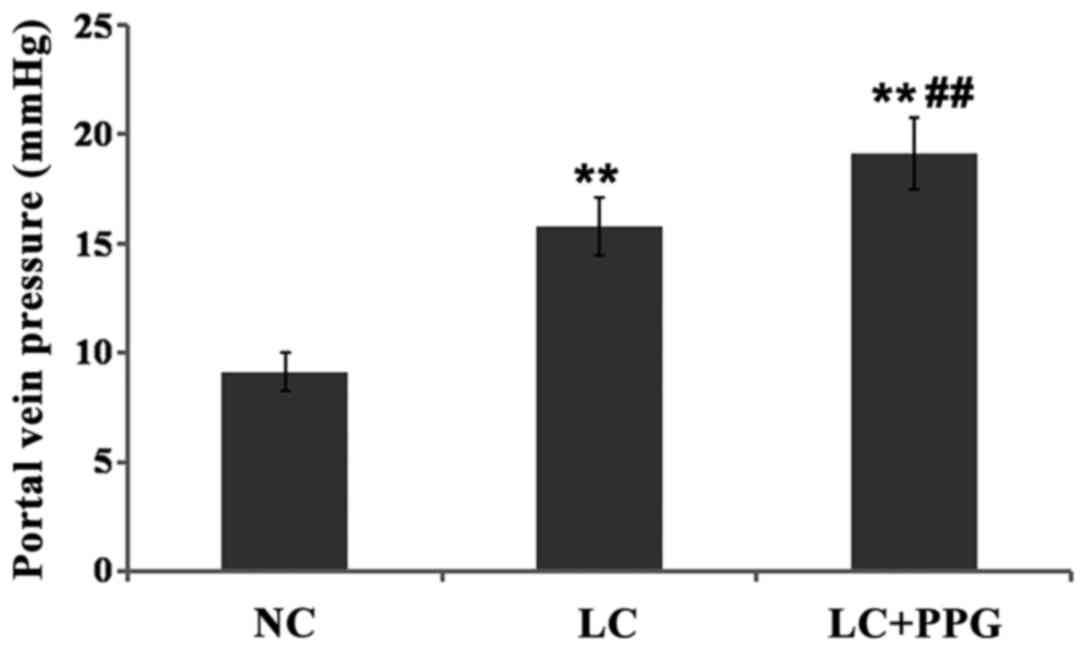
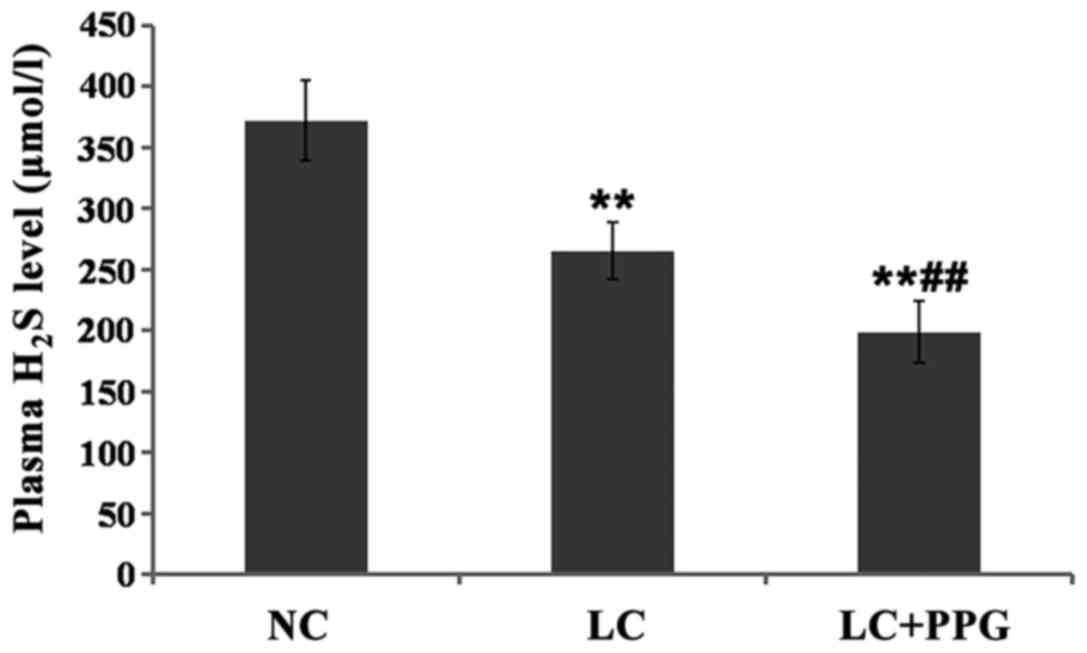
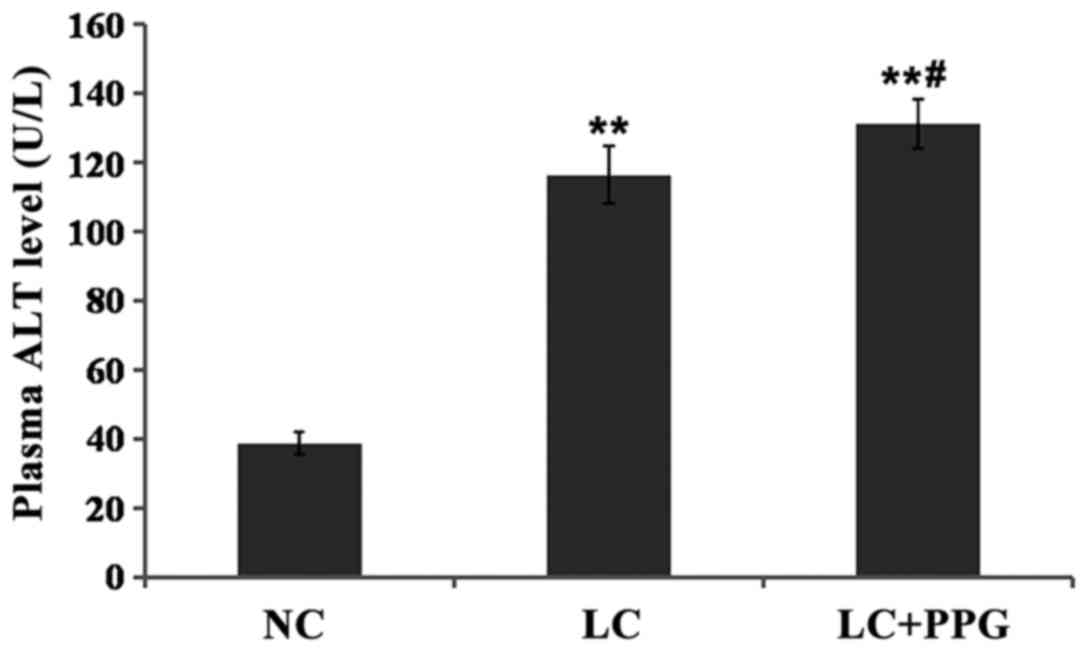
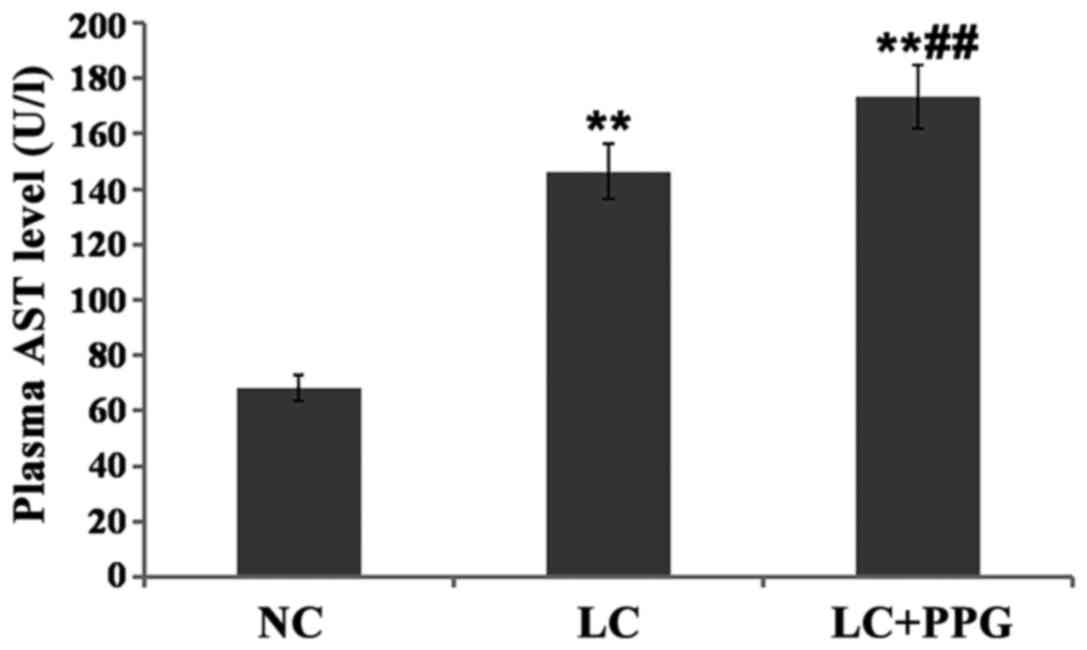
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Molecular regulation of
hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury.
