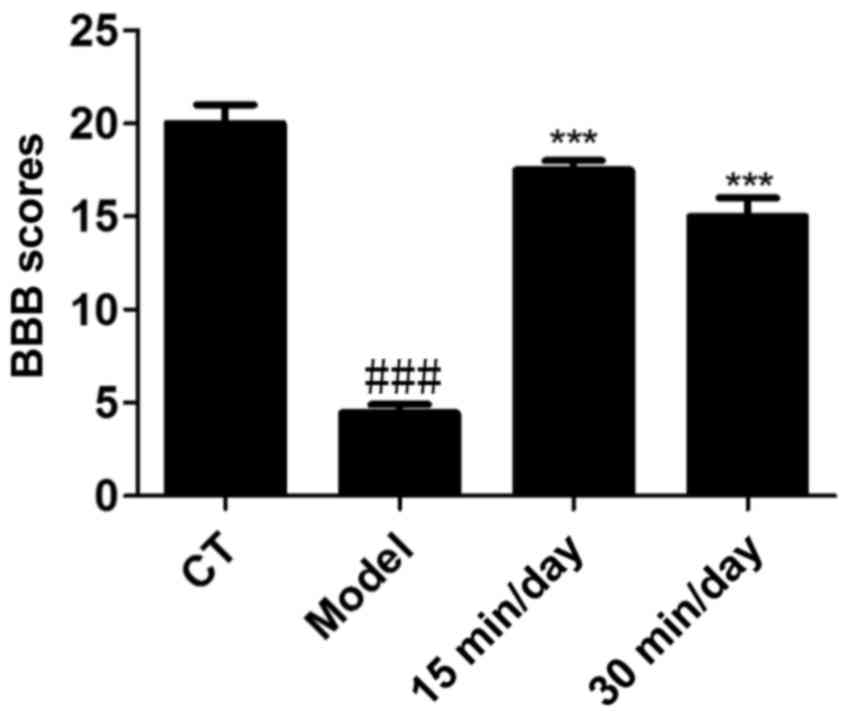
