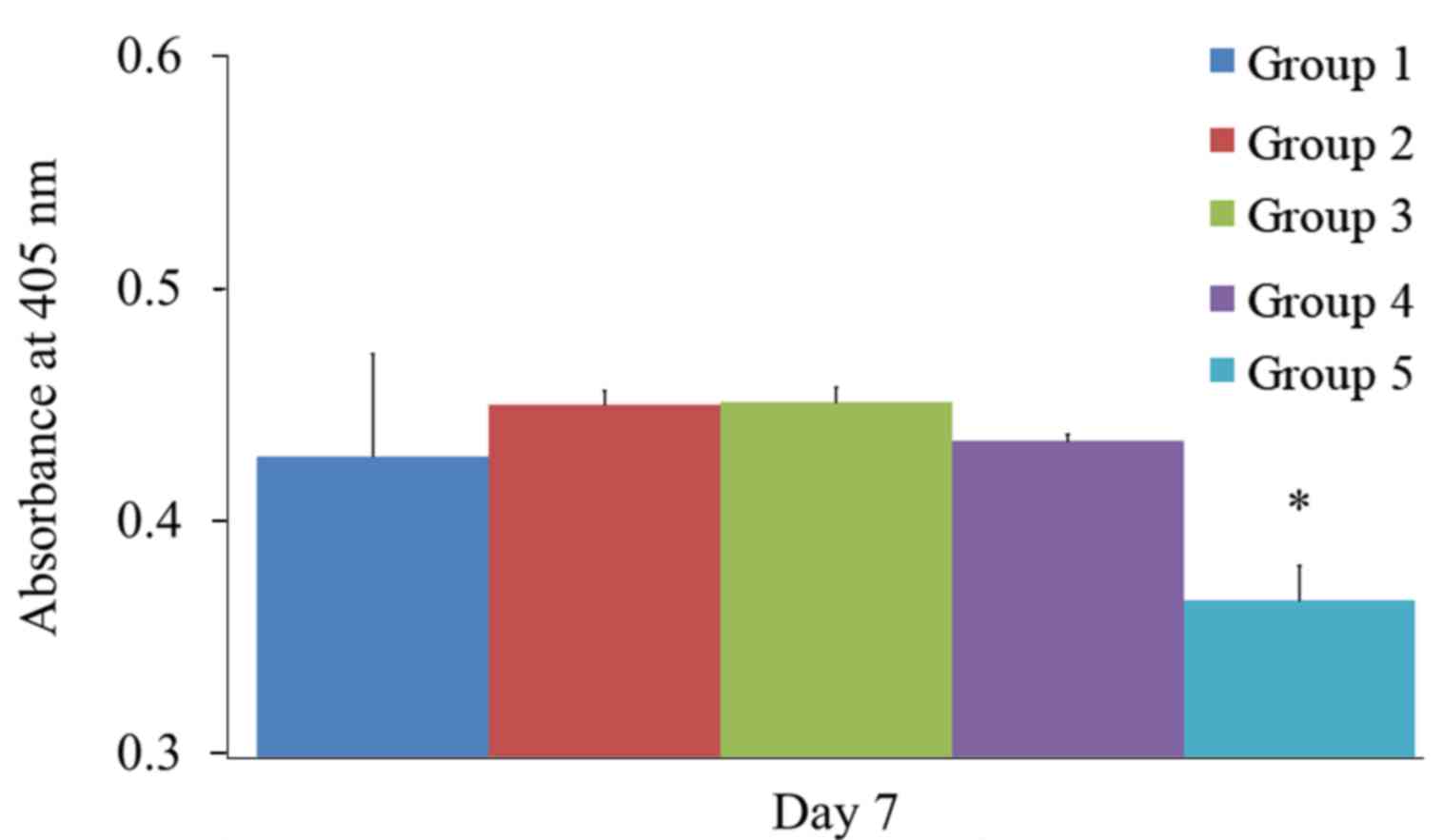
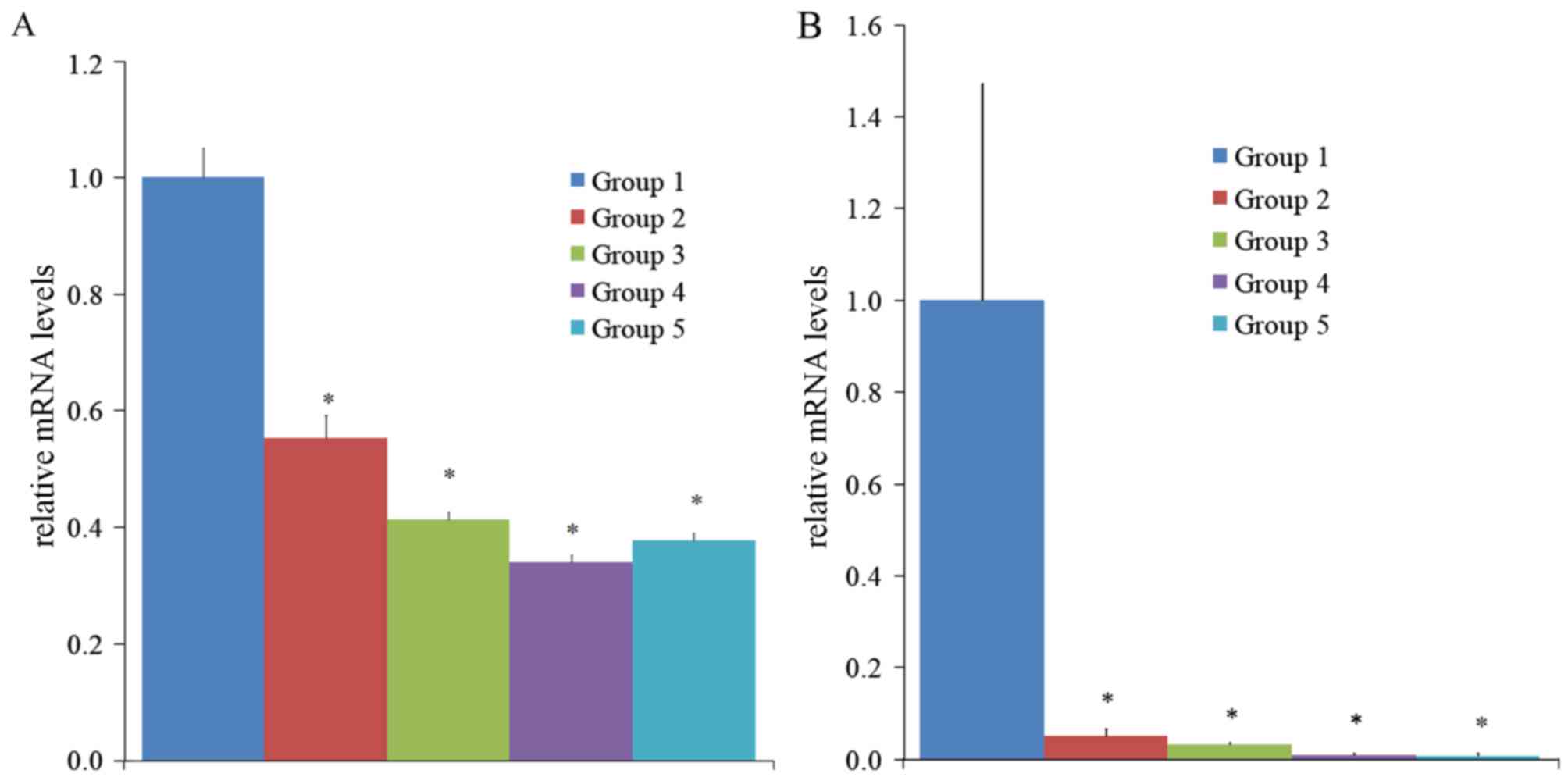
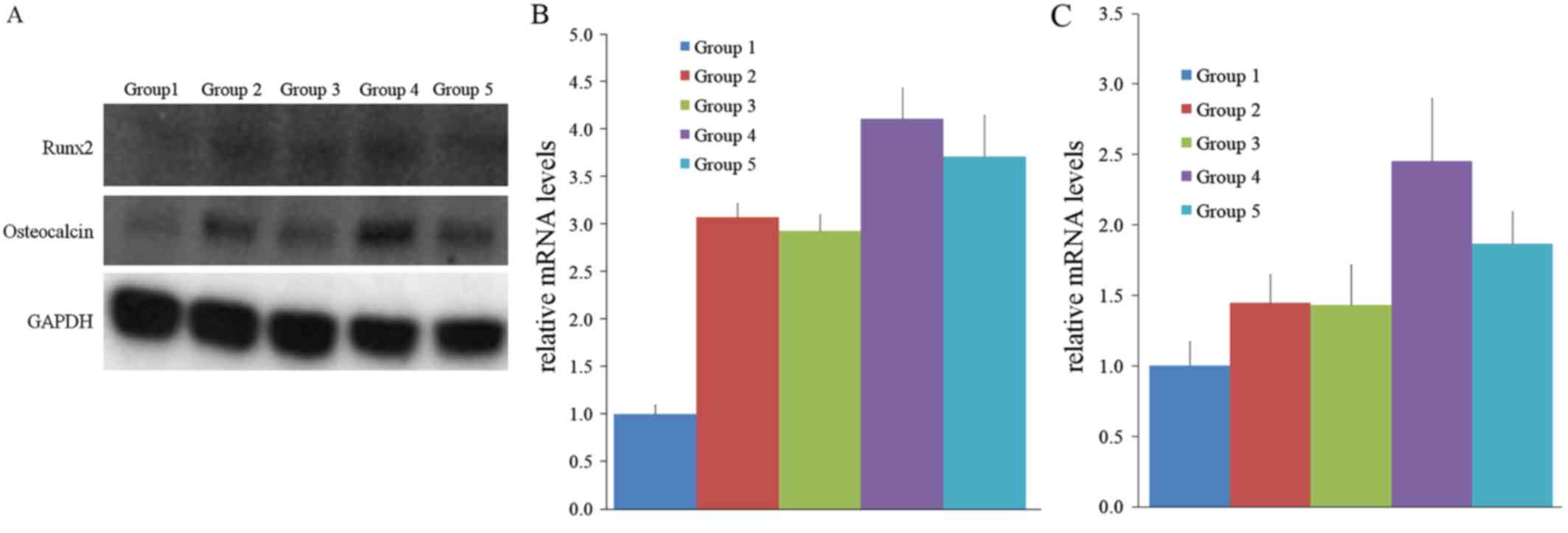
|
1
|
Kristjansson B and Honsawek S: Mesenchymal
stem cells for cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. World J
Orthop. 8:674–680. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moustaki M, Papadopoulos O, Verikokos C,
Karypidis D, Masud D, Kostakis A, Papastefanaki F, Roubelakis MG
and Perrea D: Application of adipose-derived stromal cells in fat
grafting: Basic science and literature review. Exp Ther Med.
14:2415–2423. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Z, Zhu Y, Ge R, Zhu J, He X, Yuan X
and Liu X: Combination of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells sheet
and platelet rich plasma for posterolateral lumbar fusion.
Oncotarget. 8:62298–62311. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ha DH, Pathak S, Yong CS, Kim JO, Jeong JH
and Park JB: Potential differentiation ability of gingiva
originated human mesenchymal stem cell in the presence of
tacrolimus. Sci Rep. 6:349102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Potdar PD and Jethmalani YD: Human dental
pulp stem cells: Applications in future regenerative medicine.
World J Stem Cells. 7:839–851. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang GT, Gronthos S and Shi S:
Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from
other sources: Their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J
