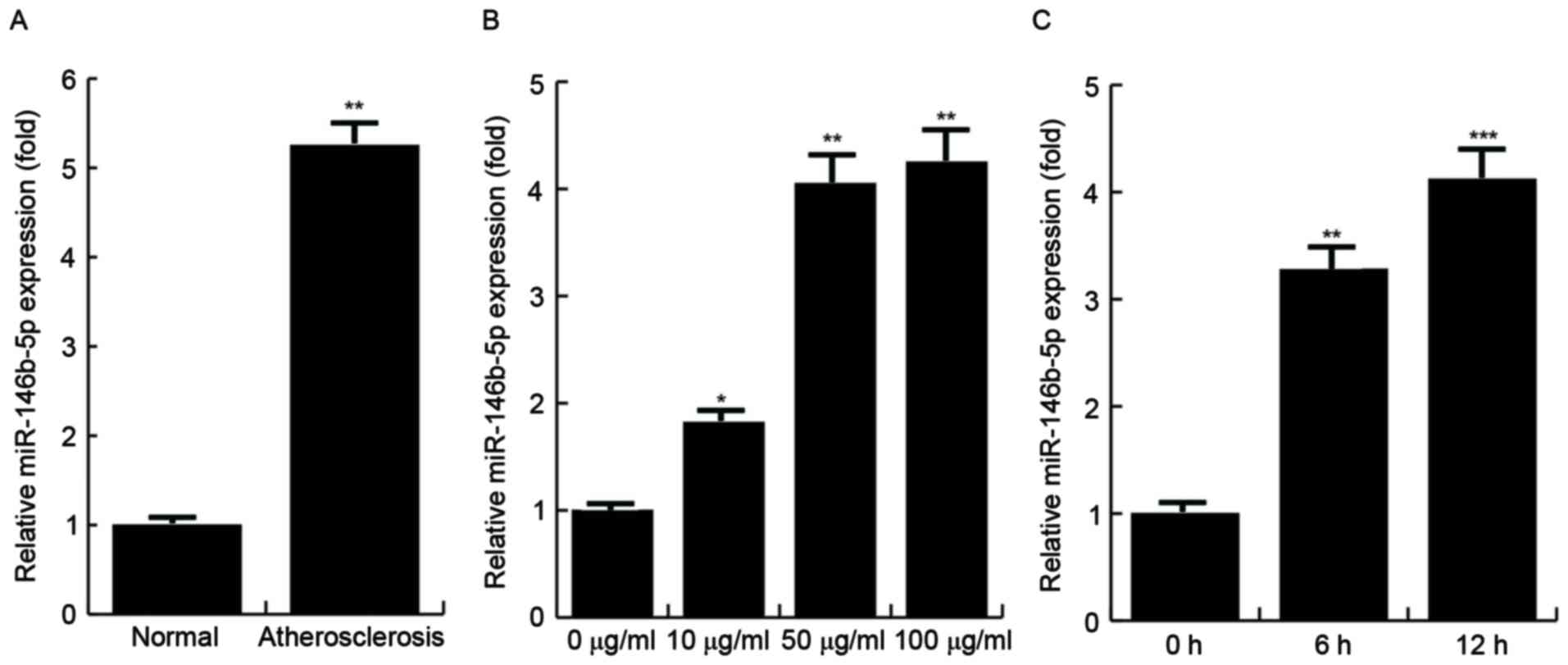
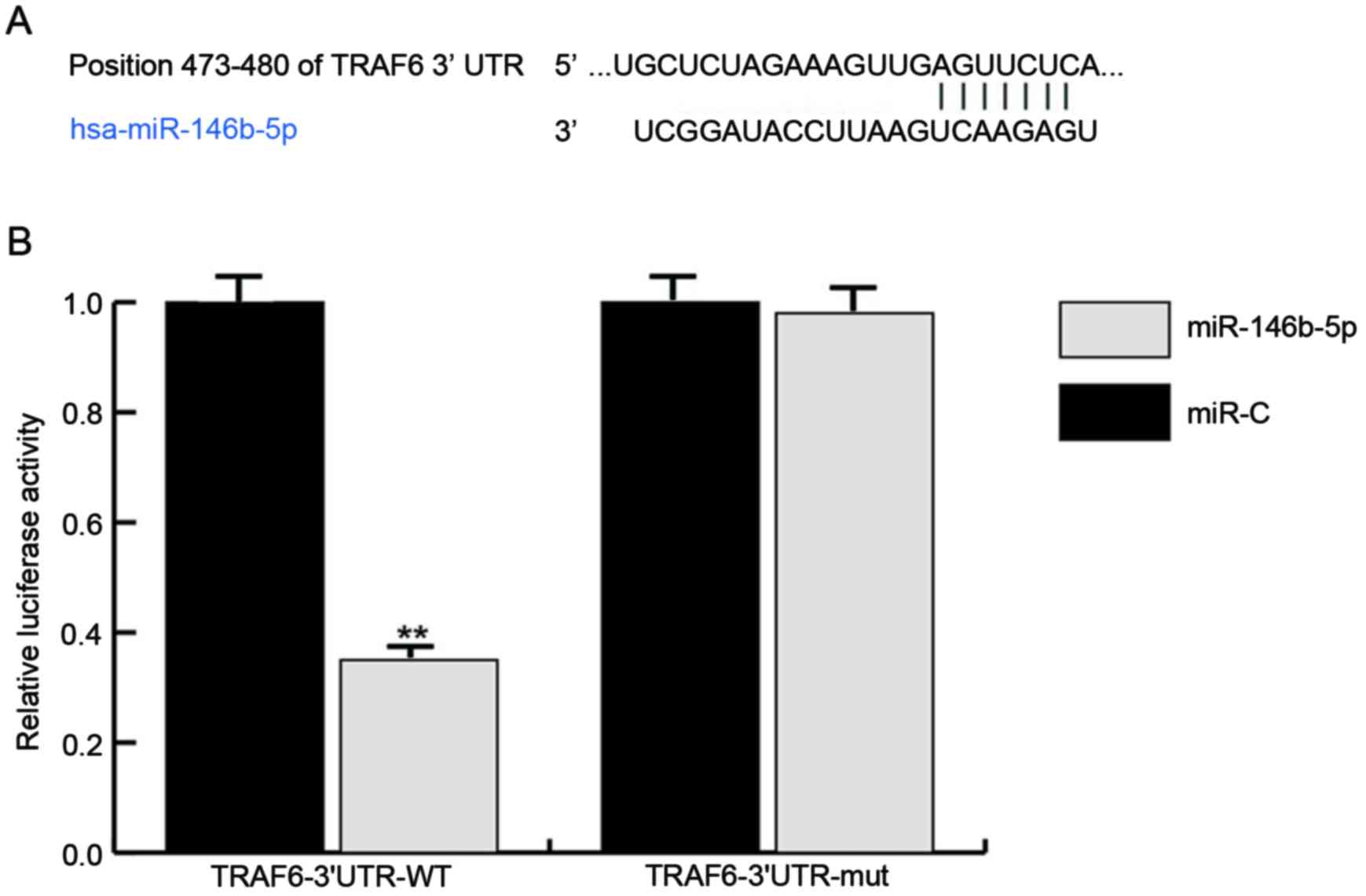
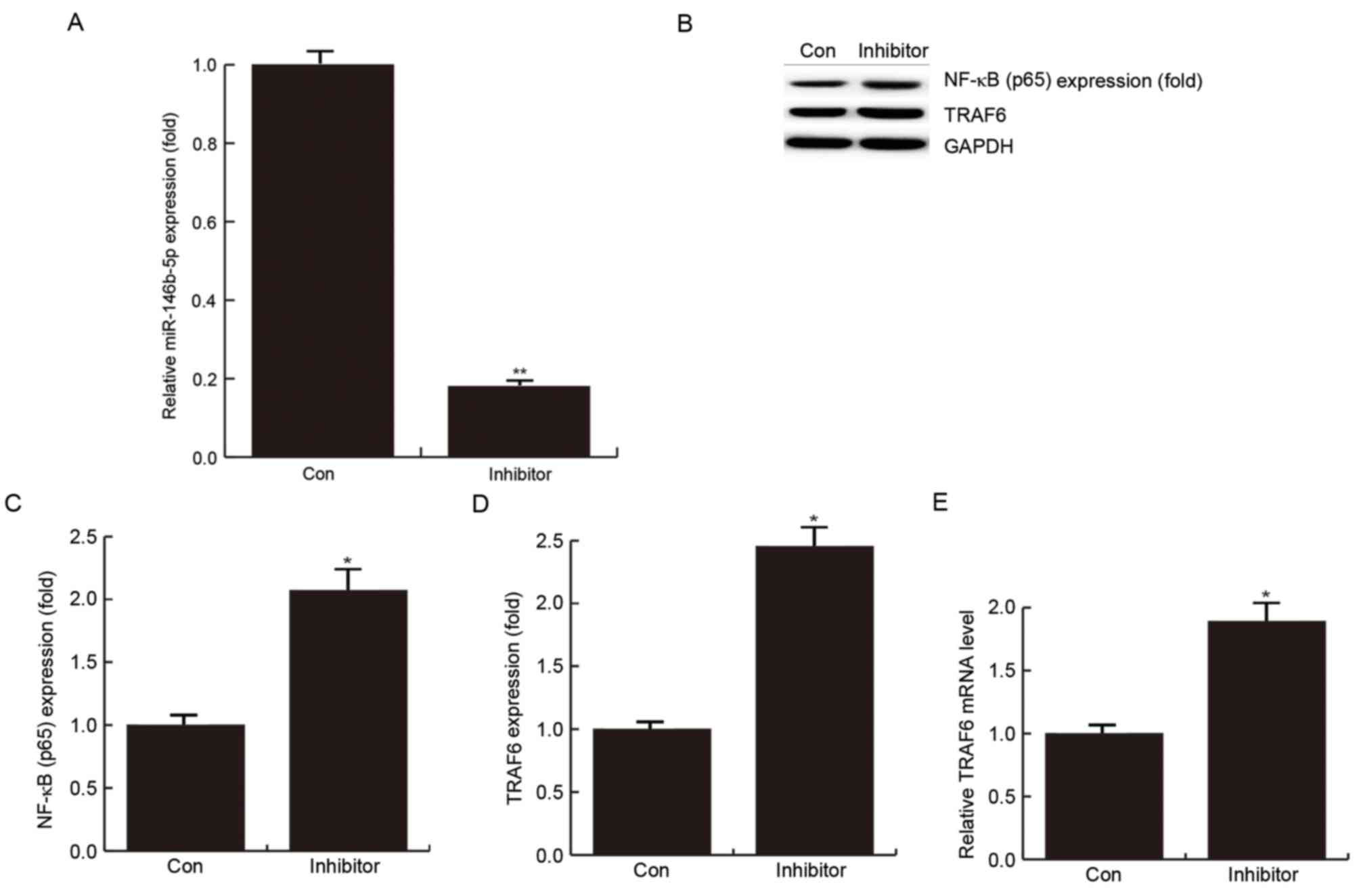
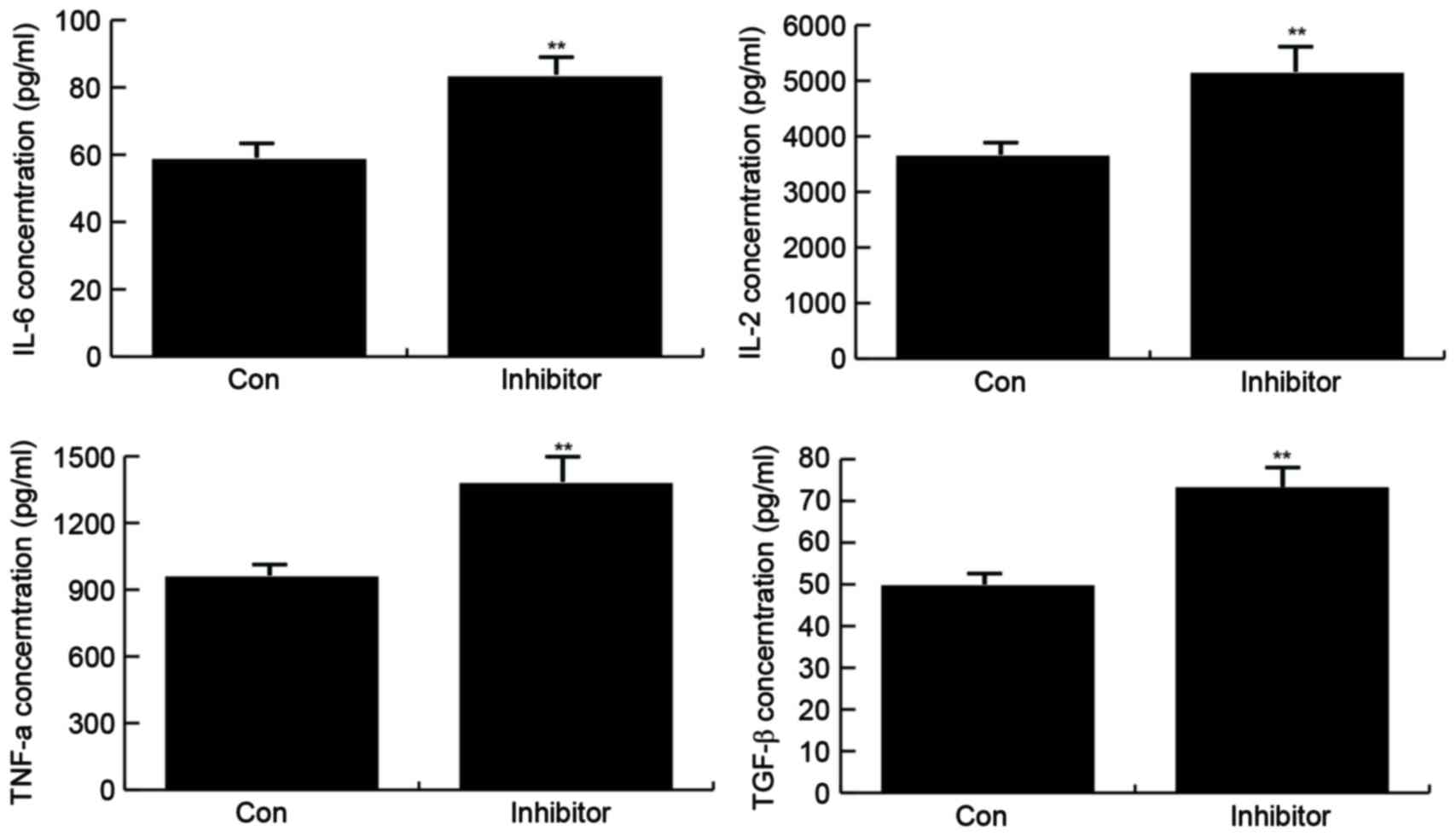
|
1
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Hansson GK:
Progress and challenges in translating the biology of
atherosclerosis. Nature. 473:317–325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Imanishi T and Akasaka T: Novel strategies
to target inflammatory processes in atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm
Des. 19:1616–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore KJ and Tabas I: Macrophages in the
pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell. 145:341–355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang C: MicroRNAs in vascular biology and
vascular disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:235–240. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang C: MicroRNAs: Role in cardiovascular
biology and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 114:699–706. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E:
Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell.
