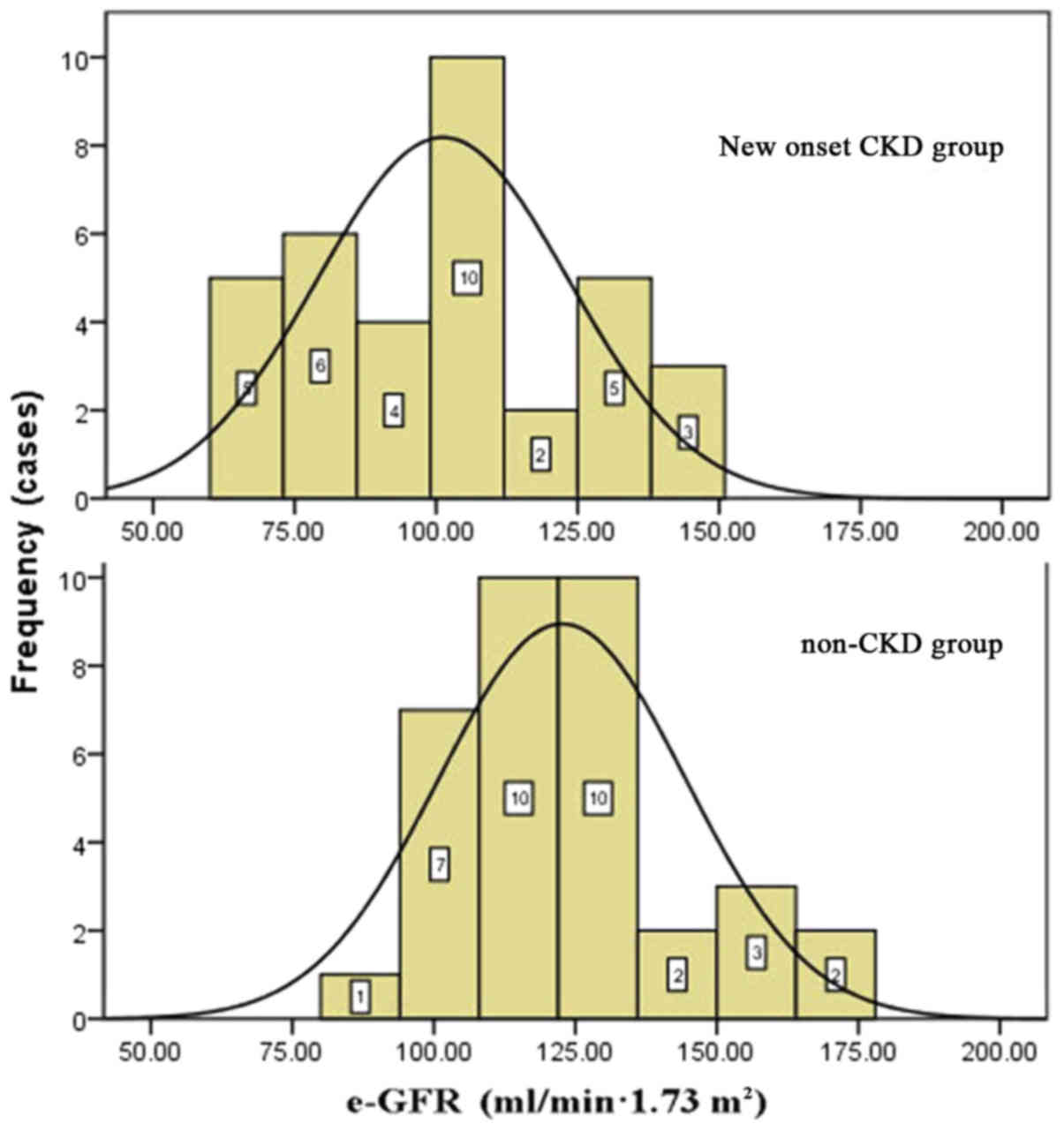
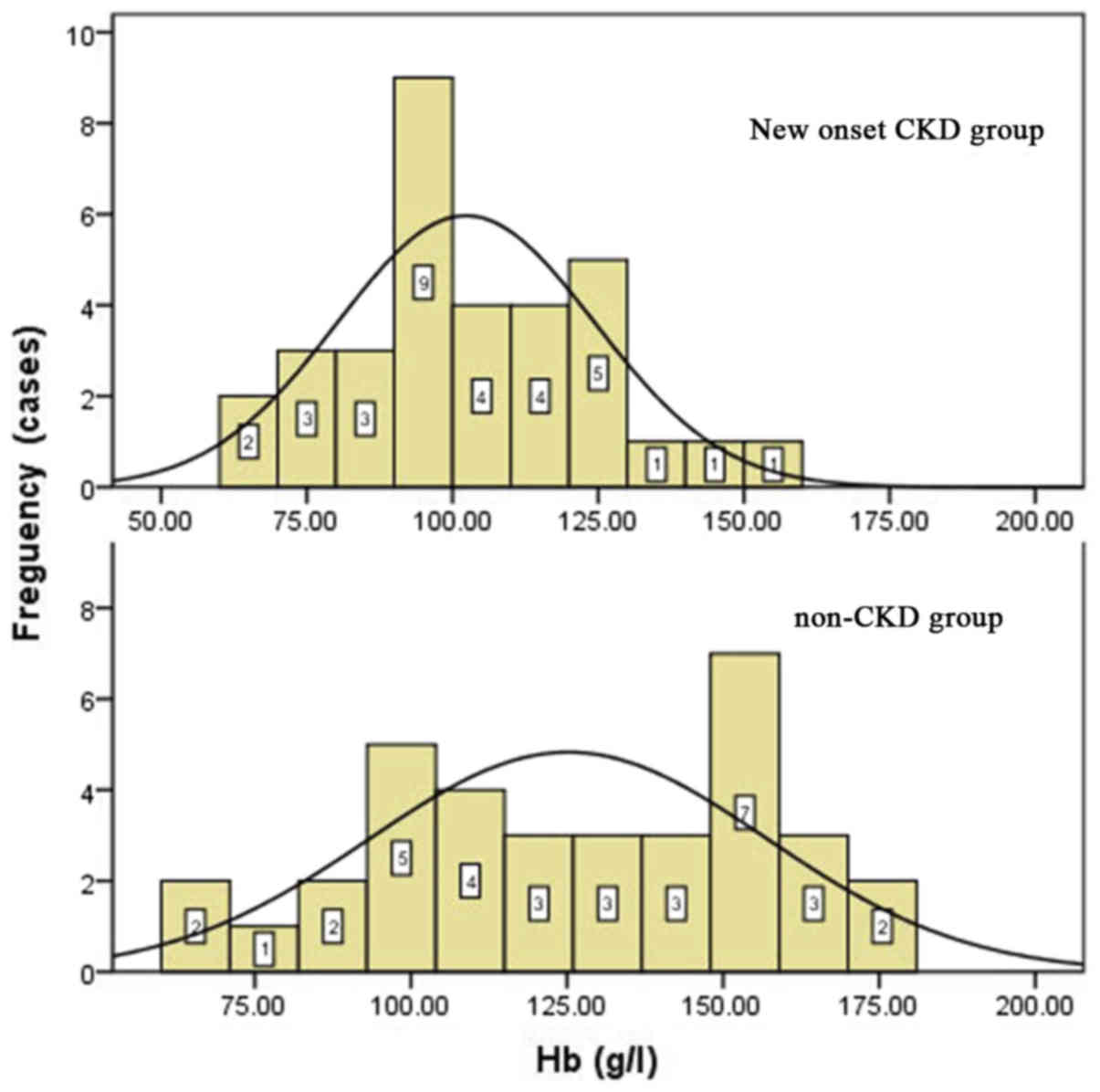
