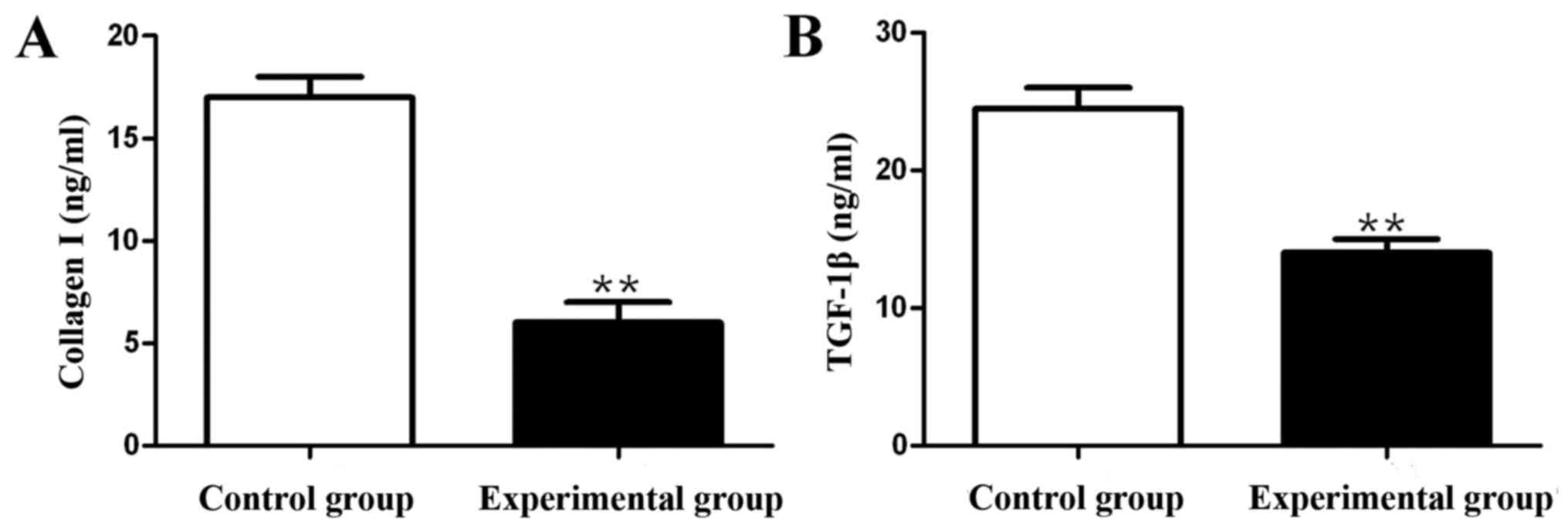
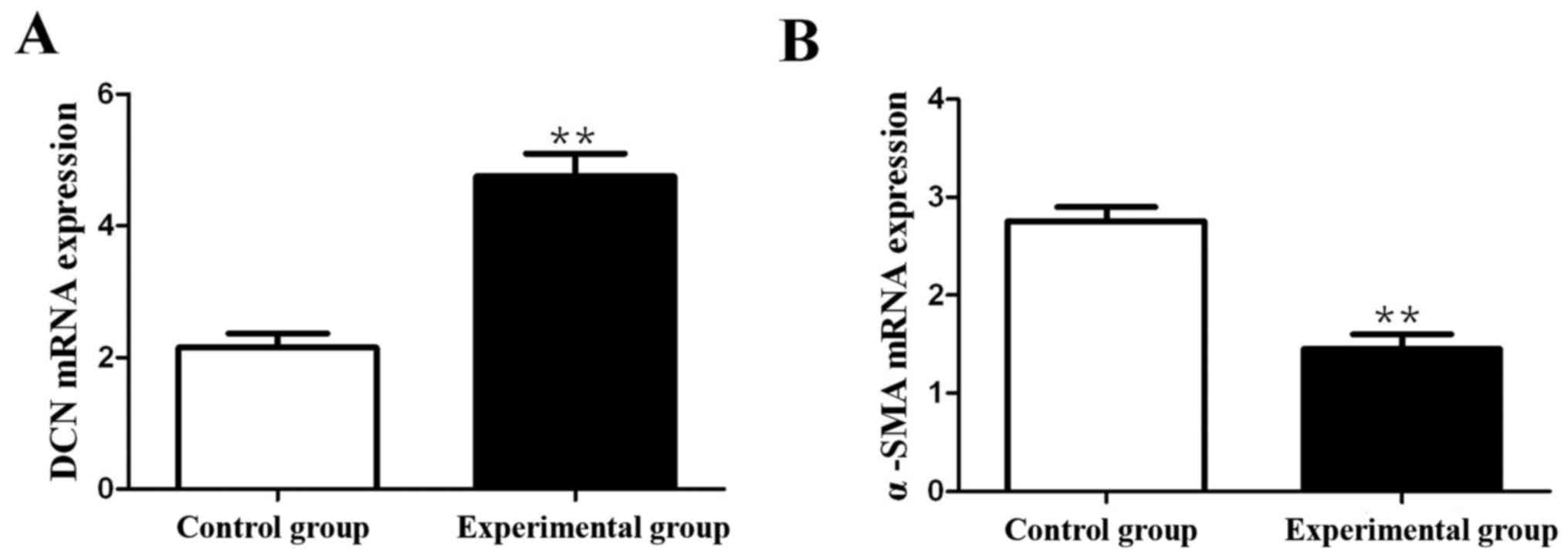
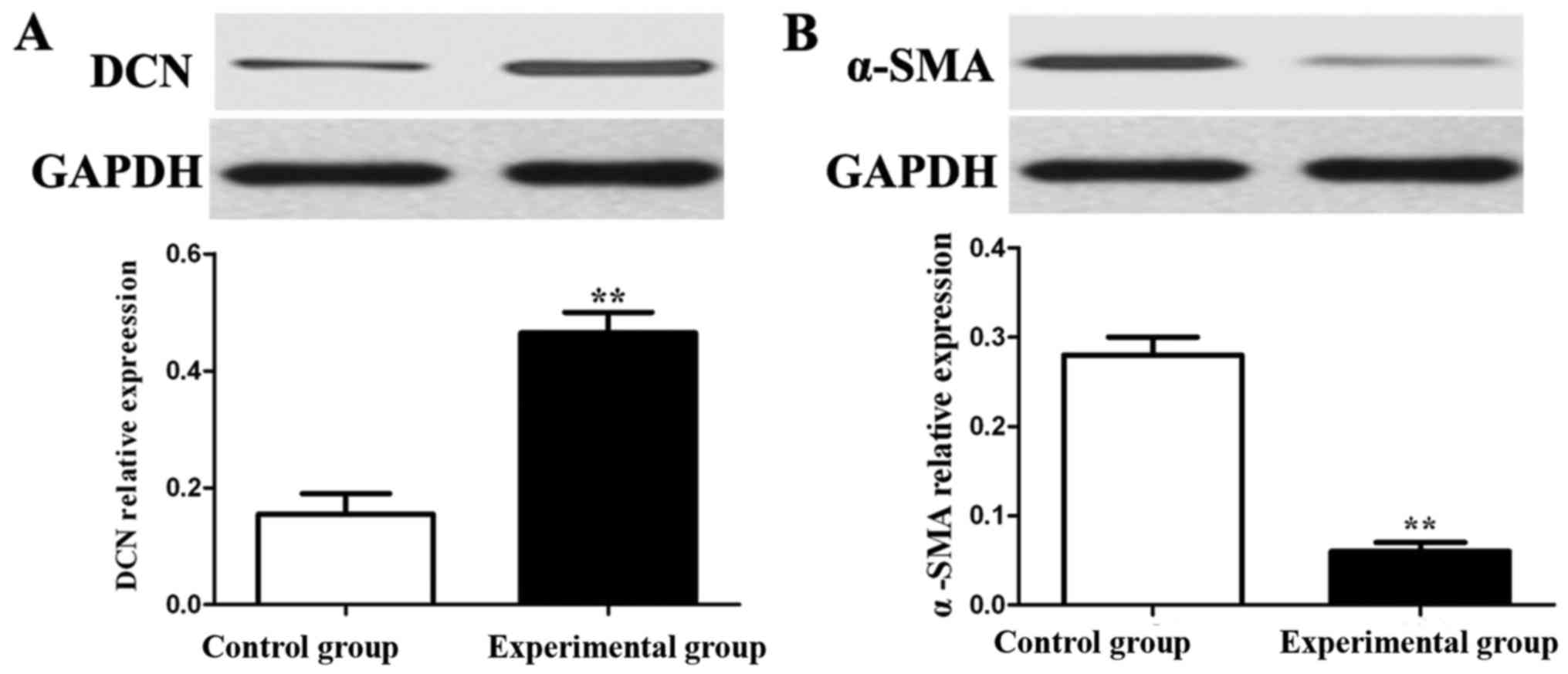
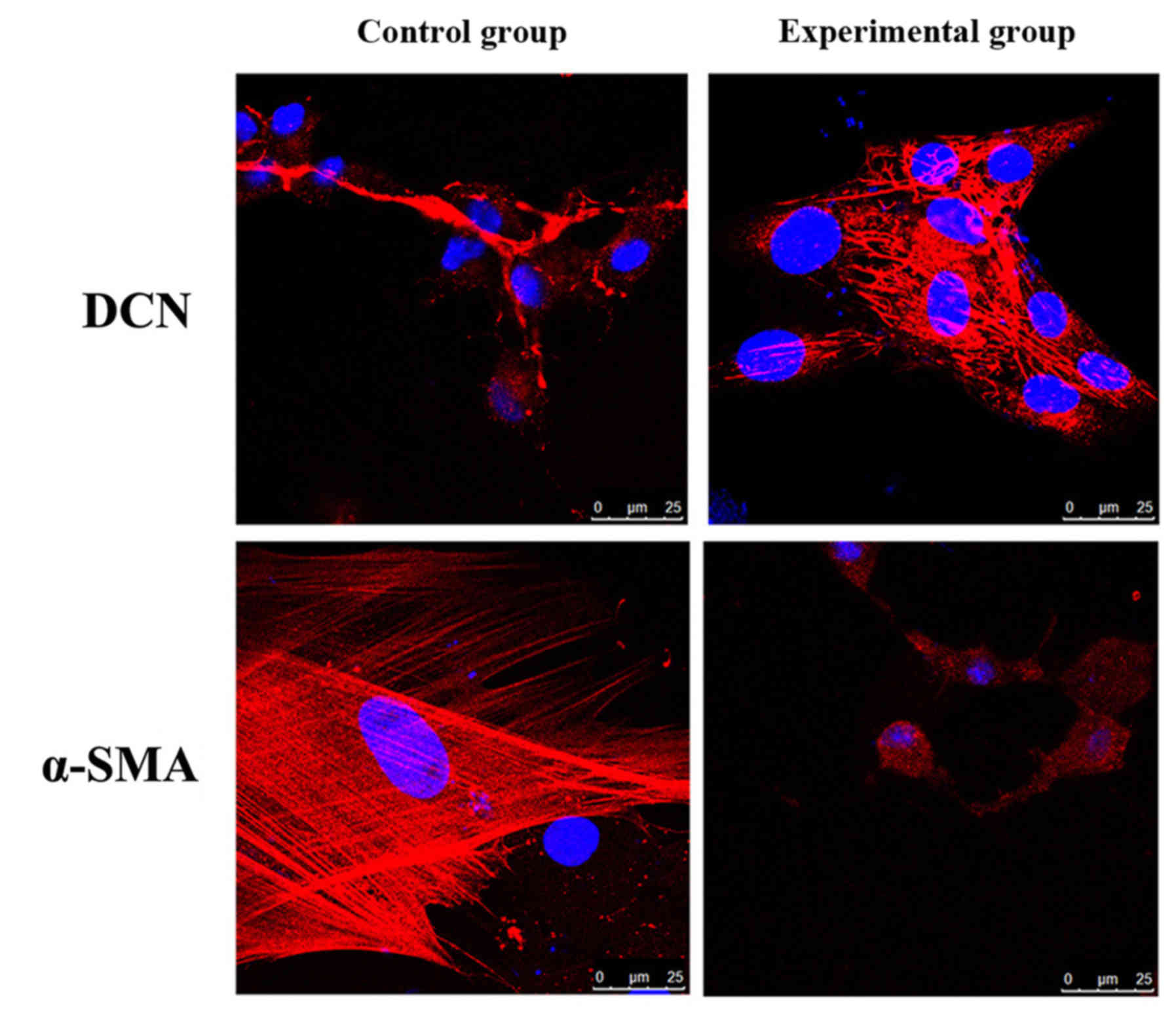
|
1
|
Kim S, Choi TH, Liu W, Ogawa R, Suh JS and
Mustoe TA: Update on scar management: Guidelines for treating Asian
patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 132:1580–1589. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA,
Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P and Hedrick
MH: Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol
Biol Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang G, Ren Y, Cao W, Yang Y and Li S:
Liposculpture and fat grafting for aesthetic correction of the
gluteal concave deformity associated with multiple intragluteal
injection of penicillin in childhood. Aesthetic Plast Surg.
