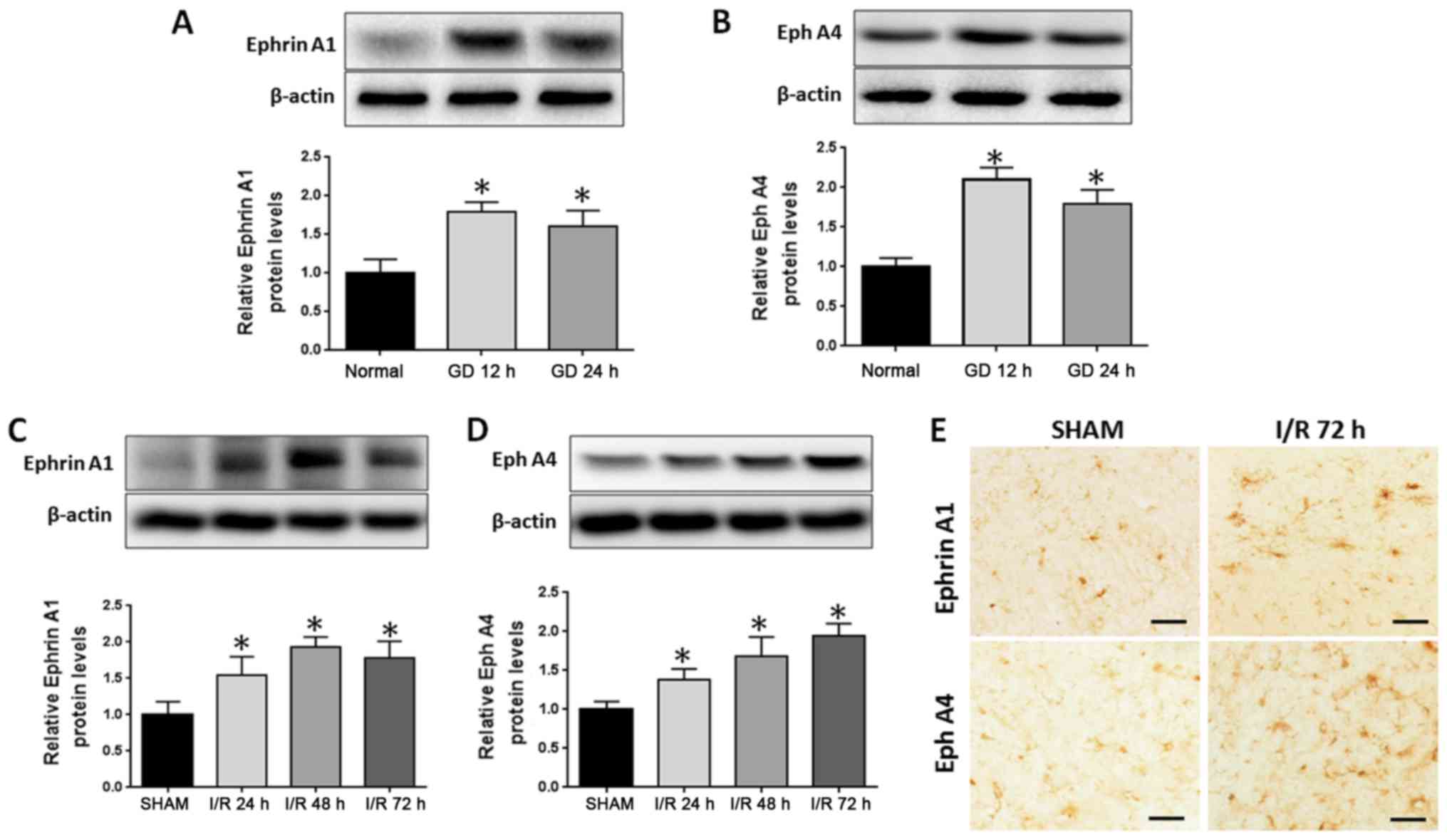
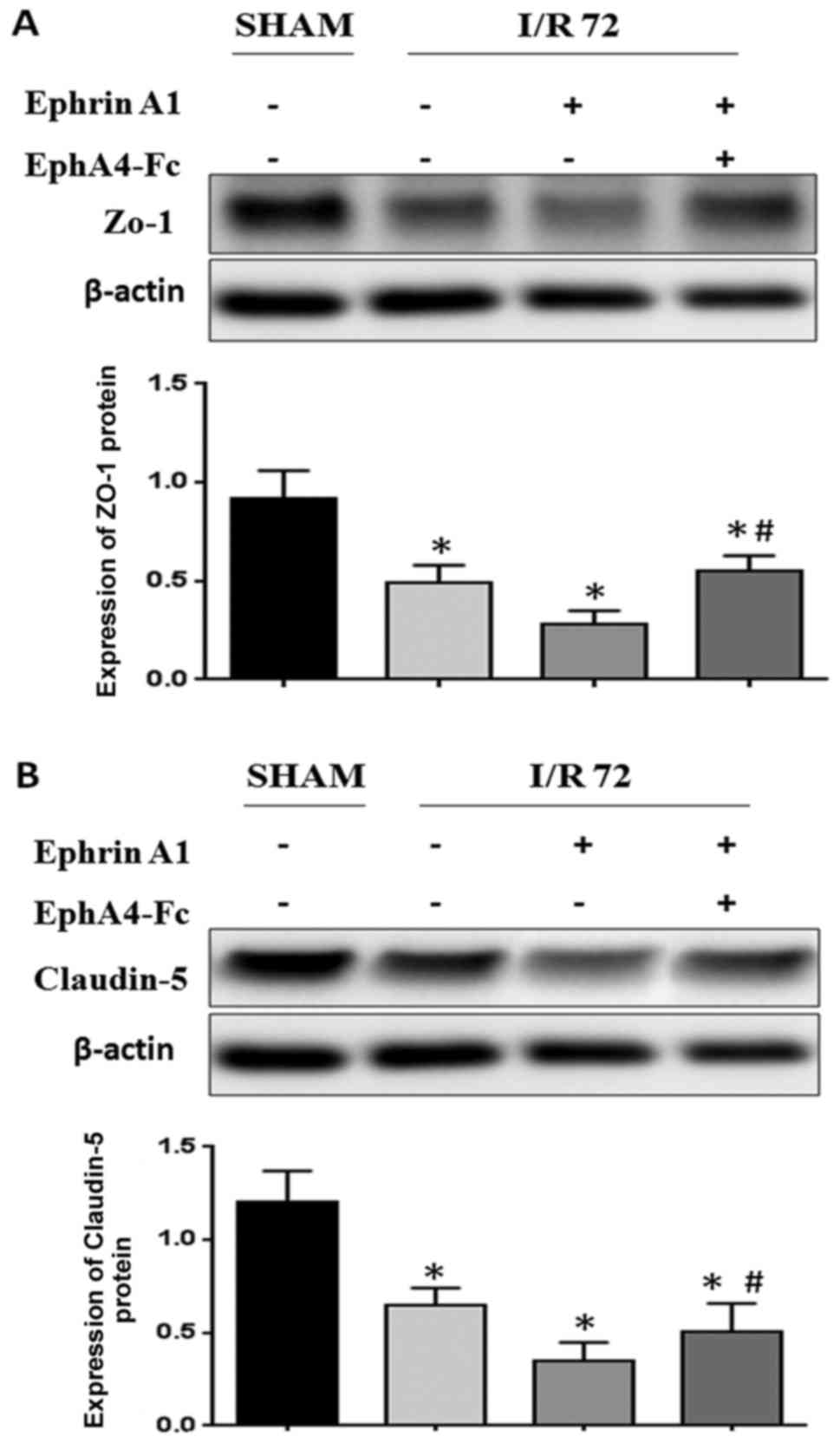
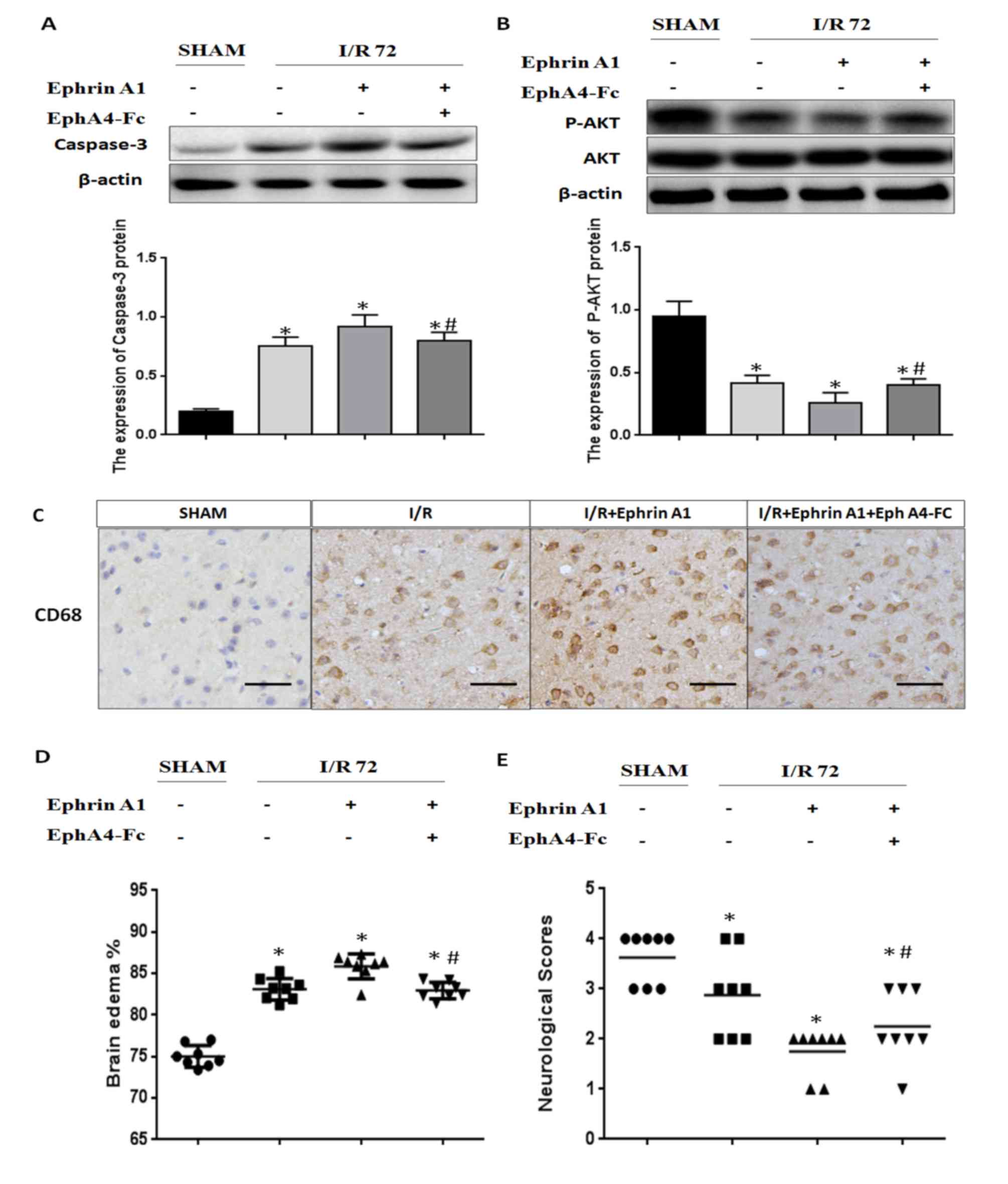
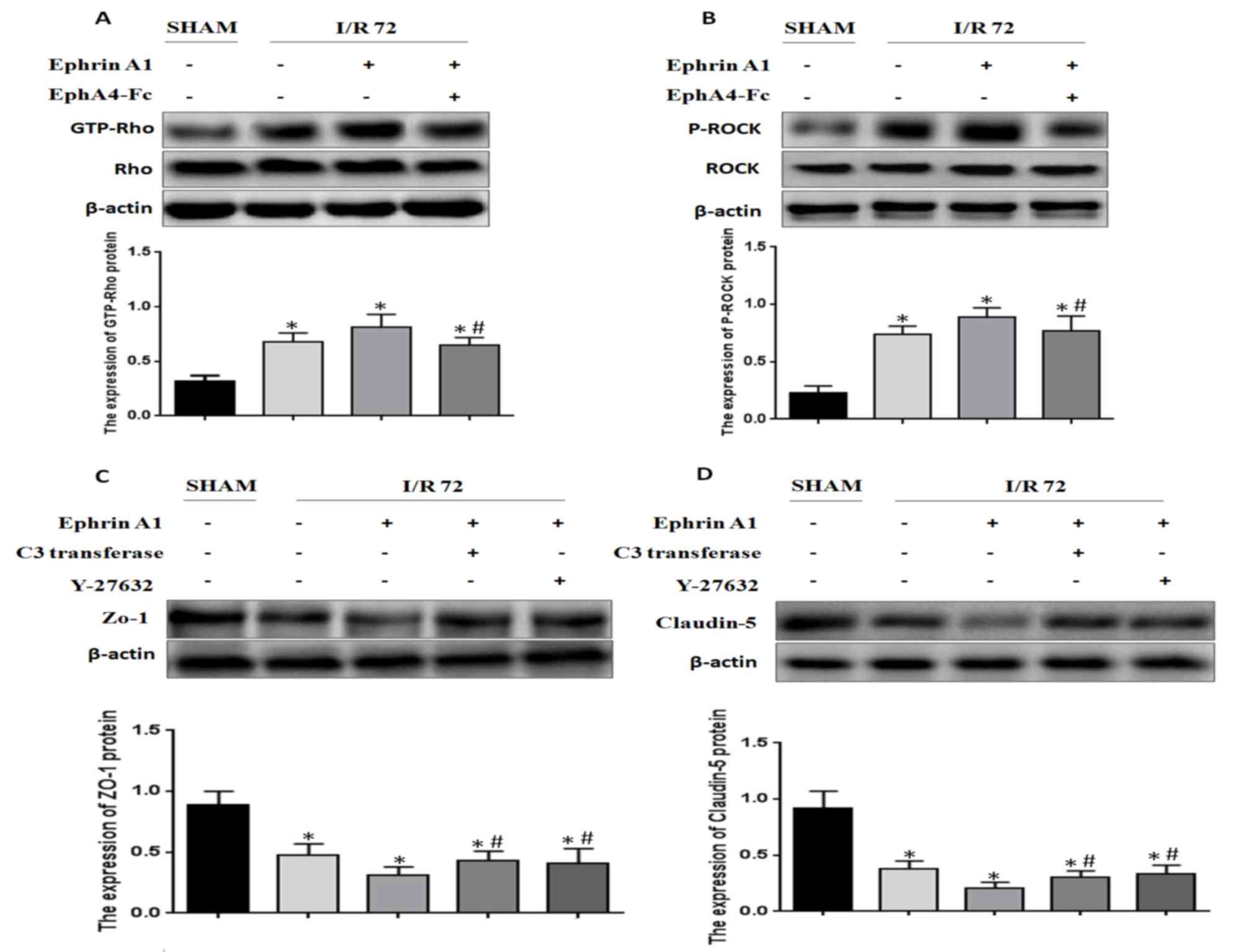
|
1
|
Plassman BL, Langa KM, Fisher GG, Heeringa
SG, Weir DR, Ofstedal MB, Burke JR, Hurd MD, Potter GG, Rodgers WL,
et al: Prevalence of dementia in the United States: The aging,
demographics and memory study. Neuroepidemiology. 29:125–132. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Erkinjuntti T: Diagnosis and management of
vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. J Neural Transm Suppl.
1–109. 2002.
|
|
3
|
Iadecola C: The pathobiology of vascular
dementia. Neuron. 80:844–866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bowler JV: Vascular cognitive impairment.
Stroke. 35:386–388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nyenhuis DL and Gorelick PB: Vascular
dementia: A contemporary review of epidemiology, diagnosis,
prevention and treatment. J Ame Geriat Soc. 46:1437–1448. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Farooq MU and Gorelick PB: Vascular
cognitive impairment. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 15:3302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jacquin A, Binquet C, Rouaud O,
Graule-Petot A, Daubail B, Osseby GV, Bonithon-Kopp C, Giroud M and
Béjot Y: Post-stroke cognitive impairment: High prevalence and
determining factors in a cohort of mild stroke. J Alzheimers Dis.
40:1029–1038. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Imfeld P, Bodmer M, Schuerch M, Jick SS
and Meier CR: Risk of incident stroke in patients with Alzheimer
disease or vascular dementia. Neurology. 81:910–919. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pendlebury ST and Rothwell PM: Prevalence,
incidence and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke
dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol.
