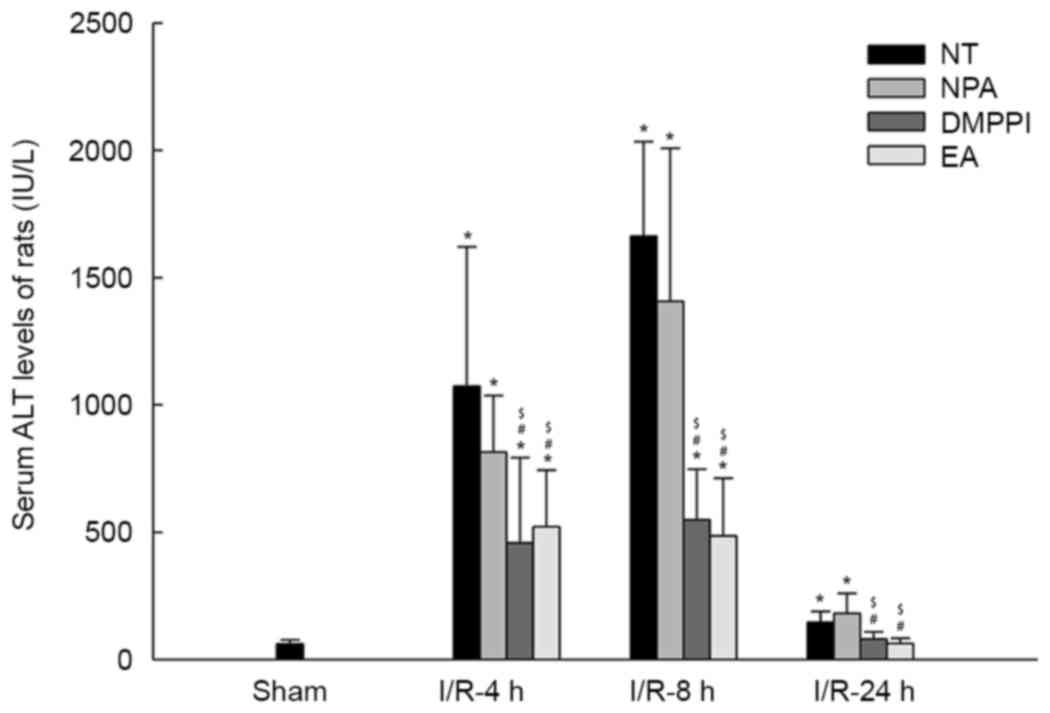
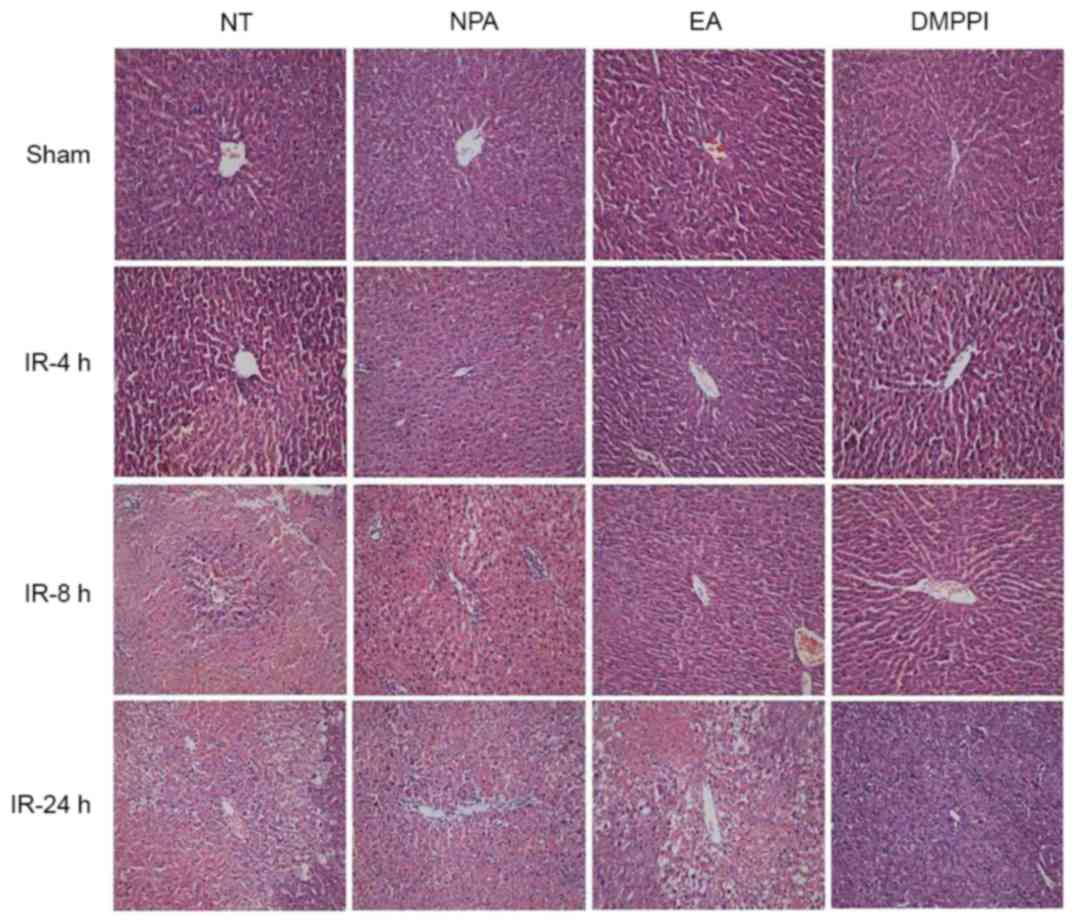
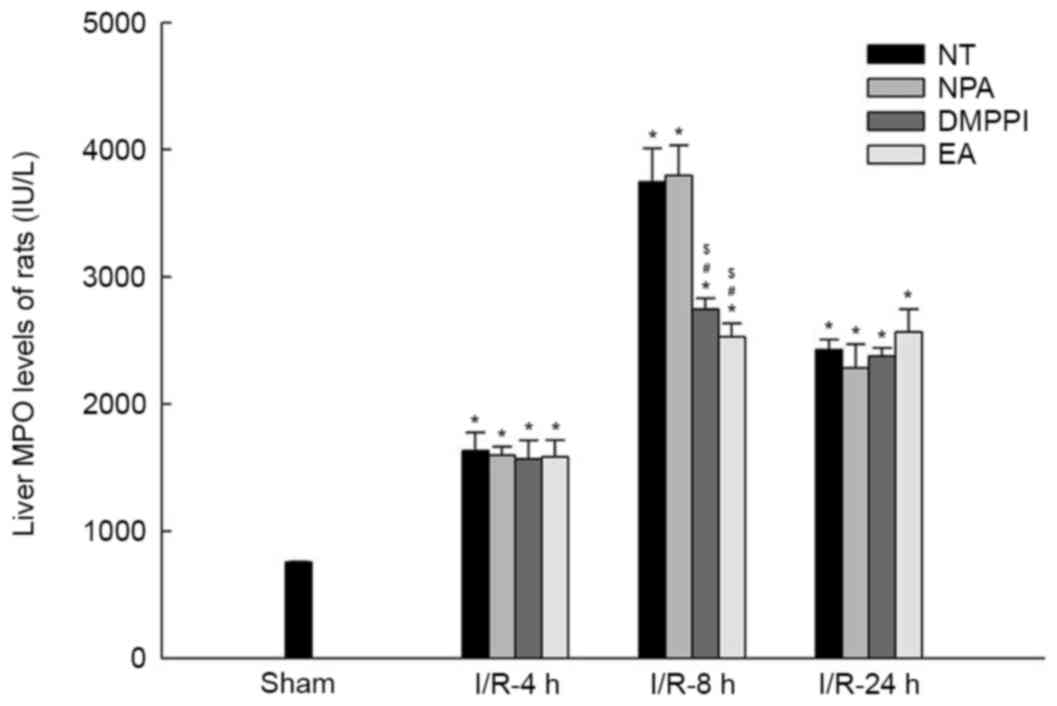
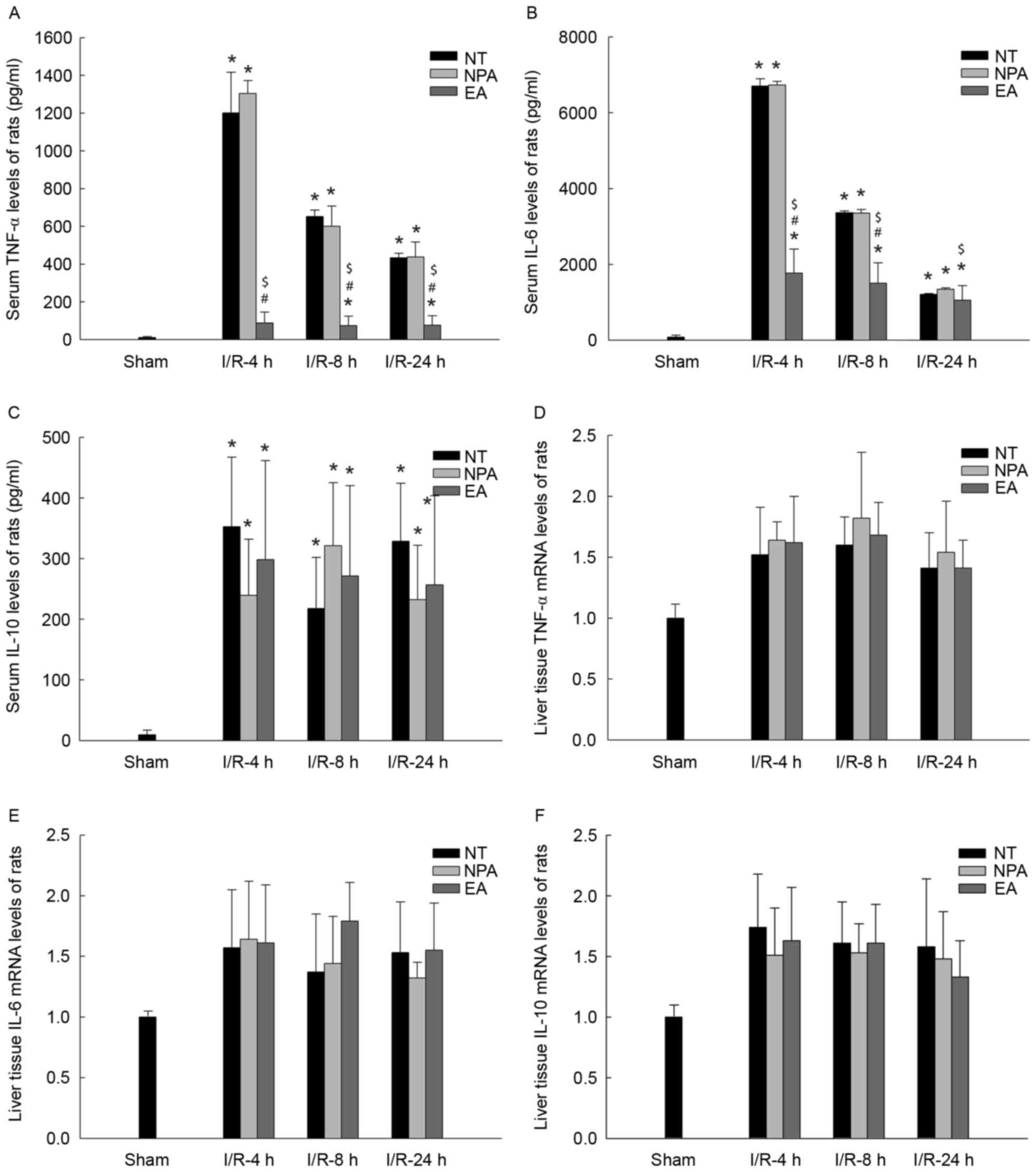
|
1
|
Nastos C, Kalimeris K, Papoutsidakis N,
Tasoulis MK, Lykoudis PM, Theodoraki K, Nastou D, Smyrniotis V and
Arkadopoulos N: Global consequences of liver ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:9069652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mourad MM, Algarni A, Liossis C and
Bramhall SR: Aetiology and risk factors of ischaemic cholangiopathy
after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 20:6159–6169.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ji H, Shen XD, Zhang Y, Gao F, Huang CY,
Chang WW, Lee C, Ke B, Busuttil RW and Kupiec-Weglinski JW:
Activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein
kinase a signaling prevents liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in
