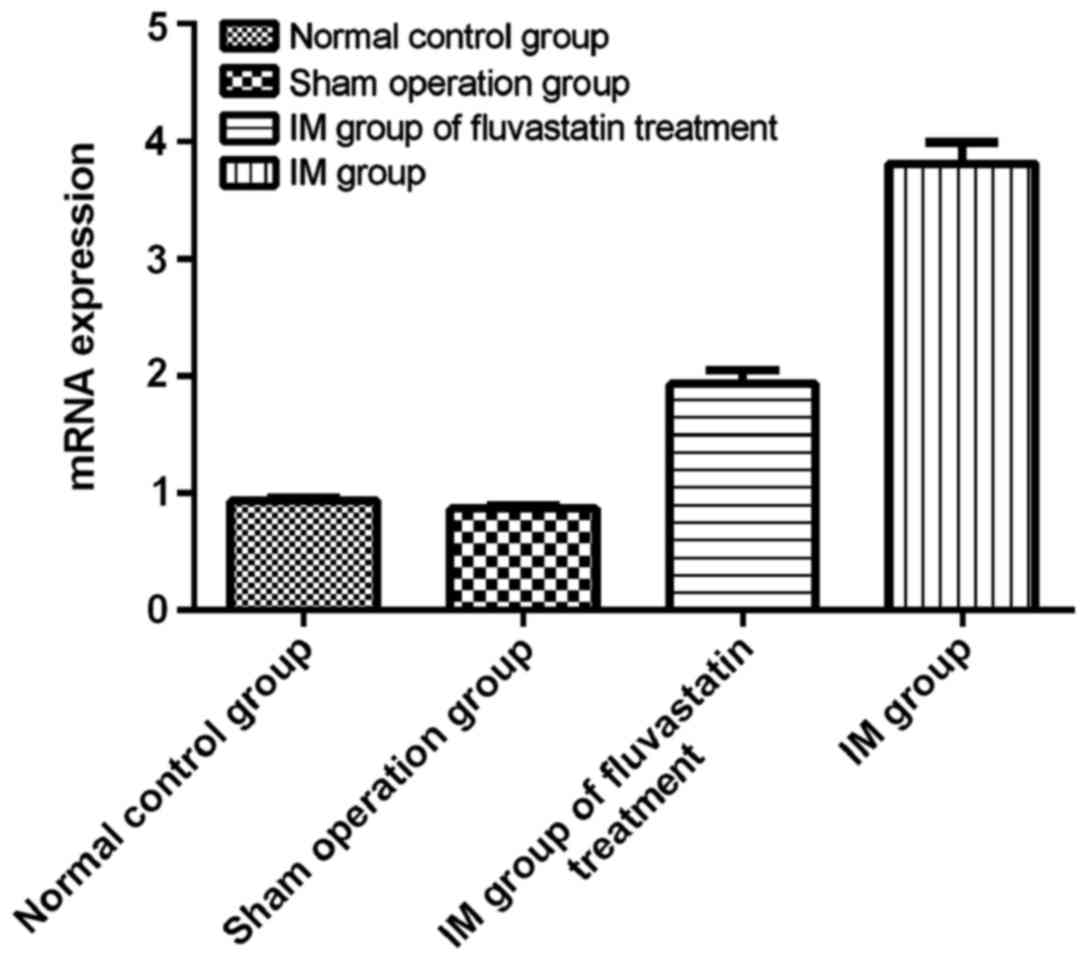
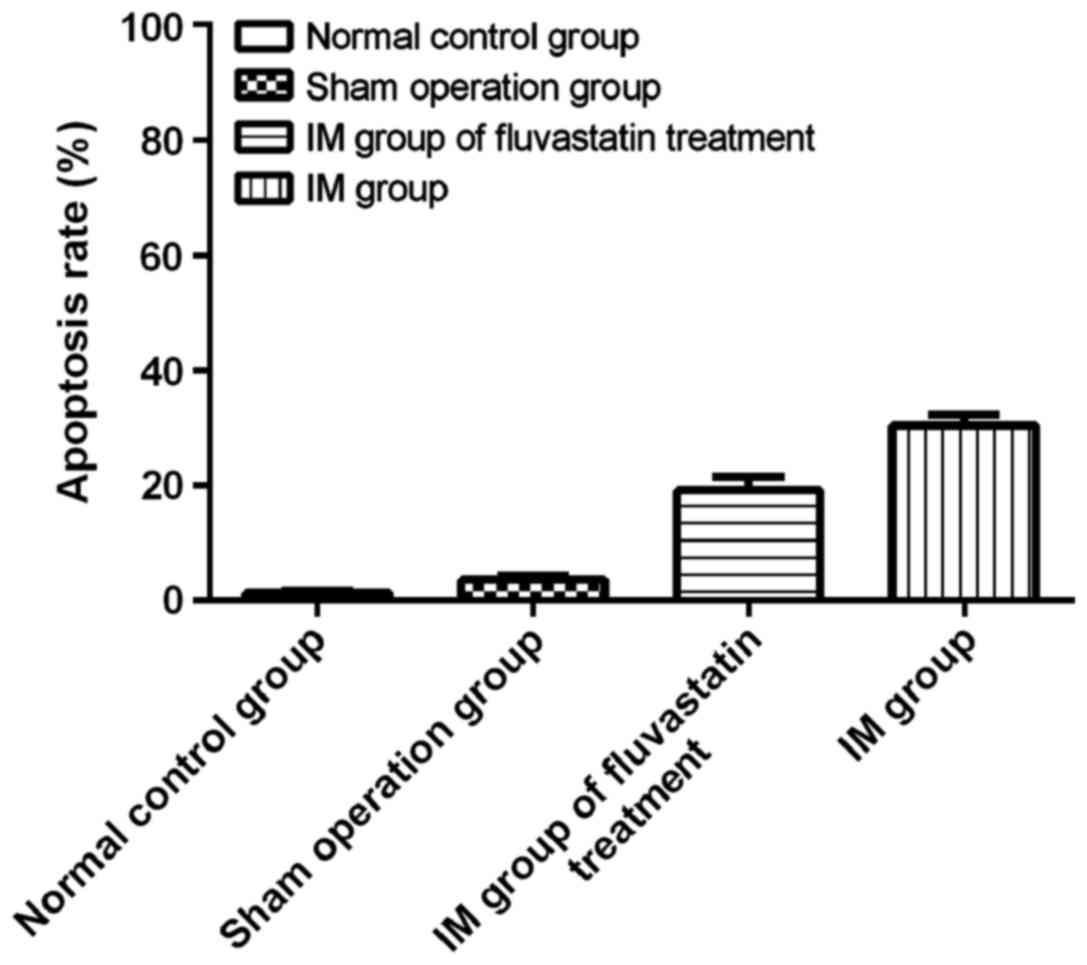
|
1
|
Thiene G, Corrado D and Basso C: Sudden
cardiac death in the young and athletes. Springer Milan.
