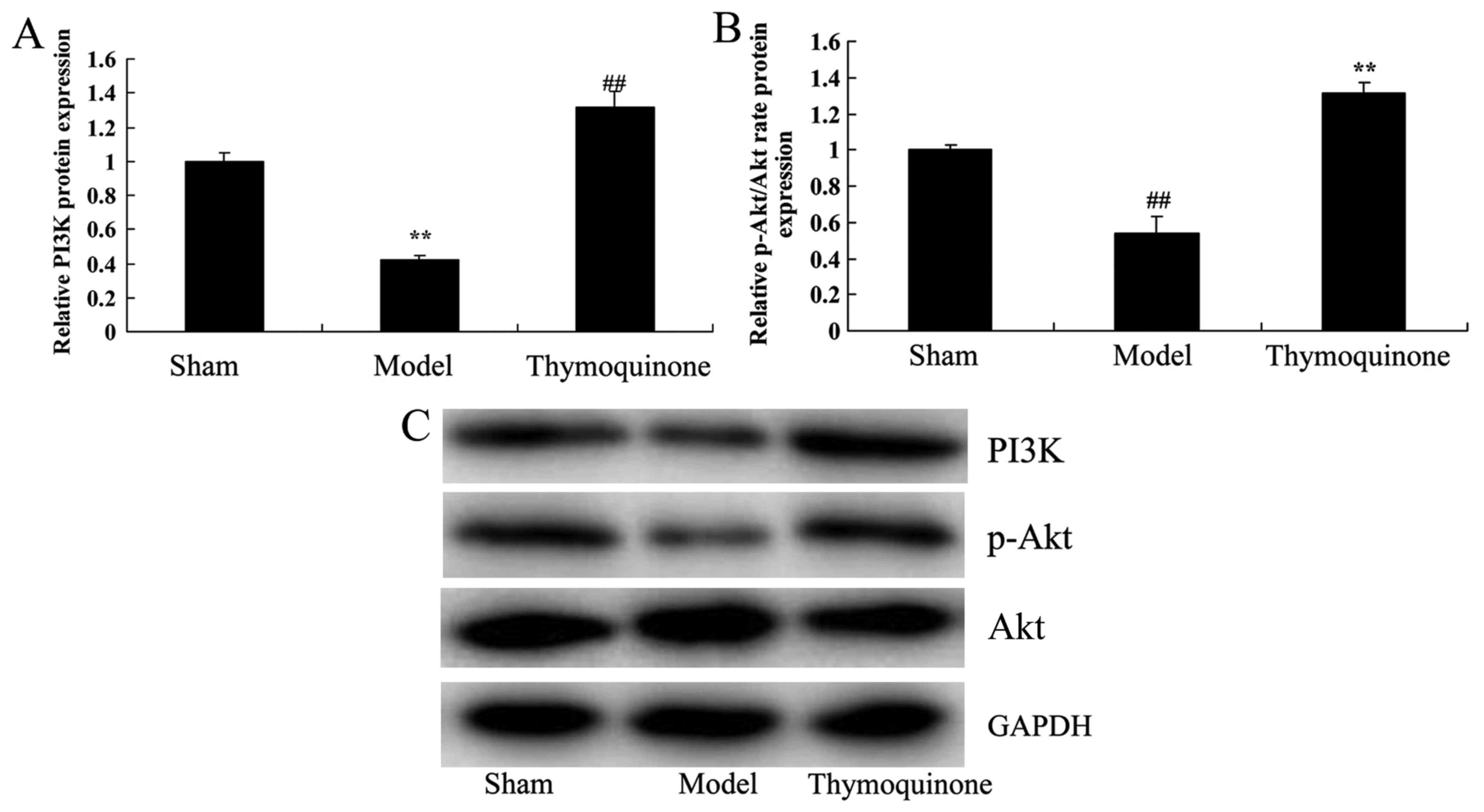
|
1
|
Arora M, Harvey LA, Hayes AJ, Chhabra HS,
Glinsky JV, Cameron ID, Lavrencic L, Arumugam N, Hossain S and Bedi
PK: Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of telephone-based support
versus usual care for treatment of pressure ulcers in people with
spinal cord injury in low-income and middle-income countries: Study
protocol for a 12-week randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open.