mice. Liver Transpl. 18:659–670. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu A, Fang H, Dirsch O, Jin H and Dahmen
U: Early release of macrophage migration inhibitory factor after
liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Cytokine.
57:150–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kang JW and Lee SM: Melatonin inhibits
type 1 interferon signaling of toll-like receptor 4 via heme
oxygenase-1 induction in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. J Pineal
Res. 53:67–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yun N, Kang JW and Lee SM: Protective
effects of chlorogenic acid against ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rat liver: Molecular evidence of its antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory properties. J Nutr Biochem. 23:1249–1255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pfab F, Schalock PC, Napadow V,
Athanasiadis GI, Huss-Marp J and Ring J: Acupuncture for allergic
disease therapy-the current state of evidence. Expert Rev Clin
Immunol. 10:831–841. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vaughn SE: Review of the third edition of
the guide for the care and use of agricultural animals in research
and teaching. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51:298–300. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources
CoLS, National Research Council: Guide for the care and use of
laboratory animals. National Academy Press; Washington, DC:
1996
|
|
10
|
Chan YY, Lo WY, Li TC, Shen LJ, Yang SN,
Chen YH and Lin JG: Clinical efficacy of acupuncture as an adjunct
to methadone treatment services for heroin addicts: A randomized
controlled trial. Am J Chin Med. 42:569–586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ha LJ, Cui JJ, Wang FC, Jing XH and Bai
WZ: The expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the
sensory and motor neurons associated with ‘Hegu’ (LI 4) in the rat.
Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 39:112–116. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Wang X and Lü R: Analgesic effect
of acupuncture at hegu (LI 4) on transvaginal oocyte retrieval with
ultrasonography. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:294–297. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kirshenbaum AP, Jackson ER, Brown SJ,
Fuchs JR, Miltner BC and Doughty AH: Nicotine-induced impulsive
action: Sensitization and attenuation by mecamylamine. Behav
Pharmacol. 22:207–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rivera RE, Eagon JC, Soper NJ,
Klingensmith ME and Brunt LM: Experience with laparoscopic gastric
resection: Results and outcomes for 37 cases. Surg Endosc.
19:1622–1626. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scognamillo-Szabó MV, Bechara GH, Ferreira
SH and Cunha FQ: Effect of various acupuncture treatment protocols
upon sepsis in Wistar rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1026:251–256. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Crockett ET, Galligan JJ, Uhal BD, Harkema
J, Roth R and Pandya K: Protection of early phase hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury by cholinergic agonists. BMC Clin
Pathol. 6:32006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He YQ, Li Y, Wang XY, He XD, Jun L, Chuai
M, Lee KK, Wang J, Wang LJ and Yang X: Dimethyl phenyl piperazine
iodide (DMPP) induces glioma regression by inhibiting angiogenesis.
Exp Cell Res. 320:354–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gujral JS, Bucci TJ, Farhood A and
Jaeschke H: Mechanism of cell death during warm hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion in rats: Apoptosis or necrosis? Hepatology.
33:397–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng CH, Zhang J, Wu J and Zhang MM: The
effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on
pregnancy rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization: A study
protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 15:1622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuboki S, Shin T, Huber N, Eismann T,
Galloway E, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Zingarelli B and Lentsch AB:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma protects against
hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Hepatology.
47:215–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiang H, Hu B, Li Z and Li J:
Dexmedetomidine controls systemic cytokine levels through the
cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Inflammation. 37:1763–1770.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiong J, Xue FS, Yuan YJ, Wang Q, Liao X
and Wang WL: Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: A possible
approach to protect against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury.
Chin Med J (Engl). 123:2720–2726. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Manhas A, Khanna V, Prakash P, Goyal D,
Malasoni R, Naqvi A, Dwivedi AK, Dikshit M and Jagavelu K: Curcuma
oil reduces endothelial cell mediated inflammation in post
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
64:228–236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dvoriantchikova G, Santos AR, Saeed AM,
Dvoriantchikova X and Ivanov D: Putative role of protein kinase C
in neurotoxic inflammation mediated by extracellular heat shock
protein 70 after ischemia-reperfusion. J Neuroinflammation.
11:812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cámara-Lemarroy CR, Guzmán-de la Garza FJ,
Alarcón-Galván G, Cordero-Pérez P, Muñoz-Espinosa L,
Torres-González L and Fernández-Garza NE: Hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury is diminished by atorvastatin in wistar
rats. Arch Med Res. 45:210–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tukhovskaya EA, Turovsky EA, Turovskaya
MV, Levin SG, Murashev AN, Zinchenko VP and Godukhin OV:
Anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 increases resistance to
brain ischemia through modulation of ischemia-induced intracellular
Ca2+ response. Neurosci Lett. 571:55–60. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zuo Z, Wang C, Carpenter D, Okada Y,
Nicolaidou E, Toyoda M, Trento A and Jordan SC: Prolongation of
allograft survival with viral IL-10 transfection in a highly
histoincompatible model of rat heart allograft rejection.
Transplantation. 71:686–691. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang CL, Tsai PS, Wang TY, Yan LP, Xu HZ
and Huang CJ: Acupuncture stimulation of ST36 (Zusanli) attenuates
acute renal but not hepatic injury in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
rats. Anesth Anal. 104:646–654. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xu F, Li YS, Lv X, et al: Protective
effect of electroacupuncture on liver ischemiareperfusion injury in
rats. Official J Int Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc.
15:1222013.
|