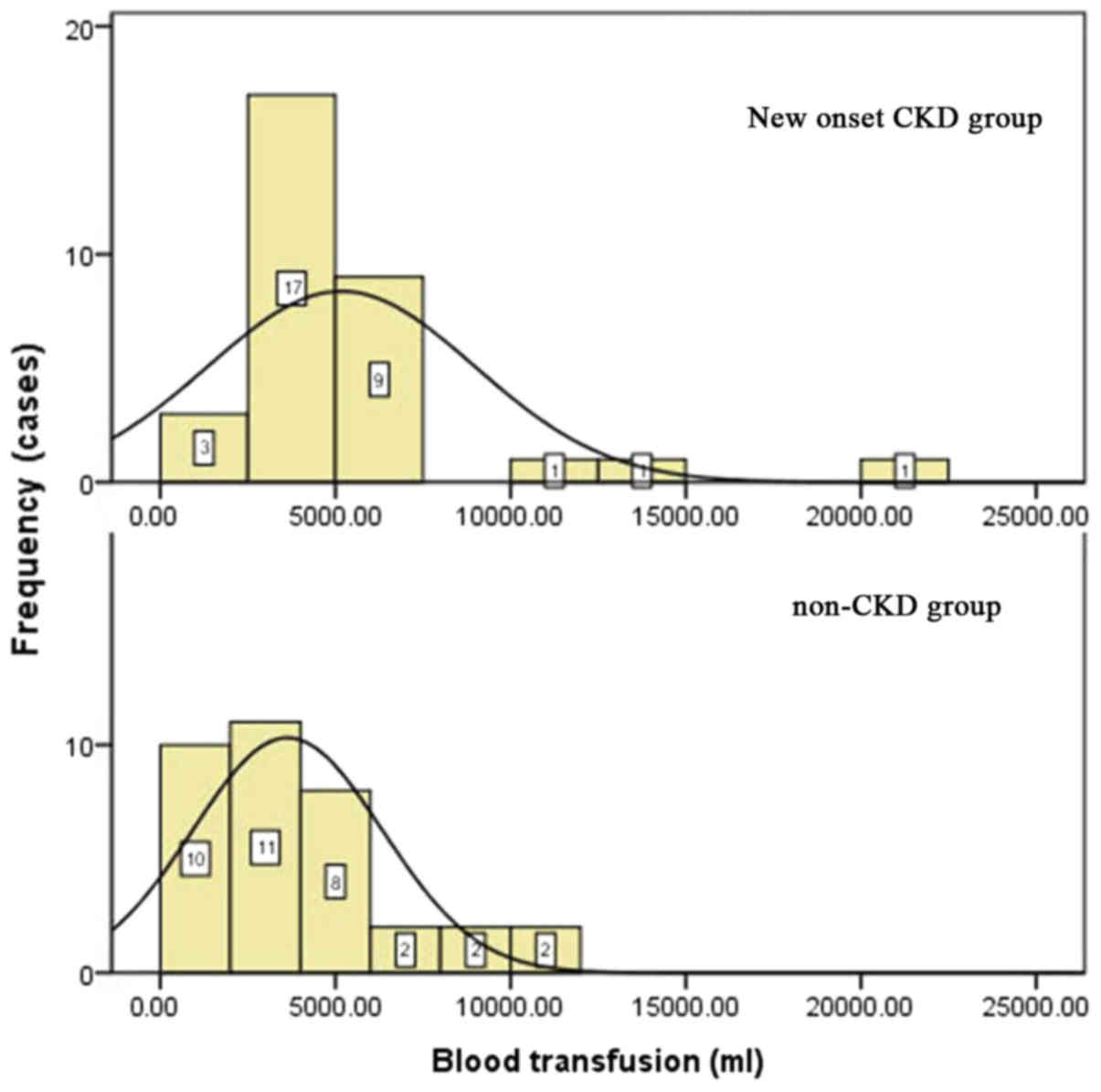
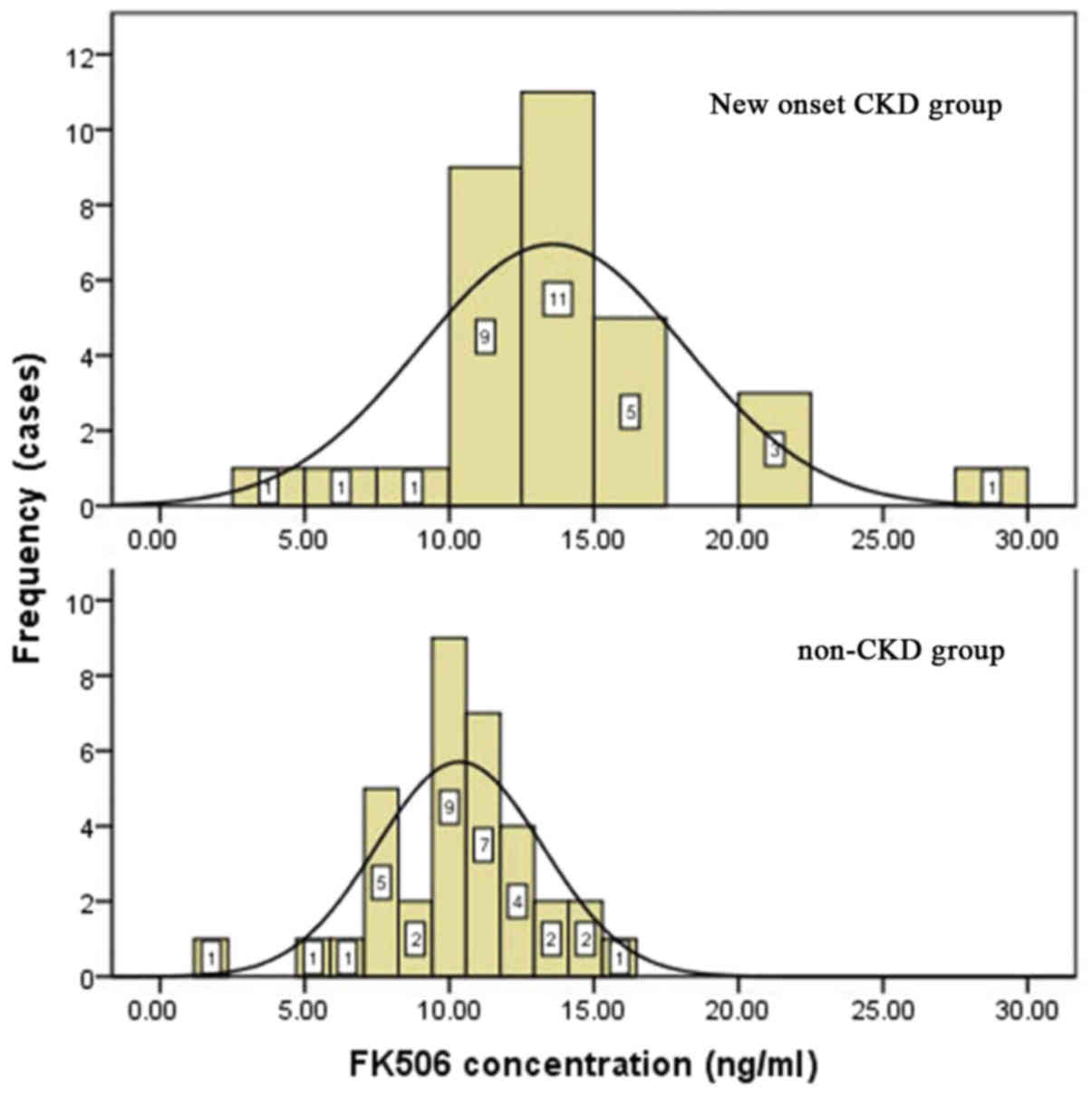
|
1
|
Kim WR, Smith JM, Skeans MA, Schladt DP,
Schnitzler MA, Edwards EB, Harper AM, Wainright JL, Snyder JJ,
Israni AK and Kasiske BL: OPTN/SRTR 2012 annual data report: Liver.