5:e0083692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dudley-Javoroski S and Shields RK:
Active-resisted stance modulates regional bone mineral density in
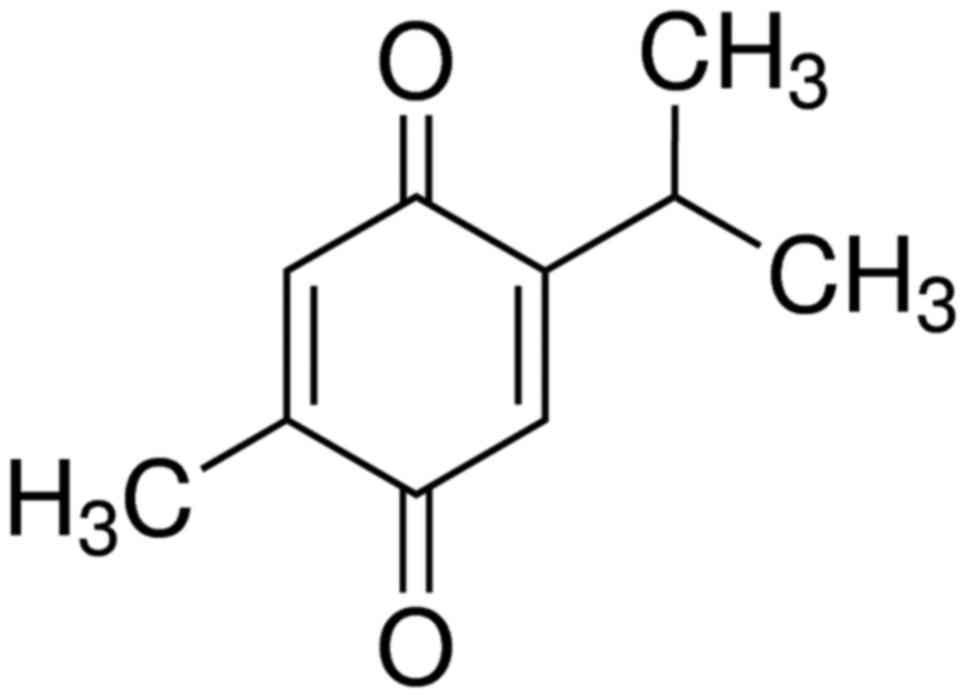
humans with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 36:191–199.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harper LA, Coleman JA, Perrin PB, Olivera
SL, Perdomo JL, Arango JA and Arango-Lasprilla JC: Comparison of
mental health between individuals with spinal cord injury and
able-bodied controls in Neiva, Colombia. J Rehabil Res Dev.
51:127–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lόpez-Larraz E, Antelis JM, Montesano L,
Gil-Agudo A and Minguez J: Continuous decoding of motor attempt and
motor imagery from EEG activity in spinal cord injury patients.
Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012:1798–1801. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jia C, Liao LM, Chen G and Sui Y: Detrusor
botulinum toxin A injection significantly decreased urinary tract
infection in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal
Cord. 51:487–490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laubacher M, Perret C and Hunt KJ:
Work-rate-guided exercise testing in patients with incomplete
spinal cord injury using a robotics-assisted tilt-table. Disabil
Rehabil Assist Technol. 10:433–438. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosety-Rodriguez M, Camacho A, Rosety I,
Fornieles G, Rosety MA, Diaz AJ, Bernardi M, Rosety M and Ordonez
FJ: Low-grade systemic inflammation and leptin levels were improved
by arm cranking exercise in adults with chronic spinal cord injury.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 95:297–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nelissen S, Vangansewinkel T, Geurts N,
Geboes L, Lemmens E, Vidal PM, Lemmens S, Willems L, Boato F,
Dooley D, et al: Mast cells protect from post-traumatic spinal cord
damage in mice by degrading inflammation-associated cytokines via
mouse mast cell protease 4. Neurobiol Dis. 62:260–272. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amin B, Abnous K, Motamedshariaty V and
Hosseinzadeh H: Attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and
apoptosis by ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Crocus sativus L.
stigma after chronic constriction injury of rats. An Acad Bras
Cienc. 86:1821–1832. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu WR and Fehlings MG: Fas/FasL-mediated
apoptosis and inflammation are key features of acute human spinal
cord injury: Implications for translational, clinical application.
Acta Neuropathol. 122:747–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yi JH, Park SW, Brooks N, Lang BT and
Vemuganti R: PPARgamma agonist rosiglitazone is neuroprotective
after traumatic brain injury via anti-inflammatory and
anti-oxidative mechanisms. Brain Res. 1244:164–172. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McTigue DM: Potential therapeutic targets
for PPARgamma after spinal cord injury. PPAR Res. 2008:5171622008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan J, Li B, Chen JW, Jiang SD and Jiang
LS: Spinal cord injury causes bone loss through peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ and Wnt signalling. J Cell Mol
Med. 16:2968–2977. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chae CH and Kim HT: Forced,
moderate-intensity treadmill exercise suppresses apoptosis by
increasing the level of NGF and stimulating phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase signaling in the hippocampus of induced aging rats.
