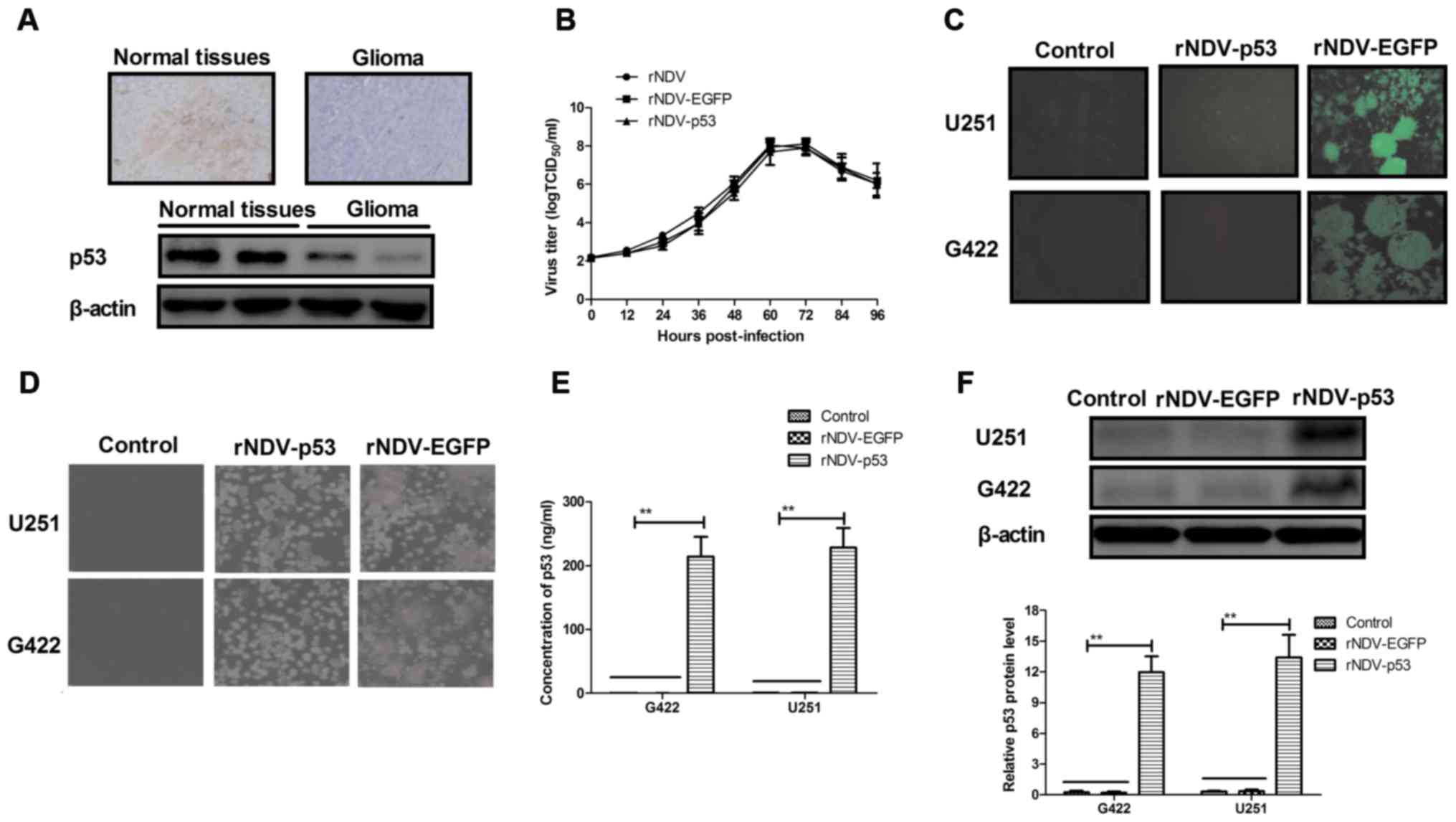
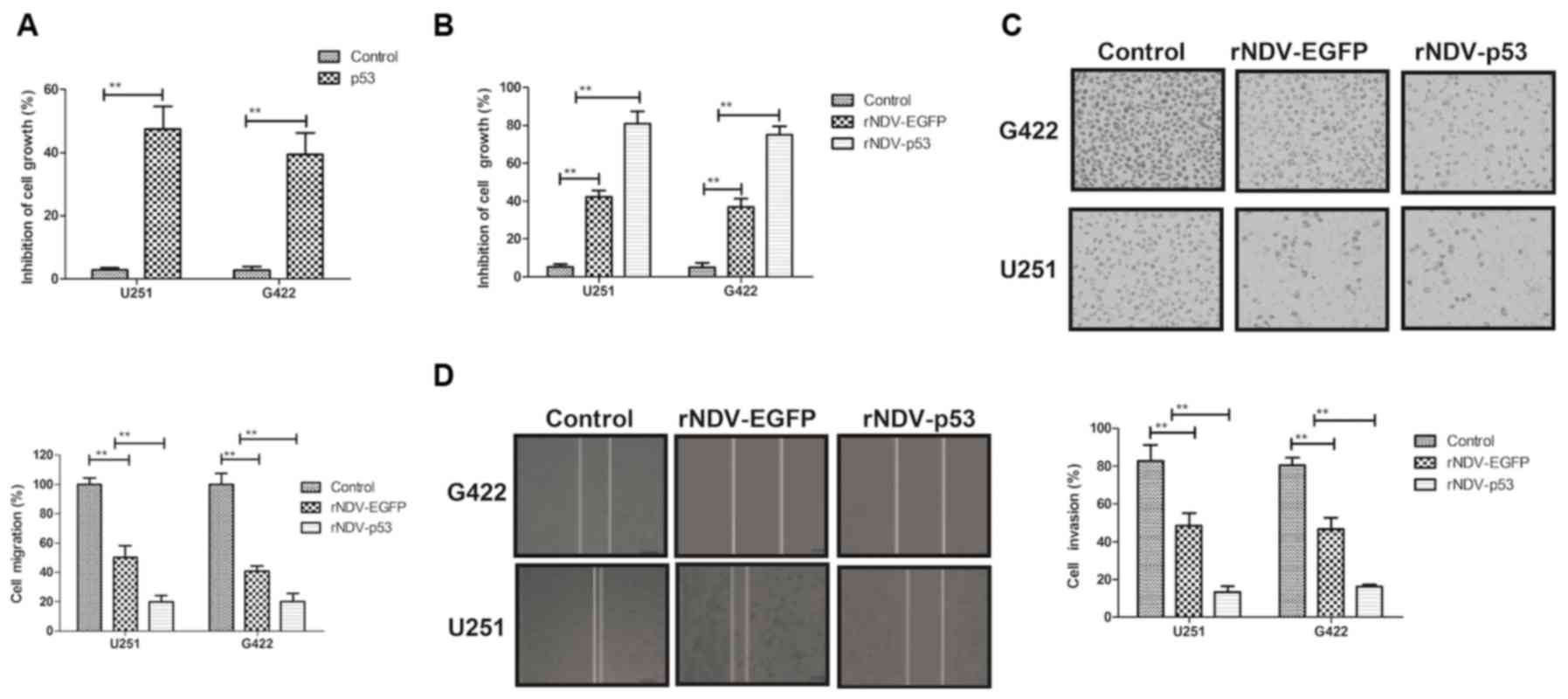
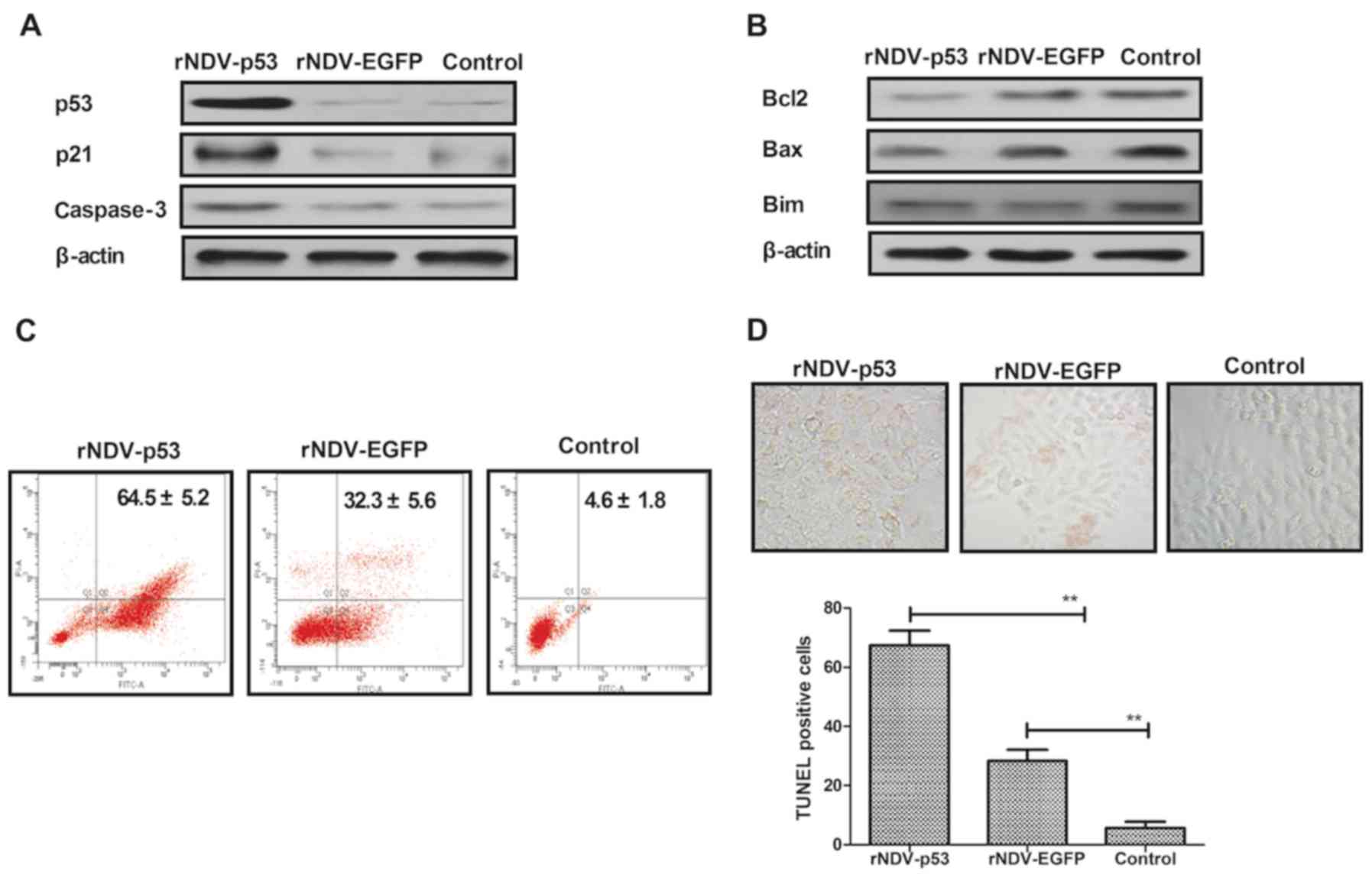
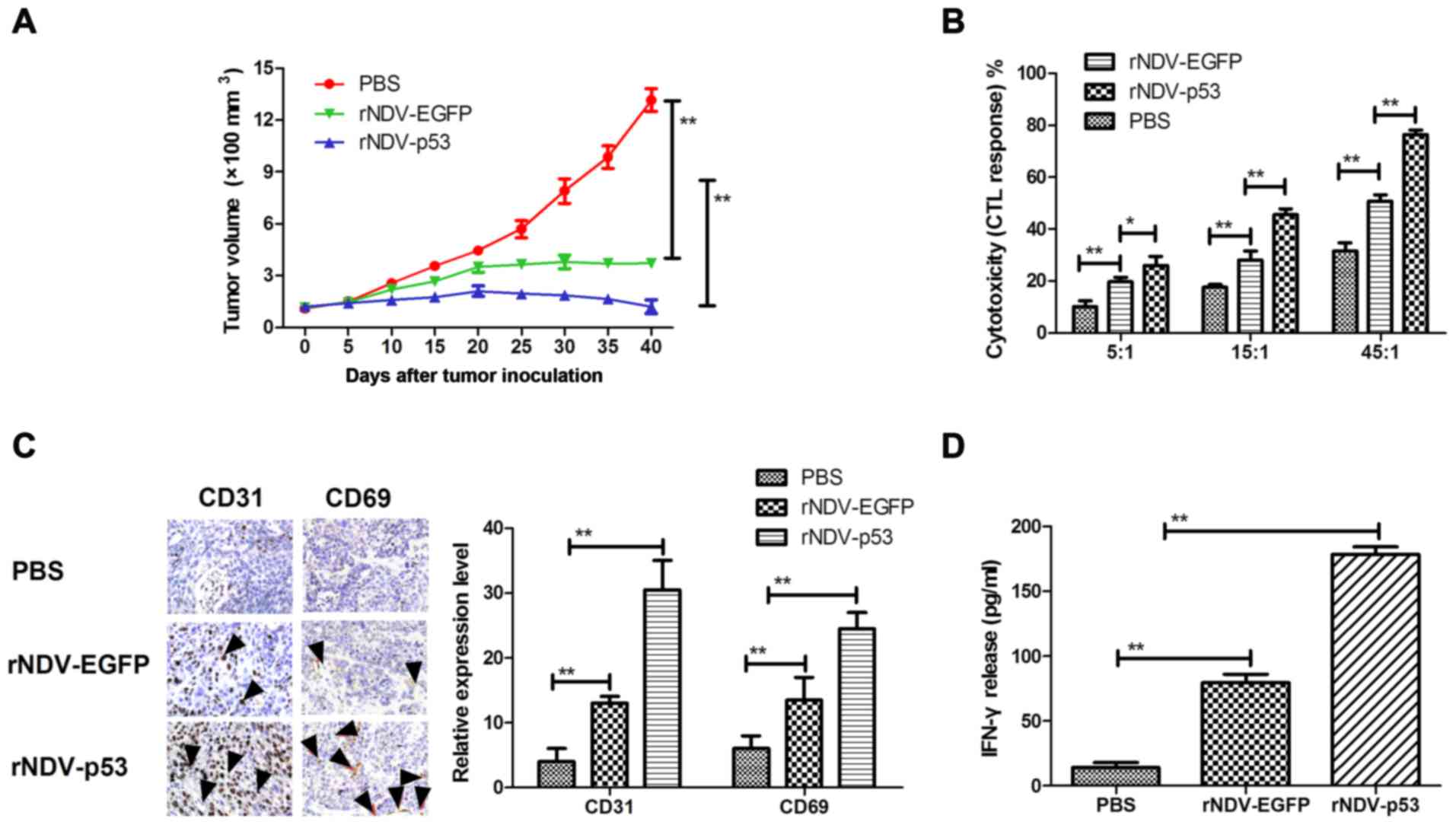
|
1
|
Lu M, Zhang X, Zhang M, Chen H, Dou W, Li
S and Dai J: Non-model segmentation of brain glioma tissues with
the combination of DWI and fMRI signals. Biomed Mater Eng.
26:S1315–S1324. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chow KK, Naik S, Kakarla S, Brawley VS,
Shaffer DR, Yi Z, Rainusso N, Wu MF, Liu H, Kew Y, et al: T cells
redirected to EphA2 for the immunotherapy of glioblastoma. Mol
Ther. 21:629–637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Englot DJ, Berger MS, Chang EF and Garcia
PA: Characteristics and treatment of seizures in patients with
high-grade glioma: A review. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 23:227–235. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siu A, Wind JJ, Iorgulescu JB, Chan TA,
Yamada Y and Sherman JH: Radiation necrosis following treatment of
high grade glioma-a review of the literature and current
understanding. Acta neurochir(Wien). 154:191–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taphoorn MJ and Bottomley A:
Health-related quality of life and symptom research in glioblastoma
multiforme patients. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res.
