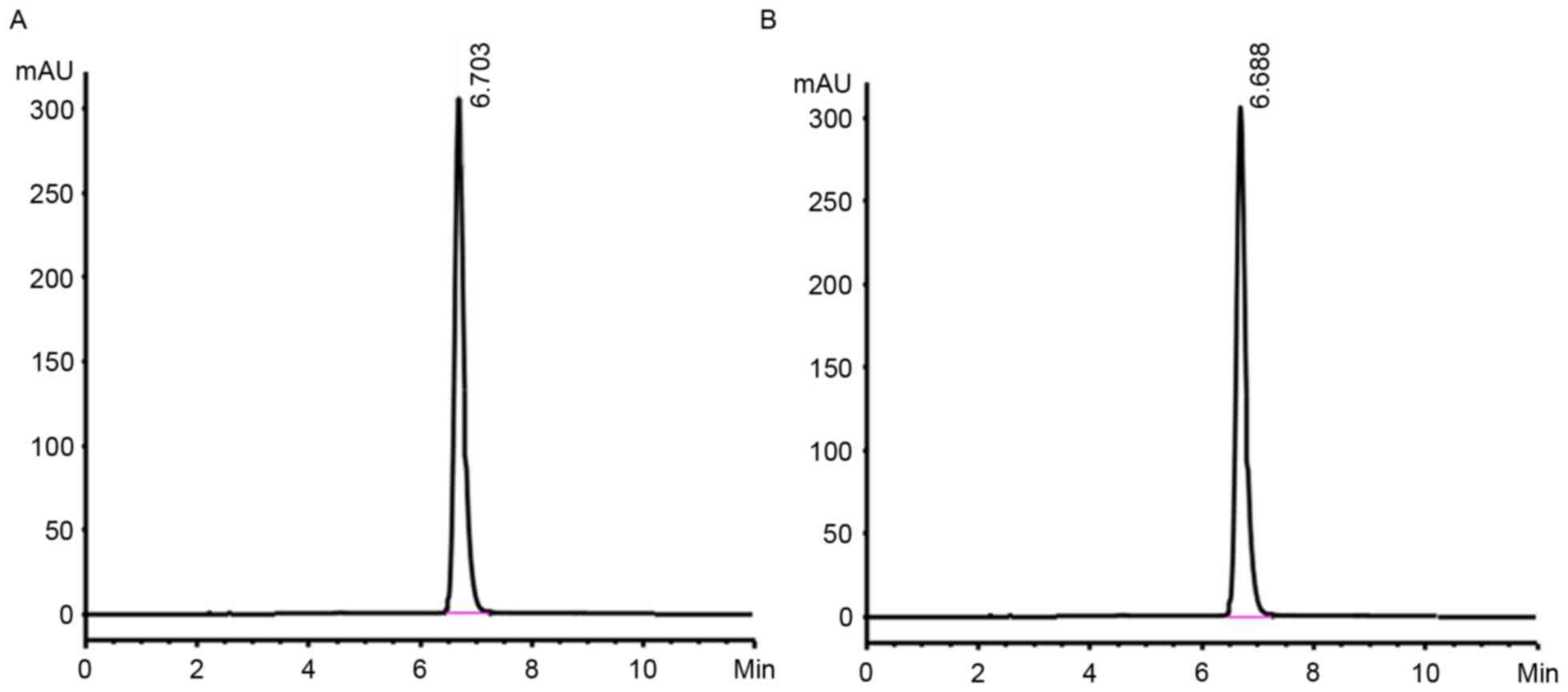
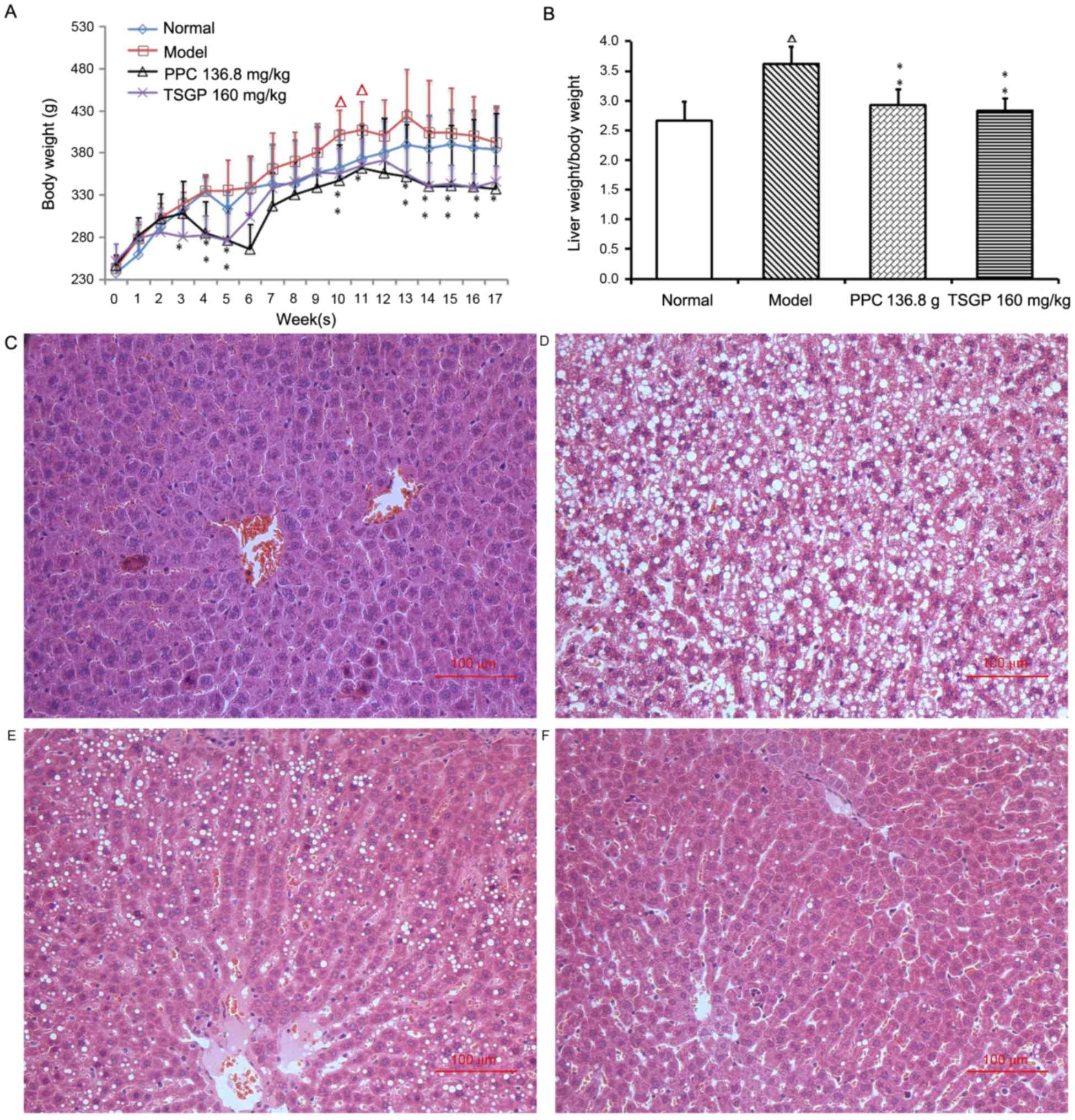
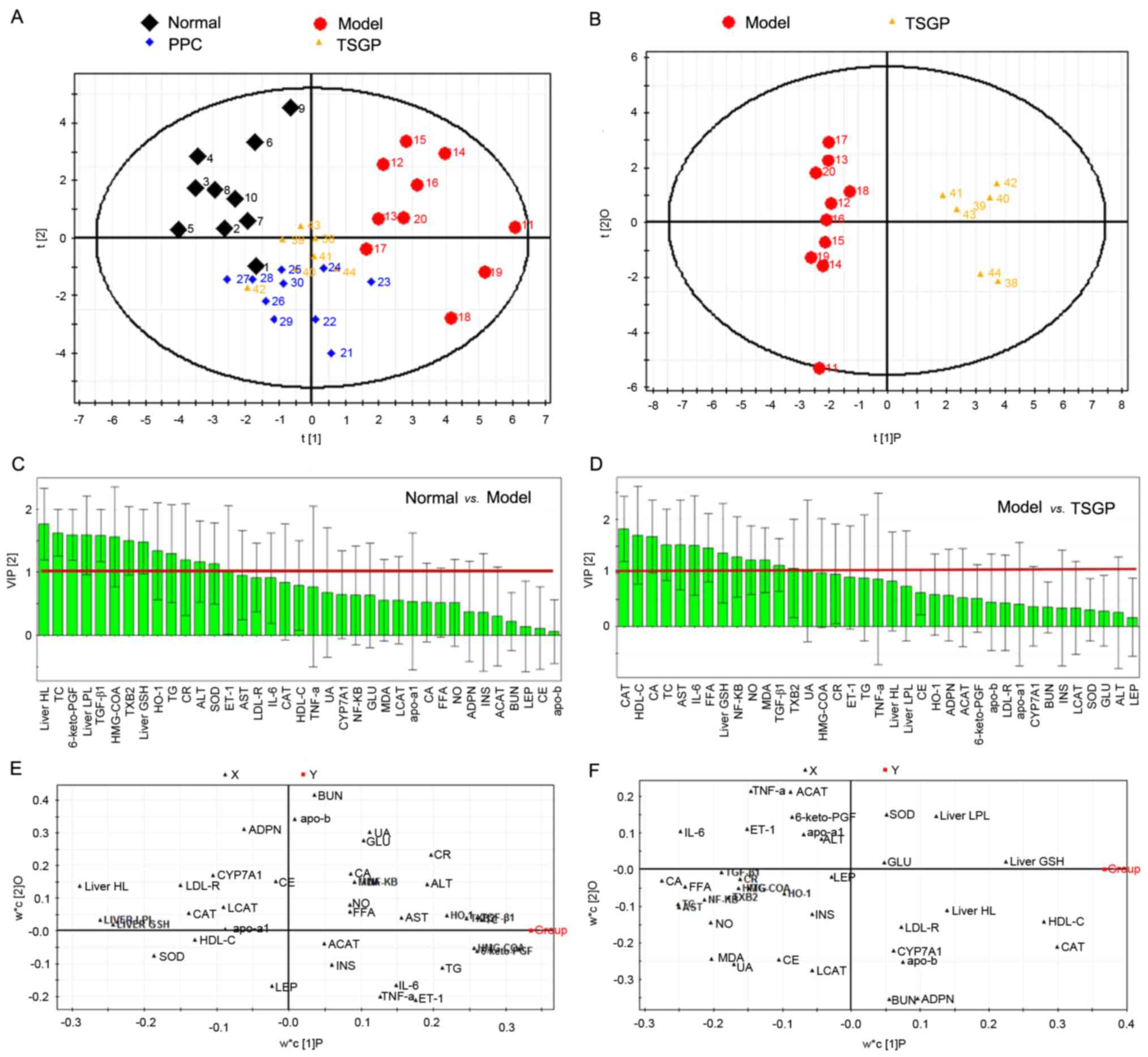
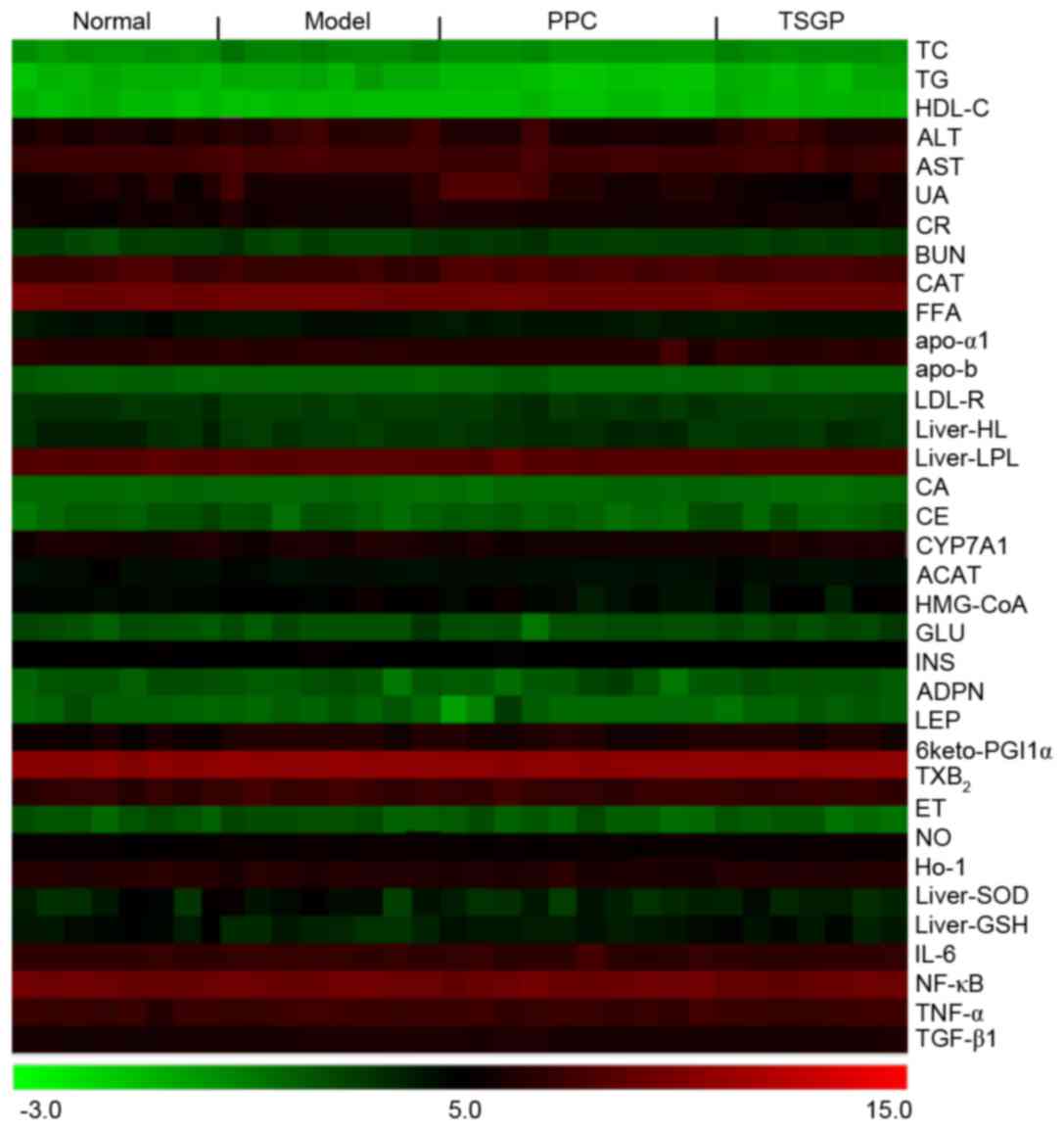
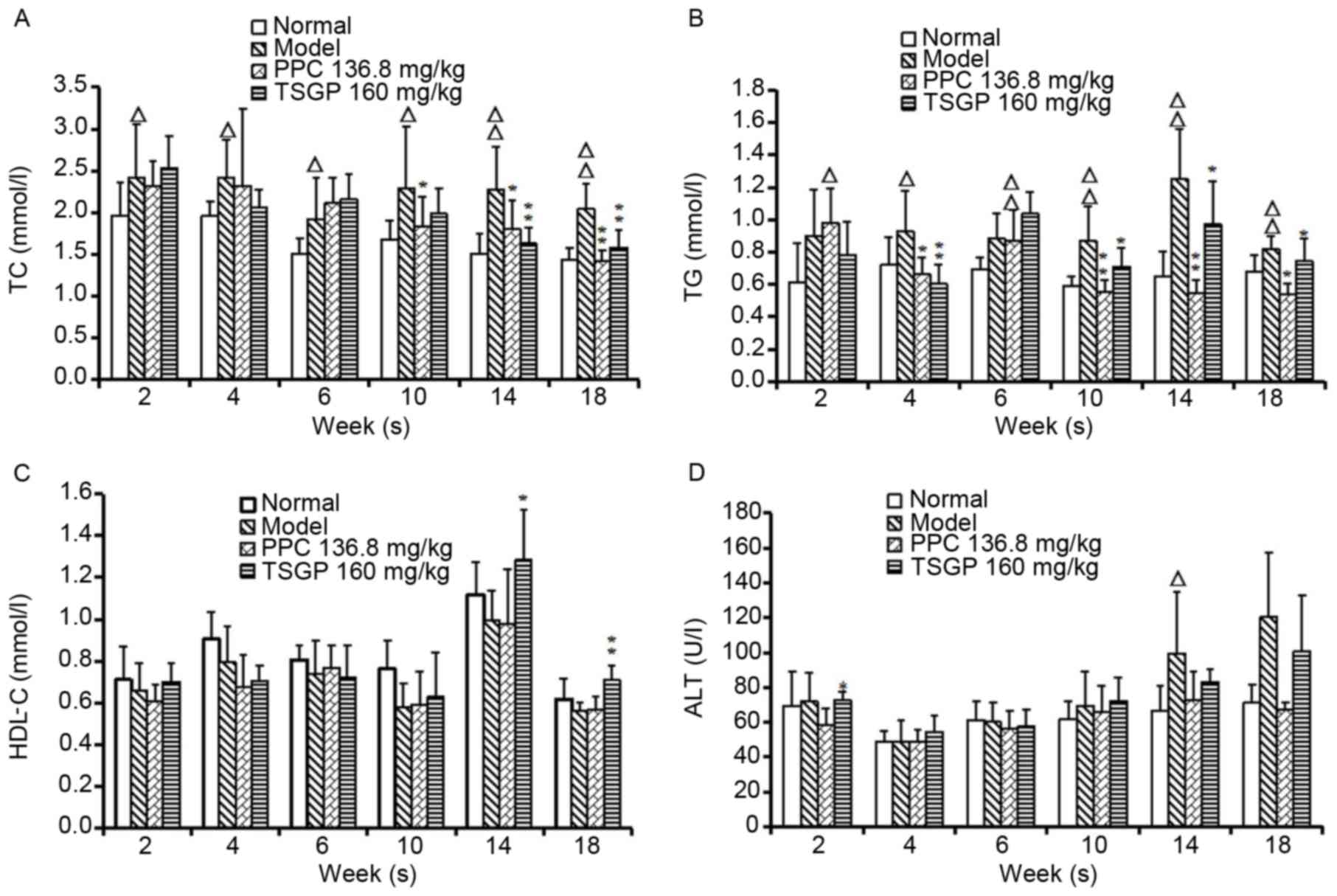
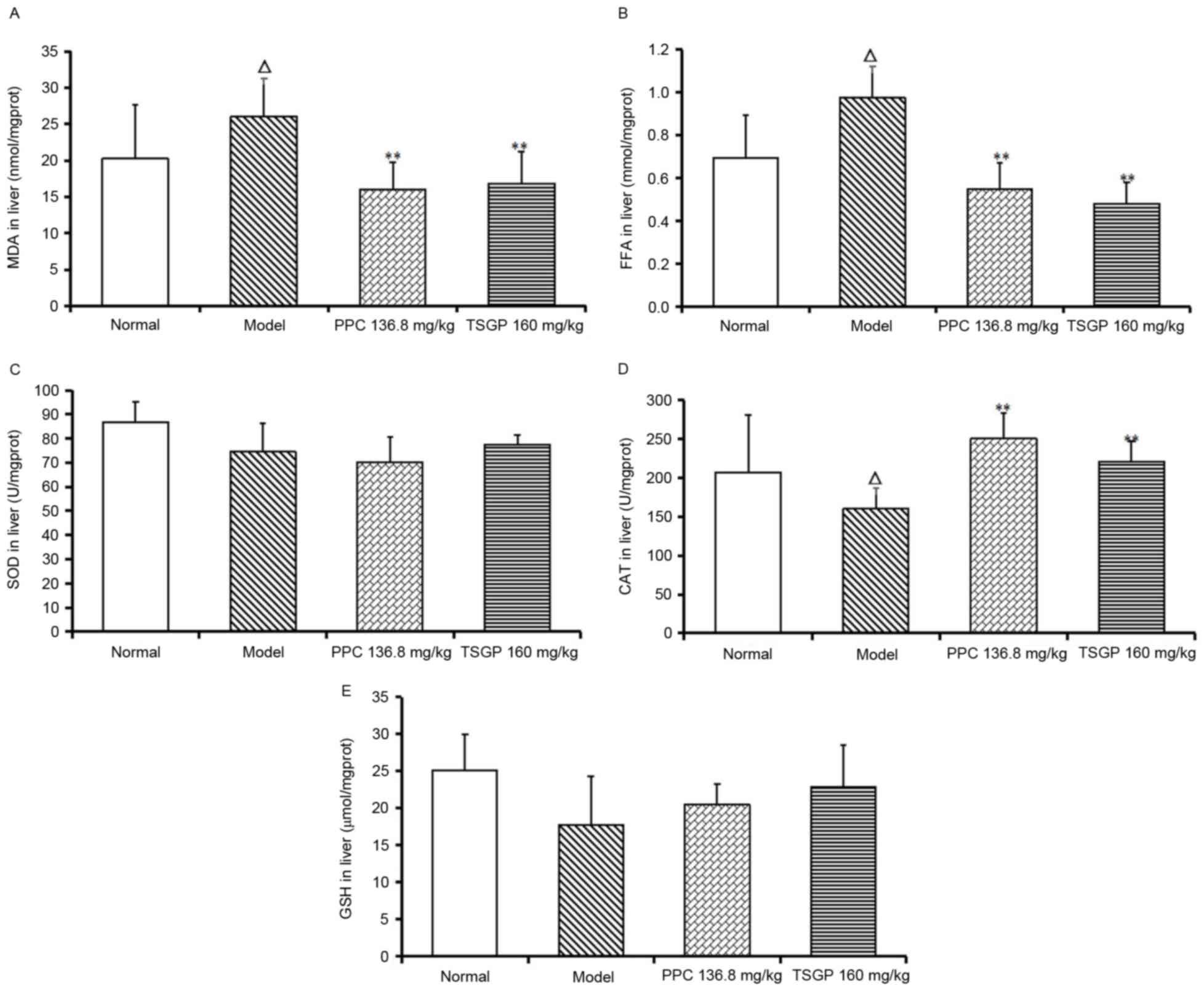
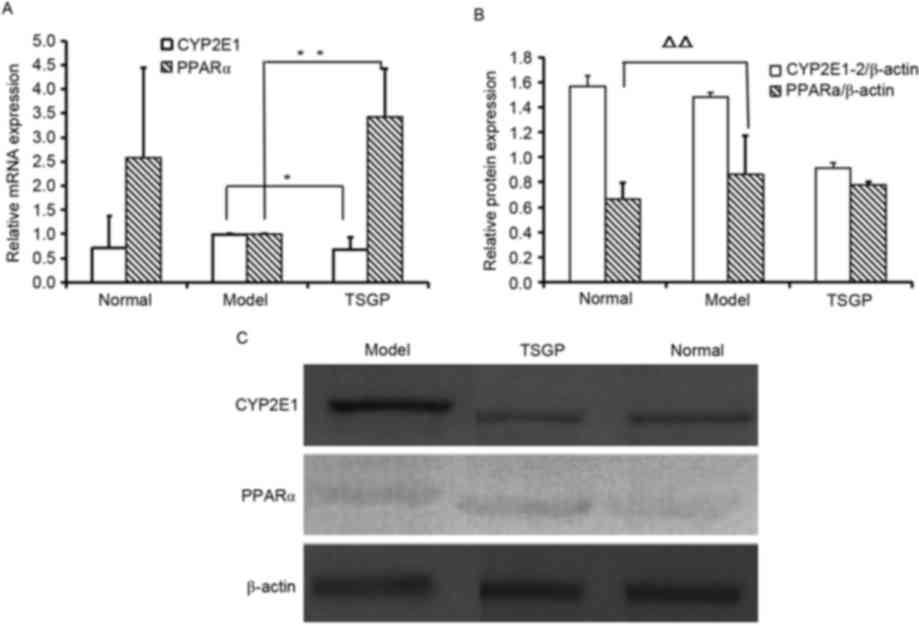
|
1
|
Tiniakos DG, Vos MB and Brunt EM:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathology and pathogenesis. Annu
Rev Pathol. 5:145–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Preiss D and Sattar N: Non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease: An overview of prevalence, diagnosis, pathogenesis
and treatment considerations. Clin Sci (Lond). 115:141–150. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kopec KL and Burns D: Nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease: A review of the spectrum of disease, diagnosis, and
