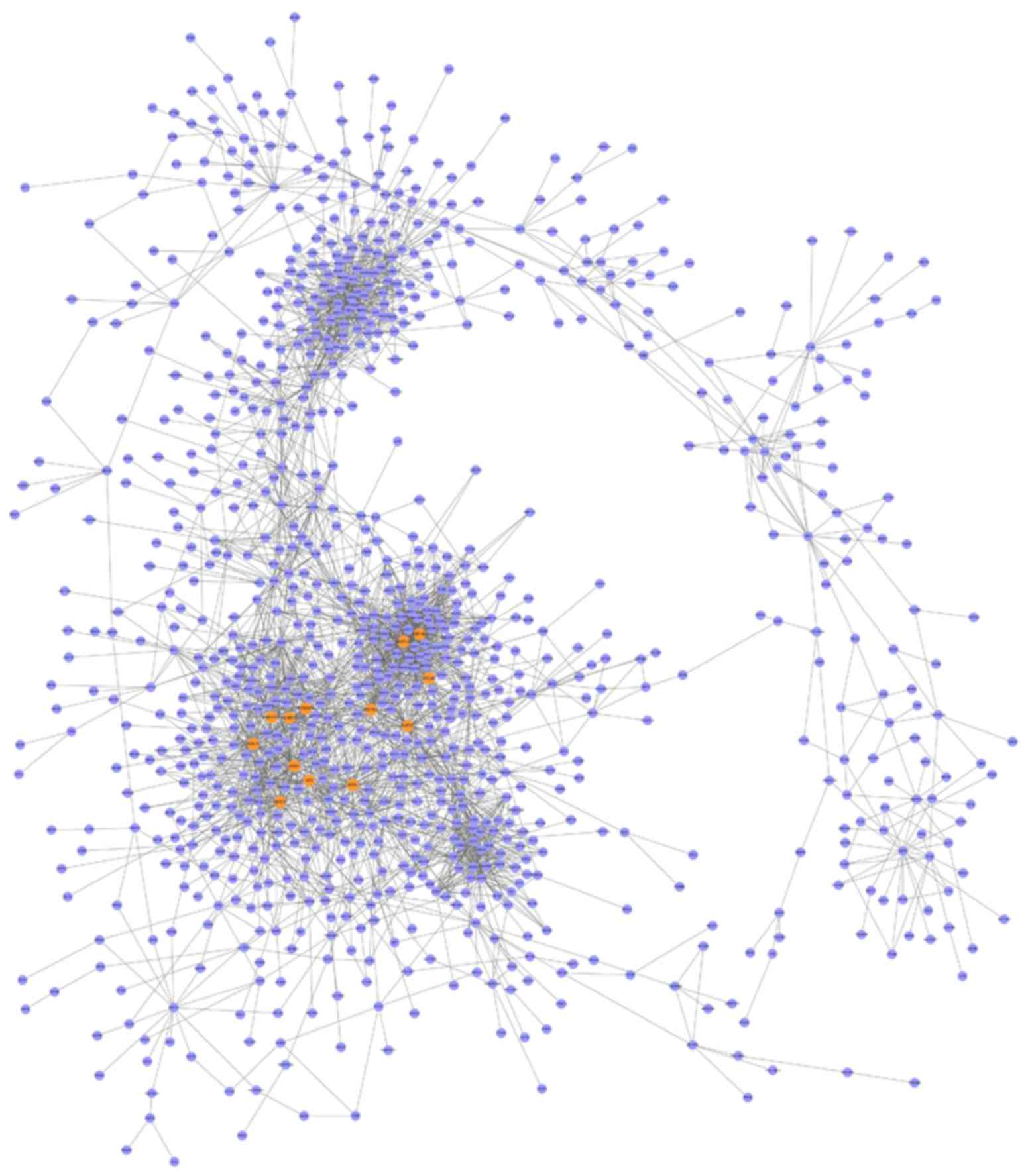
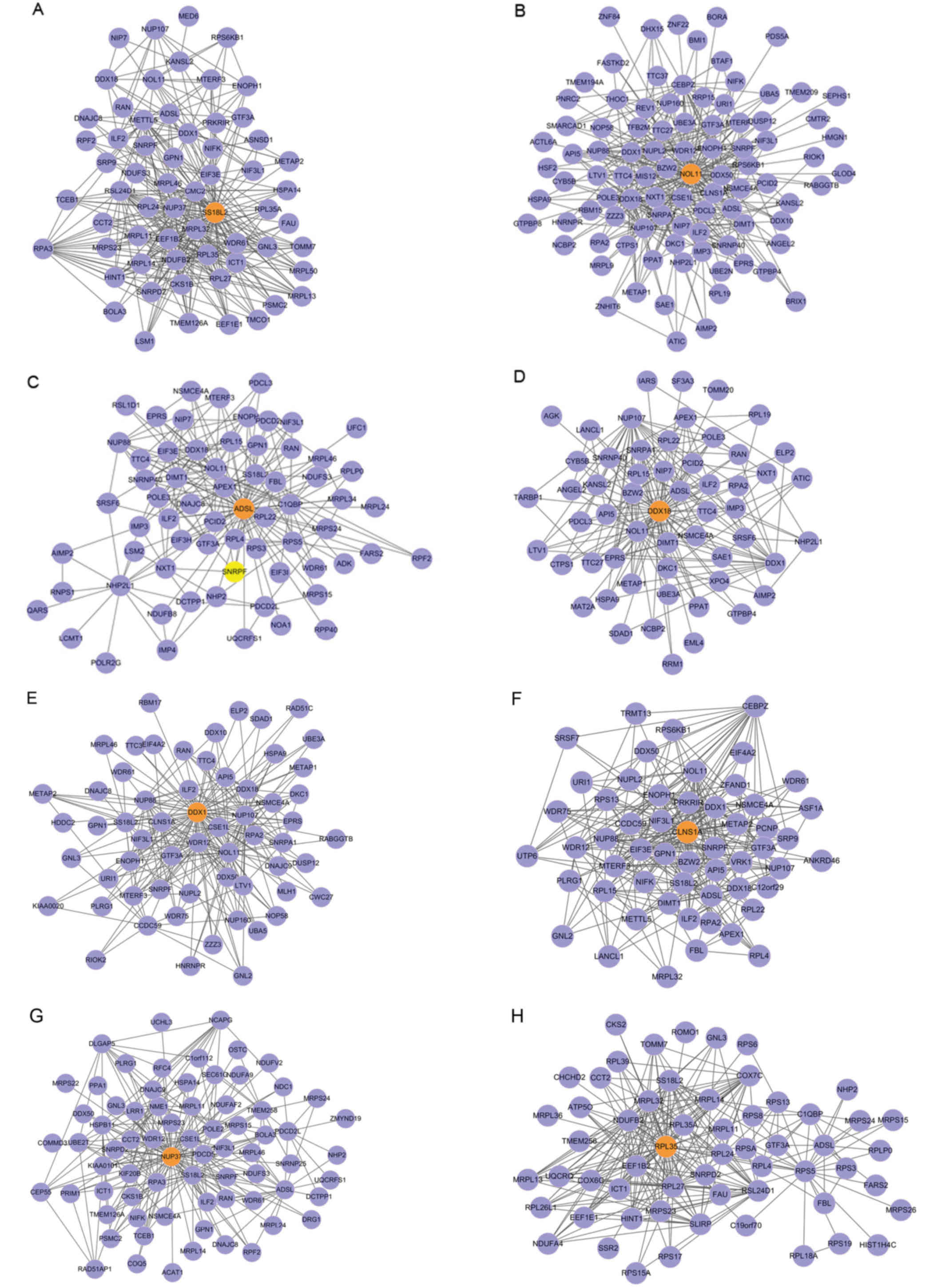
|
1
|
Rawat J, Sindhwani G and Juyal R:
Clinico-radiological profile of new smear positive pulmonary
tuberculosis cases among young adult and elderly people in a
tertiary care hospital at Deheradun (Uttarakhand). Indian J Tuberc.
55:84–90. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Starke JR: Resurgence of tuberculosis in
children. Pediatr Pulmonol Suppl. 11:16–17. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smith S, Jacobs RF and Wilson CB:
Immunobiology of childhood tuberculosis: A window on the ontogeny
of cellular immunity. J Pediatr. 131:16–26. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoo AS, Staahl BT, Chen L and Crabtree GR:
MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in
neural development. Nature. 460:642–646. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
World Health Organisation (WHO), . Global
health observatory data. 2017, http://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en/
|
|
6
|
Hamilton CD, Swaminathan S, Christopher
DJ, Ellner J, Gupta A, Sterling TR, Rolla V, Srinivasan S, Karyana
M, Siddiqui S, et al: RePORT International: Advancing tuberculosis
biomarker research through global collaboration. Clin Infect Dis.