Neurochem Int. 55:208–213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim Y, Seger R, Babu Suresh CV, Hwang SY
and Yoo YS: A positive role of the PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway in
PC12 cell differentiation. Mol Cells. 18:353–359. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Randhawa MA, Alenazy AK, Alrowaili MG and
Basha J: An active principle of Nigella sativa L.,
thymoquinone, showing significant antimicrobial activity against
anaerobic bacteria. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 6:97–101. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dur A, Kose H, Kocyigit A, Kocaman O,
Ismayilova M and Sonmez FC: The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant
effects of thymoquinone on ceruleine induced acute pancreatitis in
rats. Bratisl Lek Listy. 117:614–618. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Bai Y and Yang Y: Thymoquinone
chemosensitizes colon cancer cells through inhibition of NF-κB.
Oncol Lett. 12:2840–2845. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu X, Dong J, Cai W, Pan Y, Li R and Li
B: The effect of thymoquinone on apoptosis of SK-OV-3 ovarian
cancer cell by regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
27:1596–1601. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barkat MA, Abul H, Ahmad J, Khan MA, Beg S
and Ahmad FJ: Insights into the targeting potential of thymoquinone
for therapeutic intervention against triple-negative breast cancer.
Curr Drug Targets. 19:70–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang ZS, Pu ZC and Hao ZH: Carvacrol
protects against spinal cord injury in rats via suppressing
oxidative stress and the endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 12:5349–5354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu L, Moody J and Gall A: A quantitative,
pooled analysis and systematic review of controlled trials on the
impact of electrical stimulation settings and placement on pressure
ulcer healing rates in persons with spinal cord injuries. Ostomy
Wound Manage. 62:16–34. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Üstün N, Aras M, Ozgur T, Bayraktar HS,
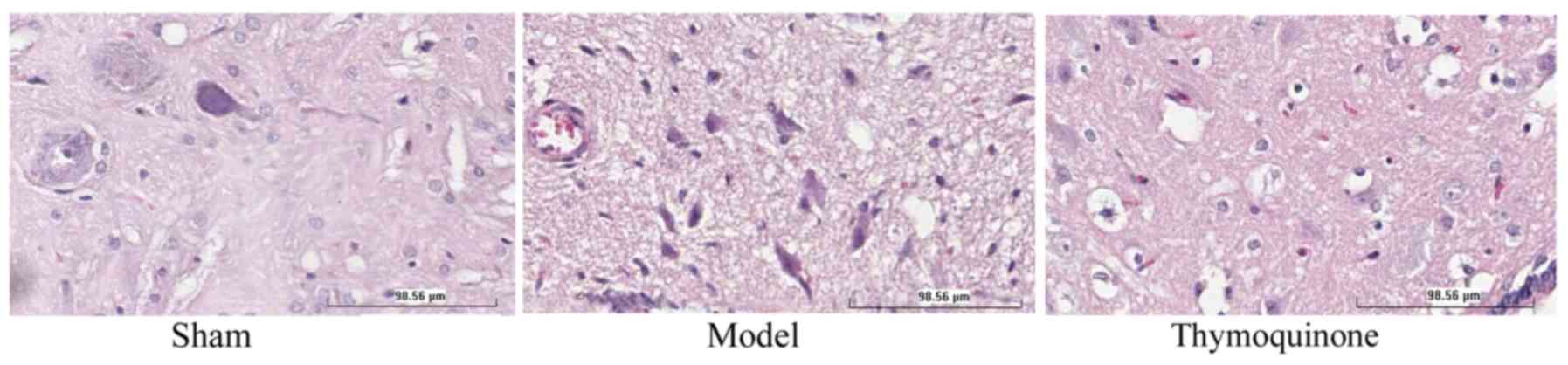
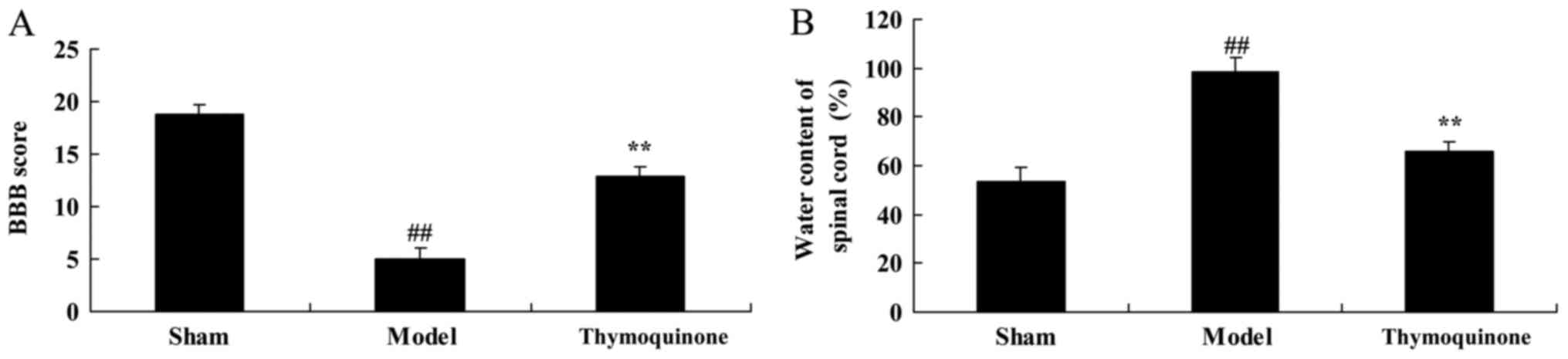
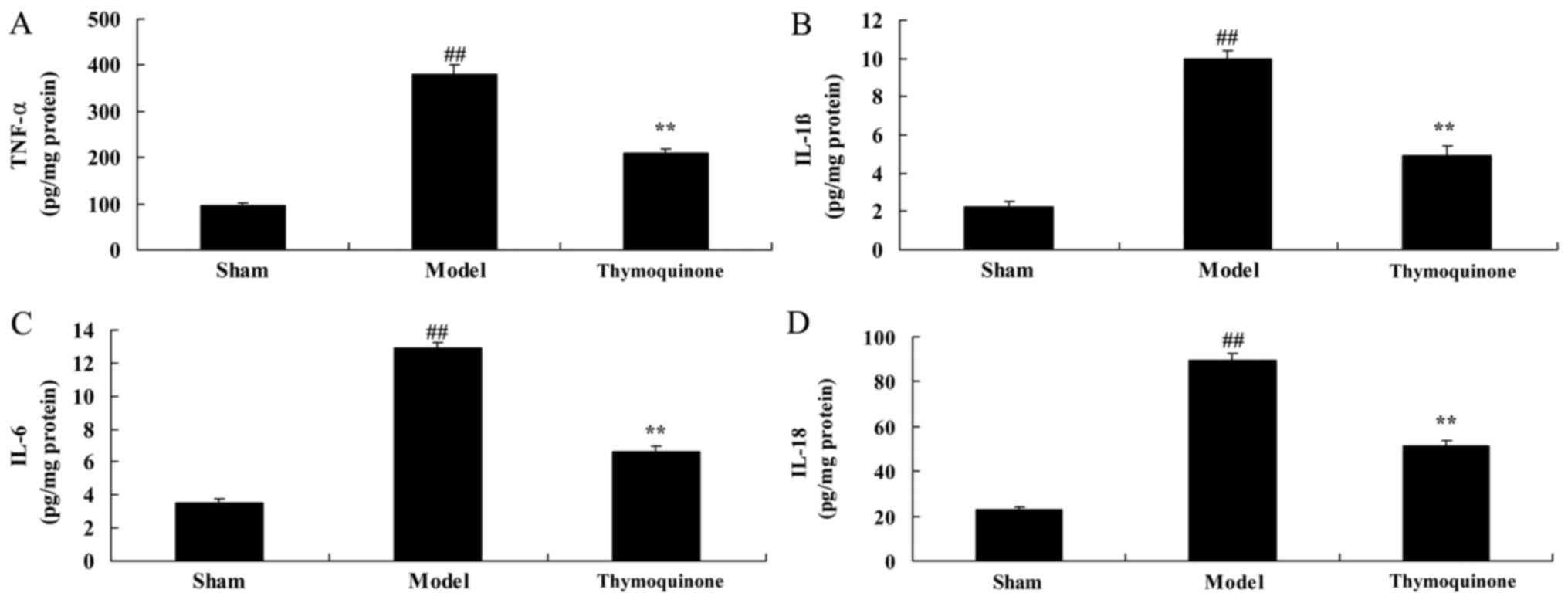
Sefil F, Ozden R and Yagiz AE: Thymoquinone attenuates trauma
induced spinal cord damage in an animal model. Ulus Travma Acil
