544–4557. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mil-Homens D, Bernardes N and Fialho AM:
The antibacterial properties of docosahexaenoic omega-3 fatty acid
against the cystic fibrosis multiresistant pathogen Burkholderia
cenocepacia. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 328:61–69. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Desbois AP, Mearns-Spragg A and Smith VJ:
A fatty acid from the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum is
antibacterial against diverse bacteria including multi-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Mar Biotechnol (NY). 11:45–52.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kaushik KS, Stolhandske J, Shindell O,
Smyth HD and Gordon VD: Tobramycin and bicarbonate synergise to
kill planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa, but antagonise to
promote biofilm survival. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2:160062016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zobell JT, Young DC, Waters CD, Ampofo K,
Stockmann C, Sherwin CM and Spigarelli MG: Optimization of
anti-pseudomonal antibiotics for cystic fibrosis pulmonary
exacerbations: VI. Executive summary. Pediatr Pulmonol. 48:525–537.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hirsch EB and Tam VH: Impact of
multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection on
patient outcomes. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 10:441–451.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Morais-Braga MF, Souza TM, Santos KK,
Guedes GM, Andrade JC, Tintino SR, Sobral-Souza CE, Costa JG,
Saraiva AA and Coutinho HD: Phenolic compounds and interaction
between aminoglycosides and natural products of Lygodium
venustum SW against multiresistant bacteria. Chemotherapy.
58:337–340. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jaffe RI, Lane JD and Bates CW: Real-time
identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa direct from
clinical samples using a rapid extraction method and polymerase
chain reaction (PCR). J Clin Lab Anal. 15:131–137. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
CLSI: Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial
Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved
Standard. 9th edition. CLSI document M07-A9. 29:17–19. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Kalia M, Yadav VK, Singh PK, Sharma D,
Pandey H, Narvi SS and Agarwal V: Effect of cinnamon oil on quorum
sensing-controlled virulence factors and biofilm formation in
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS One. 10:e01354952015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Borges A, Simões LC, Saavedra MJ and
Simões M: The action of selected isothiocyanates on bacterial
biofilm prevention and control. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad.
86:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Stepanovic S, Vukovic D, Dakic I, Savic B
and Svabic-Vlahovic M: A modified microtiter-plate test for
quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol
Methods. 40:175–179. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pettit RK, Weber CA and Pettit GR:
Application of a high throughput Alamar blue biofilm susceptibility
assay to Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Ann Clin Microbiol
Antimicrob. 8:282009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Musken M, Di Fiore S, Römling U and
Häussler S: A 96-well-plate-based optical method for the
quantitative and qualitative evaluation of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa biofilm formation and its application to
susceptibility testing. Nat Protoc. 5:1460–1469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Johnson MB and Criss AK: Fluorescence
microscopy methods for determining the viability of bacteria in
association with mammalian cells. J Vis Exp. Sep 5–2013.doi:
10.3791/50729. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Konaté K, Mavoungou JF, Lepengué AN,
Aworet-Samseny RR, Hilou A, Souza A, Dicko MH and M'batchi B:
Antibacterial activity against β-lactamase producing Methicillin
and Ampicillin-resistants Staphylococcus aureus. Fractional
inhibitory concentration index (FICI) determination. Ann Clin
Microbiol Antimicrob. 11:182012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Krishnan T, Yin WF and Chan KG: Inhibition
of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by Ayurveda spice clove
(Syzygium aromaticum) bud extract. Sensors (Basel). 12:4016–4030.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ha DG, Kuchma SL and O'Toole GA:
Plate-based assay for swarming motility in Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Methods Mol Biol. 1149:67–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheng CL, Huang SJ, Wu CL, Gong HY, Ken
CF, Hu SY and Wu JL: Transgenic expression of omega-3 PUFA
synthesis genes improves zebrafish survival during Vibrio
vulnificus infection. J Biomed Sci. 22:1032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gellatly SL and Hancock RE: Pseudomonas
aeruginosaNew insights into pathogenesis and host defenses.
Pathog Dis. 67:159–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Overhage J, Bains M, Brazas MD and Hancock
RE: Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a complex
adaptation leading to increased production of virulence factors and
antibiotic resistance. J Bacteriol. 190:2671–2679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Smith KD: Iron metabolism at the host
pathogen interface: Lipocalin 2 and the pathogen-associated iroA
gene cluster. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:1776–1780. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lamont IL, Konings AF and Reid DW: Iron
acquisition by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs of
patients with cystic fibrosis. Biometals. 22:53–60. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Andrejko M, Zdybicka-Barabas A, Janczarek
M and Cytryńska M: Three Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains with
different protease profiles. Acta Biochim Pol. 60:83–90.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Diggle SP, Cornelis P, Williams P and
Cámara M: 4-quinolone signalling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
Old molecules, new perspectives. Int J Med Microbiol. 296:83–91.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gallagher LA, McKnight SL, Kuznetsova MS,
Pesci EC and Manoil C: Functions required for extracellular
quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol.
