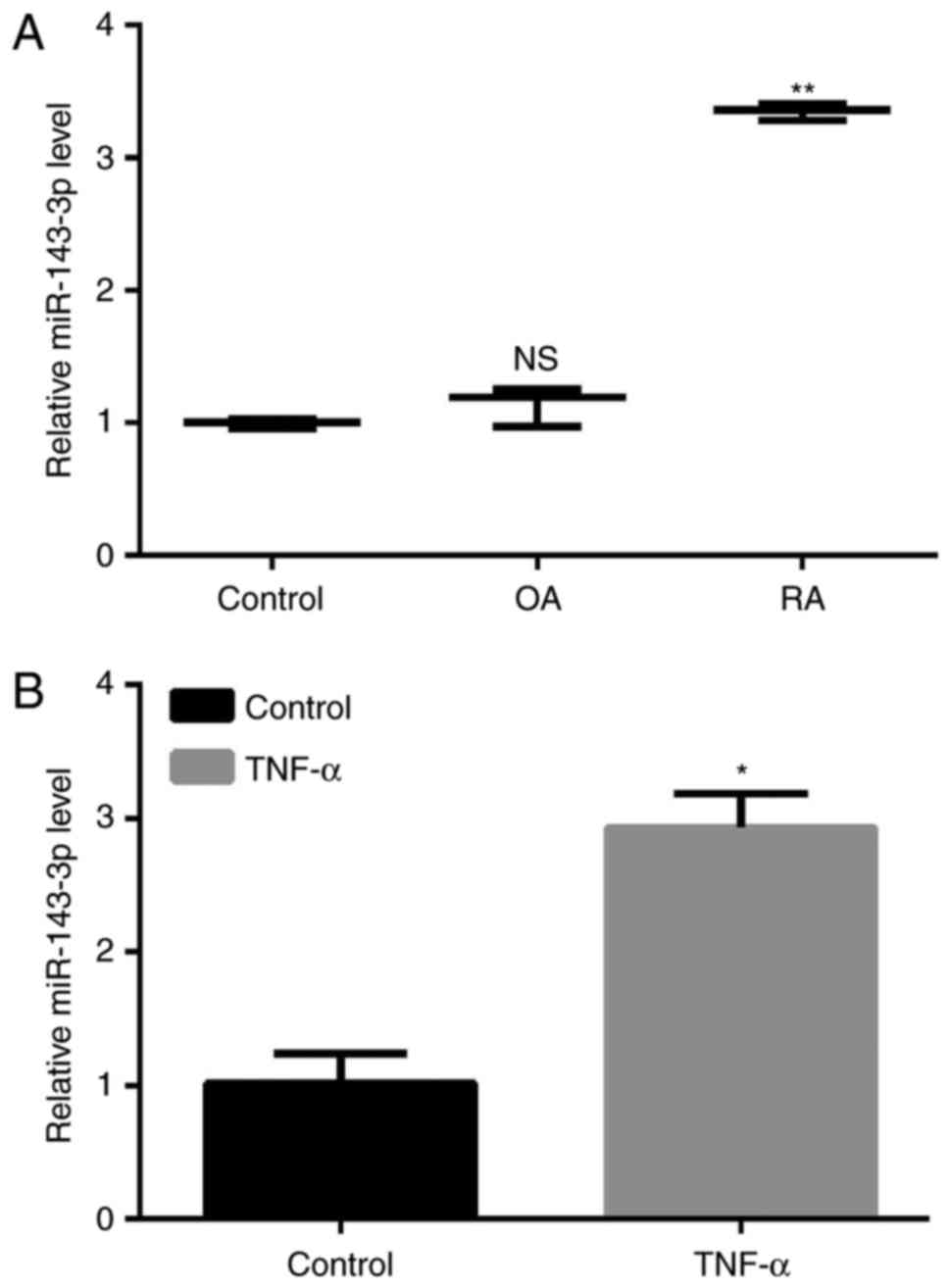
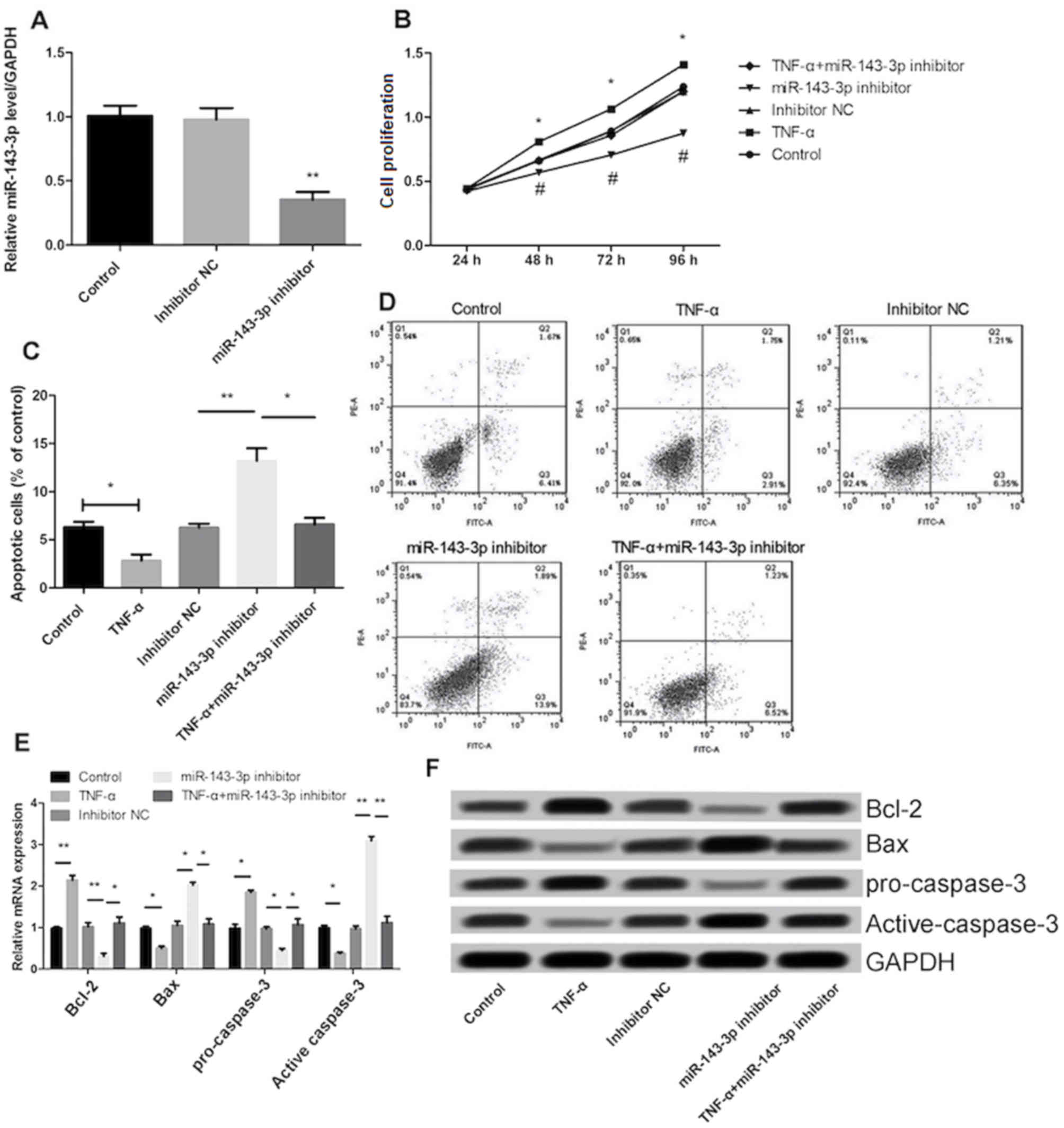
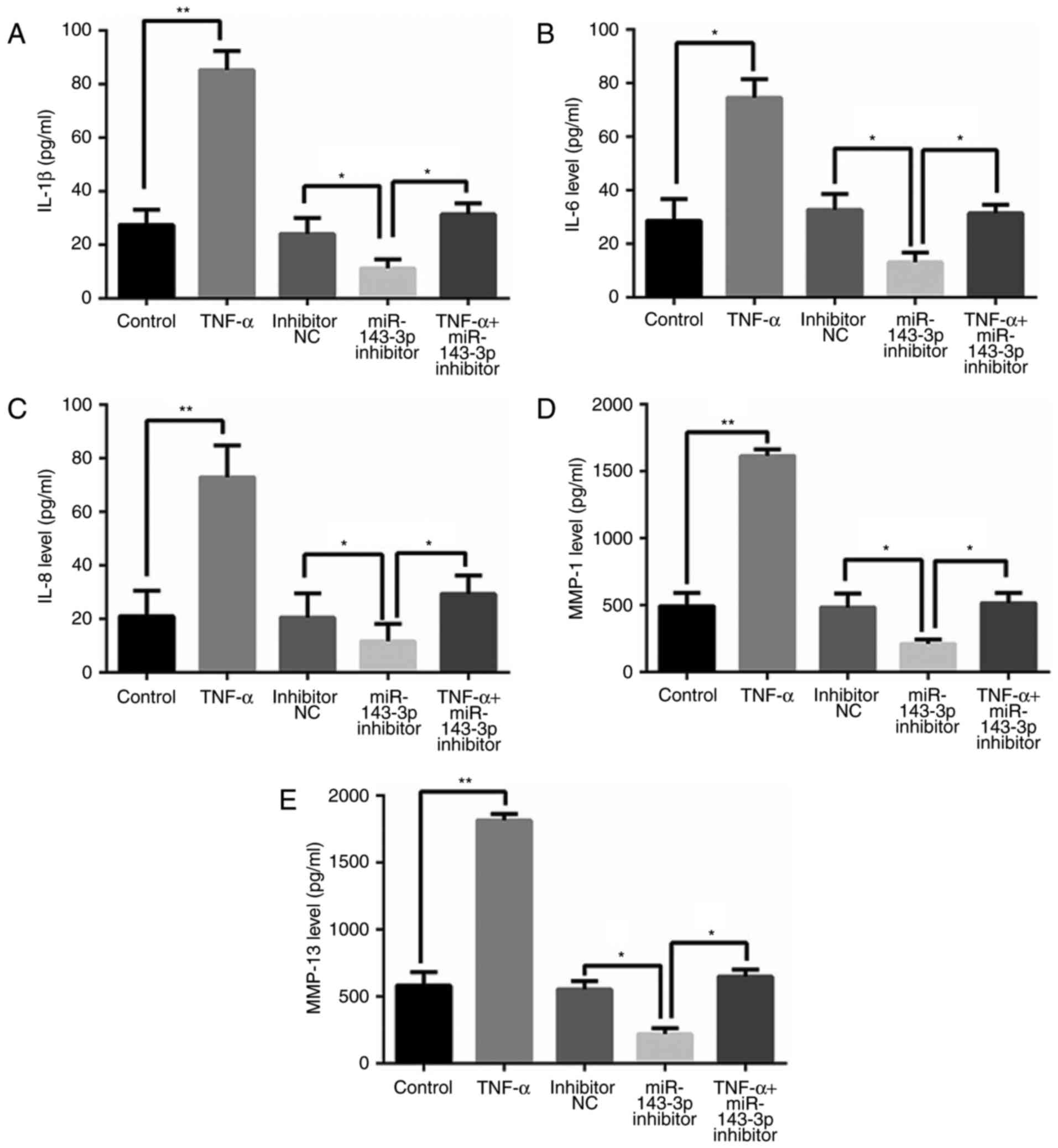