61:155–159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trunz BB, Fine P and Dye C: Effect of BCG
vaccination on childhood tuberculous meningitis and miliary
tuberculosis worldwide: A meta-analysis and assessment of
cost-effectiveness. Lancet. 367:1173–1180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zar HJ, Workman L, Isaacs W, Dheda K,
Zemanay W and Nicol MP: Rapid diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
in African children in a primary care setting by use of Xpert
MTB/RIF on respiratory specimens: A prospective study. Lancet Glob
Health. 1:97–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gous N, Scott LE, Khan S, Reubenson G,
Coovadia A and Stevens W: Diagnosing childhood pulmonary
tuberculosis using a single sputum specimen on Xpert MTB/RIF at
point of care. S Afr Med J. 105:1044–1048. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fiebig L, Hauer B, Brodhun B, Balabanova Y
and Haas W: Bacteriological confirmation of pulmonary tuberculosis
in children with gastric aspirates in Germany, 2002–2010. Int J
Tuberc Lung Dis. 18:925–930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, Haenig C,
Brembeck FH, Goehler H, Stroedicke M, Zenkner M, Schoenherr A,
Koeppen S, et al: A human protein-protein interaction network: A
resource for annotating the proteome. Cell. 122:957–968. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferrari R, Forabosco P, Vandrovcova J,
Botía JA, Guelfi S, Warren JD, Momeni P, Weale ME, Ryten M and
Hardy J: UK Brain Expression Consortium (UKBEC): Frontotemporal
dementia: Insights into the biological underpinnings of disease
through gene co-expression network analysis. Mol Neurodegener.
11:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Safaei A, Rezaei Tavirani M, Arefi Oskouei
A, Zamanian Azodi M, Mohebbi SR and Nikzamir AR: Protein-protein
interaction network analysis of cirrhosis liver disease.
Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 9:114–123. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin N, Wu H, Miao Z, Huang Y, Hu Y, Bi X,
Wu D, Qian K, Wang L, Wang C, et al: Network-based
survival-associated module biomarker and its crosstalk with cell
death genes in ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. 5:115662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ramadan E, Alinsaif S and Hassan MR:
Network topology measures for identifying disease-gene association
in breast cancer. BMC Bioinformatics. 17:2742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feser WJ, Fingerlin TE, Strand MJ and
Glueck DH: Calculating Average Power for the Benjamini-Hochberg
Procedure. J Stat Theory Appl. 8:325–352. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma X, Gao L, Karamanlidis G, Gao P, Lee
CF, Garcia-Menendez L, Tian R and Tan K: Revealing pathway dynamics
in heart diseases by analyzing multiple differential networks. PLOS
Comput Biol. 11:e10043322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schwarz E, Izmailov R, Liò P and
Meyer-Lindenberg A: Protein interaction networks link schizophrenia
risk loci to synaptic function. Schizophr Bull. 42:1334–1342. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kulshrestha A, Suman S and Ranjan R:
Network analysis reveals potential markers for pediatric
adrenocortical carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4569–4581. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
de Bruijn DR, Kater-Baats E, Eleveld M,
Merkx G and Geurts Van Kessel A: Mapping and characterization of
the mouse and human SS18 genes, two human SS18-like genes and a
mouse Ss18 pseudogene. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 92:310–319. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Bruijn DR, Allander SV, van Dijk AH,
Willemse MP, Thijssen J, van Groningen JJ, Meltzer PS and van
Kessel AG: The synovial-sarcoma-associated SS18-SSX2 fusion protein
induces epigenetic gene (de)regulation. Cancer Res. 66:9474–9482.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Freed EF, Prieto JL, McCann KL, McStay B
and Baserga SJ: NOL11, implicated in the pathogenesis of North
American Indian childhood cirrhosis, is required for pre-rRNA
transcription and processing. PLoS Genet. 8:e10028922012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kmoch S, Hartmannová H, Stibůrková B,
Krijt J, Zikánová M and Sebesta I: Human adenylosuccinate lyase
(ADSL), cloning and characterization of full-length cDNA and its
isoform, gene structure and molecular basis for ADSL deficiency in
six patients. Hum Mol Genet. 9:1501–1513. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stone RL, Aimi J, Barshop BA, Jaeken J,
van den Berghe G, Zalkin H and Dixon JE: A mutation in
adenylosuccinate lyase associated with mental retardation and
autistic features. Nat Genet. 1:59–63. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fon EA, Demczuk S, Delattre O, Thomas G
and Rouleau GA: Mapping of the human adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL)
gene to chromosome 22q13.1->q13.2. Cytogenet Cell Genet.
64:201–203. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rigo F, Hua Y, Chun SJ, Prakash TP,
Krainer AR and Bennett CF: Synthetic oligonucleotides recruit
ILF2/3 to RNA transcripts to modulate splicing. Nat Chem Biol.
8:555–561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
López-Fernández LA, Párraga M and del Mazo
J: Ilf2 is regulated during meiosis and associated to
transcriptionally active chromatin. Mech Dev. 111:153–157. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada
T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N and Shiekhattar R: The microprocessor
complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 432:235–240.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han C, Liu Y, Wan G, Choi HJ, Zhao L, Ivan
C, He X, Sood AK, Zhang X and Lu X: The RNA-binding protein DDX1
promotes primary microRNA maturation and inhibits ovarian tumor
progression. Cell Reports. 8:1447–1460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|