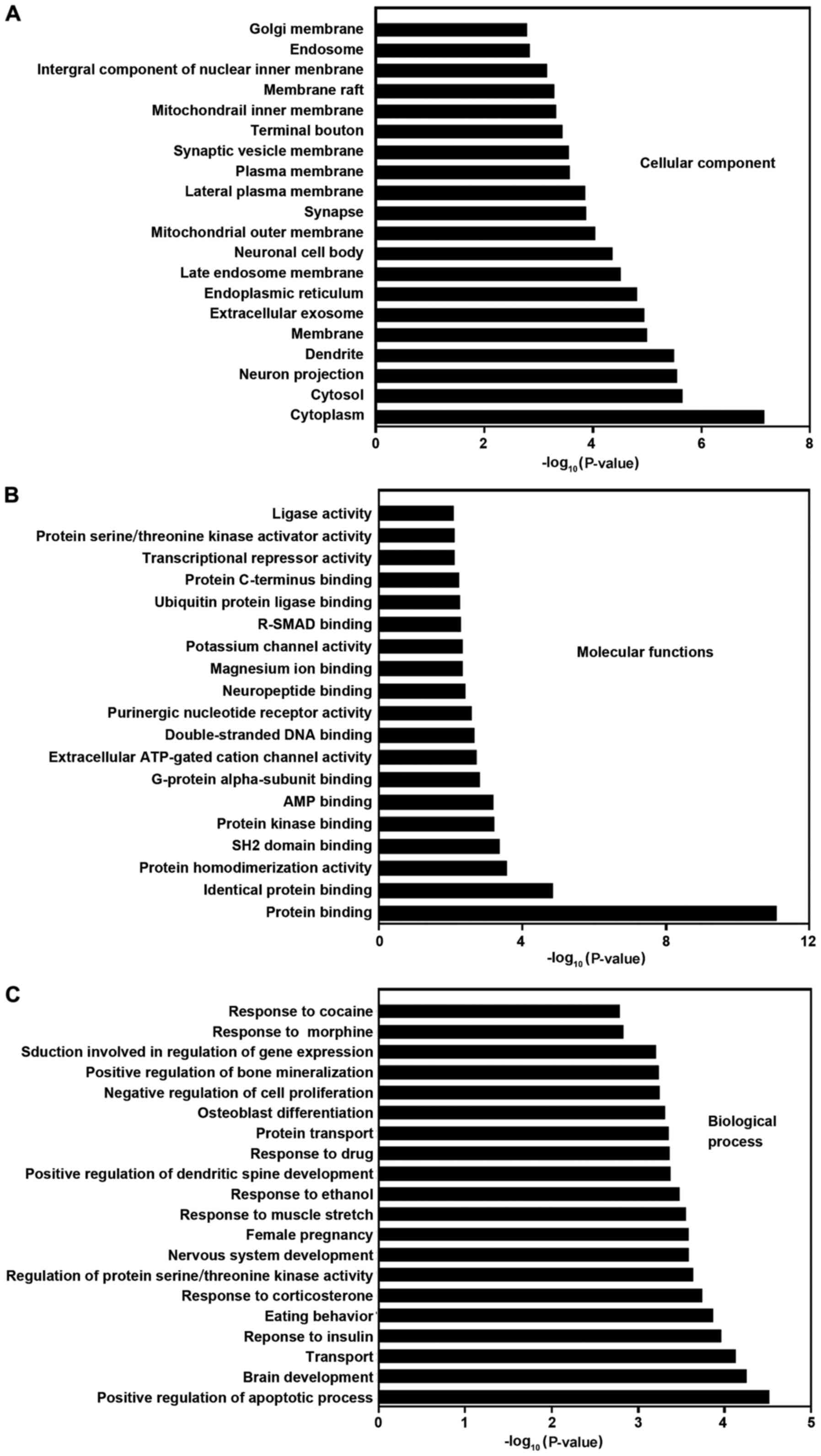
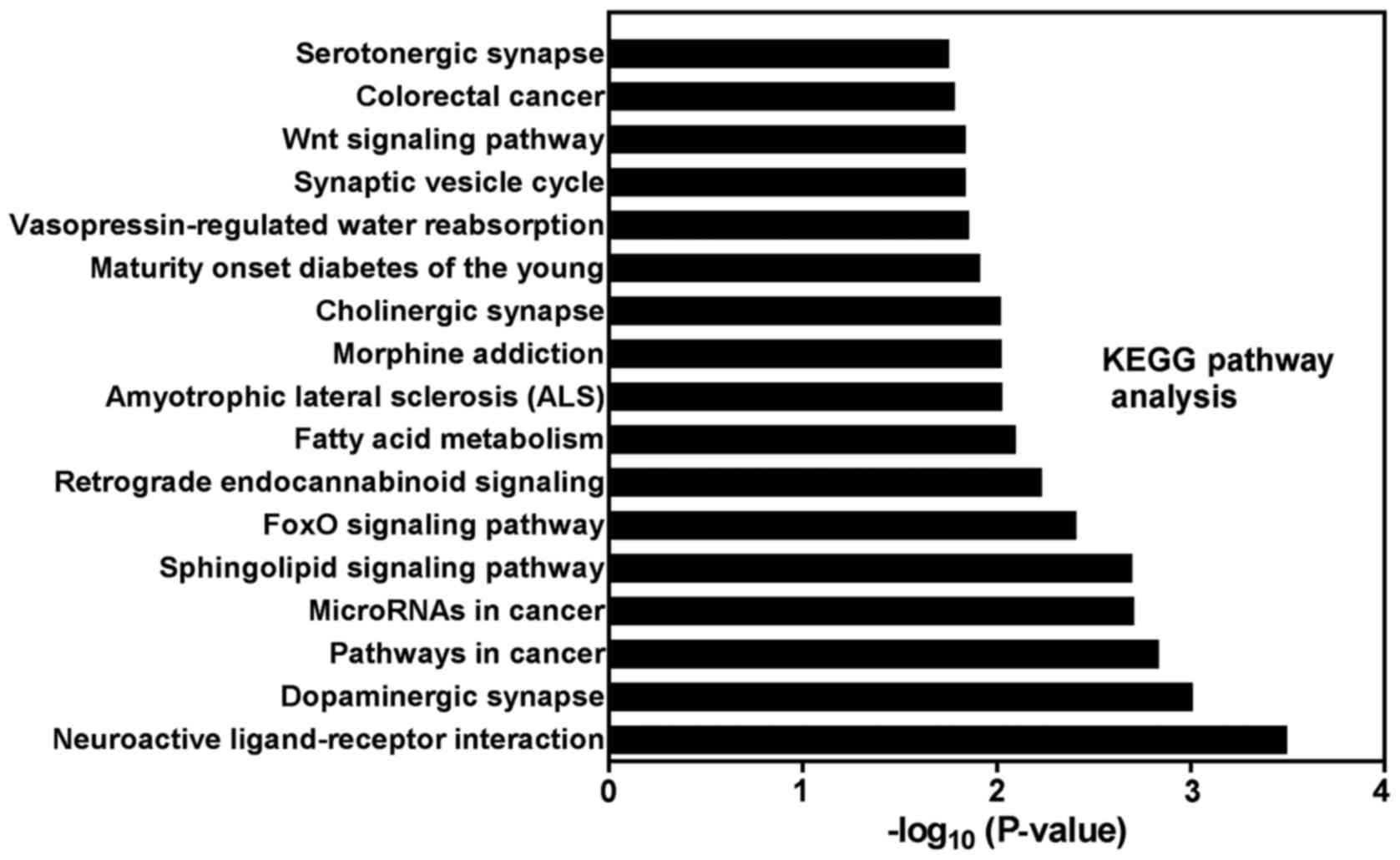
|
1
|
Berzigotti A, Seijo S, Reverter E and
Bosch J: Assessing portal hypertension in liver diseases. Expert
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:141–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bloom S, Kemp W and Lubel J: Portal
hypertension: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Intern Med
J. 45:16–26. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geerts A: History, heterogeneity,
developmental biology, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate
cells. Semin Liver Dis. 21:311–335. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reeves HL and Friedman SL: Activation of
hepatic stellate cells - a key issue in liver fibrosis. Front
Biosci. 7:d808–d826. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gäbele E, Brenner DA and Rippe RA: Liver
fibrosis: Signals leading to the amplification of the fibrogenic
hepatic stellate cell. Front Biosci. 8:d69–d77. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Puche JE, Saiman Y and Friedman SL:
Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr Physiol.
3:1473–1492. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rockey DC and Chung JJ: Reduced nitric
oxide production by endothelial cells in cirrhotic rat liver:
Endothelial dysfunction in portal hypertension. Gastroenterology.
114:344–351. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suematsu M, Goda N, Sano T, Kashiwagi S,
Egawa T, Shinoda Y and Ishimura Y: Carbon monoxide: An endogenous