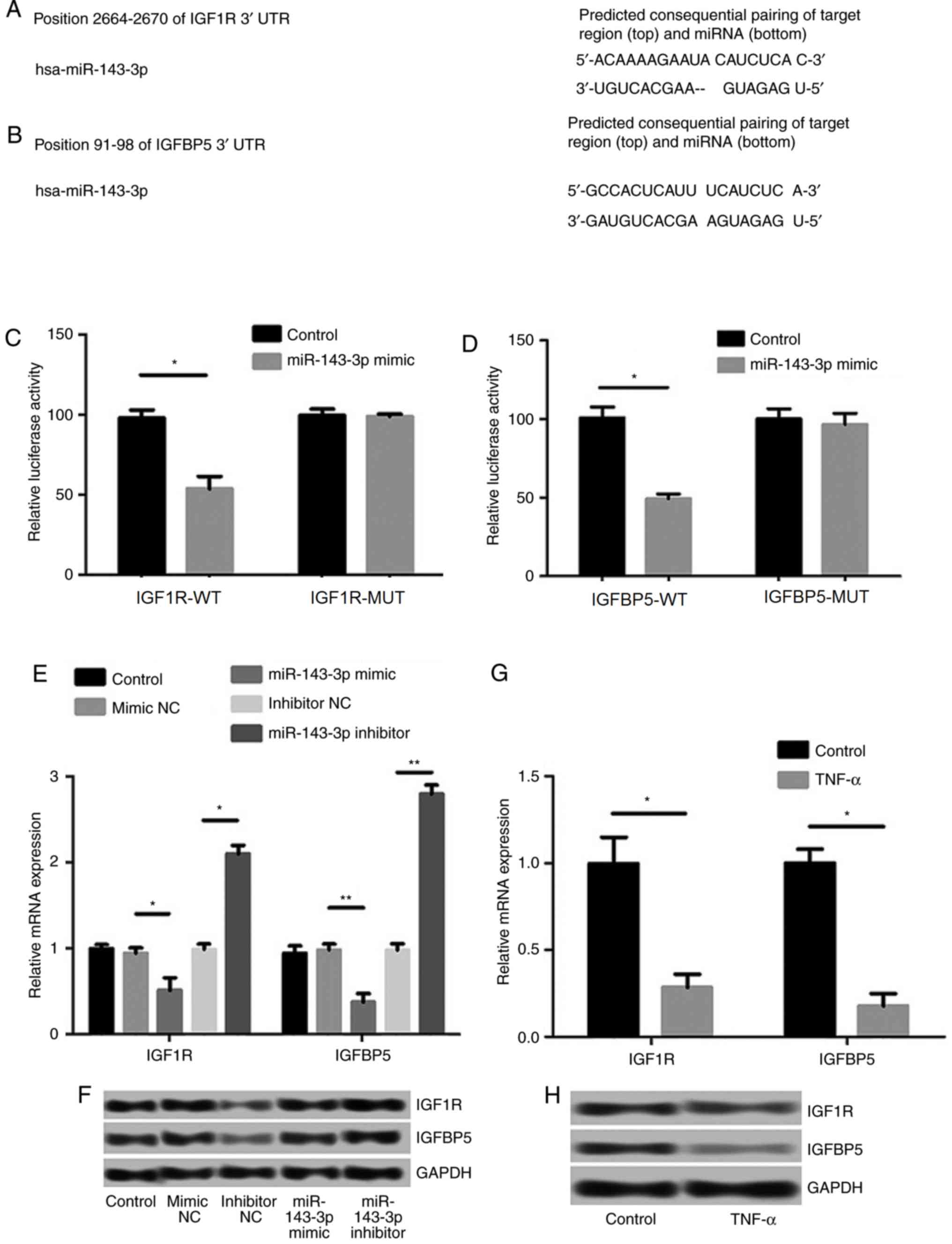
|
1
|
Mertsch S, Schmitz N, Jeibmann A, Geng JG,
Paulus W and Senner V: Slit2 involvement in glioma cell migration
is mediated by Robo1 receptor. J Neurooncol. 87:1–7. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Challal S, Minichiello E, Boissier MC and
Semerano L: Cachexia and adiposity in rheumatoid arthritis.
