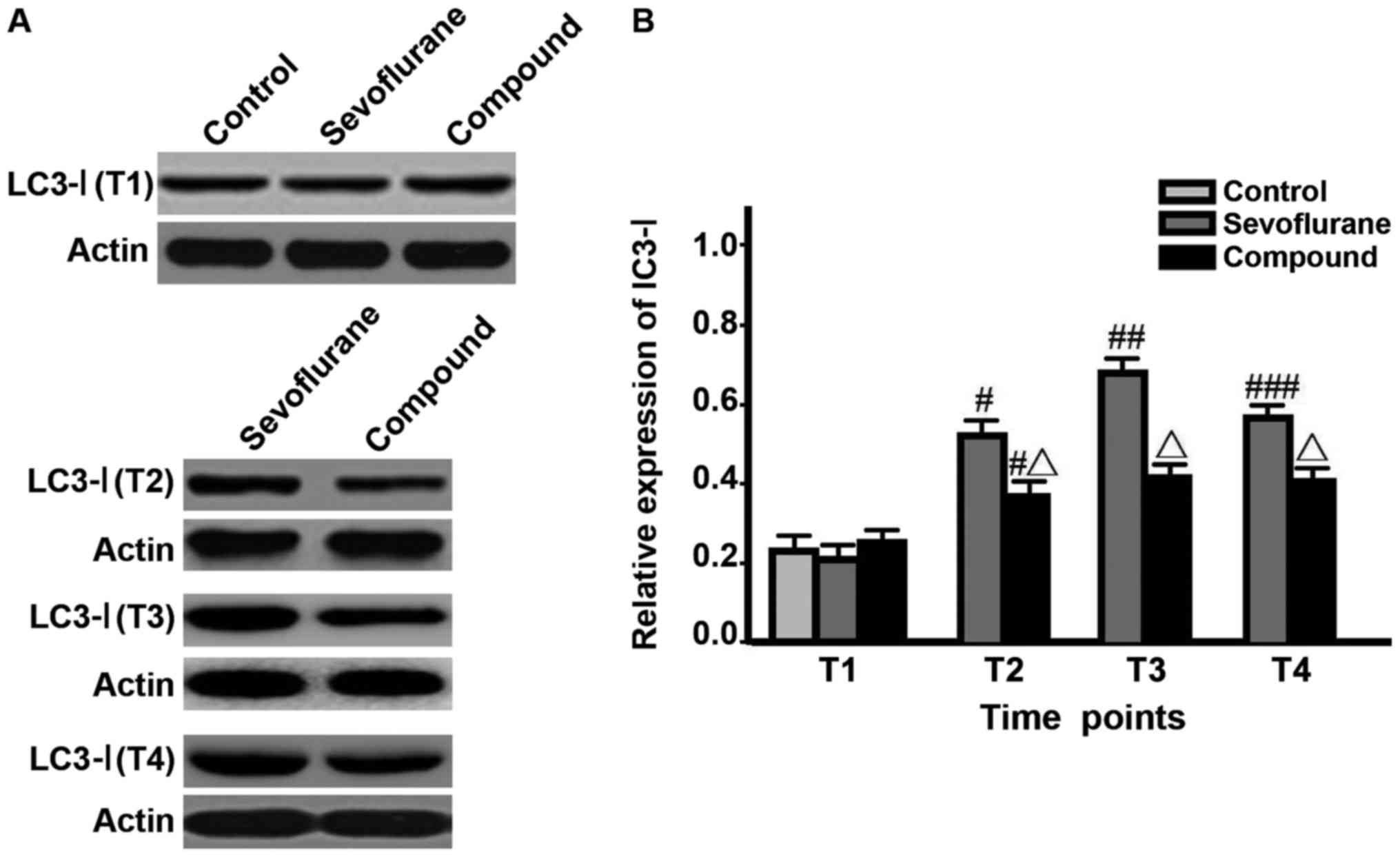
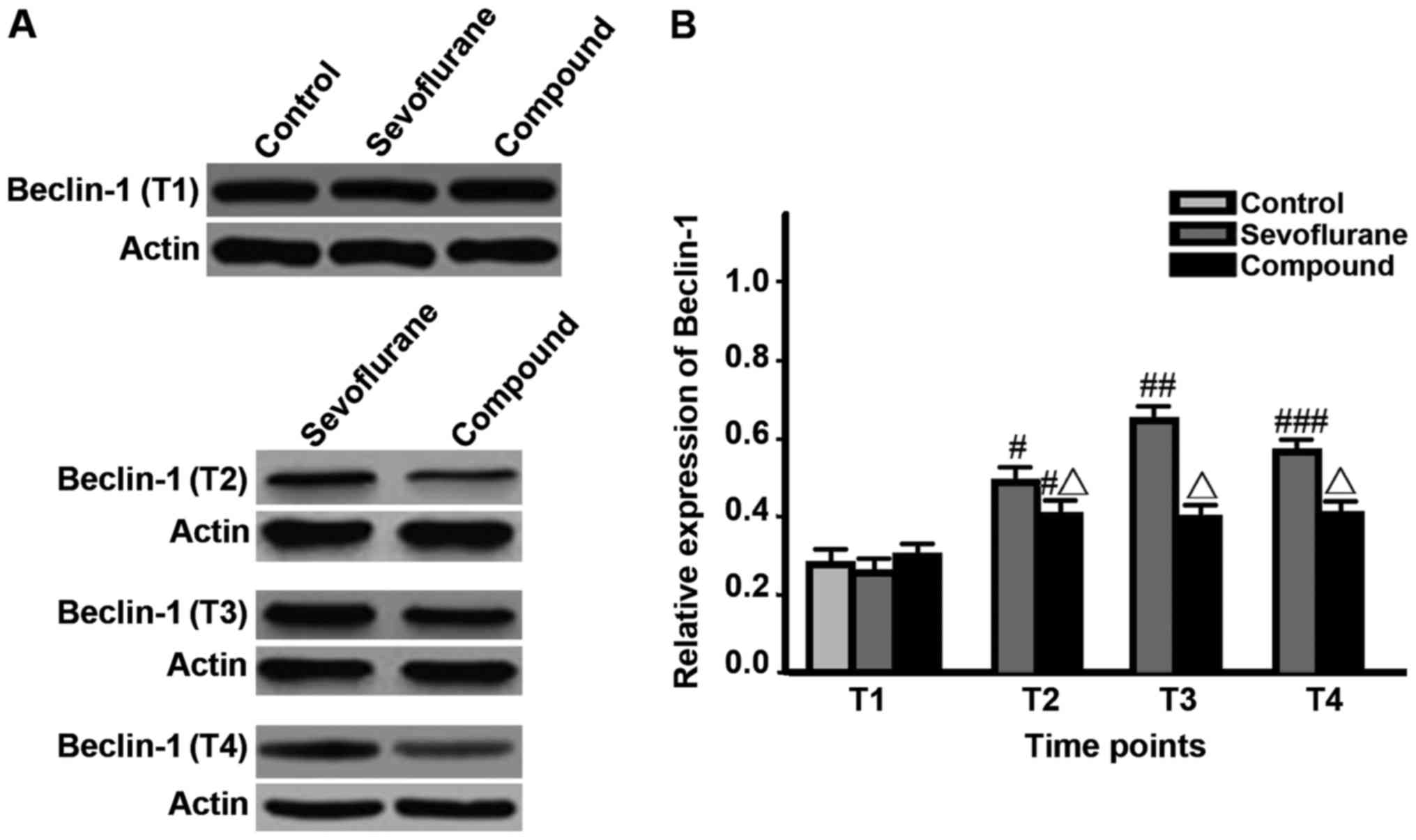
|
1
|
Tao G, Zhang J, Zhang L, Dong Y, Yu B,
Crosby G, Culley DJ, Zhang Y and Xie Z: Sevoflurane induces tau
phosphorylation and glycogen synthase kinase 3β activation in young
mice. Anesthesiology. 121:510–527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rundshagen I: Postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 111:119–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nixon RA: Autophagy, amyloidogenesis and
Alzheimer disease. J Cell Sci. 120:4081–4091. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro
JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J,
Gewirtz DA, Karantza V, et al: Autophagy in malignant
transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 34:856–880. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cai Y, Arikkath J, Yang L, Guo ML,
Periyasamy P and Buch S: Interplay of endoplasmic reticulum stress
and autophagy in neurodegenerative disorders. Autophagy.
12:225–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Whittington RA, Virág L, Gratuze M, Petry
FR, Noël A, Poitras I, Truchetti G, Marcouiller F, Papon MA, El
Khoury N, et al: Dexmedetomidine increases tau phosphorylation
under normothermic conditions in vivo and in vitro. Neurobiol
Aging. 36:2414–2428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ni J, Wei J, Yao Y, Jiang X, Luo L and Luo
D: Effect of dexmedetomidine on preventing postoperative agitation
in children: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e01284502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanders RD, Giombini M, Ma D, Ohashi Y,
Hossain M, Fujinaga M and Maze M: Dexmedetomidine exerts
dose-dependent age-independent antinociception but age-dependent
hypnosis in Fischer rats. Anesth Analg. 100:1295–1302. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu M, Wang H, Zhu A, Niu K and Wang G:
