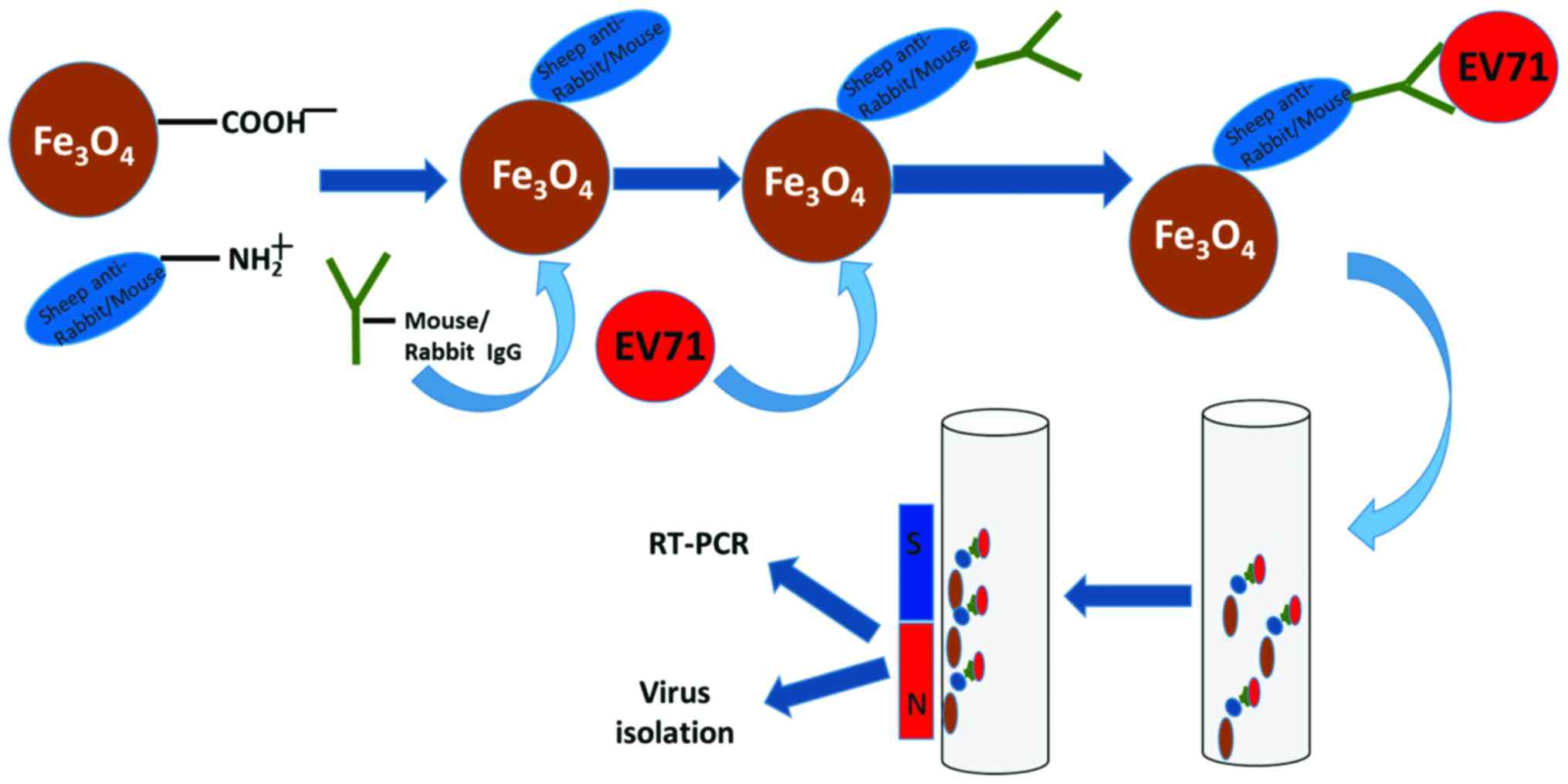
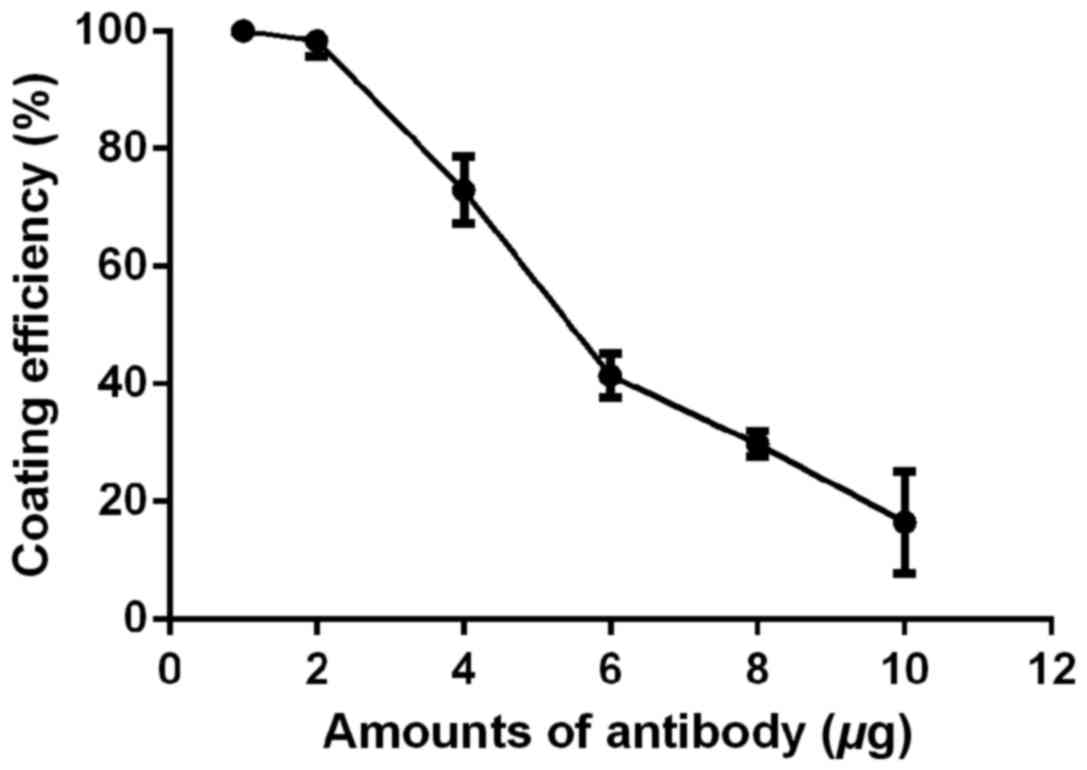
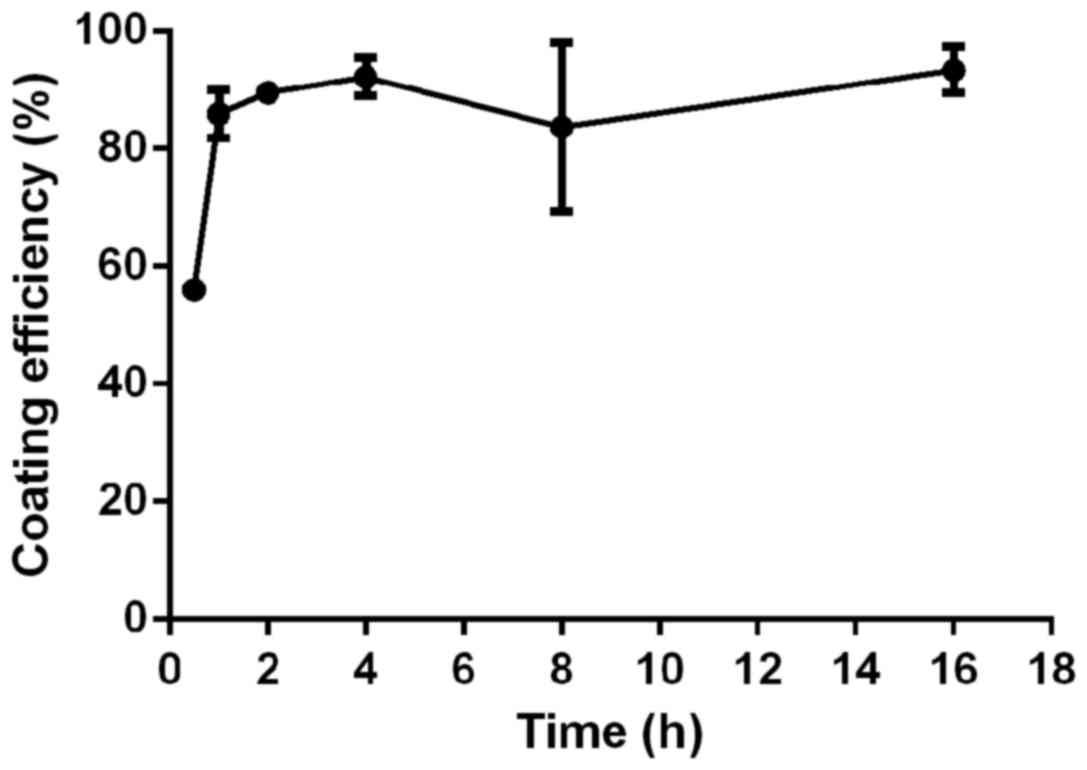
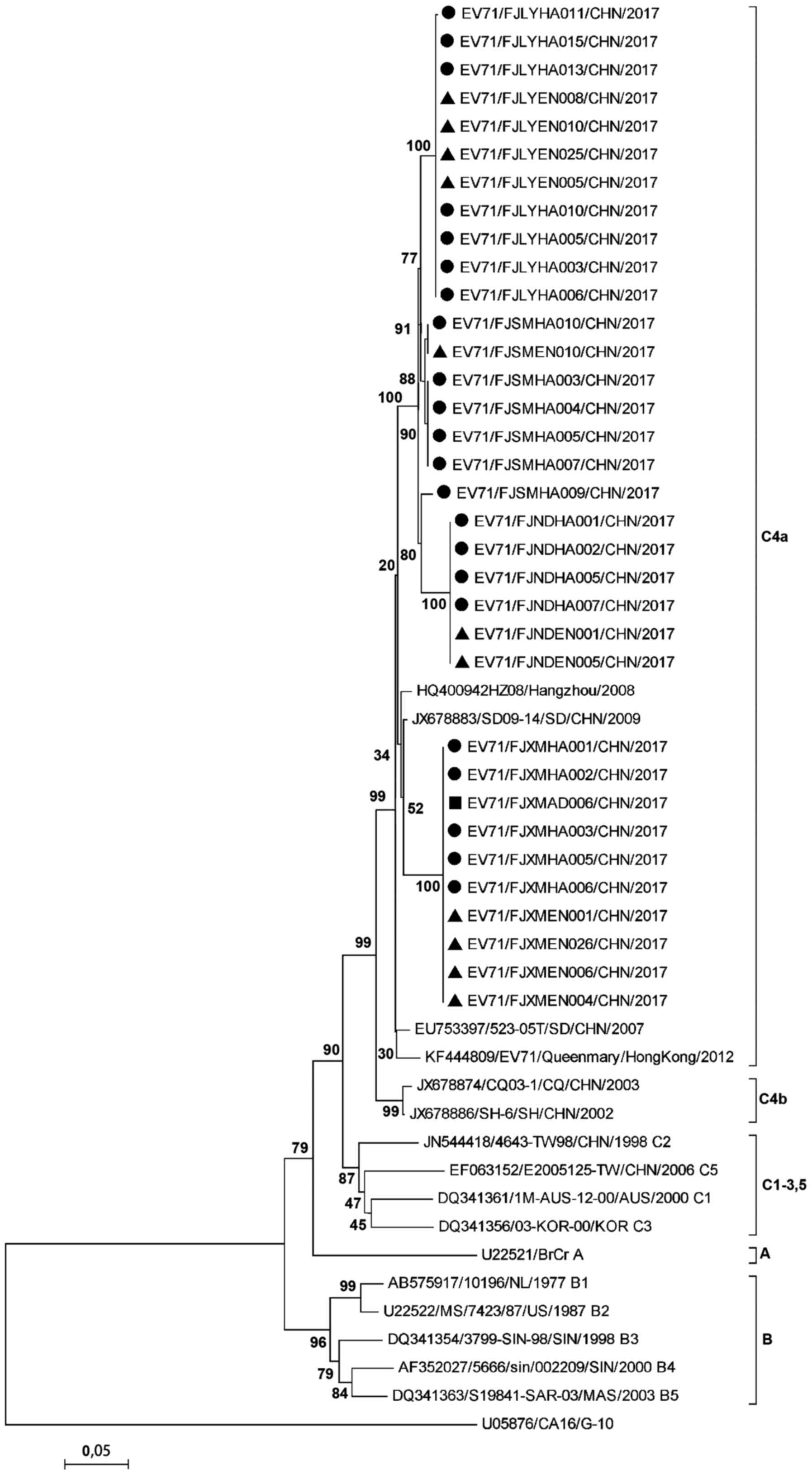
|
1
|
Ooi MH, Wong SC, Lewthwaite P, Cardosa MJ
and Solomon T: Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of
enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 9:1097–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yi EJ, Shin YJ, Kim JH, Kim TG and Chang
SY: Enterovirus 71 infection and vaccines. Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
6:4–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ho M, Chen ER, Hsu KH, Twu SJ, Chen KT,
Tsai SF, Wang JR and Shih SR: Taiwan Enterovirus Epidemic Working
Group: An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. N Engl J
Med. 341:929–935. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herrero LJ, Lee CS, Hurrelbrink RJ, Chua
BH, Chua KB and McMinn PC: Molecular epidemiology of enterovirus 71