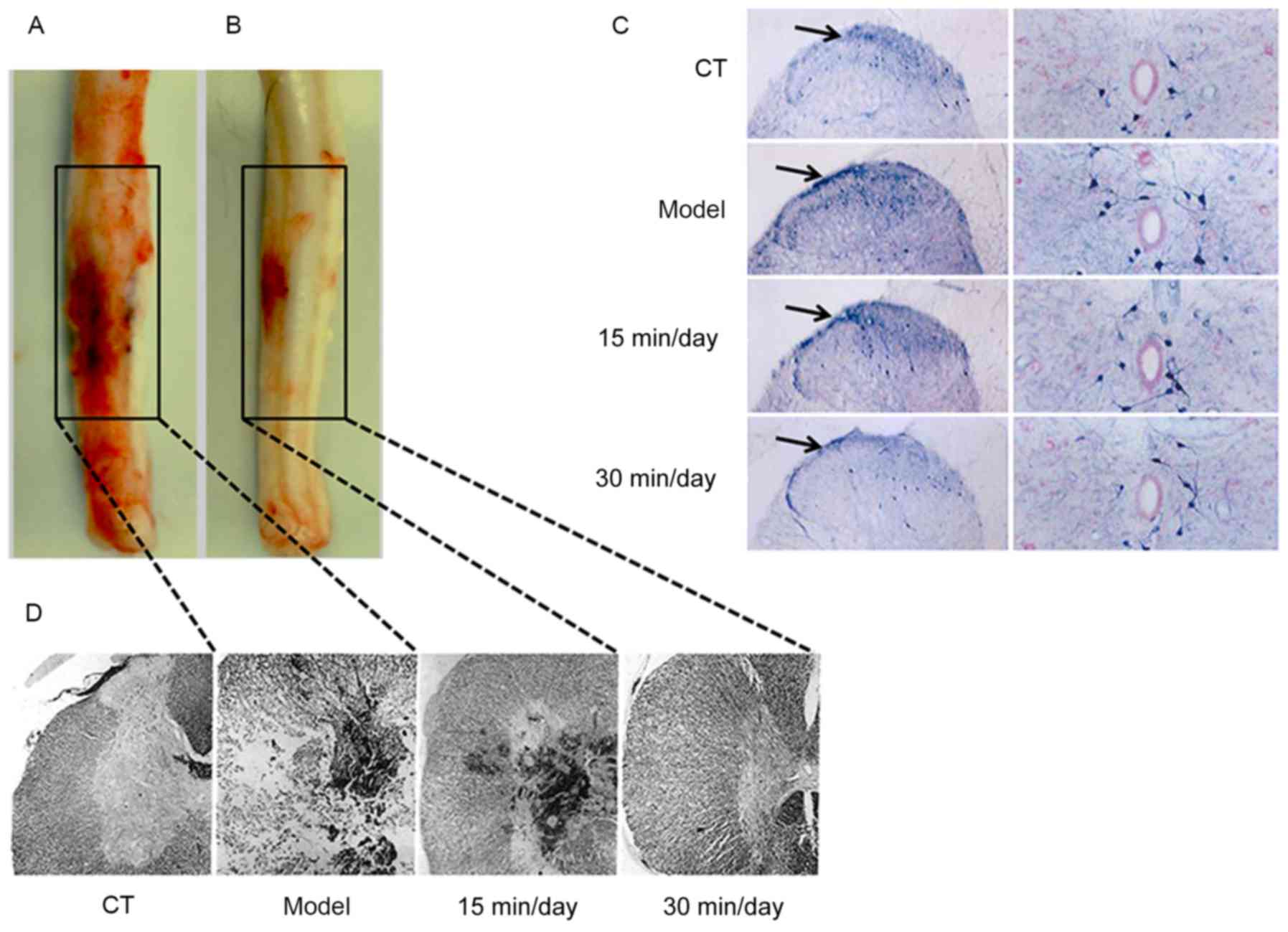
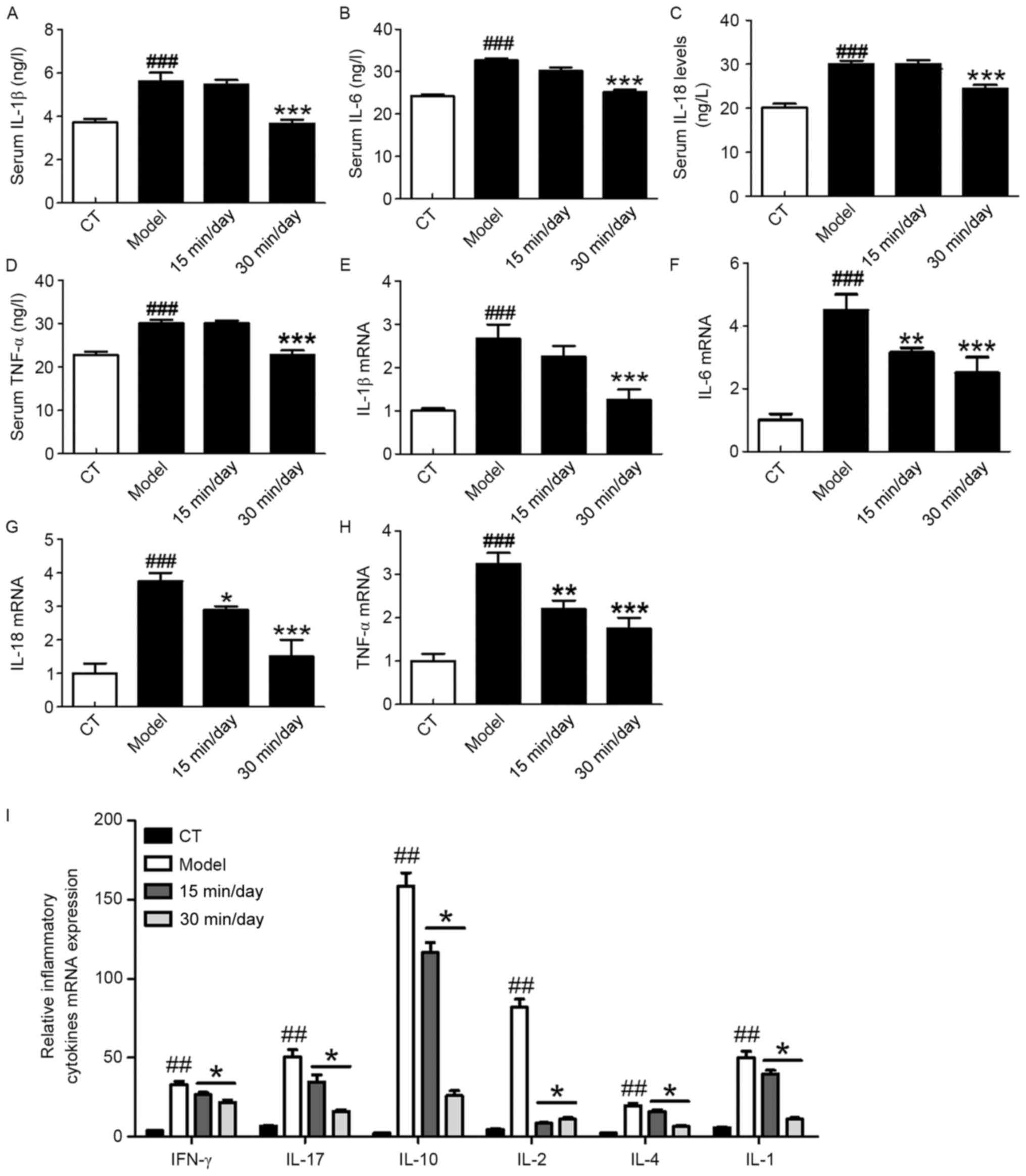
