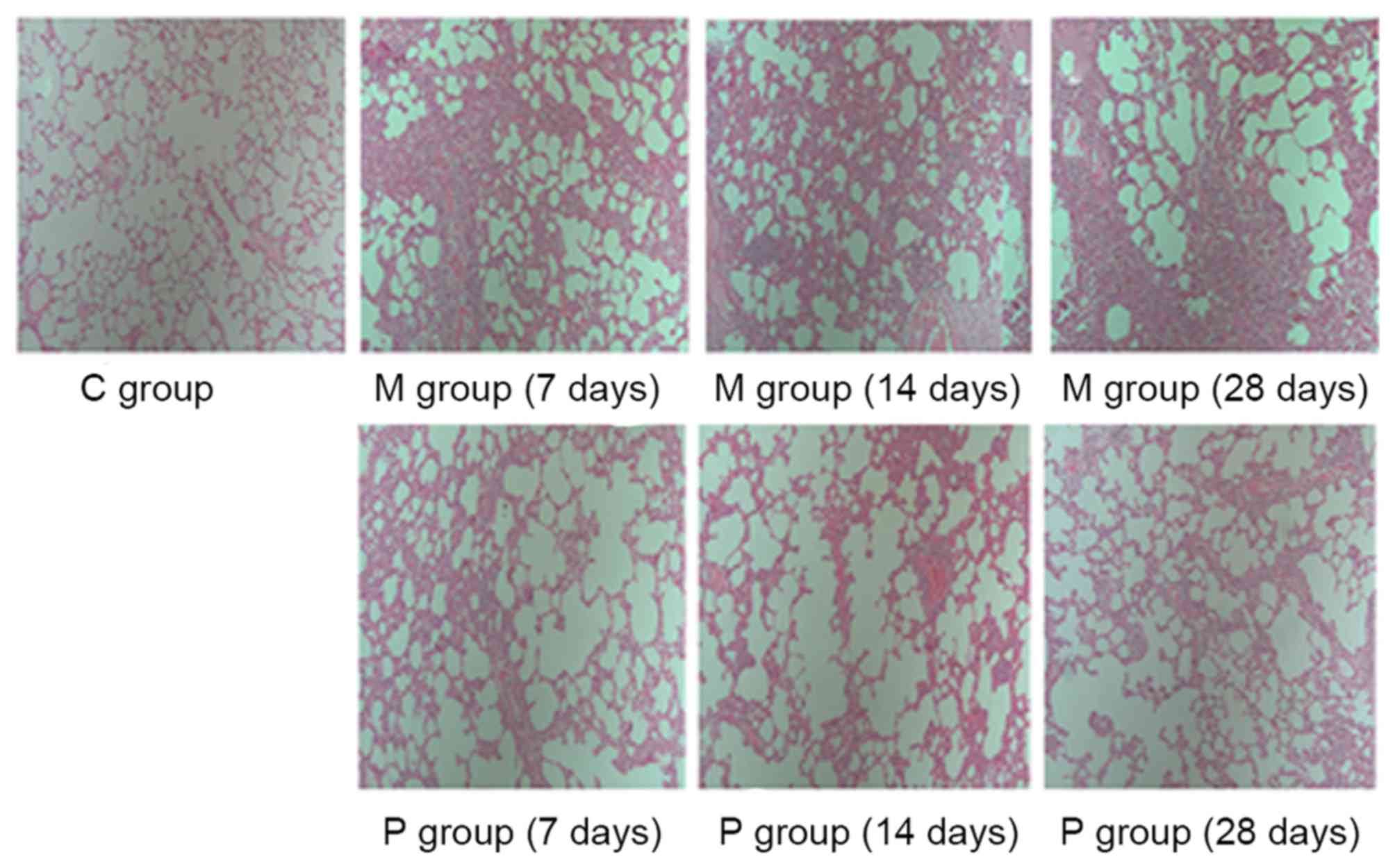
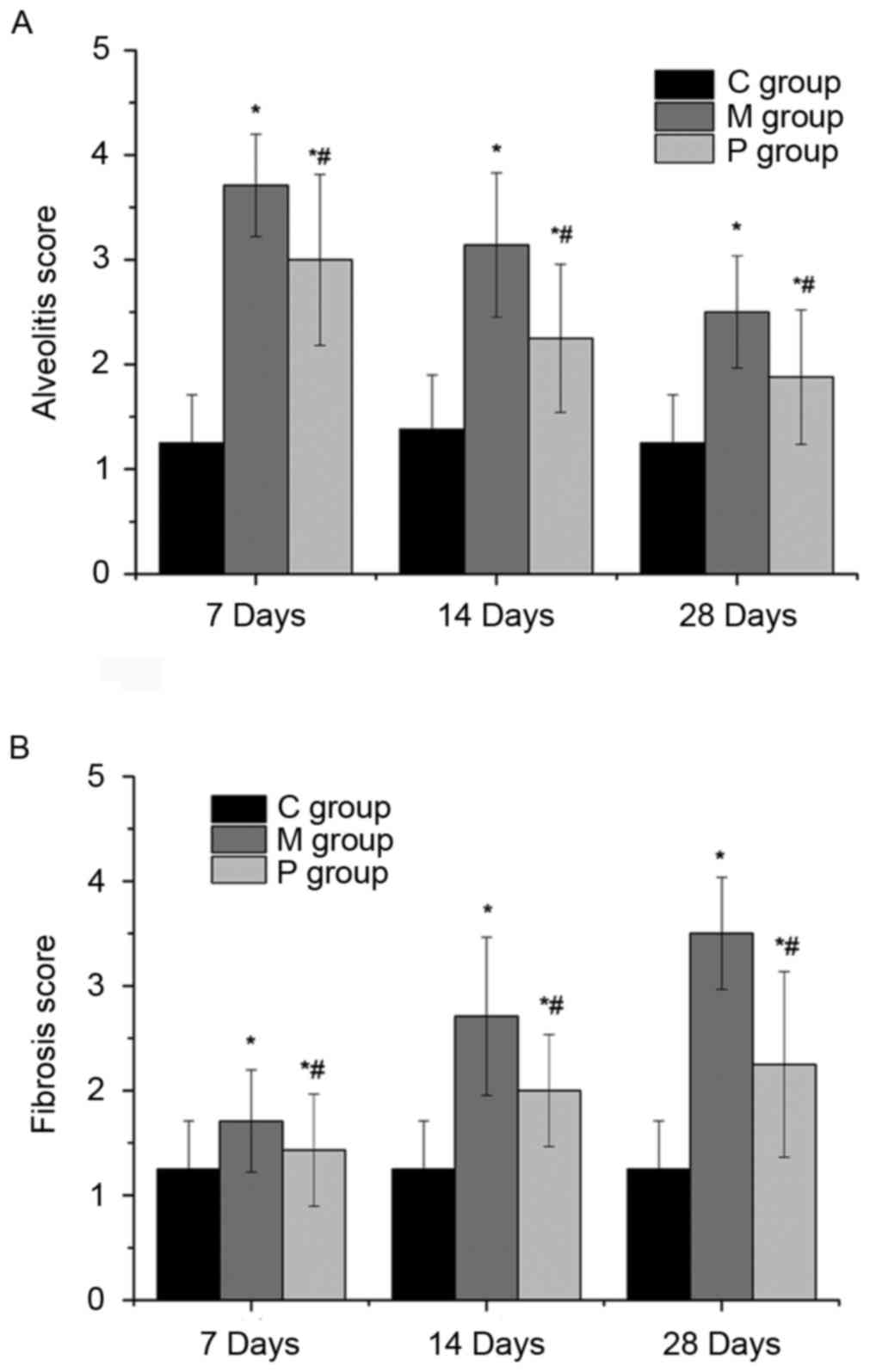
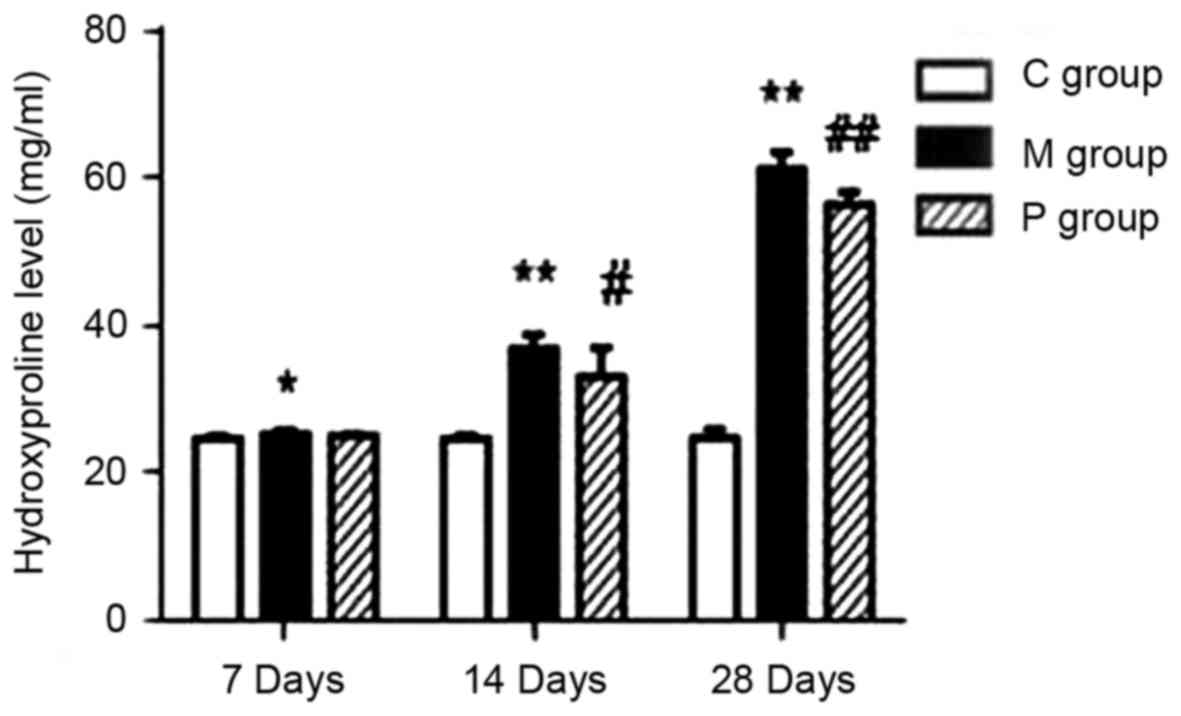
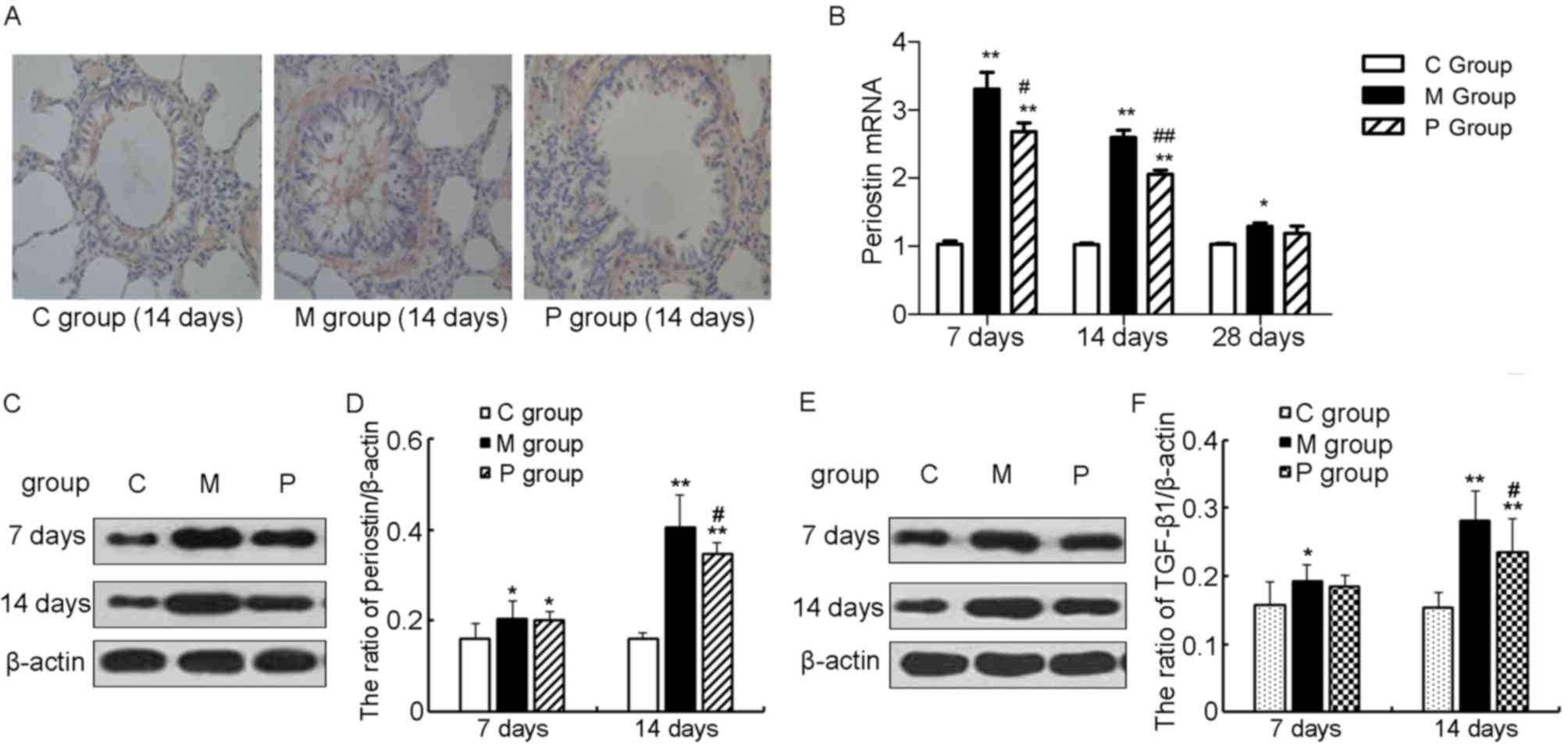
|
1
|
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ,
Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, et
al: An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Demedts M, Behr J, Buhl R, Costabel U,
Dekhuijzen R, Jansen HM, MacNee W, Thomeer M, Wallaert B, Laurent
F, et al: High-dose acetylcysteine in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 353:2229–2242. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Norris RA, Moreno-Rodriguez R, Hoffman S
