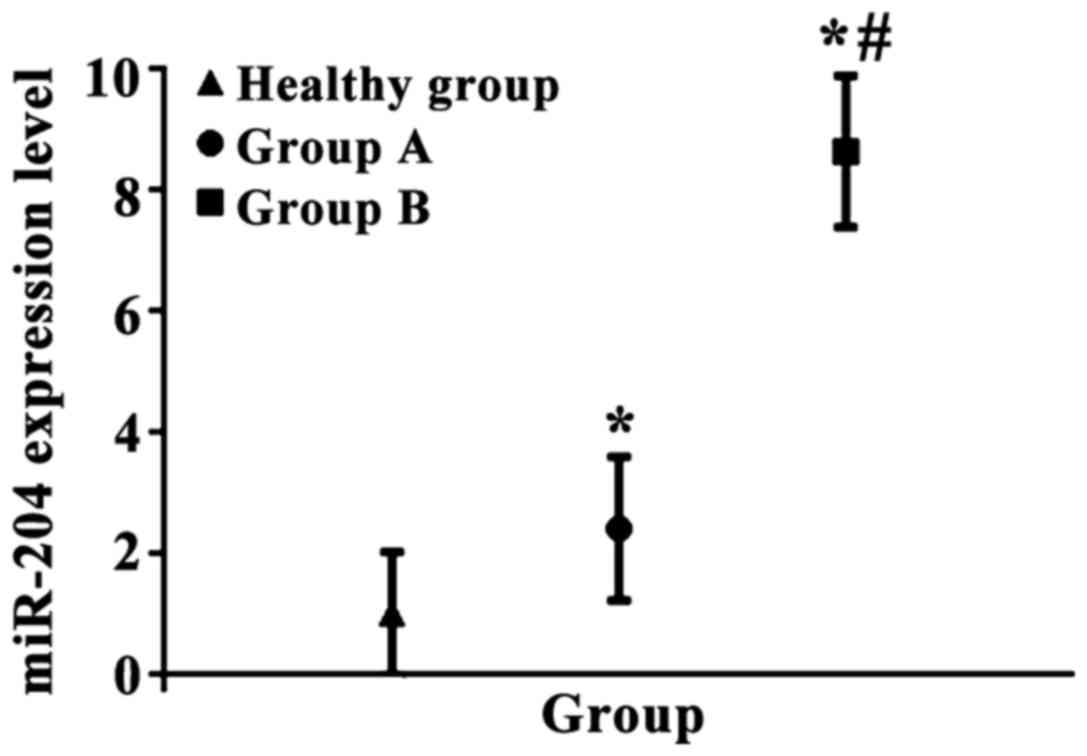
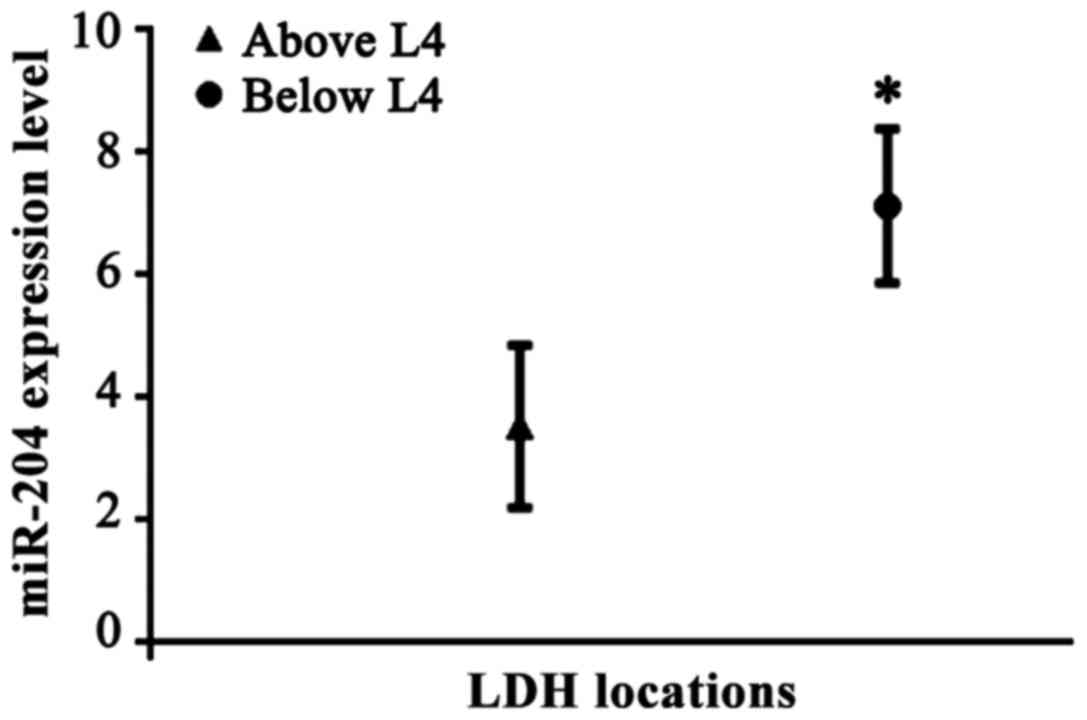