Cerrahi Derg. 20:328–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Foroughi Asl H, Talukdar HA, Kindt AS,
Jain RK, Ermel R, Ruusalepp A, Nguyen KD, Dobrin R, Reilly DF,
Schunkert H, et al: Expression quantitative trait Loci acting
across multiple tissues are enriched in inherited risk for coronary
artery disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 8:305–315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian DS, Liu JL, Xie MJ, Zhan Y, Qu WS, Yu
ZY, Tang ZP, Pan DJ and Wang W: Tamoxifen attenuates
inflammatory-mediated damage and improves functional outcome after
spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem. 109:1658–1667. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paterniti I, Genovese T, Crisafulli C,
Mazzon E, Di Paola R, Galuppo M, Bramanti P and Cuzzocrea S:
Treatment with green tea extract attenuates secondary inflammatory
response in an experimental model of spinal cord trauma. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 380:179–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang S, Bendjelloul F, Ballerini P,
D'Alimonte I, Nargi E, Jiang C, Huang X and Rathbone MP: Guanosine
reduces apoptosis and inflammation associated with restoration of
function in rats with acute spinal cord injury. Purinergic Signal.
3:411–421. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Uchida K, Nakajima H, Watanabe S, Yayama
T, Guerrero AR, Inukai T, Hirai T, Sugita D, Johnson WE and Baba H:
Apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the spinal cord of
spinal hyperostotic mouse (twy/twy): Possible pathomechanism of
human cervical compressive myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 21:490–497.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang SQ, Wu MF, Gu R, Liu JB, Li Y, Zhu
QS and Jiang JL: Senegenin inhibits neuronal apoptosis after spinal
cord contusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 11:657–663. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizuno A, Miyauchi K, Nishizaki Y, Yamazoe
M, Komatsu I, Asano T, Mitsuhashi H, Nishi Y, Niwa K and Daida H:
Impact of the augmentation time ratio on direct measurement of
central aortic pressure in the presence of coronary artery disease.
Hypertens Res. 38:684–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu GY, Liu S, Hughes MG and McAdoo DJ:
Glutamate-induced losses of oligodendrocytes and neurons and
activation of caspase-3 in the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience.