Am J Transplant. 14 Suppl 1:S69–S96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sharma P and Bari K: Chronic kidney
disease and related long-term complications following liver
transplantation. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 225:404–411. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weber ML, Ibrahim HN and Lake JR: Renal
dysfunction in liver transplant recipients: Evaluation of the
critical issues. Liver Transpl. 18:1290–1301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ruebner R, Goldberg D, Abt PL, Bahirwani
R, Levine M, Sawinski D, Bloom RD and Reese PP: Risk of end-stage
renal disease among liver transplant recipients with pretransplant
renal dysfunction. Am J Transplant. 12:2958–2965. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Israni AK, Xiong H, Liu J, Salkowski N,
Trotter JF, Snyder JJ and Kasiske BL: Predicting end-stage renal
disease after liver transplant. Am J Transplant. 13:1782–1792.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma P, Goodrich NP, Schaubel DE,
Guidinger MK and Merion RM: Patient-specific prediction of ESRD
after liver transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:2045–2052. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fischer L, Klempnauer J, Beckebaum S,
Metselaar HJ, Neuhaus P, Schemmer P, Settmacher U, Heyne N, Clavien
PA, Muehlbacher F, et al: A randomized, controlled study to assess
the conversion from calcineurin-inhibitors to everolimus after
liver transplantation-PROTECT. Am J Transplant. 12:1855–1865. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fabrizi F, Dixit V, Martin P and Messa P:
Chronic kidney disease after liver transplantation: Recent
evidence. Int J Artif Organs. 33:803–811. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li B, Chen B, Zhang G, Wang K, Zhou L and
Hu S: Cell apoptosis and Fas gene expression in liver and renal
tissues after ischemia-reperfusion injury in liver transplantation.
Transplant Proc. 42:pp. 1550–1556. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shao ZY, Yan LN, Wang WT, Li B, Wen TF,
Yang JY, Xu MQ, Zhao JC and Wei YG: Prophylaxis of chronic kidney
disease after liver transplantation - experience from west China.
World J Gastroenterol. 18:991–998. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morard I, Mentha G, Spahr L, Majno P,
Hadengue A, Huber O, Morel P and Giostra E: Long-term renal
function after liver transplantation is related to calcineurin
inhibitors blood levels. Clin Transplant. 20:96–101. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kubal C, Cockwell P, Gunson B, Jesky M,
Hanvesakul R, Dronavalli V, Bonser RS and Neil D: Chronic kidney
disease after nonrenal solid organ transplantation: A histological
assessment and utility of chronic allograft damage index scoring.
Transplantation. 93:406–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cantarovich M, Tchervenkov J, Paraskevas
S, Ghali P, Wong P, Deschênes M, Chaudhury P, Hassanain M,
Vrochides D, Metrakos P and Barkun J: Early changes in kidney
function predict long-term chronic kidney disease and mortality in
patients after liver transplantation. Transplantation.
92:1358–1363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee JP, Heo NJ, Joo KW, Yi NJ, Suh KS,
Moon KC, Kim SG and Kim YS: Risk factors for consequent kidney
impairment and differential impact of liver transplantation on
renal function. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:2772–2785. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Velidedeoglu E, Bloom RD, Crawford MD,
Desai NM, Campos L, Abt PL, Markmann JW, Mange KC, Olthoff KM,
Shaked A and Markmann JF: Early kidney dysfunction post liver
transplantation predicts late chronic kidney disease.
Transplantation. 77:553–556. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tinti F, Umbro I, Mecule A, Rossi M, Merli
M, Nofroni I, Corradini SG, Poli L, Pugliese F, Ruberto F, et al:
RIFLE criteria and hepatic function in the assessment of acute
renal failure in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc.
42:1233–1236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kamar N, Guilbeau-Frugier C, Servais A,
Tack I, Thervet E, Cointault O, Esposito L, Guitard J, Lavayssière
L, Muscari F, et al: Kidney histology and function in liver
transplant patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:2355–2361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim JY, Akalin E, Dikman S, Gagliardi R,
Schiano T, Bromberg J, Murphy B and de Boccardo G: The variable
pathology of kidney disease after liver transplantation.
Transplantation. 89:215–221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|