5:763–774. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Delgado-López PD and Corrales-Garcia EM:
Survival in glioblastoma: A review on the impact of treatment
modalities. Clin Transl Oncol. 18:1062–1071. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Benjamin R, Capparella J and Brown A:
Classification of glioblastoma multiforme in adults by molecular
genetics. Cancer J. 9:82–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ortega A, Sarmiento JM, Ly D, Nuño M,
Mukherjee D, Black KL and Patil CG: Multiple resections and
survival of recurrent glioblastoma patients in the temozolomide
era. J Clin Neurosci. 24:105–111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koekkoek JA, Postma TJ, Heimans JJ,
Reijneveld JC and Taphoorn MJ: Antiepileptic drug treatment in the
end-of-life phase of glioma patients: A feasibility study. Support
Care Cancer. 24:1633–1638. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
LaRocca CJ and Davydova J: Oncolytic
virotherapy increases the detection of microscopic metastatic
disease at time of staging laparoscopy for pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. EBioMedicine. 7:15–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cassel WA and Murray DR: A ten-year
follow-up on stage II malignant melanoma patients treated
postsurgically with Newcastle disease virus oncolysate. Med Oncol
Tumor Pharmacother. 9:169–171. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yaacov B, Eliahoo E, Lazar I, Ben-Shlomo
M, Greenbaum I, Panet A and Zakay-Rones Z: Selective oncolytic
effect of an attenuated Newcastle disease virus (NDV-HUJ) in lung
tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 15:795–807. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang W, Wang H, Sun TM, Yao WQ, Chen LL,
Jin Y, Li CL and Meng FJ: Application of autologous tumor cell
vaccine and NDV vaccine in treatment of tumors of digestive tract.
World J Gastroenterol. 9:495–498. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song KY, Wong J, Gonzalez L, Sheng G,
Zamarin D and Fong Y: Antitumor efficacy of viral therapy using
genetically engineered Newcastle disease virus [NDV(F3aa)-GFP] for
peritoneally disseminated gastric cancer. J Mol Med (Berl).
88:589–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Puhlmann J, Puehler F, Mumberg D, Boukamp
P and Beier R: Rac1 is required for oncolytic NDV replication in
human cancer cells and establishes a link between tumorigenesis and
sensitivity to oncolytic virus. Oncogene. 29:2205–2216. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Janke M, Peeters B, de Leeuw O, Moorman R,
Arnold A, Fournier P and Schirrmacher V: Recombinant Newcastle
disease virus (NDV) with inserted gene coding for GM-CSF as a new
vector for cancer immunogene therapy. Gene Ther. 14:1639–1649.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dastjerdi MN, Valiani A, Mardani M and Ra
MZ: Adenosine A1 receptor modifies P53 expression and apoptosis in
breast cancer cell line Mcf-7. Bratisl Lek Listy. 117:242–246.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohara M, Matsuura K, Akimoto E, Noma M,
Doi M, Nishizaka T, Kagawa N and Itamoto T: Prognostic value of
Ki67 and p53 in patients with estrogen receptor-positive and human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer:
Validation of the cut-off value of the Ki67 labeling index as a
predictive factor. Mol Clin Oncol. 4:648–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karsy M, Neil JA, Guan J, Mahan MA, Colman
H and Jensen RL: A practical review of prognostic correlations of
molecular biomarkers in glioblastoma. Neurosurg Focus. 38:E42015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamanishi Y, Boyle DL, Green DR, Keystone
EC, Connor A, Zollman S and Firestein GS: p53 tumor suppressor gene
mutations in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from erosion synovium and
non-erosion synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
7:R12–R18. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohgaki H, Eibl RH, Schwab M, Reichel MB,
Mariani L, Gehring M, Petersen I, Höll T, Wiestler OD and Kleihues
P: Mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in neoplasms of the
human nervous system. Mol Carcinog. 8:74–80. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sakai E, Rikimaru K, Ueda M, Matsumoto Y,
Ishii N, Enomoto S, Yamamoto H and Tsuchida N: The p53
tumor-suppressor gene and ras oncogene mutations in oral
squamous-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 52:867–872. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Greenblatt MS, Bennett WP, Hollstein M and
Harris CC: Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Clues to
cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res.
