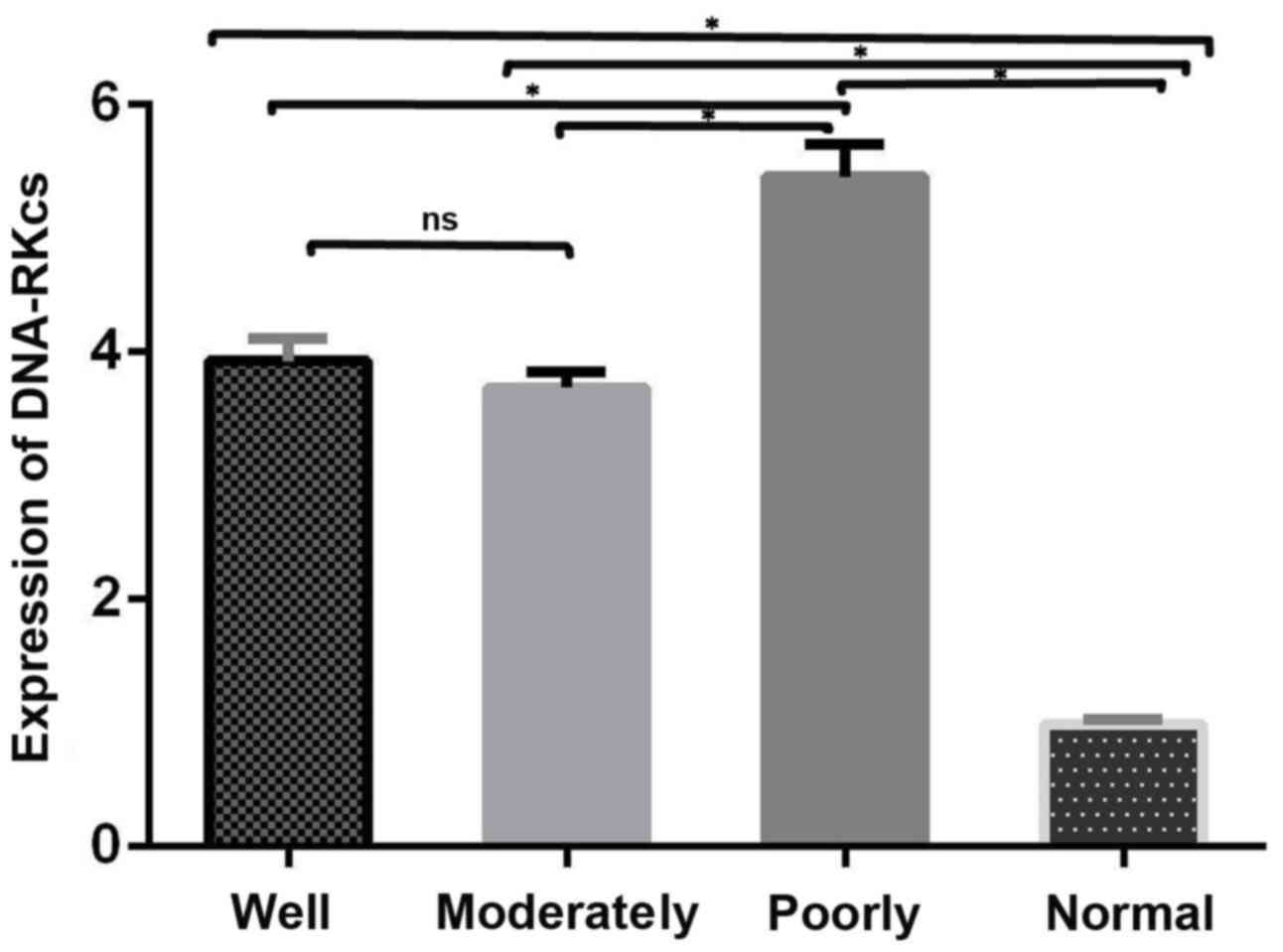
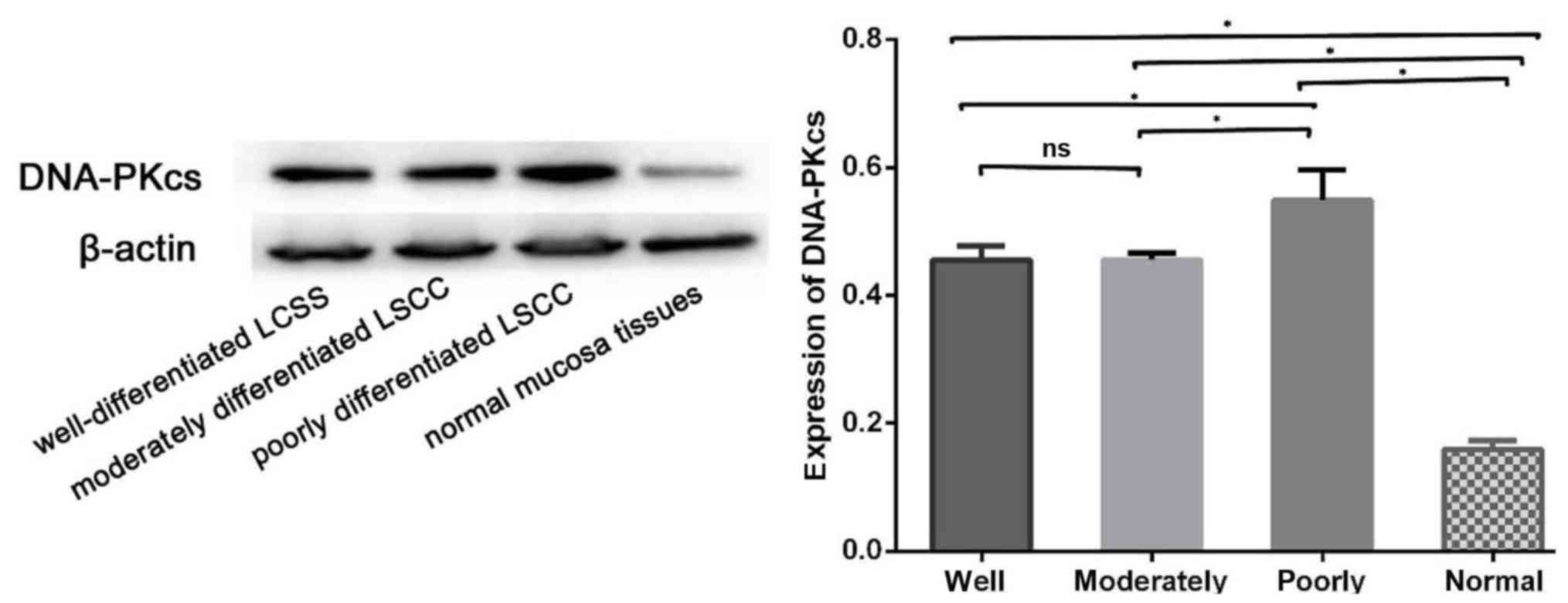
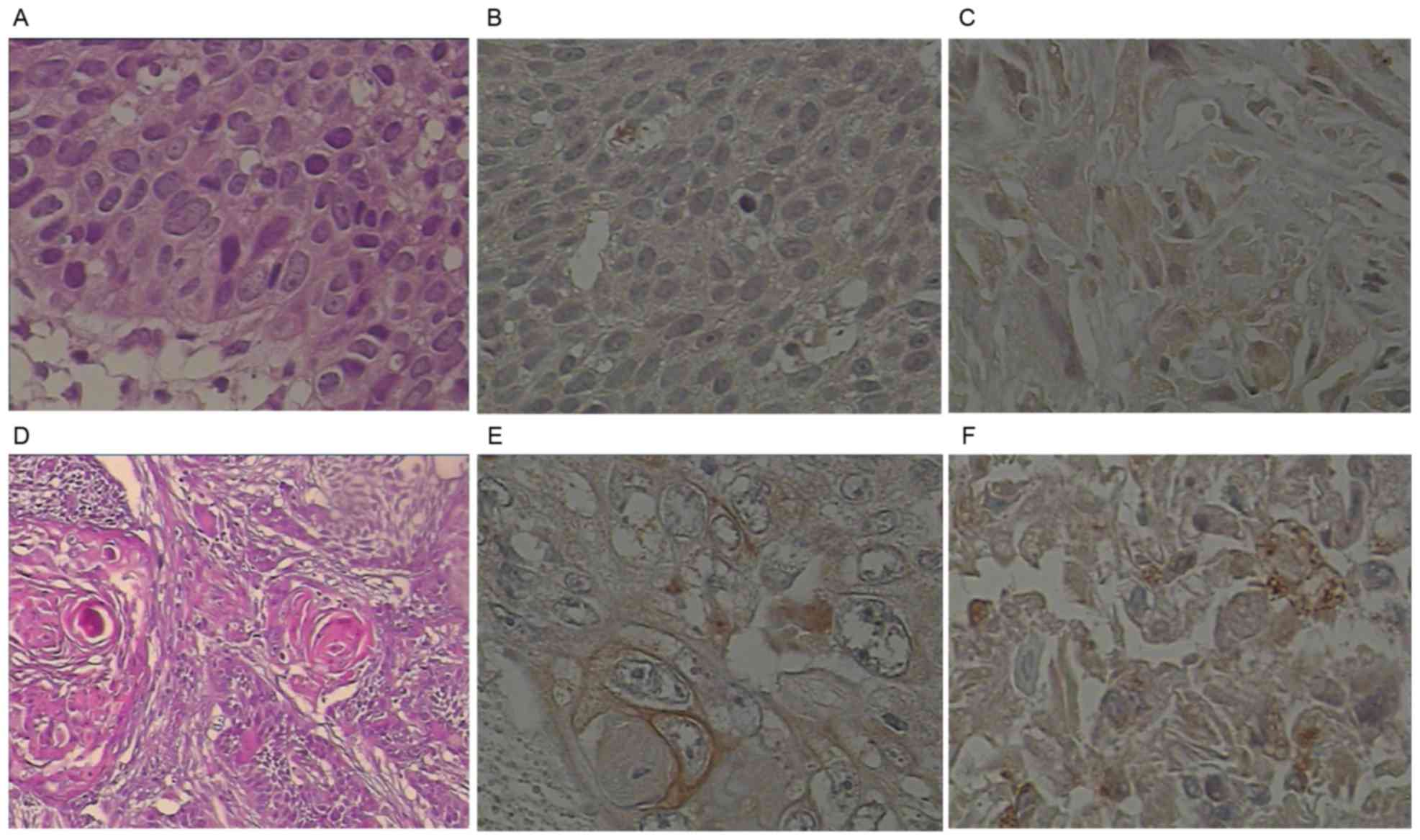
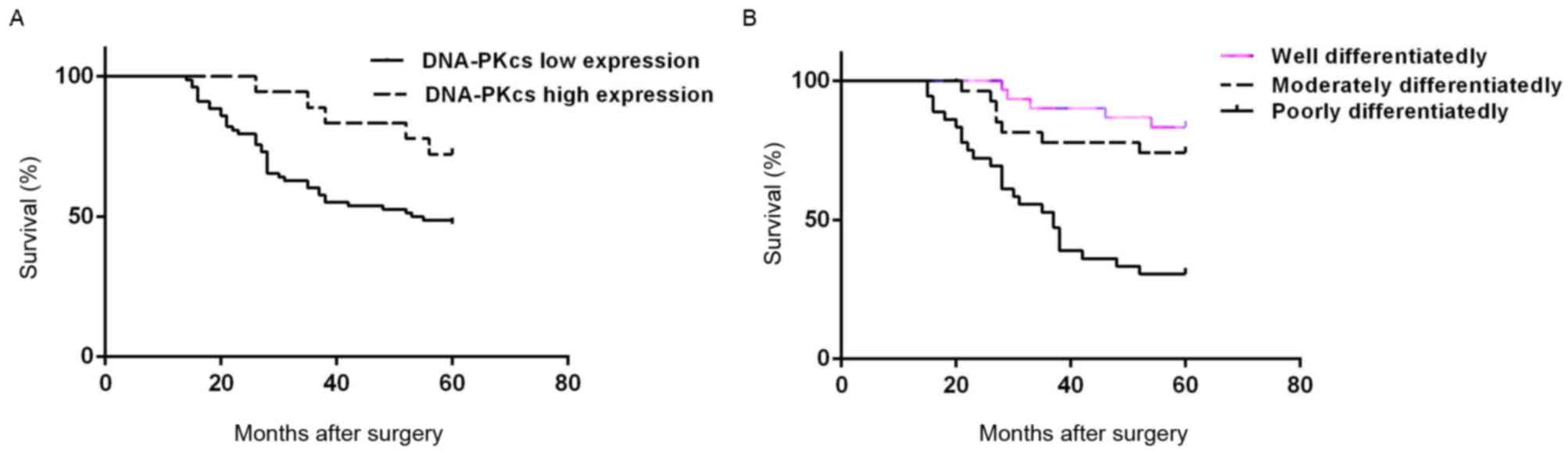
|
1
|
Mojica-Manosa P, Reidy J, Wilson K and
Douglas W: Larynx squamous cell carcinoma: Concepts and future
directions. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 13:99–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Almadori G, Bussu F, Cadoni G, Galli J,
Paludetti G and Maurizi M: Molecular markers in laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma: Towards an integrated clinicobiological approach.