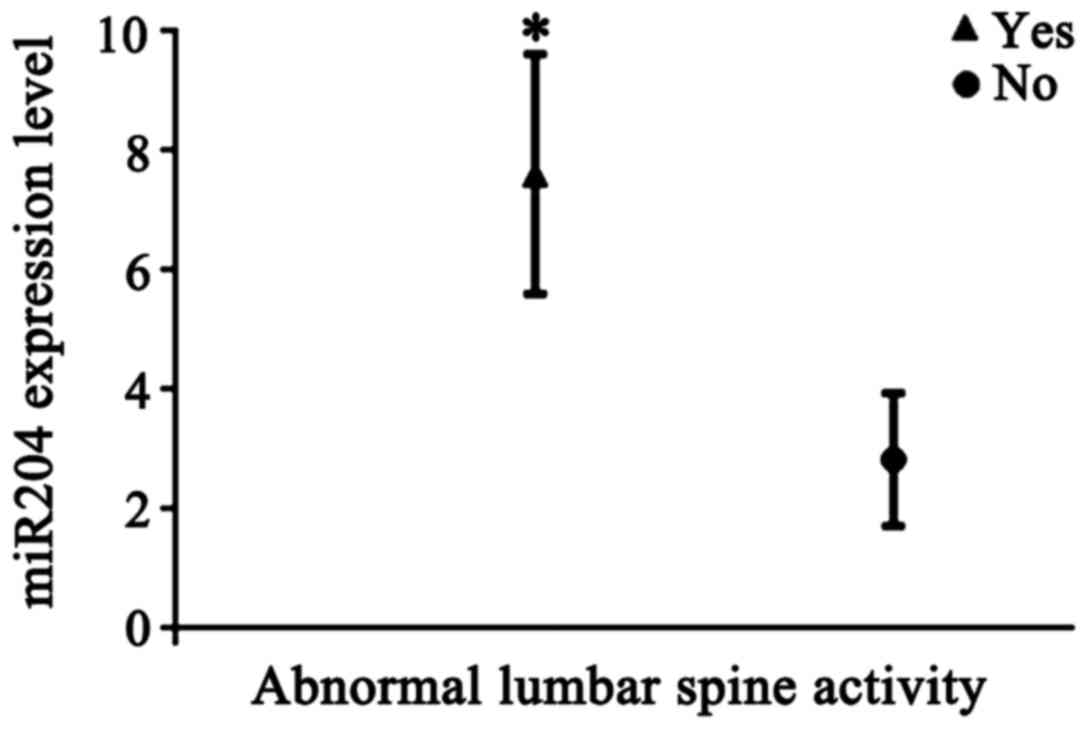
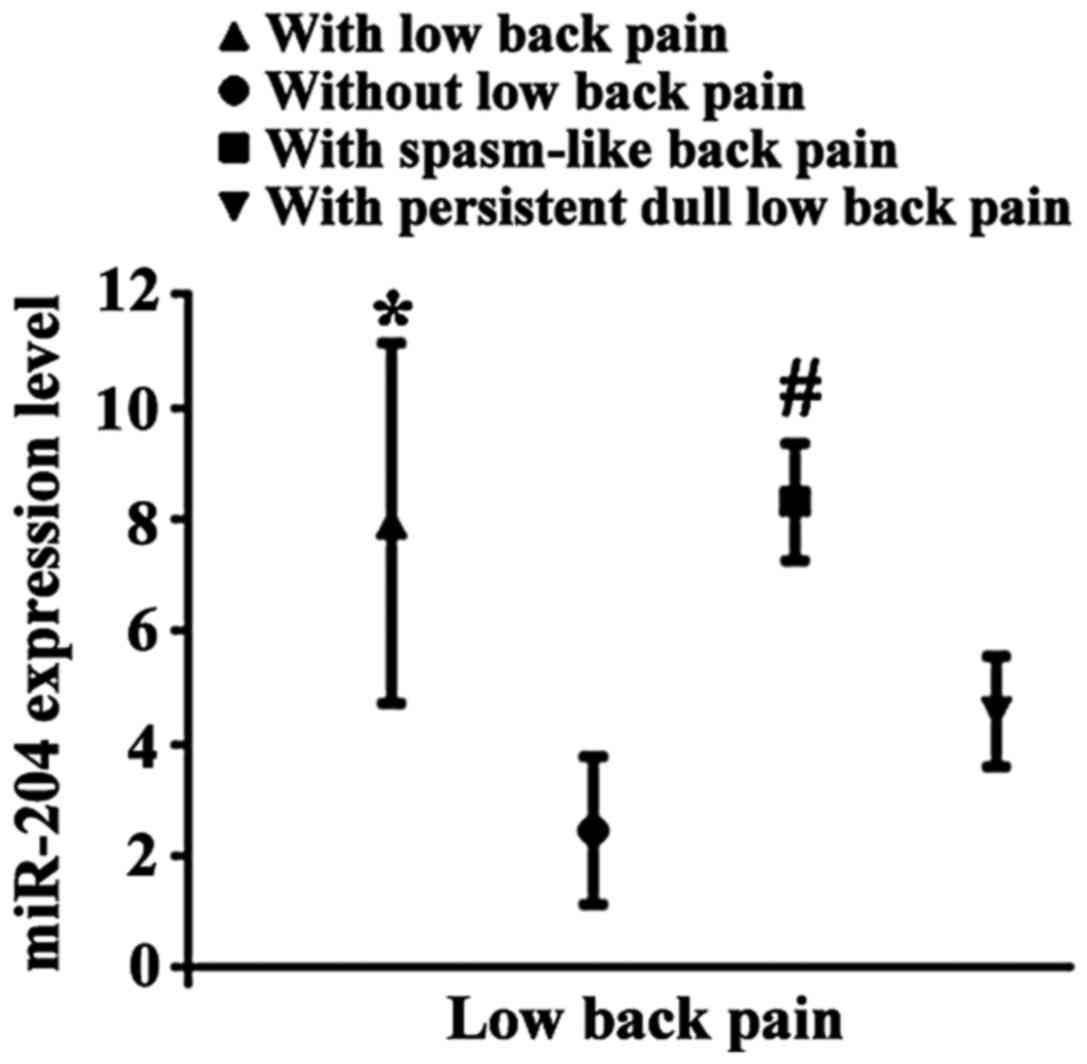
