Introduction
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) remains the main cause of
severe liver disease. Due to medical progress, the number of new
HCV infections has been decreasing. However, HCV-related morbidity
and mortality are expected to continue rising, and approximately
399,000 people die each year from hepatitis C, mostly due to
cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en).
To date, several direct-acting antiviral agents
(DAAs) have been designed and developed to target individual
portions of the viral proteins, including NS3/4A, NS5B, and NS5A
(1). A new treatment method using
DAAs is highly active against HCV and has few side effects. In
particular, twelve-week combination treatment with the DAAs
ledipasvir (LDV), an NS5A inhibitor, and sofosbuvir (SOF), an NS5B
polymerase inhibitor, is highly effective in patients with HCV
genotype 1 infection (2). However,
the treatment is not perfect, as the overall SVR at 12 weeks after
the end of treatment is 98.8%, not 100% (3). In addition, the next treatment regimen
for LDV/SOF failure cases has not been established.
Elbasvir (EBR), an NS5A inhibitor, combined with
grazoprevir (GZR), an NS3/4A protease inhibitor, is the latest
approved therapy for patients with genotype 1 or 4 chronic
hepatitis C (4). Compared to
LDV/SOF, EBR/GZR has few side effects and limited drug interactions
and can be given to patients with illnesses such as heart failure.
In the 2016 AASLD/IDSA guidelines, 12 weeks of EBR/GZR treatment
was recommended as level A therapy for treatment-experienced
patients (prior exposure to peginterferon/ribavirin) with genotype
1a or 1b infection. However, clinical experience and trial data on
the retreatment of any patient that had previously received
treatment with LDV/SOF are very limited (http://www.hcvguidelines.org.). Therefore, the present
study reported a case in which GZR/EBR was effective for the
retreatment of a patient with a history of failed LDV/SOF treatment
for chronic hepatitis C.
Case report
A 55-year-old Japanese male had a history of chronic
hepatitis C with compensated liver cirrhosis; his viral load was
6.0 log IU/ml, and his viral genotype was 1b. In addition, he
exhibited the high-frequency amino acid mutation (>99%) Y93H in
NS5A. Although his medical history included three instances of
gastroesophageal varix rupture due to excessive drinking in
addition to HCV infection, suggesting uncompensated liver
cirrhosis, the patient later stopped drinking, and the liver
function reflected compensated cirrhosis. Therefore, we started
treatment for the patient's chronic hepatitis C infection using
LDV/SOF.
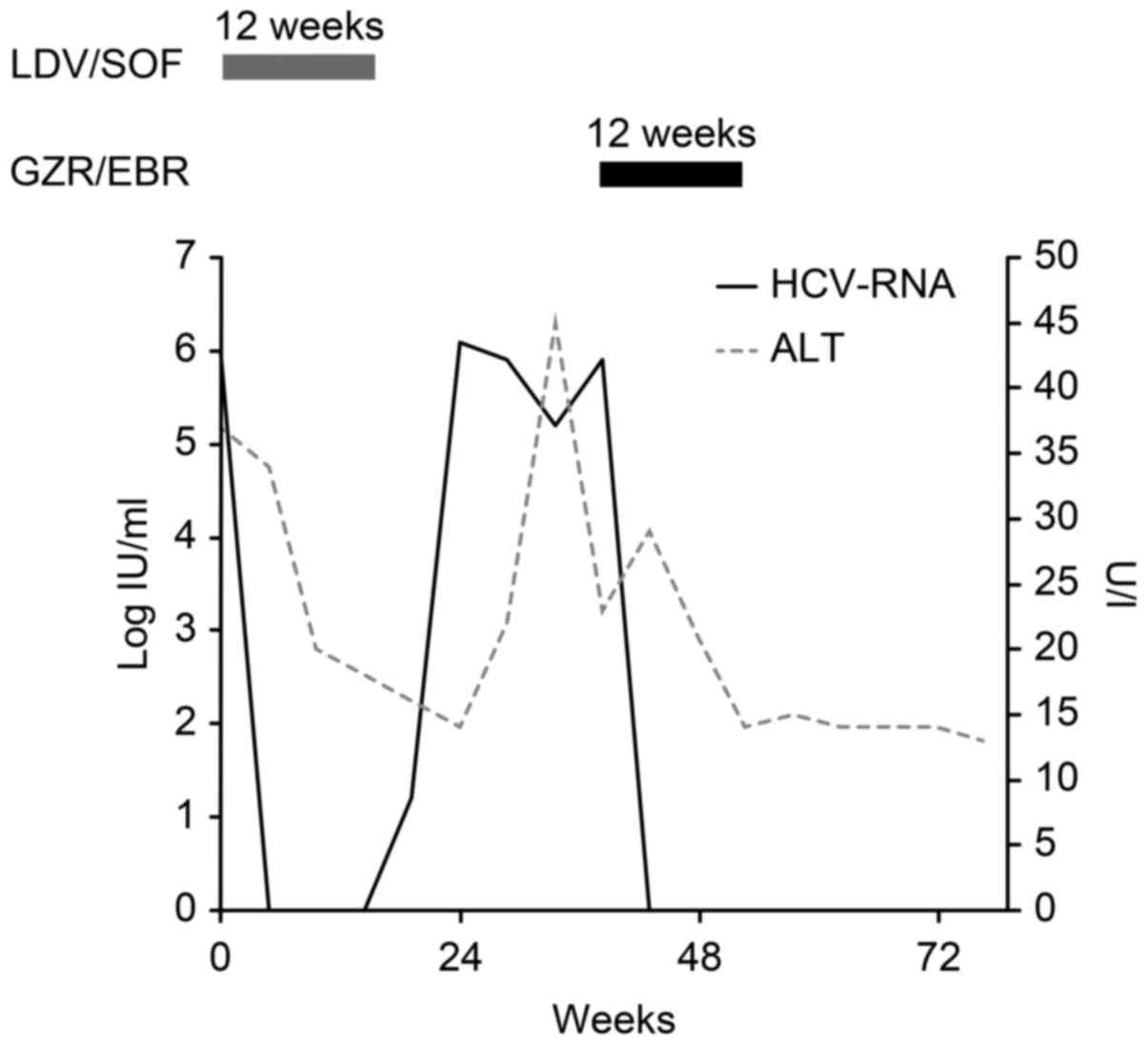
Two weeks after commencing LDV/SOF treatment, his
viral load decreased to below the detection sensitivity. However, 4
weeks after treatment, his viral load increased and returned to its
original level. No change was observed in the amino acid mutation
after LDV/SOF treatment; the high-frequency Y93H mutation (>99%)