and Markwald RR: The many facets of the matricelluar protein
periostin during cardiac development, remodeling, and
pathophysiology. J Cell Commun Signal. 3:275–286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hamilton DW: Functional role of periostin
in development and wound repair: Implications for connective tissue
disease. J Cell Commun Signal. 2:9–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ontsuka K, Kotobuki Y, Shiraishi H, Serada
S, Ohta S, Tanemura A, Yang L, Fujimoto M, Arima K, Suzuki S, et
al: Periostin, a matricellular protein, accelerates cutaneous wound
repair by activating dermal fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 21:331–336.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uchida M, Shiraishi H, Ohta S, Arima K,
Taniguchi K, Suzuki S, Okamoto M, Ahlfeld SK, Ohshima K, Kato S, et
al: Periostin, a matricellular protein, plays a role in the
induction of chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 46:677–686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ruan K, Bao S and Ouyang G: The
multifaceted role of periostin in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:2219–2230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jackson-Boeters L, Wen W and Hamilton DW:
Periostin localizes to cells in normal skin, but is associated with
the extracellular matrix during wound repair. J Cell Commun Signal.
3:125–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oka T, Xu J, Kaiser RA, Melendez J,
Hambleton M, Sargent MA, Lorts A, Brunskill EW, Dorn GW II, Conway
SJ, et al: Genetic manipulation of periostin expression reveals a
role in cardiac hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling. Circ Res.