J Biol Chem. 275:2247–2250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bonis PA, Friedman SL and Kaplan MM: Is
liver fibrosis reversible? N Engl J Med. 344:452–454. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Loguercio C and Federico A: Oxidative
stress in viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kitade Y, Watanabe S, Masaki T, Nishioka M
and Nishino H: Inhibition of liver fibrosis in LEC rats by a
carotenoid, lycopene, or a herbal medicine, Sho-saiko-to. Hepatol
Res. 22:196–205. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
La Villa G and Gentilini P: Hemodynamic
alterations in liver cirrhosis. Mol Aspects Med. 29:112–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Geng B, Yang J, Qi Y, Zhao J, Pang Y, Du J
and Tang C: H2S generated by heart in rat and its
effects on cardiac function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:362–368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Calvert JW, Coetzee WA and Lefer DJ: Novel
insights into hydrogen sulfide - mediated cytoprotection. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1203–1217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hosoki R, Matsuki N and Kimura H: The
possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous smooth muscle
relaxant in synergy with nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
237:527–531. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kang K, Zhao M, Jiang H, Tan G, Pan S and
Sun X: Role of hydrogen sulfide in hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Liver Transpl.
15:1306–1314. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tan G, Pan S, Li J, Dong X, Kang K, Zhao
M, Jiang X, Kanwar JR, Qiao H, Jiang H, et al: Hydrogen sulfide
attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity, liver
cirrhosis and portal hypertension in rats. PLoS One. 6:e259432011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ali MY, Ping CY, Mok YY, Ling L, Whiteman
M, Bhatia M and Moore PK: Regulation of vascular nitric oxide in
vitro and in vivo; a new role for endogenous hydrogen sulphide? Br
J Pharmacol. 149:625–634. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nik Mel AV, Voloshchouk NI, Pentyuk NO and
Zaichko KO: Role of hydrogen sulfide and sulfur-containing amino
acids in regulation of tone of smooth muscles of the vascular wall
in rats. Neurophysiology. 42:126–131. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Chuah SC, Moore PK and Zhu YZ:
S-allylcysteine mediates cardioprotection in an acute myocardial
infarction rat model via a hydrogen sulfide-mediated pathway. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H2693–H2701. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sidhapuriwala JN, Ng SW and Bhatia M:
Effects of hydrogen sulfide on inflammation in caerulein-induced
acute pancreatitis. J Inflamm (Lond). 6:352009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hirata I, Naito Y, Takagi T, Mizushima K,
Suzuki T, Omatsu T, Handa O, Ichikawa H, Ueda H and Yoshikawa T:
Endogenous hydrogen sulfide is an anti-inflammatory molecule in
dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Dig Dis Sci.
56:1379–1386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chunyu Z, Junbao D, Dingfang B, Hui Y,
Xiuying T and Chaoshu T: The regulatory effect of hydrogen sulfide
on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 302:810–816. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Mencarelli A,
Orlandi S, Renga B, Rizzo G, Distrutti E, Shah V and Morelli A: The
third gas: H2S regulates perfusion pressure in both the
isolated and perfused normal rat liver and in cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 42:539–548. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bauer M, Bauer I, Sonin NV, Kresge N,
Baveja R, Yokoyama Y, Harding D, Zhang JX and Clemens MG:
Functional significance of endothelin B receptors in mediating
sinusoidal and extrasinusoidal effects of endothelins in the intact
rat liver. Hepatology. 31:937–947. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bosy-Westphal A, Petersen S, Hinrichsen H,
Czech NJ and Müller M: Increased plasma homocysteine in liver
cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 20:28–38. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Siebert N, Cantré D, Eipel C and Vollmar
B: H2S contributes to the hepatic arterial buffer
response and mediates vasorelaxation of the hepatic artery via
activation of K(ATP) channels. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 295:G1266–G1273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dawe GS, Han SP, Bian JS and Moore PK:
Hydrogen sulphide in the hypothalamus causes an ATP-sensitive
K+ channel-dependent decrease in blood pressure in
freely moving rats. Neuroscience. 152:169–177. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jeong EJ, Kim NH, Heo JD, Lee KY, Rho JR,
Kim YC and Sung SH: Antifibrotic compounds from Liriodendron
tulipifera attenuating HSC-T6 proliferation and TNF-α production in
RAW264.7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 38:228–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu YF, Chu YY, Zhang XZ, Zhang M, Xie FG,
Zhou M, Wen HH and Shu AH: TGFβ1 protects myocardium from apoptosis
and oxidative damage after ischemia reperfusion. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:1551–1558. 2017.
|
|
24
|
Wang YX, Liu ML, Zhang B, Fu EQ and Li ZC:
Fasudil alleviated hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by
stabilizing the expression of angiotensin-(1–7) in rats. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3304–3312. 2016.
|