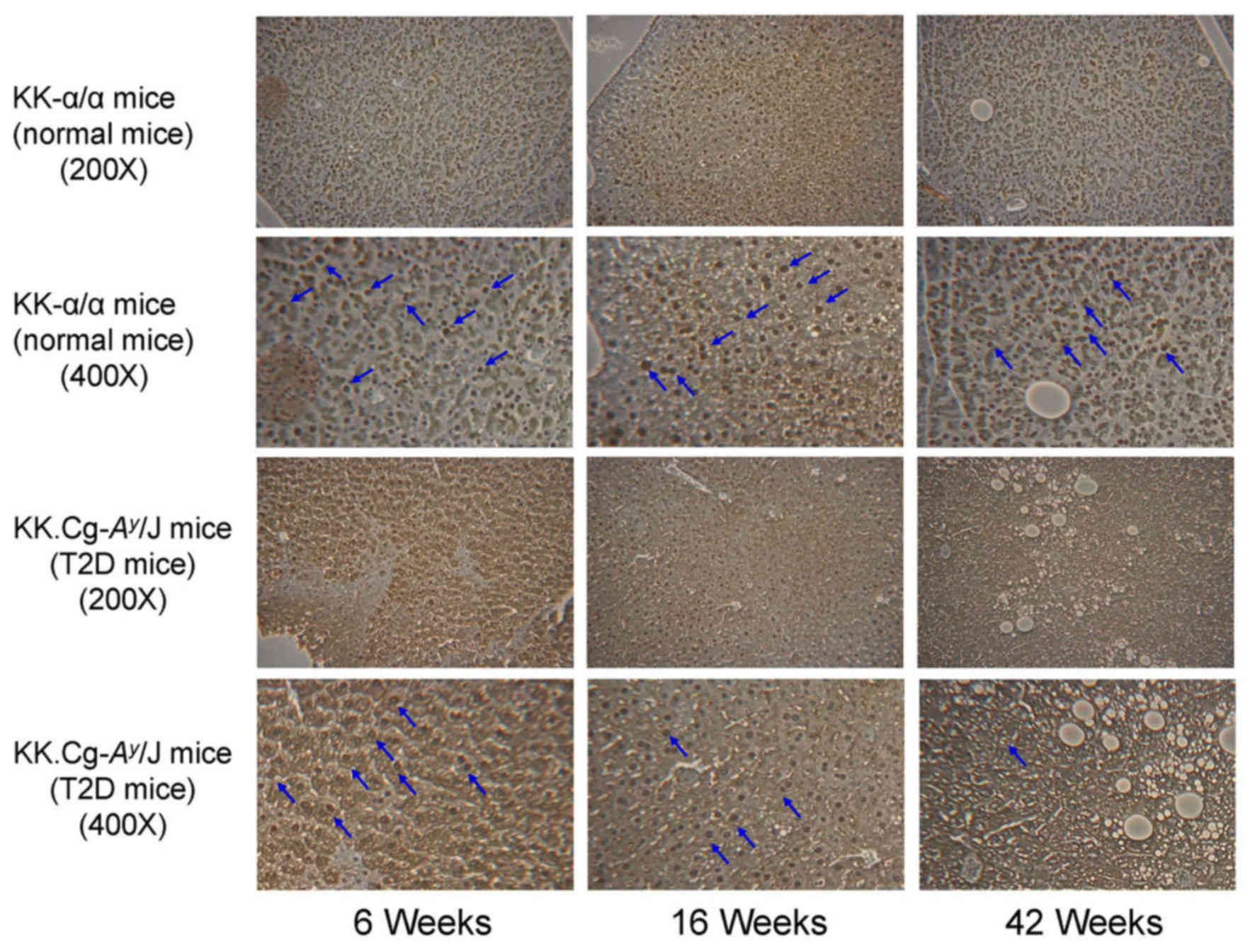
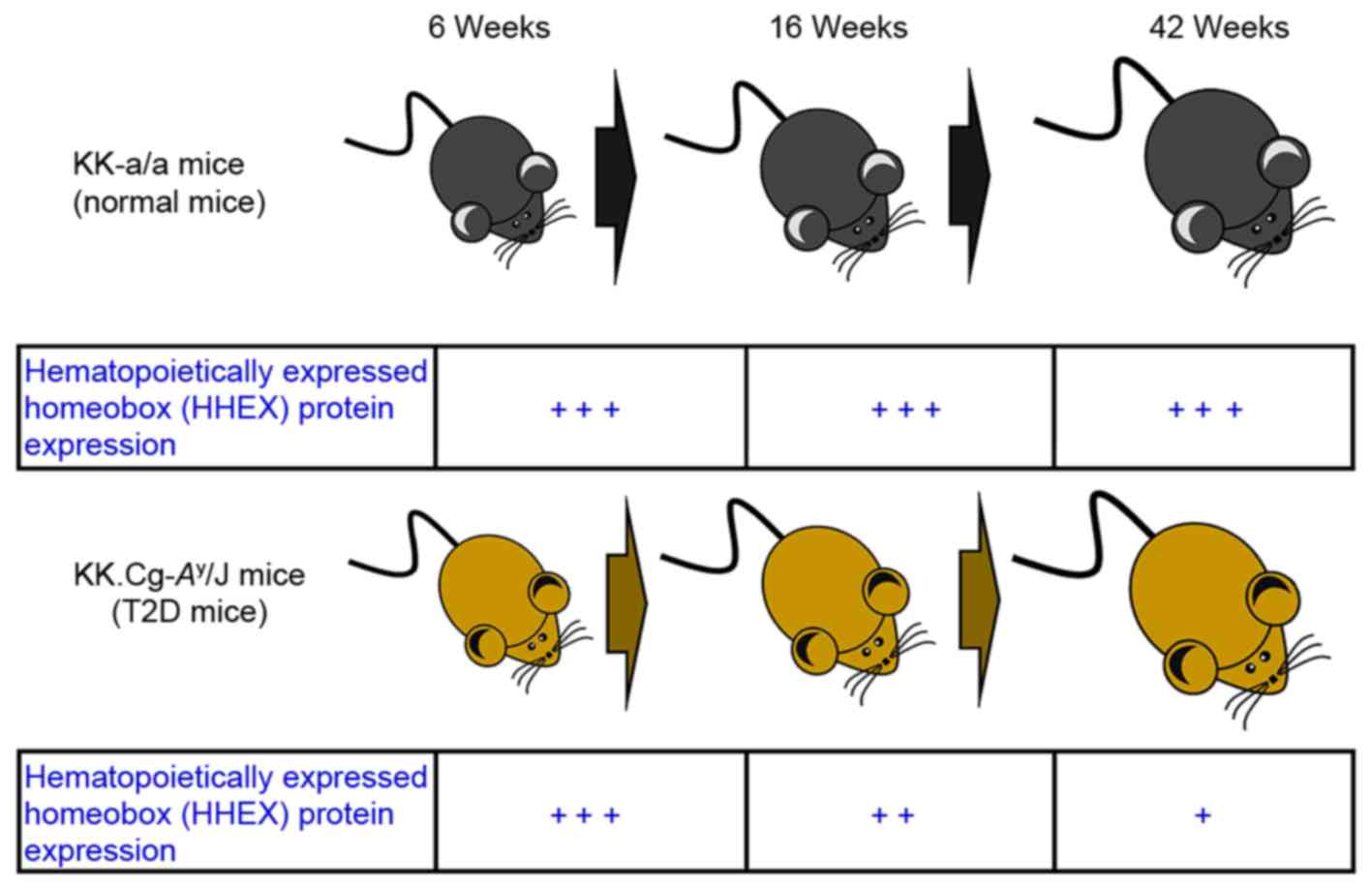
|
1
|
Hou WH, Li CY, Chen LH, Wang LY, Kuo KN,
Shen HN and Chang MF: Prevalence of hand syndromes among patients
with diabetes mellitus in Taiwan: A population-based study. J
Diabetes. 9:622–627. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen SY, Hsu YM, Lin YJ, Huang YC, Chen
CJ, Lin WD, Liao WL, Chen YT, Lin WY, Liu YH, et al: Current
concepts regarding developmental mechanisms in diabetic retinopathy
in Taiwan. Biomedicine (Taipei). 6:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Middleton P, Crowther CA and Simmonds L:
Different intensities of glycaemic control for pregnant women with
pre-existing diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD008540. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Adeshara KA, Diwan AG and Tupe RS:
Diabetes and complications: Cellular signaling pathways, current
understanding and targeted therapies. Curr Drug Targets.
