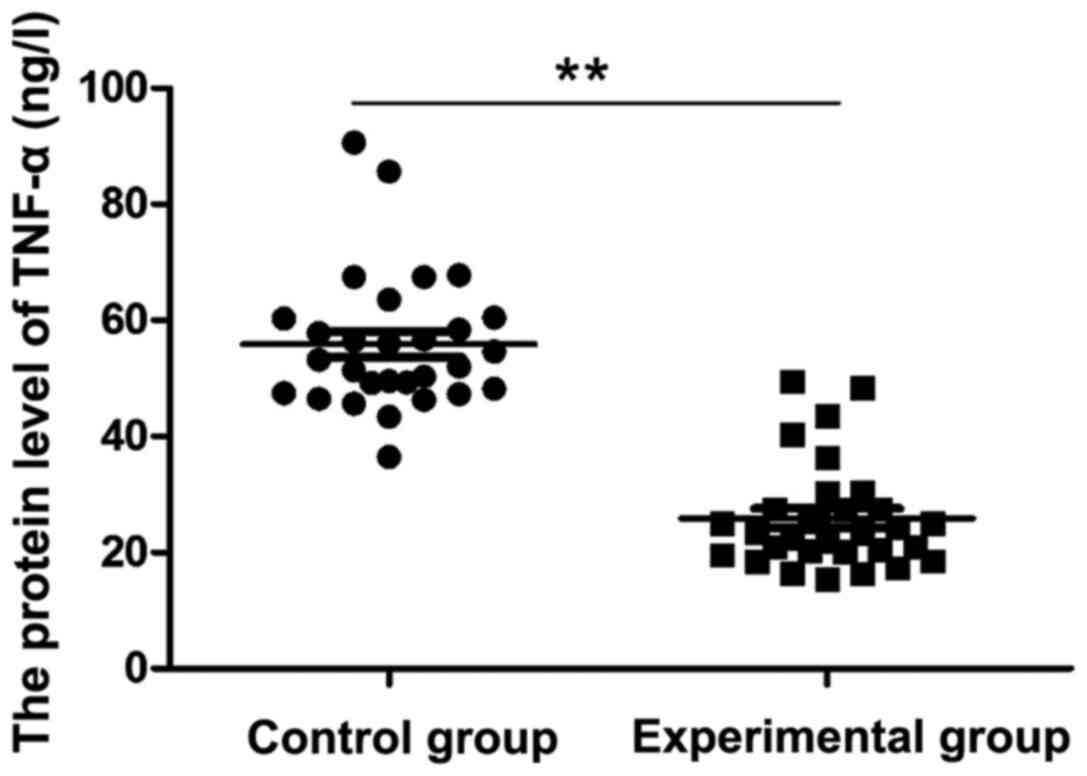
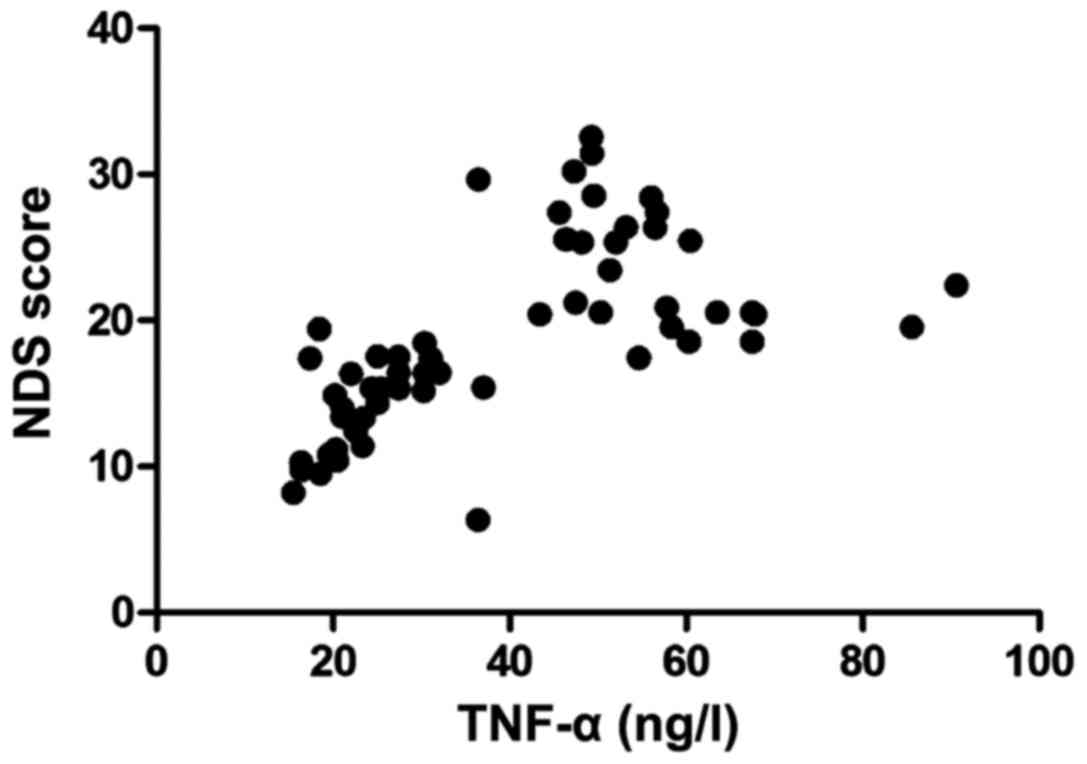
|
1
|
Broughton BRS, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–e339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kahlert P, Knipp SC, Schlamann M,
Thielmann M, Al-Rashid F, Weber M, Johansson U, Wendt D, Jakob HG,
Forsting M, et al: Silent and apparent cerebral ischemia after
percutaneous transfemoral aortic valve implantation: A
diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation.