101:313–321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takayama G, Arima K, Kanaji T, Toda S,
Tanaka H, Shoji S, McKenzie AN, Nagai H, Hotokebuchi T and Izuhara
K: Periostin: A novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of
bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 118:98–104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sidhu SS, Yuan S, Innes AL, Kerr S,
Woodruff PG, Hou L, Muller SJ and Fahy JV: Roles of epithelial
cell-derived periostin in TGF-beta activation, collagen production,
and collagen gel elasticity in asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:14170–14175. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okamoto M, Hoshino T, Kitasato Y, Sakazaki
Y, Kawayama T, Fujimoto K, Ohshima K, Shiraishi H, Uchida M, Ono J,
et al: Periostin, a matrix protein, is a novel biomarker for
idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur Respir J. 37:1119–1127.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Naik PK, Bozyk PD, Bentley JK, Popova AP,
Birch CM, Wilke CA, Fry CD, White ES, Sisson TH, Tayob N, et al:
Periostin promotes fibrosis and predicts progression in patients
with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 303:L1046–L1056. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cicko S, Grimm M, Ayata K, Beckert J,
Meyer A, Hossfold M, Zissel G, Idzko M and Müller T: Uridine
supplementation exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects
in an animal model of pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 16:105–115.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oku H, Shimizu T, Kawabata T, Nagira M,
Hikita I, Ueyama A, Matsushima S, Torii M and Arimura A:
Antifibrotic action of pirfenidone and prednisolone: Different
effects on pulmonary cytokines and growth factors in
bleomycin-induced murine pulmonary fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol.
590:400–408. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Azuma A, Nukiwa T, Tsuboi E, Suga M, Abe
S, Nakata K, Taguchi Y, Nagai S, Itoh H, Ohi M, et al:
Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pirfenidone in patients
with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
171:1040–1047. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taniguchi H, Ebina M, Kondoh Y, Ogura T,
Azuma A, Suga M, Taguchi Y, Takahashi H, Nakata K, Nakata K, et al:
Pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J.
35:821–829. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moeller A, Ask K, Warburton D, Gauldie J
and Kolb M: The bleomycin animal model: A useful tool to
investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:362–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fulmer JD, Bienkowski RS, Cowan MJ, Breul
SD, Bradley KM, Ferrans VJ, Roberts WC and Crystal RG: Collagen
concentration and rates of synthesis in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 122:289–301. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Macías-Barragán J, Sandoval-Rodríguez A,
Navarro-Partida J and Armendáriz-Borunda J: The multifaceted role
of pirfenidone and its novel targets. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair.
3:162010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iyer S, Gurujeyalakshmi G and Giri S:
Effects of pirfenidone on transforming growth factor-beta gene
expression at the transcriptional level in bleomycin hamster model
of lung fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 291:367–373.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gurujeyalakshmi G, Hollinger M and Giri S:
Pirfenidone inhibits PDGF isoforms in bleomycin hamster model of
lung fibrosis at the translational level. Am J Physiol.
276:L311–L318. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakazato H, Oku H, Yamane S, Tsuruta Y and
Suzuki R: A novel anti-fibrotic agent pirfenidone suppresses tumor
necrosis factor-alpha at the translational level. Eur J Pharmacol.
446:177–185. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gaggini F, Laleu B, Orchard M,
Fioraso-Cartier L, Cagnon L, Houngninou-Molango S, Gradia A, Duboux
G, Merlot C, Heitz F, et al: Design, synthesis and biological
activity of original pyrazolo-pyrido-diazepine,-pyrazine
and-oxazine dione derivatives as novel dual Nox4/Nox1 inhibitors.
Bioorg Med Chem. 19:6989–6999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Wu Y, Chen J, Zhao S and Li H:
Pirfenidone attenuates cardiac fibrosis in a mouse model of
TAC-induced left ventricular remodeling by suppressing NLRP3
inflammasome formation. Cardiology. 126:1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fernandez IE and Eickelberg O: The impact
of TGF-β on lung fibrosis: From targeting to biomarkers. Proc Am
Thorac Soc. 9:111–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thannickal VJ, Lee DY, White ES, Cui Z,
Larios JM, Chacon R, Horowitz JC, Day RM and Thomas PE:
Myofibroblast differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta1
is dependent on cell adhesion and integrin signaling via focal
adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 278:12384–12389. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wen W, Chau E, Jackson-Boeters L, Elliott
C, Daley T and Hamilton D: TGF-β1 and FAK regulate periostin
expression in PDL fibroblasts. J Dental Res. 89:1439–1443. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Nie F, Kang C, Chen B, Qin Z, Ma
J, Ma Y and Zhao X: Increased periostin expression affects the
proliferation, collagen synthesis, migration and invasion of keloid
fibroblasts under hypoxic conditions. Int J Mol Med. 34:253–261.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|