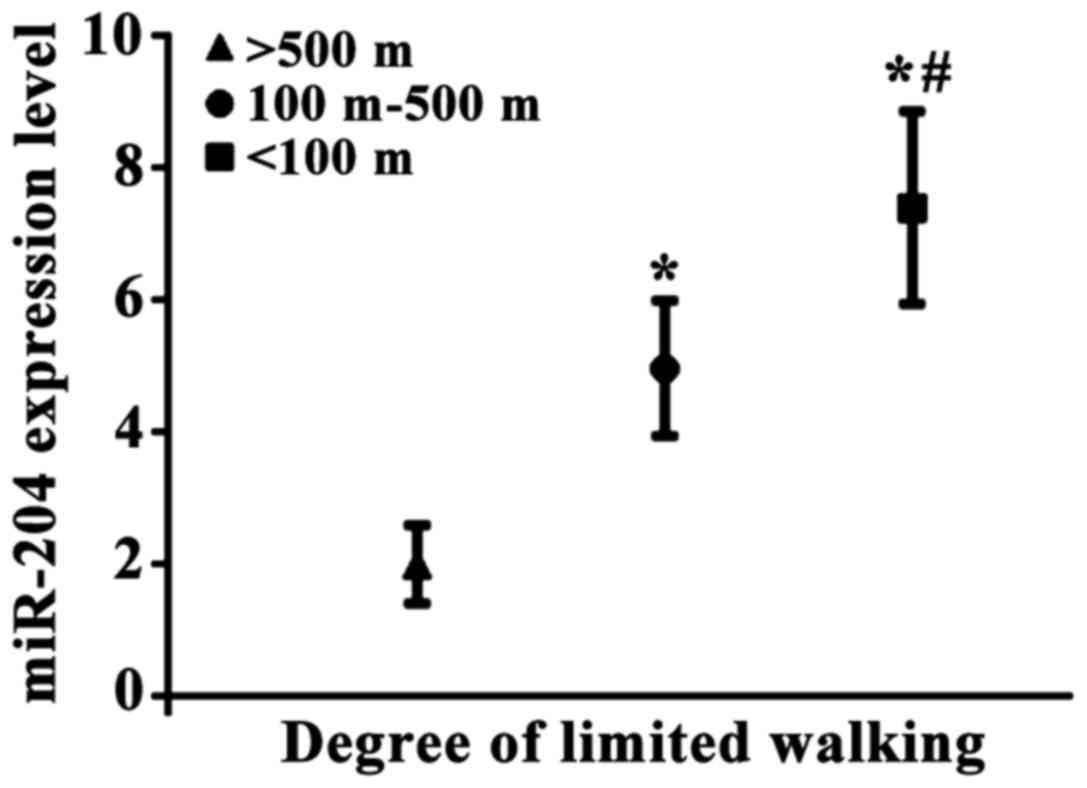
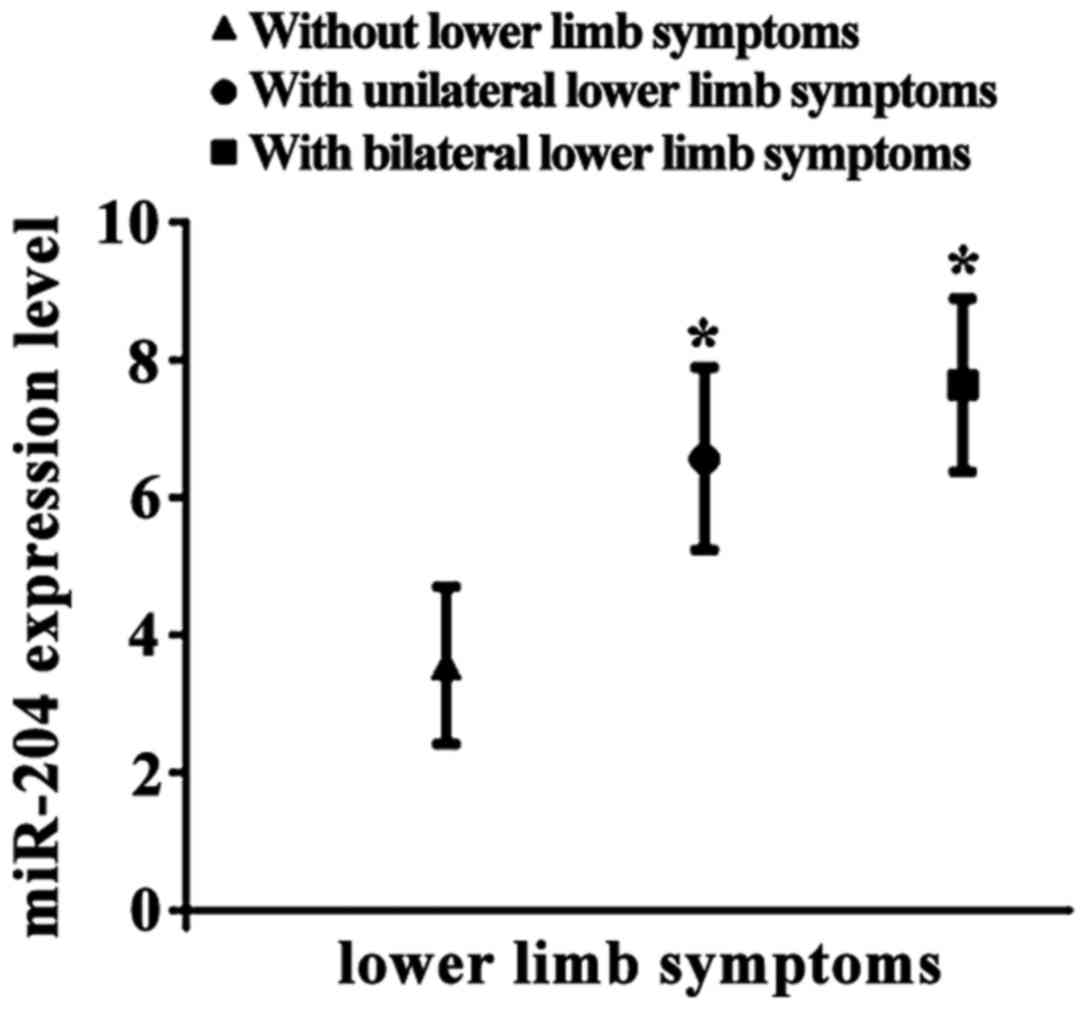