Eur J Cancer. 41:683–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ou G, Itasaka S, Zeng L, Shibuya K, Yi J,
Harada H and Hiraoka M: Usefulness of HIF-1 imaging for determining
optimal timing of combining bevacizumab and radiotherapy. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:463–467. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
García-Fernández E, De Diego JI,
Collantes-Bellido E, Mendiola M, Prim MP, Pérez-Fernández E,
Miguel-Martín M, Nistal M and Hardisson D: Aurora B kinase
expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and its prognostic
implications. Histopathology. 58:368–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi Y, Gong HL, Zhou L, Tian J and Wang Y:
CD24: A novel cancer biomarker in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 74:78–85. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong X, Shen Y, Jiang N, Fei X and Mi J:
Emerging roles of DNA-PK besides DNA repair. Cell Signal.
23:1273–1280. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neal JA and Meek K: Choosing the right
path: Does DNA-PK help make the decision. Mutat Res. 711:73–86.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hill R and Lee PW: The DNA-dependent
protein kinase (DNA-PK): More than just a case of making ends meet.
Cell Cycle. 9:3460–3469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meek K, Dang V and Lees-Miller SP: DNA-PK:
The means to justify the ends. Adv Immunol. 99:33–58. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Salles B, Calsou P, Frit P and Muller C:
The DNA repair complex DNA-PK, a pharmacological target in cancer
chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Pathol Biol (Paris). 54:185–193.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang J, Xu X, Hao Y, Chen J, Lu H, Qin J,
Peng L and Chen B: Expression of DNA-PKcs and BRCA1 as prognostic
indicators in nasopharyngeal carcinoma following
intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Oncol Lett. 5:1199–1204.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gottlieb TM and Jackson SP: The
DNA-dependent protein kinase: Requirement for DNA ends and
association with Ku antigen. Cell. 72:131–142. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ren JH, Dai XF, Yan GL, Jin M, Liu CW,
Yang KY, Wu G and Ma CM: Acute oral mucositis in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy: Association with
genetic polymorphism in DNA DSB repair genes. Int J Radiat Biol.
90:256–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jackson SP: Sensing and repairing DNA
double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis. 23:687–696. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hosoi Y, Watanabe T, Nakagawa K, Matsumoto
Y, Enomoto A, Morita A, Nagawa H and Suzuki N: Up-regulation of
DNA-dependent protein kinase activity and Sp1 in colorectal cancer.