153:1034–1047. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Griggs RB, Donahue RR, Morgenweck J, Grace
PM, Sutton A, Watkins LR and Taylor BK: Pioglitazone rapidly
reduces neuropathic pain through astrocyte and nongenomic PPARγ
mechanisms. Pain. 156:469–482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Paterniti I, Impellizzeri D, Crupi R,
Morabito R, Campolo M, Esposito E and Cuzzocrea S: Molecular
evidence for the involvement of PPAR-δ and PPAR-γ in
anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activities of
palmitoylethanolamide after spinal cord trauma. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park SW, Yi JH, Miranpuri G, Satriotomo I,
Bowen K, Resnick DK and Vemuganti R: Thiazolidinedione class of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists prevents
neuronal damage, motor dysfunction, myelin loss, neuropathic pain,
and inflammation after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:1002–1012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pei X, Li X, Chen H, Han Y and Fan Y:
Thymoquinone inhibits angiotensin II-induced proliferation and
migration of vascular smooth muscle cells through the
AMPK/PPARγ/PGC-1α pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 35:426–433. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Isele NB, Lee HS, Landshamer S, Straube A,
Padovan CS, Plesnila N and Culmsee C: Bone marrow stromal cells
mediate protection through stimulation of PI3-K/Akt and MAPK
signaling in neurons. Neurochem Int. 50:243–250. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang P, Zhang L, Zhu L, Chen F, Zhou S,
Tian T, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Li X, Zhang C, et al: The change tendency
of PI3K/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res.
7:2223–2232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Felix MS, Bauer S, Darlot F, Muscatelli F,
Kastner A, Gauthier P and Matarazzo V: Activation of Akt/FKHR in
the medulla oblongata contributes to spontaneous respiratory
recovery after incomplete spinal cord injury in adult rats.
Neurobiol Dis. 69:93–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu H, Liu HY, Jiang YN and Li N:
Protective effect of thymoquinone improves cardiovascular function,
and attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis by
mediating the PI3K/Akt pathway in diabetic rats. Mol Med Rep.
13:2836–2842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|