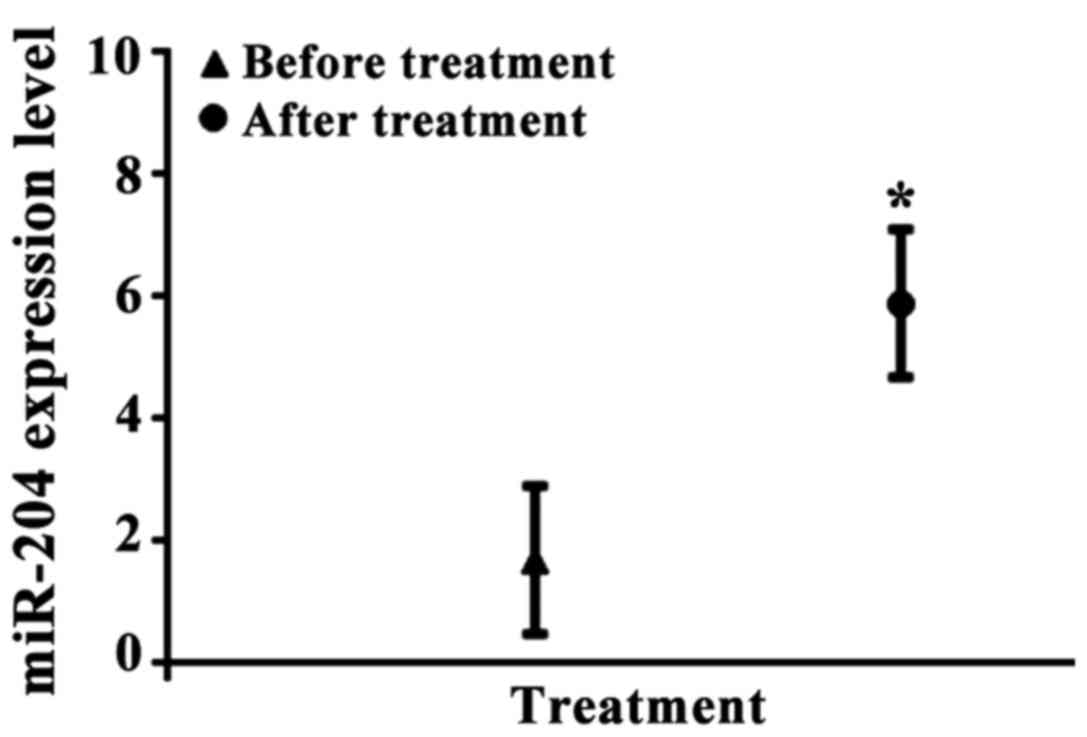
|
1
|
Adams MA and Dolan P: Intervertebral disc
degeneration: Evidence for two distinct phenotypes. J Anat.