Meta-analysis of dexmedetomidine on emergence agitation and
recovery profiles in children after sevoflurane anesthesia:
Different administration and different dosage. PLoS One.
10:e01237282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang C, Hu J, Liu X and Yan J: Effects of
intravenous dexmedetomidine on emergence agitation in children
under sevoflurane anesthesia: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. PLoS One. 9:e997182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu W, Xu J, Wang H, Xu C, Ji C, Wang Y,
Feng C, Zhang X, Xu Z, Wu A, et al: Isoflurane-induced spatial
memory impairment by a mechanism independent of amyloid-beta levels
and tau protein phosphorylation changes in aged rats. Neurol Res.
34:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H,
Takishima K, Ito M and Imaki J: Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane
induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning
in mice. Anesthesiology. 110:628–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou YF, Wang QX, Zhou HY and Chen G:
Autophagy activation prevents sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in
H4 human neuroglioma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:580–588. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu K, Shi Y, Guo X, Wang S, Ouyang Y, Hao
M, Liu D, Qiao L, Li N, Zheng J, et al: CHOP mediates ASPP2-induced
autophagic apoptosis in hepatoma cells by releasing Beclin-1 from
Bcl-2 and inducing nuclear translocation of Bcl-2. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Trisciuoglio D, de Luca T, Desideri M,
Passeri D, Gabellini C, Scarpino S, Liang C, Orlandi A and Del
Bufalo D: Removal of the BH4 domain from Bcl-2 protein triggers an
autophagic process that impairs tumor growth. Neoplasia.
15:315–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|