modulator of sinusoidal tone in the perfused rat liver. J Clin
Invest. 96:2431–2437. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fallowfield JA, Hayden AL, Snowdon VK,
Aucott RL, Stutchfield BM, Mole DJ, Pellicoro A, Gordon-Walker TT,
Henke A, Schrader J, et al: Relaxin modulates human and rat hepatic
myofibroblast function and ameliorates portal hypertension in vivo.
Hepatology. 59:1492–1504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He Y, Huang C, Zhang SP, Sun X, Long XR
and Li J: The potential of microRNAs in liver fibrosis. Cell
Signal. 24:2268–2272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lakner AM, Steuerwald NM, Walling TL,
Ghosh S, Li T, McKillop IH, Russo MW, Bonkovsky HL and Schrum LW:
Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate
cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 56:300–310. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur
M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi
M, et al: Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human
and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 53:209–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo CJ, Pan Q, Xiong H, Qiao YQ, Bian ZL,
Zhong W, Sheng L, Li H, Shen L, Hua J, et al: Dynamic expression of
miR-126* and its effects on proliferation and contraction of
hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett. 587:3792–3801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mann J, Chu DC, Maxwell A, Oakley F, Zhu
NL, Tsukamoto H and Mann DA: MeCP2 controls an epigenetic pathway
that promotes myofibroblast transdifferentiation and fibrosis.