221:497–506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Manchikanti L, Singh V, Cash KA, Pampati
V, Damron KS and Boswell MV: Effect of fluoroscopically guided
caudal epidural steroid or local anesthetic injections in the
treatment of lumbar disc herniation and radiculitis: A randomized,
controlled, double blind trial with a two-year follow-up. Pain
Physician. 15:273–286. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eguchi Y, Oikawa Y, Suzuki M, Orita S,
Yamauchi K, Suzuki M, Aoki Y, Watanabe A, Takahashi K and Ohtori S:
Diffusion tensor imaging of radiculopathy in patients with lumbar
disc herniation: Preliminary results. Bone Joint J. 98:387–394.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dower A, Chatterji R, Swart A and Winder
MJ: Surgical management of recurrent lumbar disc herniation and the
role of fusion. J Clin Neurosci. 23:44–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen BL, Guo JB, Zhang HW, Zhang YJ, Zhu
Y, Zhang J, Hu HY, Zheng YL and Wang XQ: Surgical versus
non-operative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 32:146–160. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rajasekaran S, Bajaj N, Tubaki V, Kanna RM
and Shetty AP: ISSLS Prize winner: The anatomy of failure in lumbar
disc herniation: an in vivo, multimodal, prospective study of 181
subjects. Spine. 38:1491–1500. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang YG, Zhang F, Sun Z, Guo W, Liu J,
Liu M and Guo X: A controlled case study of the relationship
between environmental risk factors and apoptotic gene polymorphism
and lumbar disc herniation. Am J Pathol. 182:56–63. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma L, Deng X, Wu M, Zhang G and Huang J:
Down-regulation of miRNA-204 by LMP-1 enhances CDC42 activity and
facilitates invasion of EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells. FEBS Lett. 588:1562–1570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ryan J, Tivnan A, Fay J, Bryan K, Meehan
M, Creevey L, Lynch J, Bray IM, O'Meara A, Tracey L, et al:
MicroRNA-204 increases sensitivity of neuroblastoma cells to
cisplatin and is associated with a favourable clinical outcome. Br
J Cancer. 107:967–976. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buric J, Rigobello L and Hooper D: Five
and ten year follow-up on intradiscal ozone injection for disc
herniation. Int J Spine Surg. 8:20142014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kreiner DS, Hwang SW, Easa JE, Resnick DK,
Baisden JL, Bess S, Cho CH, DePalma MJ, Dougherty P II, Fernand R,
et al: North American Spine Society: An evidence-based clinical
guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation
with radiculopathy. Spine J. 14:180–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Radcliff K, Hilibrand A, Lurie JD,
Tosteson TD, Delasotta L, Rihn J, Zhao W, Vaccaro A, Albert TJ and
Weinstein JN: The impact of epidural steroid injections on the
outcomes of patients treated for lumbar disc herniation: A subgroup
analysis of the SPORT trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 94:1353–1358.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang L and Lu HH: Value of a new
pathological classification of lumbar intervertebral disc
herniation based on transforaminal endoscopic observations. Exp
Ther Med. 13:1859–1867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie P, Liu B, Chen R, Yang B, Dong J and
Rong L: Comparative analysis of serum proteomes: Identification of
proteins associated with sciatica due to lumbar intervertebral disc
herniation. Biomed Rep. 2:693–698. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hall DP, Cost NG, Hegde S, Kellner E,
Mikhaylova O, Stratton Y, Ehmer B, Abplanalp WA, Pandey R, Biesiada
J, et al: TRPM3 and miR-204 establish a regulatory circuit that
controls oncogenic autophagy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Cell. 26:738–753. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Wang X and Chen P: miR-204 down
regulates SIRT1 and reverts SIRT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, anoikis resistance and invasion in gastric cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 13:2902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen PH, Chang CK, Shih CM, Cheng CH, Lin
CW, Lee CC, Liu AJ, Ho KH and Chen KC: The miR-204-3p-targeted
IGFBP2 pathway is involved in xanthohumol-induced glioma cell
apoptotic death. Neuropharmacology. 110:362–375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu L, Wang J, Li X, Ma J, Shi C, Zhu H,
Xi Q, Zhang J, Zhao X and Gu M: miR-204-5p suppresses cell
proliferation by inhibiting IGFBP5 in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:621–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi Y, Chen X, Xi B, Yu X, Ouyang J, Han
C, Qin Y, Wu D and Shen H: SNP rs3202538 in 3′UTR region of ErbB3
regulated by miR-204 and miR-211 promote gastric cancer development
in Chinese population. Cancer Cell Int. 17:812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jing W and Jiang W: MicroRNA-93 regulates
collagen loss by targeting MMP3 in human nucleus pulposus cells.
Cell Prolif. 48:284–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu X, Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Liang J, Weng X
and Qiu G: MicroRNA-10b promotes nucleus pulposus cell
proliferation through RhoC-Akt pathway by targeting HOXD10 in
intervetebral disc degeneration. PLoS One. 8:e830802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pearson AM and Lurie JD: Surgical versus
nonoperative treatment: How do we choose the right approach to
lumbar disk herniation? Pain Manag. 4:247–249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Tosteson ANA, Zhao
W, Morgan TS, Abdu WA, Herkowitz H and Weinstein JN: Surgical
versus nonoperative treatment for lumbar disc herniation:
Eight-year results for the spine patient outcomes research trial.
Spine. 39:3–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|