Relevance for disease management and clinical outcomes. Joint Bone
Spine. 83:127–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ji L, Geng Y, Zhou W and Zhang Z: A study
on relationship among apoptosis rates, number of peripheral T cell
subtypes and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum
Dis. 19:167–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis and cartilage:
The role of cytokines. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2:459–465. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okada Y, Naka K, Kawamura K, Matsumoto T,
Nakanishi I, Fujimoto N, Sato H and Seiki M: Localization of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (92-kilodalton gelatinase/type IV
collagenase=gelatinase B) in osteoclasts: Implications for bone
resorption. Lab Invest. 72:311–322. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Symmons DP: Epidemiology of rheumatoid
arthritis: Determinants of onset, persistence and outcome. Best
Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 16:707–722. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muller-Ladner U, Kriegsmann J, Franklin
BN, Matsumoto S, Geiler T, Gay RE and Gay S: Synovial fibroblasts
of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attach to and invade normal
human cartilage when engrafted into SCID mice. Am J Pathol.
149:1607–1615. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay
S and Pap T: Synovial fibroblasts: Key players in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:669–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lowin T and Straub RH: Synovial
fibroblasts integrate inflammatory and neuroendocrine stimuli to
drive rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 11:1069–1071.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McInnes IB and Schett G: Pathogenetic
insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet.
389:2328–2337. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Edhayan G, Ohara RA, Stinson WA, Amin MA,
Isozaki T, Ha CM, Haines GK III, Morgan R, Campbell PL, Arbab AS,
et al: Inflammatory properties of inhibitor of DNA binding 1
secreted by synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis
Res Ther. 18:872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Turner JD and Filer A: The role of the
synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 27:175–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada
T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N and Shiekhattar R: The Microprocessor
complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 432:235–240.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis BP,
Johnston WK, Lim LP, Burge CB and Bartel DP: The widespread impact
of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science.
310:1817–1821. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ambros V: MicroRNAs and developmental
timing. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 21:511–517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ammari M, Jorgensen C and Apparailly F:
Impact of microRNAs on the understanding and treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 25:225–233. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Olivieri F, Rippo MR, Procopio AD and
Fazioli F: Circulating inflamma-miRs in aging and age-related
diseases. Front Genet. 4:1212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: Impaired
micro-RNA pathways diminish osteoclast differentiation and
function. J Biol Chem. 284:4667–4678. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He Z, Yi J, Liu X, Chen J, Han S, Jin L,
Chen L and Song H: MiR-143-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by
regulating cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by targeting QKI-5 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 15:512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Soriano-Arroquia A, McCormick R, Molloy
AP, McArdle A and Goljanek-Whysall K: Age-related changes in
miR-143-3p: Igfbp5 interactions affect muscle regeneration. Aging
Cell. 15:361–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schett G, Zwerina J and Firestein G: The
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:909–916. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawasaki T, Inoue K, Ushiyama T and Fukuda
S: Assessment of the American College of Rheumatology criteria for
the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the knee.
Ryumachi. 38:2–5. 1998.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miyazawa K, Mori A and Okudaira H:
Establishment and characterization of a novel human rheumatoid
fibroblast-like synoviocyte line, MH7A, immortalized with SV40 T
antigen. J Biochem. 124:1153–1162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jia Q, Cheng W, Yue Y, Hu Y, Zhang J, Pan
X, Xu Z and Zhang P: Cucurbitacin E inhibits TNF-α-induced
inflammatory cytokine production in human synoviocyte MH7A cells
via suppression of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathways. Int Immunopharmacol.
29:884–890. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen H, Lin YW, Mao YQ, Wu J, Liu YF,
Zheng XY and Xie LP: MicroRNA-449a acts as a tumor suppressor in
human bladder cancer through the regulation of pocket proteins.
