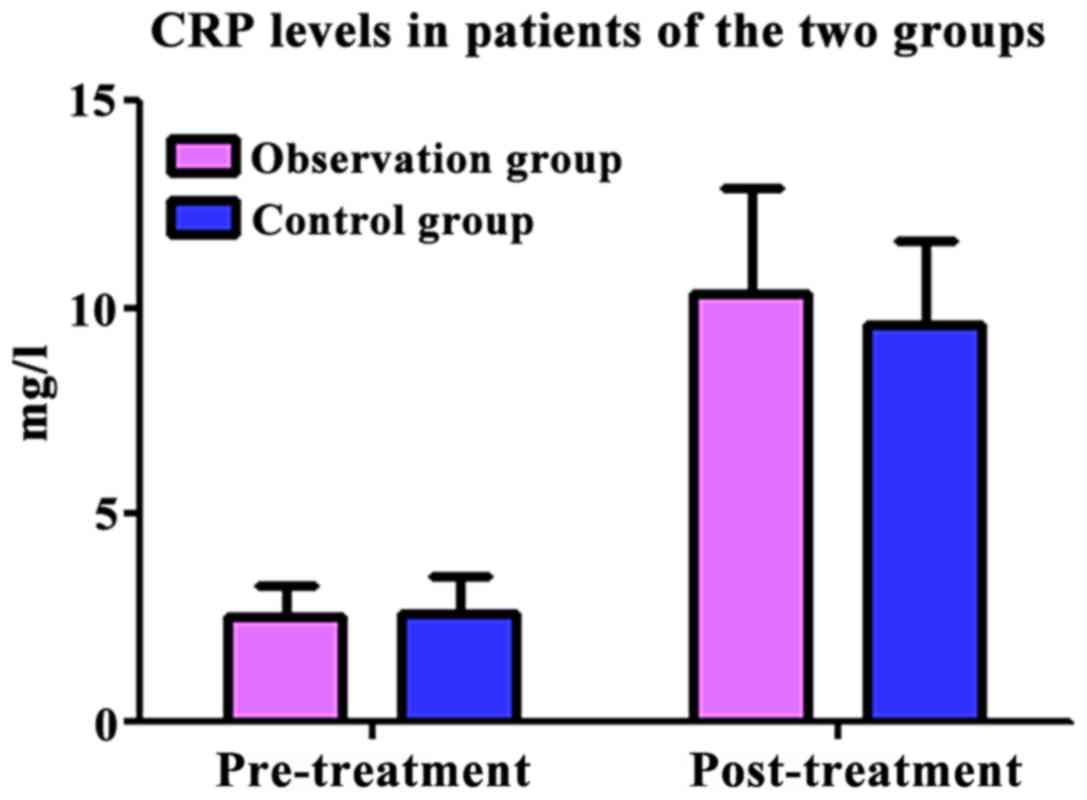
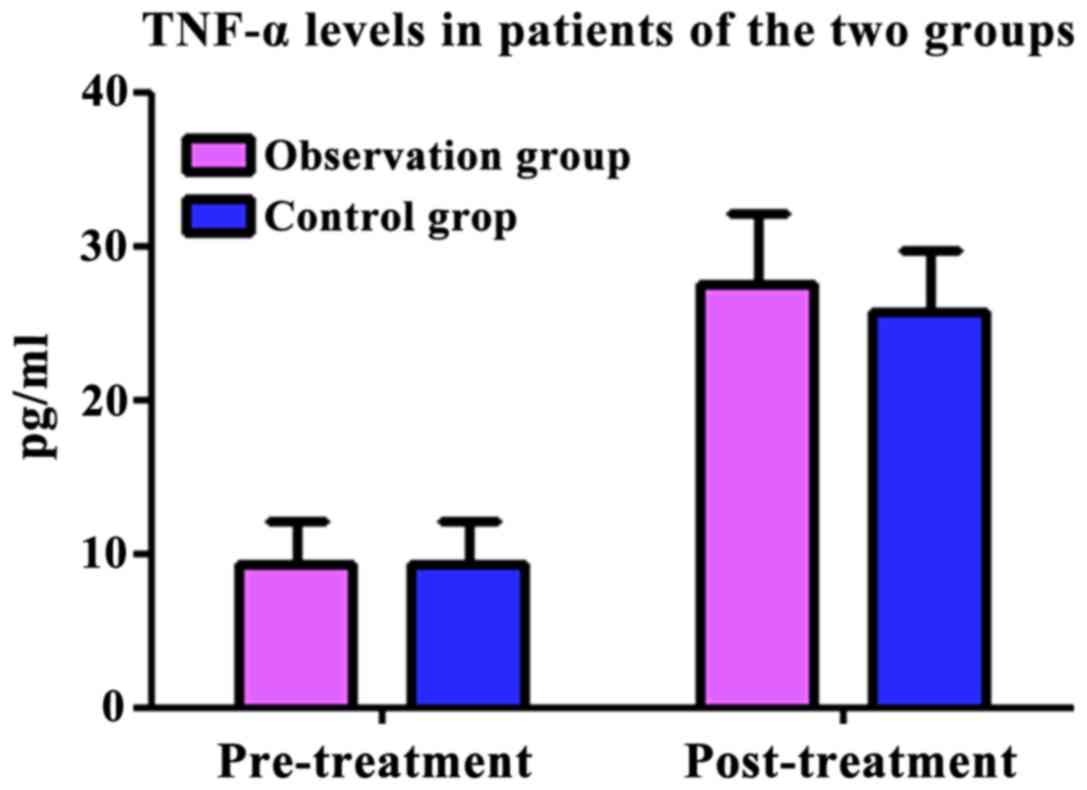
|
1
|
Siah TW and Hampton PJ: The effectiveness
of tap water iontophoresis for palmoplantar hyperhidrosis using a
Monday, Wednesday, and Friday treatment regime. Dermatol Online J.