Int J Oncol. 25:461–468. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shintani S, Mihara M, Li C, Nakahara Y,
Hino S, Nakashiro K and Hamakawa H: Up-regulation of DNA-dependent
protein kinase correlates with radiation resistance in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 94:894–900. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Um JH, Kwon JK, Kang CD, Kim MJ, Ju DS,
Bae JH, Kim DW, Chung BS and Kim SH: Relationship between
antiapoptotic molecules and metastatic potency and the involvement
of DNA-dependent protein kinase in the chemosensitization of
metastatic human cancer cells by epidermal growth factor receptor
blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 311:1062–1070. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tonotsuka N, Hosoi Y, Miyazaki S, Miyata
G, Sugawara K, Mori T, Ouchi N, Satomi S, Matsumoto Y, Nakagawa K,
et al: Heterogeneous expression of DNA-dependent protein kinase in
esophageal cancer and normal epithelium. Int J Mol Med. 18:441–447.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moll U, Lau R, Sypes MA, Gupta MM and
Anderson CW: DNA-PK, the DNA-activated protein kinase, is
differentially expressed in normal and malignant human tissues.
Oncogene. 18:3114–3126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sallmyr A, Miller A, Gabdoulkhakova A,
Safronova V, Henriksson G and Bredberg A: Expression of
DNA-dependent protein kinase in human granulocytes. Cell Res.
14:331–340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Holgersson A, Erdal H, Nilsson A,
Lewensohn R and Kanter L: Expression of DNA-PKcs and Ku86, but not
Ku70, differs between lymphoid malignancies. Exp Mol Pathol.
77:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van der Burg M, van Dongen JJ and van Gent
DC: DNA-PKcs deficiency in human: Long predicted, finally found.
Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 9:503–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hsu FM, Zhang S and Chen BP: Role of
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit in cancer
development and treatment. Transl Cancer Res. 1:22–34.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Razek AA and Huang BY: Soft tissue tumors
of the head and neck: Imaging-based review of the WHO
classification. Radiographics. 31:1923–1954. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Method. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xu LZ and Yang WT: The criteria for
judging the results of immunohistochemical reaction. Zhong Guo Ai
Zheng Za Zhi. 6:229–231. 1996.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Takata M, Sasaki MA, Sonoda E, Morrison C,
Hashimoto M, Utsumi H, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, Shinohara A and Takeda S:
Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways of
DNA double-strand bread repair have overlapping roles in the
maintenance of chromosomal integrity in vertebrate cells. EMBO J.
17:5497–5508. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rothkamm K, Kühne M, Jeggo PA and Löbrich
M: Radiation-induced genomic rearrangement formed nonhomologous end
-joining of DNA double-strand breaks. Cancer Res. 61:3886–2893.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bouchaert P, Guerif S, Debiais C, Irani J
and Fromont G: DNA-PKcs expression predicts response to
radiotherapy in prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
84:1179–1185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee HS, Choe G, Park KU, Park DJ, Yang HK,
Lee BL and Kim WH: Altered expression of DNA-dependent protein
kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) during gastric carcinogenesis
and its clinical implications on gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
31:859–866. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nacht M, Strasser A, Chan YR, Harris AW,
Schlissel M, Bronson RT and Jacks T: Mutations in the p53 and SCID
genes cooperate in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 15:2055–2066. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Treilleux I, Chapot B, Goddard S, Pisani
P, Angèle S and Hall J: The molecular causes of low ATM protein
expression in breast carcinoma; promoter methylation and levels of
the catalytic subunit of DNA-dependent protein kinase.
Histopathology. 51:63–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Someya M, Sakata K, Matsumoto Y, Yamamoto
H, Monobe M, Ikeda H, Ando K, Hosoi Y, Suzuki N and Hareyama M: The
association of DNA-dependent protein kinase activity with
chromosomal instability and risk cancer. Carcinohenesis.
27:117–122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Carter T, Vancurová I, Sun I, Lou W and
DeLeon S: A DNA-activated protein kinase from HeLa cell nuclei. Mol
Cell Boil. 10:6460–6471. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ren F, Yang ZL, Tan X, Liu D, Zou Q, Yuan
Y, Li J, Liang L, Zeng G and Chen S: DNA-PKcs and Ku70 are
predictive markers for poor prognosis of patients with gall bladder
malignancies. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 22:741–747. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Abdel-Fatah T, Arora A, Agarwal D, Moseley
P, Perry C, Thompson N, Green AR, Rakha E, Chan S, Ball G, et al:
Adverse prognostic and predictive significance of low DNA-PKcs
expression in early-stage breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
146:309–320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|