37:39–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guisantes E, Fontdevila J and Rodríguez G:
Autologous fat grafting for correction of unaesthetic scars. Ann
Plast Surg. 69:550–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klinger M, Marazzi M, Vigo D and Torre M:
Fat injection for cases of severe burn outcomes: A new perspective
of scar remodeling and reduction. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 32:465–469.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Sung JH, Yang JM, Park
SB, Kwak SJ and Park JS: Wound healing effect of adipose-derived
stem cells: A critical role of secretory factors on human dermal
fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 48:15–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bruno A, Delli Santi G, Fasciani L,
Cempanari M, Palombo M and Palombo P: Burn scar lipofilling:
Immunohistochemical and clinical outcomes. J Craniofac Surg.
24:1806–1814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Derfoul A, Perkins GL, Hall DJ and Tuan
RS: Glucocorticoids promote chondrogenic differentiation of adult
human mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing expression of cartilage
extracellular matrix genes. Stem Cells. 24:1487–1495. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, Locatelli
F, Roelofs H, Lewis I, Lanino E, Sundberg B, Bernardo ME, Remberger
M, et al: Developmental Committee of the European Group for Blood
and Marrow Transplantation: Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of
steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase
II study. Lancet. 371:1579–1586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sensebé L, Krampera M, Schrezenmeier H,
Bourin P and Giordano R: Mesenchymal stem cells for clinical
application. Vox Sang. 98:93–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Varkey M, Ding J and Tredget EE:
Differential collagen-glycosaminoglycan matrix remodeling by
superficial and deep dermal fibroblasts: Potential therapeutic
targets for hypertrophic scar. Biomaterials. 32:7581–7591. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li NY, Chen F, Dikkers FG and Thibeault
SL: Dose-dependent effect of mitomycin C on human vocal fold
fibroblasts. Head Neck. 36:401–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
King SN, Chen F, Jetté ME and Thibeault
SL: Vocal fold fibroblasts immunoregulate activated macrophage
phenotype. Cytokine. 61:228–236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bi X, Tong C, Dockendorff A, Bancroft L,
Gallagher L, Guzman G, Iozzo RV, Augenlicht LH and Yang W: Genetic
deficiency of decorin causes intestinal tumor formation through
disruption of intestinal cell maturation. Carcinogenesis.
29:1435–1440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu BH, Chen L, Li SR, Wang ZX and Cheng
WG: Smac/DIABLO regulates the apoptosis of hypertrophic scar
fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 32:615–622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Siebert JW, Burd AR, McCarthy JG,
Weinzweig J and Ehrlich HP: Fetal wound healing: A biochemical
study of scarless healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 85:495–502;
discussion 503–504. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sander EA, Barocas VH and Tranquillo RT:
Initial fiber alignment pattern alters extracellular matrix
synthesis in fibroblast-populated fibrin gel cruciforms and
correlates with predicted tension. Ann Biomed Eng. 39:714–729.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deitch EA, Wheelahan TM, Rose MP, Clothier
J and Cotter J: Hypertrophic burn scars: Analysis of variables. J
Trauma. 23:895–898. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang K, Garner W, Cohen L, Rodriguez J
and Phan S: Increased types I and III collagen and transforming
growth factor-beta 1 mRNA and protein in hypertrophic burn scar. J
Invest Dermatol. 104:750–754. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Martinez FO, Helming L and Gordon S:
Alternative activation of macrophages: An immunologic functional
perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:451–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|