132:9–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Kong D, Chen H, Liu S, Hu H, Wu T,
Wang J, Chen W, Ning Y, Li Y and Lu Z: miR-155 acts as an
anti-inflammatory factor in atherosclerosis-associated foam cell
formation by repressing calcium-regulated heat stable protein 1.
Sci Rep. 6:217892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu Z, Han Y, Liu J, Jiang F, Hu H, Wang Y,
Liu Q, Gong Y and Li X: miR-135b-5p and miR-499a-3p promote cell
proliferation and migration in atherosclerosis by directly
targeting MEF2C. Sci Rep. 5:122762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Qin W, Zhang L, Wu X, Du N, Hu Y,
Li X, Shen N, Xiao D, Zhang H, et al: MicroRNA-26a prevents
endothelial cell apoptosis by directly targeting TRPC6 in the
setting of atherosclerosis. Sci Rep. 5:94012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ouimet M, Ediriweera HN, Gundra UM, Sheedy
FJ, Ramkhelawon B, Hutchison SB, Rinehold K, van Solingen C,
Fullerton MD, Cecchini K, et al: MicroRNA-33-dependent regulation
of macrophage metabolism directs immune cell polarization in
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 125:4334–4348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen T, Huang Z, Wang L, Wang Y, Wu F,
Meng S and Wang C: MicroRNA-125a-5p partly regulates the
inflammatory response, lipid uptake, and ORP9 expression in
oxLDL-stimulated monocyte/macrophages. Cardiovasc Res. 83:131–139.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu J, Chen T, Yang L, Li Z, Wong MM,
Zheng X, Pan X, Zhang L and Yan H: Regulation of microRNA-155 in
atherosclerotic inflammatory responses by targeting MAP3K10. PLoS
One. 7:e465512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Daigneault M, Preston JA, Marriott HM,
Whyte MK and Dockrell DH: The identifcation of markers of
macrophage differentiation in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells and
monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS One. 5:e86682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bao Y, Wang L, Xu Y, Yang Y, Wang L, Si S,
Cho S and Hong B: Salvianolic acid B inhibits macrophage uptake of
modifed low density lipoprotein (mLDL) in a scavenger receptor
CD36-dependent manner. Atherosclerosis. 223:152–159. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu GF, Yang LX, Guo RW, Liu H, Shi YK,
Wang H, Ye JS, Yang ZH and Liang X: miR-155 inhibits oxidized
low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells. Mol
Cell Biochem. 382:253–261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weber C and Noels H: Atherosclerosis:
Current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med.
17:1410–1422. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zernecke A, Bidzhekov K, Noels H,
Shagdarsuren E, Gan L, Denecke B, Hristov M, Köppel T, Jahantigh
MN, Lutgens E, et al: Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies
induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci Signal.
2:ra812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schober A, Nazari-Jahantigh M, Wei Y,
Bidzhekov K, Gremse F, Grommes J, Megens RT, Heyll K, Noels H,
Hristov M, et al: MicroRNA-126-5p promotes endothelial
proliferation and limits atherosclerosis by suppressing Dlk1. Nat
Med. 20:368–376. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tabet F, Vickers KC, Torres Cuesta LF,
Wiese CB, Shoucri BM, Lambert G, Catherinet C, Prado-Lourenco L,
Levin MG, Thacker S, et al: HDL-transferred microRNA-223 regulates
ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Nat Commun. 5:32922014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen X, Li J, Li L, Bian
Z, Sun F, Lu J, Yin Y, Cai X, et al: Secreted monocytic miR-150
enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell. 39:133–144.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang H, Lin J, Wang L, Xie P, Wang X, Fu
J, Ai W, Chen S, Chen F, Zhang F, et al: Kruppel-like factor 2
regulates dendritic cell activation in patients with acute coronary
syndrome. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:931–941. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meng Z, Yan C, Deng Q, Dong X, Duan ZM,
Gao DF and Niu XL: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces
inflammatory responses in cultured human mast cells via Toll-like
receptor 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:842–853. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|