17:1309–1328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zatalia SR and Sanusi H: The role of
antioxidants in the pathophysiology, complications, and management
of diabetes mellitus. Acta Med Indones. 45:141–147. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Resl M and Clodi M: Diabetes and
cardiovascular complications. Wien Med Wochenschr. 160:3–7.
2010.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hahr AJ and Molitch ME: Diabetes,
cardiovascular risk and nephropathy. Cardiol Clin. 28:467–475.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
World Health Organization, . Global report
on diabetes. WHO; Geneva: 2016, http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ministry of Health and Welfare: 2015
statistics of causes of deathMinistry of Health and Welfare.
Taiwan, R.O.C.: https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-3265-30093-2.htmlLast
Updated July 18. 2017
|
|
10
|
Yang X, Xu Z, Zhang C, Cai Z and Zhang J:
Metformin, beyond an insulin sensitizer, targeting heart and
pancreatic β cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:1984–1990. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murillo-Maldonado JM and Riesgo-Escovar
JR: Development and diabetes on the fly. Mech Dev. 144:150–155.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boldison J and Wong FS: Immune and
pancreatic β cell interactions in type 1 diabetes. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:856–867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kesavadev J: Insulin pump therapy in
pregnancy. J Pak Med Assoc. 66 9 Suppl 1:S39–S44. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn
P, Kröger J and Weitgasser R: Novel glucose-sensing technology and
hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: A multicentre, non-masked,
randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 388:2254–2263. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zou D, Ye Y, Zou N and Yu J: Analysis of
risk factors and their interactions in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A
cross-sectional survey in Guilin, China. J Diabetes Investig.
8:188–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hotta-Iwamura C and Tarbell KV: Type 1
diabetes genetic susceptibility and dendritic cell function:
Potential targets for treatment. J Leukoc Biol. 100:65–80. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng CA, Chien WC, Hsu CY, Lin HC and
Chiu HW: Risk analysis of carotid stent from a population-based
database in Taiwan. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e47472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakai S, Tanimoto K, Imbe A, Inaba Y,
Shishikura K, Tanimoto Y, Ushiroyama T, Terasaki J and Hanafusa T:
Decreased β-cell function is associated with reduced skeletal
muscle mass in japanese subjects without diabetes. PLoS One.
11:e01626032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rezai S, LoBue S and Henderson CE:
Diabetes prevention: Reproductive age women affected by insulin
resistance. Womens Health (Lond). 12:427–432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arias-Loste MT, Ranchal I, Romero-Gómez M
and Crespo J: Irisin, a link among fatty liver disease, physical
inactivity and insulin resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 15:23163–23178.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Skliros NP, Vlachopoulos C and Tousoulis
D: Treatment of diabetes: Crossing to the other side. Hellenic J
Cardiol. 57:304–310. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Marín-Peñalver JJ, Martín-Timón I,
Sevillano-Collantes C and Del Cañizo-Gómez FJ: Update on the
treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. 7:354–395.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nenquin M and Henquin JC: Sulphonylurea
receptor-1, sulphonylureas and amplification of insulin secretion
by Epac activation in β cells. Diabetes Obes Metab. 18:698–701.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abdelmoneim AS, Welsh RC, Eurich DT and
Simpson SH: Sulfonylurea use is associated with larger infarct size
in patients with diabetes and ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Int J Cardiol. 202:126–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Winkler G: Metformin-new data for an
‘old’, but efficient, safe and reliable antidiabetic drug. Orv
Hetil. 157:882–891. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Souza A, Khawaja KI, Masud F and Saif
MW: Metformin and pancreatic cancer: Is there a role? Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 77:235–242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Chen Q, Li L, Kwong JS, Jia P,
Zhao P, Wang W, Zhou X, Zhang M and Sun X: Alpha-glucosidase
inhibitors and hepatotoxicity in type 2 diabetes: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 6:326492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Smith JD, Mills E and Carlisle SE:
Treatment of pediatric type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacother.