54:4855–4878. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rivlin N, Brosh R, Oren M and Rotter V:
Mutations in the p53 Tumor suppressor gene: Important milestones at
the various steps of tumorigenesis. Genes Cancer. 2:466–474. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yue Q, Yulong G, Liting Q, Shuai Y, Delong
L, Yubao L, Lili J, Sidang L and Xiaomei W: Mutations in and
expression of the tumor suppressor gene p53 in egg-type chickens
infected with subgroup j avian leukosis virus. Vet Pathol.
52:1052–1056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sitarek P, Skala E, Toma M, Wielanek M,
Szemraj J, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Kolasa M, Skorski T, Wysokińska H
and Śliwiński T: A preliminary study of apoptosis induction in
glioma cells via alteration of the Bax/Bcl-2-p53 axis by
transformed and non-transformed root extracts of Leonurus sibiricus
L. Tumour Biol. 37:8753–8764. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen GX, Zheng LH, Liu SY and He XH:
rAd-p53 enhances the sensitivity of human gastric cancer cells to
chemotherapy. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4289–4297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xie Q, Liang BL, Wu YH, Zhang J, Chen MW,
Liu HY, Gu XF and Xu J: Synergistic anticancer effect of rAd/P53
combined with 5-fluorouracil or iodized oil in the early
therapeutic response of human colon cancer in vivo. Gene.
499:303–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Walker A, Taylor J, Rowe D and Summers D:
A method for generating sticky-end PCR products which facilitates
unidirectional cloning and the one-step assembly of complex DNA
constructs. Plasmid. 59:155–162. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan F, Zheng Y and Huang L:
Adenovirus-mediated combined anti-angiogenic and pro-apoptotic gene
therapy enhances antitumor efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 5:348–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bai FL, Yu YH, Tian H, Ren GP, Wang H,
Zhou B, Han XH, Yu QZ and Li DS: Genetically engineered Newcastle
disease virus expressing interleukin-2 and TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:1226–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abd El Hafeez S, Torino C, D'Arrigo G,
Bolignano D, Provenzano F, Mattace-Raso F, Zoccali C and Tripepi G:
An overview on standard statistical methods for assessing
exposure-outcome link in survival analysis (Part II): The
kaplan-meier analysis and the cox regression method. Aging Clin Exp
Res. 24:203–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Greaves MF and Brown G: Purification of
human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 112:420–423. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zamarin D, Vigil A, Kelly K, Garcia-Sastre
A and Fong Y: Genetically engineered Newcastle disease virus for
malignant melanoma therapy. Gene Ther. 16:796–804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wai-Hoe L, Wing-Seng L, Ismail Z and
Lay-Harn G: SDS-PAGE-Based quantitative assay for screening of
kidney stone disease. Biol Proced Online. 11:145–160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang R, Wang R, Chen Q and Chang H:
Inhibition of autophagy using 3-methyladenine increases
cisplatin-induced apoptosis by increasing endoplasmic reticulum
stress in U251 human glioma cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:1727–1732. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stoeck M, Marland-Noske C, Manasterski M,
Zawatzky R, Horn S, Möbus V, Schlag P and Schirrmacher V: In vitro
expansion and analysis of T lymphocyte microcultures obtained from
the vaccination sites of cancer patients undergoing active specific
immunization with autologous Newcastle-disease-virus-modified
tumour cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 37:240–244. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vigil A, Martinez O, Chua MA and
Garcia-Sastre A: Recombinant Newcastle disease virus as a vaccine
vector for cancer therapy. Mol Ther. 16:1883–1890. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schirrmacher V and Fournier P: Newcastle
disease virus: A promising vector for viral therapy, immune therapy
and gene therapy of cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 542:565–605. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Keshelava VV, Dobrovol'skaia Nlu, Chazova
NL, Bershchanskaia AM, Podol'skaia MV, Garmarnik TV and Mel'nikova
NV: Neoadjuvant therapy of breast cancer using Newcastle disease
virus. Vopr Onkol. 55:433–435. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schulze T, Kemmner W, Weitz J, Wernecke