therapy. Nutr Clin Pract. 26:565–576. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chalasani N, Deeg MA and Crabb DW:
Systemic levels of lipid peroxidation and its metabolic and dietary
correlates in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 99:1497–1502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Day CP and James OF: Steatohepatitis: A
tale of two ‘hits’? Gastroenterology. 114:842–845. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Phung N, Pera N, Farrell G, Leclercq I,
Hou JY and George J: Pro-oxidant-mediated hepatic fibrosis and
effects of antioxidant intervention in murine dietary
steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Med. 24:171–180. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seki S, Kitada T, Yamada T, Sakaguchi H,
Nakatani K and Wakasa K: In situ detection of lipid peroxidation
and oxidative DNA damage in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. J
Hepatol. 37:56–62. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zivkovic AM, German JB and Sanyal AJ:
Comparative review of diets for the metabolic syndrome:
Implications for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Clin Nutr.
86:285–300. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl
AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, Charlton M and Sanyal AJ; American
Gastroenterological Association; American Association for the Study
of Liver Diseases; American College of Gastroenterology, : The
diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association,
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American
College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 142:1592–1609. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakajima K: Multidisciplinary
pharmacotherapeutic options for nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease.
Int J Hepatol. 2012:9506932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu JY, Zhang L, Li ZP and Ji G: Natural
products on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Drug Targets.
16:1347–1355. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pharmacopoeia CoC: Pharmacopoeia of the
People's Republic of China. China Medical Science Press; Beijin:
2015
|
|
13
|
Chen CQ and Zhang TJ: Regulation of Blood
Lipid Research and Application of Modern Traditional Chinese
Medicine. People's Medical Publishing House; Beijing: 2007, (In
Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Jiang LD, He YS, Chen X, Tao O, Li GY and
Zhang YL: Study on anti-hyperlipidemia mechanism of high frequency