50:768–777. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ahuja V and Chou CH: Novel therapeutics
for diabetes: Uptake, usage trends, and comparative effectiveness.
Curr Diab Rep. 16:472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salazar JJ, Ennis WJ and Koh TJ: Diabetes
medications: Impact on inflammation and wound healing. J Diabetes
Complications. 30:746–752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bae EJ: DPP-4 inhibitors in diabetic
complications: Role of DPP-4 beyond glucose control. Arch Pharm
Res. 39:1114–1128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bonora E and Cigolini M: DPP-4 inhibitors
and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Expectations, observations and perspectives. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc
Dis. 26:273–284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
King AJ: The use of animal models in
diabetes research. Br J Pharmacol. 166:877–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
O'Brien SP, Smith M, Ling H, Phillips L,
Weber W, Lydon J, Maloney C, Ledbetter S, Arbeeny C and Wawersik S:
Glomerulopathy in the KK. Cg-A(y)/J mouse reflects the pathology of
diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2013:4989252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ikeda H: KK mouse. Diabetes Res Clin
Pract. 24 Suppl:S313–S316. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Iwatsuka H, Shino A and Suzuoki Z: General
survey of diabetic features of yellow KK mice. Endocrinol Jpn.
17:23–35. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Qiao W, Zhao X and Tao M:
Quantitative assessment of the influence of hematopoietically
expressed homeobox variant (rs1111875) on type 2 diabetes risk. Mol
Genet Metab. 102:194–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
van Vliet-Ostaptchouk JV, Onland-Moret NC,
van Haeften TW, Franke L, Elbers CC, Shiri-Sverdlov R, van der
Schouw YT, Hofker MH and Wijmenga C: HHEX gene polymorphisms are
associated with type 2 diabetes in the Dutch Breda cohort. Eur J
Hum Genet. 16:652–656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pechlivanis S, Scherag A, Mühleisen TW,
Möhlenkamp S, Horsthemke B, Boes T, Bröcker-Preuss M, Mann K, Erbel
R, Jöckel KH, et al: Coronary artery calcification and its
relationship to validated genetic variants for diabetes mellitus
assessed in the Heinz Nixdorf recall cohort. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 30:1867–1872. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao J, Deliard S, Aziz AR and Grant SF:
Expression analyses of the genes harbored by the type 2 diabetes
and pediatric BMI associated locus on 10q23. BMC Med Genet.
13:892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Feuk L, McCarthy S, Andersson B, Prince JA
and Brookes AJ: Mutation screening of a haplotype block around the
insulin degrading enzyme gene and association with Alzheimer's
disease. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 136B:69–71. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bort R, Signore M, Tremblay K, Barbera
Martinez JP and Zaret KS: Hex homeobox gene controls the transition
of the endoderm to a pseudostratified, cell emergent epithelium for
liver bud development. Dev Biol. 290:44–56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hindy G, Mollet IG, Rukh G, Ericson U and
Orho-Melander M: Several type 2 diabetes-associated variants in
genes annotated to WNT signaling interact with dietary fiber in
relation to incidence of type 2 diabetes. Genes Nutr. 11:62016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kommoju UJ, Samy SK, Maruda J, Irgam K,
Kotla JP, Velaga L and Reddy BM: Association of CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B
& HHEX gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the
population of Hyderabad, India. Indian J Med Res. 143:455–463.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qian Y, Lu F, Dong M, Lin Y, Li H, Chen J,
Shen C, Jin G, Hu Z and Shen H: Genetic variants of IDE-KIF11-HHEX
at 10q23.33 associated with type 2 diabetes risk: A fine-mapping
study in Chinese population. PLoS One. 7:e350602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen YT, Liao JW, Tsai YC and Tsai FJ:
Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 1 increases nuclear receptor
subfamily 4 group A member 1 expression and decreases blood glucose
in type 2 diabetes. Oncotarget. 7:39162–39170. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Steneberg P, Bernardo L, Edfalk S,
Lundberg L, Backlund F, Ostenson CG and Edlund H: The type 2
diabetes-associated gene ide is required for insulin secretion and
suppression of α-synuclein levels in β-cells. Diabetes.