in NS5A remained stable (Fig 1;
Table I).
 | Table I.RAV alignment of NS3 and NS5A in
patient before and after the treatment of LDV/SOF. |
Table I.
RAV alignment of NS3 and NS5A in
patient before and after the treatment of LDV/SOF.
| RAVs | Before LDV/SOF | After LDV/SOF |
|---|
| NS3/V36A | – | – |
| NS3/T54A | – | – |
| NS3/T54S | – | – |
| NS3/Q80L | – | – |
| NS3/Q80R | – | – |
| NS3/A156S | – | – |
| NS3/A156T | – | – |
| NS3/A156V | – | – |
| NS3/D168A | – | – |
| NS3/D168E | – | – |
| NS3/D168H | – | – |
| NS3/D168T | – | – |
| NS3/D168V | – | – |
| NS5A/L31F | – | – |
| NS5A/L31M | – | – |
| NS5A/L31V | – | – |
| NS5A/Y93H | H>99% | H>99% |
There was no evidence for subsequent treatments
after failure on LDV/SOF. His liver function reflected the
compensated cirrhoss as before treatment with LDV/SOF (Table II). Therefore, after the patient
gave informed consent, we started treatment with GZR/EBR, including
an NS3/4A protease inhibitor, which was not used in the previous
treatment. No side effects of GZR/EBR, such as headache, nausea,
fatigue, decreased appetite, anemia, pyrexia, or ALT elevations
(4), were observed during the
treatment, and the patient achieved an SVR at 12 weeks
posttreatment.
 | Table II.Laboratory patient data before
treatment with grazoprevir/elbasvir. |
Table II.
Laboratory patient data before
treatment with grazoprevir/elbasvir.
| Variables | Value | Units | Reference range |
|---|
| Total protein | 8.3 | g/dl | 6.5–8.2 |
| Albumin | 4 | g/dl | 3.5–5.5 |
| Albumin/globulin
ratio | 0.93 |
| 1–1.8 |
| Blood urea
nitrogen | 19.8 | mg/dl | 8.2–4.3 |
| Creatinine | 0.97 | mg/dl | 0.5–1 |
| Total bilirubin | 1.2 | mg/dl | 0.1–1.2 |
| Direct bilirubin | 0.5 | mg/dl | 0.1–0.6 |
| Aspartate
transaminase | 32 | U/l | 10–35 |
| Alanine
transaminase | 29 | U/l | 5–40 |
| Alkaline
phosphatase; | 509 | U/l | 100–340 |
| Lactate
dehydrogenase | 113 | U/l | 110–220 |
| γ-glutamyl
transpeptidase | 18 | U/l | 0–30 |
| Total
cholesterol | 99 | mg/dl | 130–219 |
| Triglyceride | 47 | mg/dl | 30–149 |
| Na | 138 | mmol/l | 135–146 |
| K | 4.2 | mmol/l | 3.5–4.6 |
| Cl | 104 | mmol/l | 96–110 |
| White blood
cells | 1,410 | /µl | 4,700–8,700 |
| Red blood cells |
375×104 | /µl | 370–490 |
| Hemoglobin | 10 | g/dl | 13–17 |
| Hematocrit | 31.3 | % | 35–45 |
| Platelets |
2.9×104 | /µl | 15–35 |
| Neutrophils | 78.5 | % | 38–71.9 |
| Eosinophils | 1 | % | 0.2–6.8 |
| Basophils | 0 | % | 0–1 |
| Lymphocytes | 11.5 | % | 26–46.6 |
| Monocytes | 9.5 | % | 2.3–7.7 |
| Prothrombin time | 49 | % | 80–100 |
Discussion
This case report provides two important clinical
suggestions regarding retreatment after failure of LDV/SOF therapy
for patients with chronic hepatitis C. First, GZR/EBR treatment
might be useful for treating relapsed HCV genotype 1b infection
after LDV/SOF treatment. Second, GZR/EBR was effective in a patient
with advanced cirrhosis who exhibited the high-frequency amino acid
mutation Y93H in NS5A.