KD, Schirrmacher V and Schlag PM: Efficiency of adjuvant active
specific immunization with Newcastle disease virus modified tumor
cells in colorectal cancer patients following resection of liver
metastases: Results of a prospective randomized trial. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 58:61–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bai F, Niu Z, Tian H, Li S, Lv Z, Zhang T,
Ren G and Li D: Genetically engineered Newcastle disease virus
expressing interleukin 2 is a potential drug candidate for cancer
immunotherapy. Immunol Lett. 159:36–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chai Z, Zhang P, Fu F, Zhang X, Liu Y, Hu
L and Li X: Oncolytic therapy of a recombinant Newcastle disease
virus D90 strain for lung cancer. Virol J. 11:842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Meng C, Zhou Z, Jiang K, Yu S, Jia L, Wu
Y, Liu Y, Meng S and Ding C: Newcastle disease virus triggers
autophagy in U251 glioma cells to enhance virus replication. Arch
Virol. 157:1011–1018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mustafa Z, Shamsuddin HS, Ideris A,
Ibrahim R, Jaafar H, Ali AM and Abdullah JM: Viability reduction
and Rac1 gene downregulation of heterogeneous ex-vivo glioma acute
slice infected by the oncolytic Newcastle disease virus strain
V4UPM. Biomed Res Int. 2013:2485072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bressy C, Hastie E and Grdzelishvili VZ:
Combining oncolytic virotherapy with p53 tumor suppressor gene
therapy. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 5:20–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and
Harris CC: p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 253:49–53.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hamzehloie T, Mojarrad M, Hasanzadeh
Nazarabadi M and Shekouhi S: The role of tumor protein 53 mutations
in common human cancers and targeting the murine double minute
2-p53 interaction for cancer therapy. Iran J Med Sci. 37:3–8.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fagin JA: Tumor suppressor genes in human
thyroid neoplasms: p53 mutations are associated undifferentiated
thyroid cancers. J Endocrinol Invest. 18:140–142. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Harris CC and Hollstein M: Clinical
implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. N Engl J Med.
329:1318–1327. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Casson AG, Evans SC, Gillis A, Porter GA,
Veugelers P, Darnton SJ, Guernsey DL and Hainaut P: Clinical
implications of p53 tumor suppressor gene mutation and protein
expression in esophageal adenocarcinomas: Results of a ten-year
prospective study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 125:1121–1131. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kuczyk MA, Serth J, Hervatin C, Arndt H,
Derendorf L, Thon WF and Jonas U: Detection of P53
tumor-suppressor-gene protein in bladder tumors and prostate
cancer: Possible clinical implications. World J Urol. 12:345–351.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Thomas AA, Ernstoff MS and Fadul CE:
Immunotherapy for the treatment of glioblastoma. Cancer J.
18:59–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Larsen CJ: Cellular immunotherapy and
glioblastoma: A hopeful treatment? Bull Cancer.
98:4572011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Varghese S, Rabkin SD, Nielsen GP,
MacGarvey U, Liu R and Martuza RL: Systemic therapy of spontaneous
prostate cancer in transgenic mice with oncolytic herpes simplex
viruses. Cancer Res. 67:9371–9379. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Husain SR, Behari N, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I
and Puri RK: Complete regression of established human glioblastoma
tumor xenograft by interleukin-4 toxin therapy. Cancer Res.
58:3649–3653. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Debinski W, Gibo DM, Obiri NI, Kealiher A
and Puri RK: Novel anti-brain tumor cytotoxins specific for cancer
cells. Nat Biotechnol. 16:449–453. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bera TK, Viner J, Brinkmann E and Pastan
I: Pharmacokinetics and antitumor activity of a bivalent
disulfide-stabilized Fv immunotoxin with improved antigen binding
to erbB2. Cancer Res. 59:4018–4022. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ghetie MA, Richardson J, Tucker T, Jones
D, Uhr JW and Vitetta ES: Antitumor activity of Fab' and
IgG-anti-CD22 immunotoxins in disseminated human B lymphoma grown
in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency disease: Effect on
tumor cells in extranodal sites. Cancer Res. 51:5876–5880.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|