62:2004–2014. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Asrafuzzaman M, Cao Y, Afroz R, Kamato D,
Gray S and Little PJ: Animal models for assessing the impact of
natural products on the aetiology and metabolic pathophysiology of
Type 2 diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:1242–1251. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kaul N and Ali S: Genes, genetics, and
environment in Type 2 diabetes: Implication in personalized
medicine. DNA Cell Biol. 35:1–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cornelis MC, Zaitlen N, Hu FB, Kraft P and
Price AL: Genetic and environmental components of family history in
type 2 diabetes. Hum Genet. 134:259–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Flannick J and Florez JC: Type 2 diabetes:
Genetic data sharing to advance complex disease research. Nat Rev
Genet. 17:535–549. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fuchsberger C, Flannick J, Teslovich TM,
Mahajan A, Agarwala V, Gaulton KJ, Ma C, Fontanillas P, Moutsianas
L, McCarthy DJ, et al: The genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes.
Nature. 536:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kong X, Zhang X, Xing X, Zhang B, Hong J
and Yang W: The association of Type 2 diabetes loci identified in
genome-wide association studies with metabolic syndrome and its
components in a chinese population with Type 2 diabetes. PLoS One.
10:e01436072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ma RC, So WY, Tam CH, Luk AO, Ho JS, Wang
Y, Lam VK, Lee HM, Kong AP, Tong PC, et al: Genetic variants for
type 2 diabetes and new-onset cancer in Chinese with type 2
diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 103:328–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Klimentidis YC, Lemas DJ, Wiener HH,
O'Brien DM, Havel PJ, Stanhope KL, Hopkins SE, Tiwari HK and Boyer
BB: CDKAL1 and HHEX are associated with type 2 diabetes-related
traits among Yup'ik people. J Diabetes. 6:251–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sanghera DK, Ortega L, Han S, Singh J,
Ralhan SK, Wander GS, Mehra NK, Mulvihill JJ, Ferrell RE, Nath SK
and Kamboh MI: Impact of nine common type 2 diabetes risk
polymorphisms in Asian Indian Sikhs: PPARG2 (Pro12Ala), IGF2BP2,
TCF7L2 and FTO variants confer a significant risk. BMC Med Genet.
9:592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Scott LJ, Mohlke KL, Bonnycastle LL,
Willer CJ, Li Y, Duren WL, Erdos MR, Stringham HM, Chines PS,
Jackson AU, et al: A genome-wide association study of type 2
diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants.
Science. 316:1341–1345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Diabetes Genetics Initiative of Broad
Institute of Harvard and MIT, Lund University, and Novartis
Institutes of BioMedical Research, . Saxena R, Voight BF, Lyssenko
V, Burtt NP, de Bakker PI, Chen H, Roix JJ, Kathiresan S,
Hirschhorn JN, et al: Genome-wide association analysis identifies
loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science.