8:1006–1018. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y and Rosenberg GA: Blood-brain
barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease.
Stroke. 42:3323–3328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kamada H, Yu F, Nito C and Chan PH:
Influence of hyperglycemia on oxidative stress and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 activation after focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in rats: Relation to blood-brain barrier
dysfunction. Stroke. 38:1044–1049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khatri R, McKinney AM, Swenson B and
Janardhan V: Blood-brain barrier, reperfusion injury and
hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 79
13 Suppl 1:S52–S57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weekman EM and Wilcock DM: Matrix
metalloproteinase in blood-brain barrier breakdown in dementia. J
Alzheimers Dis. 49:893–903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rochfort KD and Cummins PM: The
blood-brain barrier endothelium: A target for pro-inflammatory
cytokines. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:702–706. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blanchette M and Daneman R: Formation and
maintenance of the BBB. Mech Dev. 138:8–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haseloff RF, Dithmer S, Winkler L, Wolburg
H and Blasig IE: Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at
the blood-brain barrier: Structural and functional aspects. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 38:16–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE,
Yusof SR and Begley DJ: Structure and function of the blood-brain
barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 37:13–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF and Andjelkovic AV:
Brain endothelial cell-cell junctions: How to ‘open’ the blood
brain barrier. Curr Neuropharmacol. 6:179–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sandoval KE and Witt KA: Blood-brain
barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol
Dis. 32:200–219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lucke-Wold BP, Logsdon AF, Turner RC,
Rosen CL and Huber JD: Aging, the metabolic syndrome and ischemic
stroke: redefining the approach for studying the blood-brain
barrier in a complex neurological disease. Adv Pharmacol.
71:411–449. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lisabeth EM, Falivelli G and Pasquale EB:
Eph receptor signaling and ephrins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:a0091592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ieguchi K: Eph as a target in
inflammation. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 15:119–128.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jellinghaus S, Poitz DM, Ende G, Augstein
A, Weinert S, Stütz B, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Pasquale EB and Strasser
RH: Ephrin-A1/EphA4-mediated adhesion of monocytes to endothelial
cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:2201–2211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gliem M, Schwaninger M and Jander S:
Protective features of peripheral monocytes/macrophages in stroke.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:329–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thundyil J, Manzanero S, Pavlovski D,
Cully TR, Lok KZ, Widiapradja A, Chunduri P, Jo DG, Naruse C, Asano
M, et al: Evidence that the EphA2 receptor exacerbates ischemic
brain injury. PLoS One. 8:e535282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi JS, Kim SJ, Shin JA, Lee KE and Park
EM: Effects of estrogen on temporal expressions of IL-1beta and
IL-1ra in rat organotypic hippocampal slices exposed to
oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neurosci Lett. 438:233–237. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khedr EM, Hamed SA, El-Shereef HK, Shawky
OA, Mohamed KA, Awad EM, Ahmed MA, Shehata GA and Eltahtawy MA:
Cognitive impairment after cerebrovascular stroke: Relationship to
vascular risk factors. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 5:103–116.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
del Ser T, Barba R, Morin MM, Domingo J,
Cemillan C, Pondal M and Vivancos J: Evolution of cognitive
impairment after stroke and risk factors for delayed progression.
Stroke. 36:2670–2675. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van de Haar HJ, Burgmans S, Hofman PA,
Verhey FR, Jansen JF and Backes WH: Blood-brain barrier impairment
in dementia: Current and future in vivo assessments. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 49:71–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borlongan CV, Rodrigues AA Jr and Oliveira
MC: Breaking the barrier in stroke: What should we know? A
mini-review. Curr Pharm Des. 18:3615–3623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F,
Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M and Vogt T:
Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign
human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem. 50:490–499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation and
functions. Small GTPases. 5:e298462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shin HK, Salomone S and Ayata C: Targeting
cerebrovascular Rho-kinase in stroke. Exp Opin Ther Targets.
12:1547–1564. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gibson CL, Srivastava K, Sprigg N, Bath PM
and Bayraktutan U: Inhibition of Rho-kinase protects cerebral
barrier from ischaemia-evoked injury through modulations of
endothelial cell oxidative stress and tight junctions. J Neurochem.
129:816–826. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|