herb pairs by molecular docking method. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
40:2413–2419. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li N, Chen Z, Mao X, Yu J and Zhao R:
Effects of lipid regulation using raw and processed radix polygoni
multiflori in rats fed a high-fat diet. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012:3291712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang YX, Ge AH, Jiang Y, Azietaku J Teye,
Li J and Gao XM: A Bioactivity-based method for screening,
identification of lipase inhibitors, and clarifying the effects of
processing time on lipase inhibitory activity of Polygonum
multiflorum. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:59650672016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen HF, Chen YH, Liu CH, Wang L, Chen X,
Yu BY and Qi J: Integrated chemometric fingerprints of antioxidant
activities and HPLC-DAD-CL for assessing the quality of the
processed roots of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. (Heshouwu). Chin
Med. 11:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang M, Zhao R, Wang W, Mao X and Yu J:
Lipid regulation effects of Polygoni Multiflori Radix, its
processed products and its major substances on steatosis human
liver cell line L02. J Ethnopharmacol. 139:287–293. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu QL, Xiao JH, Ma R, Ban Y and Wang JL:
Effect of 2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-D-glucoside on
lipoprotein oxidation and proliferation of coronary arterial smooth
cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 9:689–697. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang W, He Y, Lin P, Li Y, Sun R, Gu W, Yu
J and Zhao R: In vitro effects of active components of Polygonum
Multiflorum Radix on enzymes involved in the lipid metabolism. J
Ethnopharmacol. 153:763–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin P, Lu J, Wang Y, Gu W, Yu J and Zhao
R: Naturally occurring stilbenoid TSG reverses non-alcoholic fatty
liver diseases via gut-liver axis. PLoS One. 10:e01403462015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lv G, Gu H, Chen S, Lou Z and Shan L:
Pharmacokinetic profile of
2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside in mice after oral
administration of Polygonum multiflorum extract. Drug Dev Ind
Pharm. 38:248–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lou ZH, Lu GY, Chen SH and Gu H:
Determination of 2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxy-stilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside
in Shouwugan preparation and its tissue distribution in mouse.