316:1331–1336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Malhotra A, Coon H, Feitosa MF, Li WD,
North KE, Price RA, Bouchard C, Hunt SC and Wolford JK: American
Diabetes Association GENNID Study Group: Meta-analysis of
genome-wide linkage studies for quantitative lipid traits in
African Americans. Hum Mol Genet. 14:3955–3962. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kong X, Xing X, Hong J, Zhang X and Yang
W: Genetic variants associated with lean and obese type 2 diabetes
in a Han Chinese population: A case-control study. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e38412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kong X, Xing X, Hong J, Zhang X and Yang
W: Association of a type 2 diabetes genetic risk score with insulin
secretion modulated by insulin sensitivity among Chinese Hans. Clin
Genet. 91:832–842. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, Dina C,
Shen L, Serre D, Boutin P, Vincent D, Belisle A, Hadjadj S, et al:
A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type
2 diabetes. Nature. 445:881–885. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Arterbery AS and Bogue CW: Hhex is
necessary for the hepatic differentiation of mouse ES cells and
Acts via Vegf signaling. PLoS One. 11:e01468062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Watanabe H, Takayama K, Inamura M,
Tachibana M, Mimura N, Katayama K, Tashiro K, Nagamoto Y, Sakurai
F, Kawabata K, et al: HHEX promotes hepatic-lineage specification
through the negative regulation of eomesodermin. PLoS One.
9:e907912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hunter MP, Wilson CM, Jiang X, Cong R,
Vasavada H, Kaestner KH and Bogue CW: The homeobox gene Hhex is
essential for proper hepatoblast differentiation and bile duct
morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 308:355–367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Deng XP, Zhao LX, Wang BB, Wang J, Cheng
LF, Cheng Z, Suo PS, Li H and Ma X: The HHEX gene is not related to
congenital heart disease in 296 Chinese patients. World J Pediatr.
9:278–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Foley AC and Mercola M: Heart induction by
Wnt antagonists depends on the homeodomain transcription factor
Hex. Genes Dev. 19:387–396. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu S, Chai J, Zheng G, Li H, Lu D and Ge
Y: Screening of HHEX mutations in chinese children with thyroid
dysgenesis. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 8:21–25. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
McLin VA, Rankin SA and Zorn AM:
Repression of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the anterior endoderm
is essential for liver and pancreas development. Development.
134:2207–2217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang J, McKenna LB, Bogue CW and Kaestner
KH: The diabetes gene Hhex maintains δ-cell differentiation and
islet function. Genes Dev. 28:829–834. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rong R, Hanson RL, Ortiz D, Wiedrich C,
Kobes S, Knowler WC, Bogardus C and Baier LJ: Association analysis
of variation in/near FTO, CDKAL1, SLC30A8, HHEX, EXT2, IGF2BP2,
LOC387761, and CDKN2B with type 2 diabetes and related quantitative
traits in Pima Indians. Diabetes. 58:478–488. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Moore AF, Jablonski KA, McAteer JB, Saxena
R, Pollin TI, Franks PW, Hanson RL, Shuldiner AR, Knowler WC,
Altshuler D, et al: Extension of type 2 diabetes genome-wide
association scan results in the diabetes prevention program.
Diabetes. 57:2503–2510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chiasson JL: Early insulin use in type 2
diabetes: What are the cons? Diabetes Care. 32 Suppl 2:S270–S274.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Fonseca VA: Defining and characterizing
the progression of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 32 Suppl
2:S151–S156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Vigneri R, Goldfine ID and Frittitta L:
Insulin, insulin receptors, and cancer. J Endocrinol Invest.
39:1365–1376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
de Miguel-Díez J, Muñoz-Rivas N,
Jiménez-García R, Hernández-Barrera V, Carrasco-Garrido P, Monreal
M, Jiménez D, Guijarro R and de Andrés López A: Type 2 diabetes is
associated with a higher incidence of hospitalization for pulmonary
embolism in Spain: Analysis of hospital discharge data during
2004–2013. Respirology. 21:1277–1284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yu F, Guo Y, Wang H, Feng J, Jin Z, Chen
Q, Liu Y and He J: Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal
adenoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Cancer.
16:6422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sun R, Liu JP, Gao C, Xiong YY, Li M, Wang
YP, Su YW, Lin M, Jiang AL, Xiong LF, et al: Two variants on T2DM
susceptible gene HHEX are associated with CRC risk in a Chinese
population. Oncotarget. 7:29770–29779. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|