Cancer Lett. 320:40–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao X, Liu D, Gong W, Zhao G, Liu L, Yang
L and Hou Y: The toll-like receptor 3 ligand, poly(I:C), improves
immunosuppressive function and therapeutic effect of mesenchymal
stem cells on sepsis via inhibiting MiR-143. Stem Cells.
32:521–533. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song T, Zhang X, Wang C, Wu Y, Cai W, Gao
J and Hong B: MiR-138 suppresses expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1alpha (HIF-1α) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 786-O
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1307–1311. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ruedel A, Dietrich P, Schubert T,
Hofmeister S, Hellerbrand C and Bosserhoff AK: Expression and
function of microRNA-188-5p in activated rheumatoid arthritis
synovial fibroblasts. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4953–4962.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Le XF, Merchant O, Bast RC and Calin GA:
The roles of MicroRNAs in the cancer invasion-metastasis cascade.
Cancer Microenviron. 3:137–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin H, Tan W, Zhang Z, Bao L, Shen H, Wang
F, Xu F and Wang Z: 15d-prostaglandin J2 protects cortical neurons
against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury:
Involvement of inhibiting autophagy through upregulation of Bcl-2.
Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:303–312. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang H and Li W: Dysregulation of
micro-143-3p and BALBP1 contributes to the pathogenesis of the
development of ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 36:3605–3610. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wegner N, Lundberg K, Kinloch A, Fisher B,
Malmström V, Feldmann M and Venables PJ: Autoimmunity to specific
citrullinated proteins gives the first clues to the etiology of
rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 233:34–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hwang SY, Kim JY, Kim KW, Park MK, Moon Y,
Kim WU and Kim HY: IL-17 induces production of IL-6 and IL-8 in
rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via NF-kappaB- and
PI3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 6:R120–R128.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Erlandsson MC, Töyrä Silfverswärd S,
Nadali M, Turkkila M, Svensson MND, Jonsson IM, Andersson KME and
Bokarewa MI: IGF-1R signalling contributes to IL-6 production and T
cell dependent inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:2158–2170. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tardif G, Hum D, Pelletier JP, Duval N and
Martel-Pelletier J: Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by
the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic
chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 10:1482009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhu C, Qi X, Chen Y, Sun B, Dai Y and Gu
Y: PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in
IGF-1-induced VEGF-C upregulation in breast cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 137:1587–1594. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Z, Li C, Du L, Zhou Y and Wu W: Human
chorionic gonadotropin beta induces migration and invasion via
activating ERK1/2 and MMP-2 in human prostate cancer DU145 cells.
PLoS One. 8:e545922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liedert A, Kaspar D, Blakytny R, Claes L
and Ignatius A: Signal transduction pathways involved in
mechanotransduction in bone cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
349:1–5. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Perdiguero E, Ruiz-Bonilla V, Gresh L, Hui
L, Ballestar E, Sousa-Victor P, Baeza-Raja B, Jardí M, Bosch-Comas
A, Esteller M, et al: Genetic analysis of p38 MAP kinases in
myogenesis: Fundamental role of p38alpha in abrogating myoblast
proliferation. EMBO J. 26:1245–1256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hong C, Shen C, Ding H, Huang S, Mu Y, Su
H, Wei W, Ma J and Zheng F: An involvement of SR-B1 mediated p38
MAPK signaling pathway in serum amyloid A-induced angiogenesis in
rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 66:340–345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li CH, Xu LL, Zhao JX, Sun L, Yao ZQ, Deng
XL, Liu R, Yang L, Xing R and Liu XY: CXCL16 upregulates RANKL
expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through the
JAK2/STAT3 and p38/MAPK signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 65:193–202.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang ZC, Lu H, Zhou Q, Yu SM, Mao YL,
Zhang HJ, Zhang PC and Yan WJ: MiR-451 inhibits synovial
fibroblasts proliferation and inflammatory cytokines secretion in
rheumatoid arthritis through mediating p38MAPK signaling pathway.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14562–14567. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|