Zhongguo Xian Dai Ying Yong Yao Xue. 28:89–91. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Lv G, Lou Z, Chen S, Gu H and Shan L:
Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of
2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside from traditional
Chinese medicine Polygonum multiflorum following oral
administration to rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:449–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong LH, Guo PP, Yan WY, Yang H and Wang
CY: Comparative study on hypolipidemic effect of
cis-2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside and
trans-2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside. Shenyang Yao
Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:989–993. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Wang CY, Zhang LT, Yuan ZF, Jin YB and
Zhang Z: Blood lipid regulation of ethyl acetate extracting fration
and stilbene glycoside from tuber of Polygonum multiflorum. Chin
Traditional Herbal Drugs. 39:78–83. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Zhang W, Wang CH, Shen Y, Li F and Wang
YQ: Treatment of 2,3,4′,5-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside on
atherosclerosis in rats. Zhongguo Yao Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
38:261–264. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Lv L, Gu X, Tang J and Ho CT: Antioxidant
activity of stilbene glycoside from Polygonum multiflorum Thunb in
vivo. Food Chemistry. 104:1678–1681. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bro R and Smilde AK: Principal component
analysis. Anal Methods. 6:2812–2831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Boccard J and Rutledge DN: A consensus
orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA)
strategy for multiblock Omics data fusion. Anal Chim Acta.
769:30–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nobili V, Donati B, Panera N,
Vongsakulyanon A, Alisi A, Dallapiccola B and Valenti L: A
4-polymorphism risk score predicts steatohepatitis in children with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
58:632–636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Han L, Zhu L and Yu Y: Free fatty
acids, not triglycerides, are associated with non-alcoholic liver
injury progression in high fat diet induced obese rats. Lipids
Health Dis. 15:272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Papackova Z and Cahova M: Fatty acid
signaling: The new function of intracellular lipases. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:3831–3855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leamy AK, Egnatchik RA and Young JD:
Molecular mechanisms and the role of saturated fatty acids in the
progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Prog Lipid Res.
52:165–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Serviddio G, Bellanti F and Vendemiale G:
Free radical biology for medicine: Learning from nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:952–968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qiang M, Xu Y, Lu Y, He Y, Han C, Liu Y
and He R: Autofluorescence of MDA-modified proteins as an in vitro
and in vivo probe in oxidative stress analysis. Protein Cell.
5:484–487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sayed AA: Ferulsinaic acid modulates SOD,
GSH, and antioxidant enzymes in diabetic kidney. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:5801042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Suzuki M, Takeuchi H, Kakita T, Unno M,
Katayose Y and Matsuno S: The involvement of the intracellular
superoxide production system in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
injury. In vivo and in vitro experiments using transgenic mice
manifesting excessive CuZn-SOD activity. Free Radic Biol Med.
29:756–763. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mateos R, Lecumberri E, Ramos S, Goya L
and Bravo L: Determination of malondialdehyde (MDA) by
high-performance liquid chromatography in serum and liver as a
biomarker for oxidative stress. Application to a rat model for
hypercholesterolemia and evaluation of the effect of diets rich in
phenolic antioxidants from fruits. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol
Biomed Life Sci. 827:76–82. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheng N, Ren N, Gao H, Lei X, Zheng J and
Cao W: Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of Schisandra
chinensis pollen extract on CCl4-induced acute liver damage in
mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 55:234–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heck DE, Shakarjian M, Kim HD, Laskin JD
and Vetrano AM: Mechanisms of oxidant generation by catalase. Ann N
Y Acad Sci. 1203:120–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|