121:870–878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beck H and Plate KH: Angiogenesis after
cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 117:481–496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hossmann KA: Treatment of experimental
cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2:275–297. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maher J and Hachinski V: Hypothermia as a
potential treatment for cerebral ischemia. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab
Rev. 5:277–300. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ginsberg MD: Current status of
neuroprotection for cerebral ischemia: Synoptic overview. Stroke.
40 Suppl 3:S111–S114. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ledeen RW and Wu G: The multi-tasked life
of GM1 ganglioside, a true factotum of nature. Trends Biochem Sci.
40:407–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Q, Song YH, Tang Z, Wang ZP, Xu Q and
Bao N: Effects of ganglioside GM1 and neural growth factor on
neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Genet Mol Res.
Aug 5–2016.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15038376.
|
|
9
|
Gao M, Ding H, Zhong G, Lu J, Wang H, Li Q
and Wang Z: The effects of transrectal radiofrequency hyperthermia
on patients with chronic prostatitis and the changes of MDA, NO,
SOD, and Zn levels in pretreatment and posttreatment. Urology.
79:391–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Daousi C, Benbow SJ, Woodward A and
MacFarlane IA: The natural history of chronic painful peripheral
neuropathy in a community diabetes population. Diabet Med.
23:1021–1024. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu X: Summary of the Fourth National
Cerebrovascular Disease Conference. Stroke Nerv Dis:. 4:105–109.
1997.
|
|
12
|
Niizuma K, Yoshioka H, Chen H, Kim GS,
Jung JE, Katsu M, Okami N and Chan PH: Mitochondrial and apoptotic
neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Mol Basis
Dis. 1802:92–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang JY, Xia Q, Chu KT, Pan J, Sun LN,
Zeng B, Zhu YJ, Wang Q, Wang K and Luo BY: Severe global cerebral
ischemia-induced programmed necrosis of hippocampal CA1 neurons in
rat is prevented by 3-methyladenine: A widely used inhibitor of
autophagy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 70:314–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang F and Chen J: Leptin protects
hippocampal CA1 neurons against ischemic injury. J Neurochem.
107:578–587. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee JJ, Li L, Jung H and Zuo Z:
Postconditioning with isoflurane reduced ischemia-induced brain
injury in rats. Anesthesiology. 108:1055–1062. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
del Zoppo GJ and Zoppo G: Inflammation and
the neurovascular unit in the setting of focal cerebral ischemia.
Neuroscience. 158:972–982. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei L, Fraser JL, Lu ZY, Hu X and Yu SP:
Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells enhances angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral
ischemia in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 46:635–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Niatsetskaya ZV, Sosunov SA, Matsiukevich
D, Utkina-Sosunova IV, Ratner VI, Starkov AA and Ten VS: The oxygen
free radicals originating from mitochondrial complex I contribute
to oxidative brain injury following hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal
mice. J Neurosci. 32:3235–3244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar A, Mittal R, Khanna HD and Basu S:
Free radical injury and blood-brain barrier permeability in
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 122:e722–e727. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Candelario-Jalil E, Yang Y and Rosenberg
GA: Diverse roles of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue
inhibitors of metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral
ischemia. Neuroscience. 158:983–994. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iadecola C and Alexander M: Cerebral
ischemia and inflammation. Curr Opin Neurol. 14:89–94. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Günther C, Buchen B, He GW, Hornef M,
Torow N, Neumann H, Wittkopf N, Martini E, Basic M, Bleich A, et
al: Caspase-8 controls the gut response to microbial challenges by
TNF-α-dependent and independent pathways. Gut. 64:601–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|