19:142013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hougaard MG and Thyssen JP: Treatment of
hand eczema caused by hyperhidrosisTextbook of Hand Eczema. Alikhan
A, Lachapelle JM and Maibach H: Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg: pp.
361–370. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ak M, Dinçer D, Haciomeroglu B, Akarsu S,
Lapsekili N and Ada S: The evaluation of primary idiopathic focal
hyperhidrosis patients in terms of alexithymia. J Health Psychol.
18:704–710. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yanagishita T, Tamada Y, Ohshima Y, Ito K,
Akita Y and Watanabe D: Histological localization of aluminum in
topical aluminum chloride treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. J
Dermatol Sci. 67:69–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rieger R, Loureiro MP, Pedevilla S and de
Oliveira RA: Endoscopic lumbar sympathectomy following thoracic
sympathectomy in patients with palmoplantar hyperhidrosis. World J
Surg. 35:49–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inoue M, Yokoyama T, Ishii A, Watanabe T,
Yamato T and Kumon H: The effect of hochuekkito on female stress
urinary incontinence. Kampo Med. 61:853–855. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Inukai YS, Iwase S, Shimizu Y and Sato M,
Nishimura N, Onizuka C, Kuwahara Y, Sugenoya J and Sato M:
Pathogenesis of the hemifacial hyperhidrosis. J Neurol Sci.
333:e712–e713. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Weitz G, Elam M, Born J, Fehm HL and Dodt
C: Postmenopausal estrogen administration suppresses muscle
sympathetic nerve activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:344–348.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nedvetsky PI, Emmerson E, Finley JK,
Ettinger A, Cruz-Pacheco N, Prochazka J, Haddox CL, Northrup E,
Hodges C, Mostov KE, et al: Parasympathetic innervation regulates
tubulogenesis in the developing salivary gland. Dev Cell.
30:449–462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cerfolio RJ, De Campos JR, Bryant AS,
Connery CP, Miller DL, DeCamp MM, McKenna RJ and Krasna MJ: The
Society of Thoracic Surgeons expert consensus for the surgical
treatment of hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 91:1642–1648. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wolosker N, Schvartsman C, Krutman M,
Campbell TP, Kauffman P, de Campos JR and Puech-Leão P: Efficacy
and quality of life outcomes of oxybutynin for treating palmar
hyperhidrosis in children younger than 14 years old. Pediatr
Dermatol. 31:48–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bovell DL, MacDonald A, Meyer BA, Corbett
AD, MacLaren WM, Holmes SL and Harker M: The secretory clear cell
of the eccrine sweat gland as the probable source of excess sweat
production in hyperhidrosis. Exp Dermatol. 20:1017–1020. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuncu G, Turk F, Ozturk G and Atinkaya C:
Comparison of only T3 and T3-T4 sympathectomy for axillary
hyperhidrosis regarding treatment effect and compensatory sweating.
Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 17:263–267. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mazzocchio R and Caleo M: More than at the
neuromuscular synapse: Actions of botulinum neurotoxin A in the
central nervous system. Neuroscientist. 21:44–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Zeng L, An Z, Wang L and Hu J:
Minimally invasive thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis
via a single unilateral incision approach by the pleura videoscope.
J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 24:328–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nishiofuku H, Tanaka T, Marugami N, Sho M,
Akahori T, Nakajima Y and Kichikawa K: Increased tumour ADC value
during chemotherapy predicts improved survival in unresectable
pancreatic cancer. Eur Radiol. 26:1835–1842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qin CF and Zhao FL: Long non-coding RNA
TUG1 can promote proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer
via EMT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:2377–2384.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Christensen MB, Eriksen T and
Kjelgaard-Hansen M: C-reactive protein: quantitative marker of
surgical trauma and post-surgical complications in dogs: a
systematic review. Acta Vet Scand. 57:712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mauer J, Chaurasia B, Goldau J, Vogt MC,
Ruud J, Nguyen KD, Theurich S, Hausen AC, Schmitz J, Brönneke HS,
et al: Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of
macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance
to insulin. Nat Immunol. 15:423–430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zigmond E, Bernshtein B, Friedlander G,
Walker CR, Yona S, Kim KW, Brenner O, Krauthgamer R, Varol C,
Müller W, et al: Macrophage-restricted interleukin-10 receptor
deficiency, but not IL-10 deficiency, causes severe spontaneous
colitis. Immunity. 40:720–733. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
DeBerge MP, Ely KH and Enelow RI: Soluble,
but not transmembrane, TNF-α is required during influenza infection
to limit the magnitude of immune responses and the extent of
immunopathology. J Immunol. 192:5839–5851. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|