Dent Res. 88:792–806. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
the osteogenic differentiation of gingiva-derived stem cells grown
on culture plates or in stem cell spheroids: Comparison of two- and
three-dimensional cultures. Exp Ther Med. 14:2434–2438. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Horst OV, Chavez MG, Jheon AH, Desai T and
Klein OD: Stem cell and biomaterials research in dental tissue
engineering and regeneration. Dent Clin North Am. 56:495–520. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Estrela C, Alencar AH, Kitten GT, Vencio
EF and Gava E: Mesenchymal stem cells in the dental tissues:
Perspectives for tissue regeneration. Braz Dent J. 22:91–98. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitsiadis TA, Orsini G and Jimenez-Rojo L:
Stem cell-based approaches in dentistry. Eur Cell Mater.
30:248–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu B, Liu Y, Li D and Jin Y: Somatic stem
cell biology and periodontal regeneration. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Implants. 28:e494–e502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu L, Liu Y and Wang S: Stem cell-based
tooth and periodontal regeneration. Oral Dis. 24:696–705. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Frith JE, Thomson B and Genever PG:
Dynamic three-dimensional culture methods enhance mesenchymal stem
cell properties and increase therapeutic potential. Tissue Eng Part
C Methods. 16:735–749. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF and
Yang L: Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their
applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay
Drug Dev Technol. 12:207–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Nguyen AL, Shi S, Hill C,
Wilder-Smith P, Krasieva TB and Le AD: Three-dimensional spheroid
culture of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances
mitigation of chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis. Stem Cells Dev.
21:937–947. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JH, Han YS and Lee SH: Long-duration
Three-dimensional spheroid culture promotes angiogenic activities
of Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
24:260–267. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Achilli TM, Meyer J and Morgan JR:
Advances in the formation, use and understanding of multi-cellular
spheroids. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 12:1347–1360. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jeong CH, Kim SM, Lim JY, Ryu CH, Jun JA
and Jeun SS: Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived
neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic
stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1291452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin SH, Lee JE, Yun JH, Kim I, Ko Y and
Park JB: Isolation and characterization of human mesenchymal stem
cells from gingival connective tissue. J Periodontal Res.