in peninsular Malaysia, 1997–2000. Arch Virol. 148:1369–1385. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan KP, Goh KT, Chong CY, Teo ES, Lau G
and Ling AE: Epidemic hand, foot and mouth disease caused by human
enterovirus 71, Singapore. Emerg Infect Dis. 9:78–85. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Tan XJ, Wang HY, Yan DM, Zhu SL,
Wang DY, Ji F, Wang XJ, Gao YJ, Chen L, et al: An outbreak of hand,
foot, and mouth disease associated with subgenotype C4 of human
enterovirus 71 in Shandong, China. J Clin Virol. 44:262–267. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang F, Ren L, Xiong Z, Li J, Xiao Y, Zhao
R, He Y, Bu G, Zhou S, Wang J, et al: Enterovirus 71 outbreak in
the People's Republic of China in 2008. J Clin Microbiol.
47:2351–2352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xing W, Liao Q, Viboud C, Zhang J, Sun J,
Wu JT, Chang Z, Liu F, Fang VJ, Zheng Y, et al: Hand, foot, and
mouth disease in China, 2008–12: An epidemiological study. Lancet
Infect Dis. 14:308–318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park SK, Park B, Ki M, Kim H, Lee K, Jung
C, Sohn YM, Choi SM, Kim DK, Lee DS, et al: Transmission of
seasonal outbreak of childhood enteroviral aseptic meningitis and
hand-foot-mouth disease. J Korean Med Sci. 25:677–683. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goh KT, Doraisingham S, Tan JL, Lim GN and
Chew SE: An outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Singapore.
Bull World Health Organ. 60:965–969. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li P, Li T, Gu Q, Chen X, Li J, Chen X,
Chen Y, Zhang D, Gao R, He Z, et al: Children's caregivers and
public playgrounds: Potential reservoirs of infection of
hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Sci Rep. 6:363752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Casas N and Suñén E: Detection of
enteroviruses, hepatitis A virus and rotaviruses in sewage by means
of an immunomagnetic capture reverse transcription-PCR assay.
Microbiol Res. 157:169–175. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu P, Kim M, Schlesinger D, Kranz C, Ha
S, Ha J, Slauch J, Baek S and Moe C: Immunomagnetic separation
combined with RT-qPCR for determining the efficacy of disinfectants
against human noroviruses. J Infect Public Health. 8:145–154. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kobayashi S, Natori K, Takeda N and Sakae
K: Immunomagnetic capture RT-PCR for detection of norovirus from
foods implicated in a foodborne outbreak. Microbiol Immunol.
48:201–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ooi MH, Solomon T, Podin Y, Mohan A, Akin
W, Yusuf MA, del Sel S, Kontol KM, Lai BF, Clear D, et al:
Evaluation of different clinical sample types in diagnosis of human
enterovirus 71-associated hand-foot-and-mouth disease. J Clin
Microbiol. 45:1858–1866. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|