184:6472–6480. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Déziel E, Lépine F, Milot S, He J,
Mindrinos MN, Tompkins RG and Rahme LG: Analysis of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role
for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:1339–1344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Déziel E, Gopalan S, Tampakaki AP, Lépine
F, Padfield KE, Saucier M, Xiao G and Rahme LG: The contribution of
MvfR to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis and quorum
sensing circuitry regulation: Multiple quorum sensing-regulated
genes are modulated without affecting lasRI, rhlRI or the
production of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones. Mol Microbiol.
55:998–1014. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rawling EG, Brinkman FS and Hancock RE:
Roles of the carboxy-terminal half of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
major outer membrane protein OprF in cell shape, growth in
low-osmolarity medium, and peptidoglycan association. J Bacteriol.
180:3556–3562. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fito-Boncompte L, Chapalain A,
Bouffartigues E, Chaker H, Lesouhaitier O, Gicquel G, Bazire A,
Madi A, Connil N, Véron W, et al: Full virulence of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa requires OprF. Infect Immun. 79:1176–1186. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lin YM, Wu SJ, Chang TW, Wang CF, Suen CS,
Hwang MJ, Chang MD, Chen YT and Liao YD: Outer membrane protein I
of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a target of cationic
antimicrobial peptide/protein. J Biol Chem. 285:8985–8994. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu H, Boucher JC, Hibler NS and Deretic V:
Virulence properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lacking the
extreme-stress sigma factor AlgU (sigmaE). Infect Immun.
64:2774–2781. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stacey SD and Pritchett CL: Pseudomonas
aeruginosa AlgU contributes to posttranscriptional activity by
increasing rsma expression in a mucA22 strain. J Bacteriol.
198:1812–1826. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Prince AS: Biofilms, antimicrobial
resistance, and airway infection. N Engl J Med. 347:1110–1111.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kim HS, Lee SH, Byun Y and Park HD:
6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation
and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Sci Rep. 5:86562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gujrati VB and Jon S: Bioengineered
bacterial outer membrane vesicles: What is their potential in
cancer therapy? Nanomedicine (Lond). 9:933–935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Schertzer JW and Whiteley M: A
bilayer-couple model of bacterial outer membrane vesicle
biogenesis. MBio. 3:pii: e00297. –11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wessel AK, Liew J, Kwon T, Marcotte EM and
Whiteley M: Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane proteins in vesicle
formation. J Bacteriol. 195:213–219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ramsey DM and Wozniak DJ: Understanding
the control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate synthesis and
the prospects for management of chronic infections in cystic
fibrosis. Mol Microbiol. 56:309–322. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Franklin MJ, Nivens DE, Weadge JT and
Howell PL: Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Extracellular Polysaccharides, Alginate, Pel, and Psl. Front
Microbiol. 2:1672011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Price KE, Orazi G, Ruoff KL, Hebert WP,
O'Toole GA and Mastoridis P: Mannitol does not enhance tobramycin
killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis model
system of biofilm formation. PLoS One. 10:e01411922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Furiga A, Lajoie B, El Hage S, Baziard G
and Roques C: Impairment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm
resistance to antibiotics by combining the drugs with a new
quorum-sensing inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
60:1676–1686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Anderson GG, Kenney TF, Macleod DL, Henig
NR and O'Toole GA: Eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
biofilms on cultured airway cells by a fosfomycin/tobramycin
antibiotic combination. Pathog Dis. 67:39–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lawrence GD: The Fats of Life: Essential
Fatty Acids in Health and Disease. Rutgers University Press;
2010
|
|
70
|
Pontes-Arruda A, Martins LF, de Lima SM,
Isola AM, Toledo D, Rezende E, Maia M and Magnan GB: Investigating
Nutritional Therapy with EPA, GLA and Antioxidants Role in Sepsis
Treatment (INTERSEPT) Study Group: Enteral nutrition with
eicosapentaenoic acid, γ-linolenic acid and antioxidants in the
early treatment of sepsis: Results from a multicenter, prospective,
randomized, double-blinded, controlled study: The INTERSEPT study.
Crit Care. 15:R1442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen W, Jiang H, Zhou ZY, Tao YX, Cai B,
Liu J, Yang H, Lu CD and Zeng J: Is omega-3 fatty acids enriched
nutrition support safe for critical ill patients? A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 6:2148–2164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|