50:461–467. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
the shape, viability, stemness and osteogenic differentiation of
cell spheroids formed from human gingiva-derived stem cells and
osteoprecursor cells. Exp Ther Med. 13:3467–3473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee H, Son J, Na CB, Yi G, Koo H and Park
JB: The effects of doxorubicin-loaded liposomes on viability, stem
cell surface marker expression and secretion of vascular
endothelial growth factor of three-dimensional stem cell spheroids.
Exp Ther Med. 15:4950–4960. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ,
Ostell J and Wheeler DL: GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Database
Issue): D25–D30. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim BB, Kim M, Park YH, Ko Y and Park JB:
Short-term application of dexamethasone on stem cells derived from
human gingiva reduces the expression of RUNX2 and β-catenin. J Int
Med Res. 45:993–1006. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
the maintenance of stemness, viability, and differentiation
potential of gingiva-derived stem-cell spheroids. Exp Ther Med.
13:1757–1764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morrison SJ and Spradling AC: Stem cells
and niches: Mechanisms that promote stem cell maintenance
throughout life. Cell. 132:598–611. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ullah I, Subbarao RB and Rho GJ: Human
mesenchymal stem cells-current trends and future prospective.
Biosci Rep. 35(pii): e001912015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomar GB, Srivastava RK, Gupta N,
Barhanpurkar AP, Pote ST, Jhaveri HM, Mishra GC and Wani MR: Human
gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells are superior to bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for cell therapy in
regenerative medicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:377–383.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ryu S, Yoo J, Jang Y, Han J, Yu SJ, Park
J, Jung SY, Ahn KH, Im SG, Char K and Kim BS: Nanothin coculture
membranes with tunable pore architecture and thermoresponsive
functionality for Transfer-printable stem Cell-derived cardiac
sheets. ACS Nano. 9:10186–10202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun K, Zhou Z, Ju X, Zhou Y, Lan J, Chen
D, Chen H, Liu M and Pang L: Combined transplantation of
mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells for tissue
engineering: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int.
7:1512016.
|
|
31
|
Seebach C, Henrich D, Wilhelm K, Barker JH
and Marzi I: Endothelial progenitor cells improve directly and
indirectly early vascularization of mesenchymal stem cell-driven
bone regeneration in a critical bone defect in rats. Cell
Transplant. 21:1667–1677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ewa-Choy YW, Pingguan-Murphy B,
Abdul-Ghani NA, Jahendran J and Chua KH: Effect of alginate
concentration on chondrogenesis of co-cultured human
adipose-derived stem cells and nasal chondrocytes: A biological
study. Biomater Res. 21:192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Q and Wang Z: Influence of mesenchymal
stem cells with endothelial progenitor cells in co-culture on
osteogenesis and angiogenesis: An in vitro study. Arch Med Res.
44:504–513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aguirre A, Planell JA and Engel E:
Dynamics of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor
cell/mesenchymal stem cell interaction in co-culture and its
implications in angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
400:284–291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raida M, Heymann AC, Gunther C and
Niederwieser D: Role of bone morphogenetic protein 2 in the
crosstalk between endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem
cells. Int J Mol Med. 18:735–739. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Steiner D, Köhn K, Beier JP, Stürzl M,
Horch RE and Arkudas A: Cocultivation of mesenchymal stem cells and
endothelial progenitor cells reveals antiapoptotic and
proangiogenic effects. Cells Tissues Organs. 204:218–227. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Park JB: Effects of 17-α ethynyl estradiol
on proliferation, differentiation & mineralization of
osteoprecursor cells. Indian J Med Res. 136:466–470.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee SI, Yeo SI, Kim BB, Ko Y and Park JB:
Formation of size-controllable spheroids using gingiva-derived stem
cells and concave microwells: Morphology and viability tests.
Biomed Rep. 4:97–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Neville ME: 51Cr-uptake assay. A sensitive
and reliable method to quantitate cell viability and cell death. J
Immunol Methods. 99:77–82. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Madhavan H: Simple laboratory methods to
measure cell proliferation using DNA synthesis property. J Stem
Cells Regen Med. 3:12–14. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee H and Park JB: Evaluation of the
effects of dimethylsulphoxide on morphology, cellular viability,
mRNA, and protein expression of stem cells culture in growth media.
Biomed Rep. 7:291–296. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bruderer M, Richards RG, Alini M and
Stoddart MJ: Role and regulation of RUNX2 in osteogenesis. Eur Cell
Mater. 28:269–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stein GS, Lian JB and Owen TA:
Relationship of cell growth to the regulation of tissue-specific
gene expression during osteoblast differentiation. FASEB J.
4:3111–3123. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nakamura A, Dohi Y, Akahane M, Ohgushi H,
Nakajima H, Funaoka H and Takakura Y: Osteocalcin secretion as an
early marker of in vitro osteogenic differentiation of rat
mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 15:169–180.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|