Gastroenterology. 138(705–714): 7142010.
|
|
15
|
Venugopal SK, Jiang J, Kim TH, Li Y, Wang
SS, Torok NJ, Wu J and Zern MA: Liver fibrosis causes
downregulation of miRNA-150 and miRNA-194 in hepatic stellate
cells, and their overexpression causes decreased stellate cell
activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G101–G106.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huebert RC, Jagavelu K, Hendrickson HI,
Vasdev MM, Arab JP, Splinter PL, Trussoni CE, Larusso NF and Shah
VH: Aquaporin-1 promotes angiogenesis, fibrosis, and portal
hypertension through mechanisms dependent on osmotically sensitive
microRNAs. Am J Pathol. 179:1851–1860. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jansen C, Reiberger T, Huang J, Eischeid
H, Schierwagen R, Mandorfer M, Anadol E, Schwabl P, Schwarze-Zander
C, Warnecke-Eberz U, et al: Circulating miRNA-122 levels are
associated with hepatic necroinflammation and portal hypertension
in HIV/HCV coinfection. PLoS One. 10:e01167682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yi SH, Zhang Y, Tang D and Zhu L:
Mechanical force and tensile strain activated hepatic stellate
cells and inhibited retinol metabolism. Biotechnol Lett.
37:1141–1152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y
and Hattori M: The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D277–D280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yi M, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH and
Stephens RM: WholePathwayScope: A comprehensive pathway-based
analysis tool for high-throughput data. BMC Bioinformatics.
7:302006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Draghici S, Khatri P, Tarca AL, Amin K,
Done A, Voichita C, Georgescu C and Romero R: A systems biology
approach for pathway level analysis. Genome Res. 17:1537–1545.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baba S, Fujii H, Hirose T, Yasuchika K,
Azuma H, Hoppo T, Naito M, Machimoto T and Ikai I: Commitment of
bone marrow cells to hepatic stellate cells in mouse. J Hepatol.
40:255–260. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Di Sario A, Bendia E, Macarri G,
Candelaresi C, Taffetani S, Marzioni M, Omenetti A, De Minicis S,
Trozzi L and Benedetti A: The anti-fibrotic effect of pirfenidone
in rat liver fibrosis is mediated by downregulation of procollagen
alpha1(I), TIMP-1 and MMP-2. Dig Liver Dis. 36:744–751. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Szabo G and Bala S: MicroRNAs in liver
disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:542–552. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dolganiuc A, Petrasek J, Kodys K, Catalano
D, Mandrekar P, Velayudham A and Szabo G: MicroRNA expression
profile in Lieber-DeCarli diet-induced alcoholic and methionine
choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis models
in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 33:1704–1710. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ura S, Honda M, Yamashita T, Ueda T,
Takatori H, Nishino R, Sunakozaka H, Sakai Y, Horimoto K and Kaneko
S: Differential microRNA expression between hepatitis B and
hepatitis C leading disease progression to hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:1098–1112. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Navon R, Wang H, Steinfeld I, Tsalenko A,
Ben-Dor A and Yakhini Z: Novel rank-based statistical methods
reveal microRNAs with differential expression in multiple cancer
types. PLoS One. 4:e80032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fang F, Chang RM, Yu L, Lei X, Xiao S,
Yang H and Yang LY: MicroRNA-188-5p suppresses tumor cell
proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting FGF5 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 63:874–885. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han H, Peng J, Hong Y, Zhang M, Han Y, Fu
Z, Shi Y, Xu J, Tao J and Lin J: Comparison of the differential
expression miRNAs in Wistar rats before and 10 days after S.
japonicum infection. Parasit Vectors. 6:1202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hsieh CH, Rau CS, Jeng JC, Chen YC, Lu TH,
Wu CJ, Wu YC, Tzeng SL and Yang JC: Whole blood-derived microRNA
signatures in mice exposed to lipopolysaccharides. J Biomed Sci.
19:692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Adachi M, Osawa Y, Uchinami H, Kitamura T,
Accili D and Brenner DA: The forkhead transcription factor FoxO1
regulates proliferation and transdifferentiation of hepatic
stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 132:1434–1446. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang F, Parsons CJ and Stefanovic B: Gene
expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate
cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation. J Hepatol.
45:401–409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Myung SJ, Yoon JH, Gwak GY, Kim W, Lee JH,
Kim KM, Shin CS, Jang JJ, Lee SH, Lee SM, et al: Wnt signaling
enhances the activation and survival of human hepatic stellate
cells. FEBS Lett. 581:2954–2958. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|