2016:21–71. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Sankar NM, Ramani SS and Anantharaman R:
Coronary artery disease in women. Indian Heart J. 69:807–808. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Forman DE, Alexander K, Brindis RG, Curtis
AB, Maurer M, Rich MW, Sperling L and Wenger NK: Improved
cardiovascular disease outcomes in older adults. F1000Res. 5:1–9.
2016.
|
|
4
|
Zhou M, Wang H, Zhu J, Chen W, Wang L, Liu
S, Li Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Yin P, et al: Cause-specific mortality for
240 causes in China during 1990–2013: A systematic subnational
analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet.
387:251–272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan NY: Sudden cardiac death in Asia and
China: Are we different? J Am Coll Cardiol. 67:590–592. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reed GW, Rossi JE and Cannon CP: Acute
myocardial infarction. Lancet. 389:197–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stewart WJ: Atrial myocardial infarction:
A neglected stalker in coronary patients. J Am Coll Cardiol.
70:2890–2892. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li S, Guo LZ, Kim MH, Han JY and
Serebruany V: Platelet microRNA for predicting acute myocardial
infarction. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 44:556–564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kataoka Y, Andrews J, Puri R, Psaltis P
and Nicholls SJ: Lipid lowering therapy to modify plaque
microstructures. J Atheroscler Thromb. 24:360–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ruel I, Aljenedil S, Sadri I, de Varennes
É, Hegele RA, Couture P, Bergeron J, Wanneh E, Baass A, Dufour R,
et al: Imputation of baseline LDL cholesterol concentration in
patients with familial hypercholesterolemia on statins or
ezetimibe. Clin Chem. 70:20222017.
|
|
11
|
Zhai Y, Ao L, Cleveland JC, Zeng Q, Reece
TB, Fullerton DA and Meng X: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates the
inflammatory responses and matrix protein remodeling in remote
non-ischemic myocardium in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion. PLoS One. 10:e01218532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Sun Y, Yang H, Lu Y and Li L:
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces apoptosis in cultured
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes by modulating the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.
Sci Rep. 6:278662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tixeira R, Caruso S, Paone S, Baxter AA,
Atkin-Smith GK, Hulett MD and Poon IK: Defining the morphologic
features and products of cell disassembly during apoptosis.
Apoptosis. 22:475–477. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Wu Z, Huang C, Zhao Y, Zhou Y,
Zhou X, Lu X, Mao L and Li S: Effect of lipoxin A4 on myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury following cardiac arrest in a rabbit
model. Inflammation. 36:468–475. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kleinbongard P, Schulz R and Heusch G:
TNFα in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion, remodeling and heart
failure. Heart Fail Rev. 16:49–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Q, Zhang J, Xu Y, Huang Y and Wu C:
Effect of carvedilol on cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rat model of
myocardial infarction: A role for toll-like receptor 4. Indian J
Pharmacol. 45:458–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SC, Stice JP, Chen L, Jung JS, Gupta
S, Wang Y, Baumgarten G, Trial J and Knowlton AA: Extracellular
heat shock protein 60, cardiac myocytes, and apoptosis. Circ Res.
105:1186–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Satoh M, Shimoda Y, Maesawa C, Akatsu T,
Ishikawa Y, Minami Y, Hiramori K and Nakamura M: Activated
toll-like receptor 4 in monocytes is associated with heart failure
after acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 109:226–234.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhai Y, Shen XD, OConnell R, Gao F,
Lassman C, Busuttil RW, Cheng G and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Cutting
edge: TLR4 activation mediates liver ischemia/reperfusion
inflammatory response via IFN regulatory factor 3-dependent
MyD88-independent pathway. J Immunol. 173:7115–7119. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Wang L, Hu X, Zhang P, Chen Y, Liu
X, Xu M, Zhang Y and Zhang M: Effect of rosuvastatin on
atherosclerotic plaque stability: An intravascular ultrasound
elastography study. Atherosclerosis. 248:27–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang J, Yang J, Ding JW, Chen LH, Wang YL,
Li S and Wu H: Sequential expression of TLR4 and its effects on the
myocardium of rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Inflammation. 31:304–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu L, Wang Y, Cao ZY, Wang MM, Liu XM,
Gao T, Hu QK, Yuan WJ and Lin L: Up-regulated TLR4 in
cardiomyocytes exacerbates heart failure after long-term myocardial
infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2728–2740. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun Y, Huang J and Song K: BET protein
inhibition mitigates acute myocardial infarction damage in rats via
the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. Exp Ther Med. 10:2319–2324. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|