Some reports have related a poor response to LDV/SOF
with resistance-associated variant (RAV)-positivity and high values
of the FIB4 index (5). On the other
hand, RAVs in the NS5B region, such as S282T, have not been
confirmed in Japan (6). In
particular, because a mutant form of NS5A (Y93H) shows diminished
binding to LDV, HCVs expressing this mutant are resistant to LDV
(7). However, RAV-positivity is also
related to a poor response to GZR/EBR (8). To elucidate why GZR/EBR was effective
in this case, it will be necessary to examine a large number of
cases, and obtaining appropriate informed consent is necessary
before initiating this treatment. Despite these facts, GZR/EBR was
useful in this case and may provide an option for patients who
undergo ineffective LDV/SOF treatment.
In the near future, it will be necessary to examine
a large number of cases to determine whether the administration of
GZR/EBR may serve as a potential treatment option for relapsed
cases of HCV genotype 1b infection after LDV/SOF treatment.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this article.
Authors' contributions
TT, SM and TM designed the case report. AM, KF, TS,
TN, JT, HY and TM acquired and interpreted the patient's data. TT
and KO collected the patient clinical data and TT was a major
contributor in writing the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki,
informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from the
patient.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
DAA
|
direct-acting antiviral agent
|
|
LDV
|
ledipasvir
|
|
SOF
|
sofosbuvir
|
|
HCV
|
hepatitis C virus
|
|
SVR
|
sustained virological response
|
|
EBR
|
elbasvir
|
|
GZR
|
grazoprevir
|
References
|
1
|
Zopf S, Kremer AE, Neurath MF and Siebler
J: Advances in hepatitis C therapy: What is the current state-what
come's next? World J Hepatol. 8:139–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P, Chojkier M,
Gitlin N, Puoti M, Romero-Gomez M, Zarski JP, Agarwal K, Buggisch
P, et al: Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1
infection. N Engl J Med. 370:1889–1898. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ogawa E, Furusyo N, Nomura H, Dohmen K,
Higashi N, Takahashi K, Kawano A, Azuma K, Satoh T, Nakamuta M, et
al: NS5A resistance-associated variants undermine the effectiveness
of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for cirrhotic patients infected with
HCV genotype 1b. J Gastroenterol. 52:845–854. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bell AM, Wagner JL, Barber KE and Stover
KR: Elbasvir/grazoprevir: A review of the latest agent in the fight
against hepatitis C. Int J Hepatol. 2016:38521262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Akuta N, Sezaki H, Suzuki F, Fujiyama S,
Kawamura Y, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S, Suzuki Y,
et al: Retreatment efficacy and predictors of ledipasvir plus
sofosbuvir to HCV genotype 1 in Japan. J Med Virol. 89:284–290.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanda T, Yasui S, Nakamura M, Suzuki E,
Arai M, Ooka Y, Ogasawara S, Chiba T, Saito T, Haga Y, et al:
Real-world experiences with the combination treatment of ledipasvir
plus sofosbuvir for 12 weeks in hcv genotype 1-infected Japanese
patients: Achievement of a sustained virological response in
previous users of peginterferon plus ribavirin with HCV NS3/4A
inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E9062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kwon HJ, Xing W, Chan K, Niedziela-Majka
A, Brendza KM, Kirschberg T, Kato D, Link JO, Cheng G, Liu X and
Sakowicz R: Direct binding of ledipasvir to HCV NS5A: Mechanism of
resistance to an HCV antiviral agent. PLoS One. 10:e01228442015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Komatsu TE, Boyd S, Sherwat A, Tracy L,
Naeger LK, O'Rear JJ and Harrington PR: Regulatory analysis of
effects of hepatitis C virus NS5A polymorphisms on efficacy of
elbasvir and grazoprevir. Gastroenterology. 152:586–597. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|