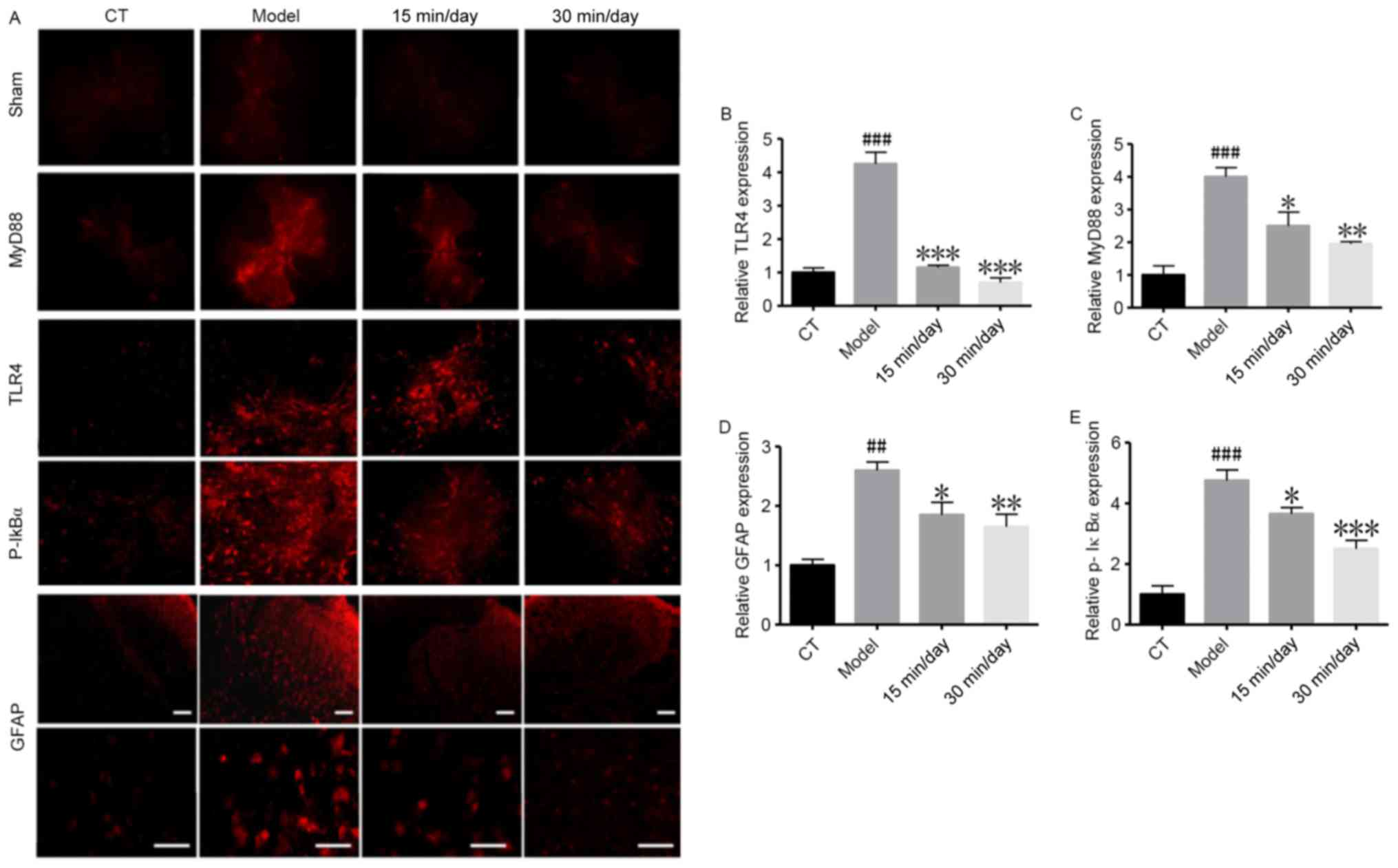
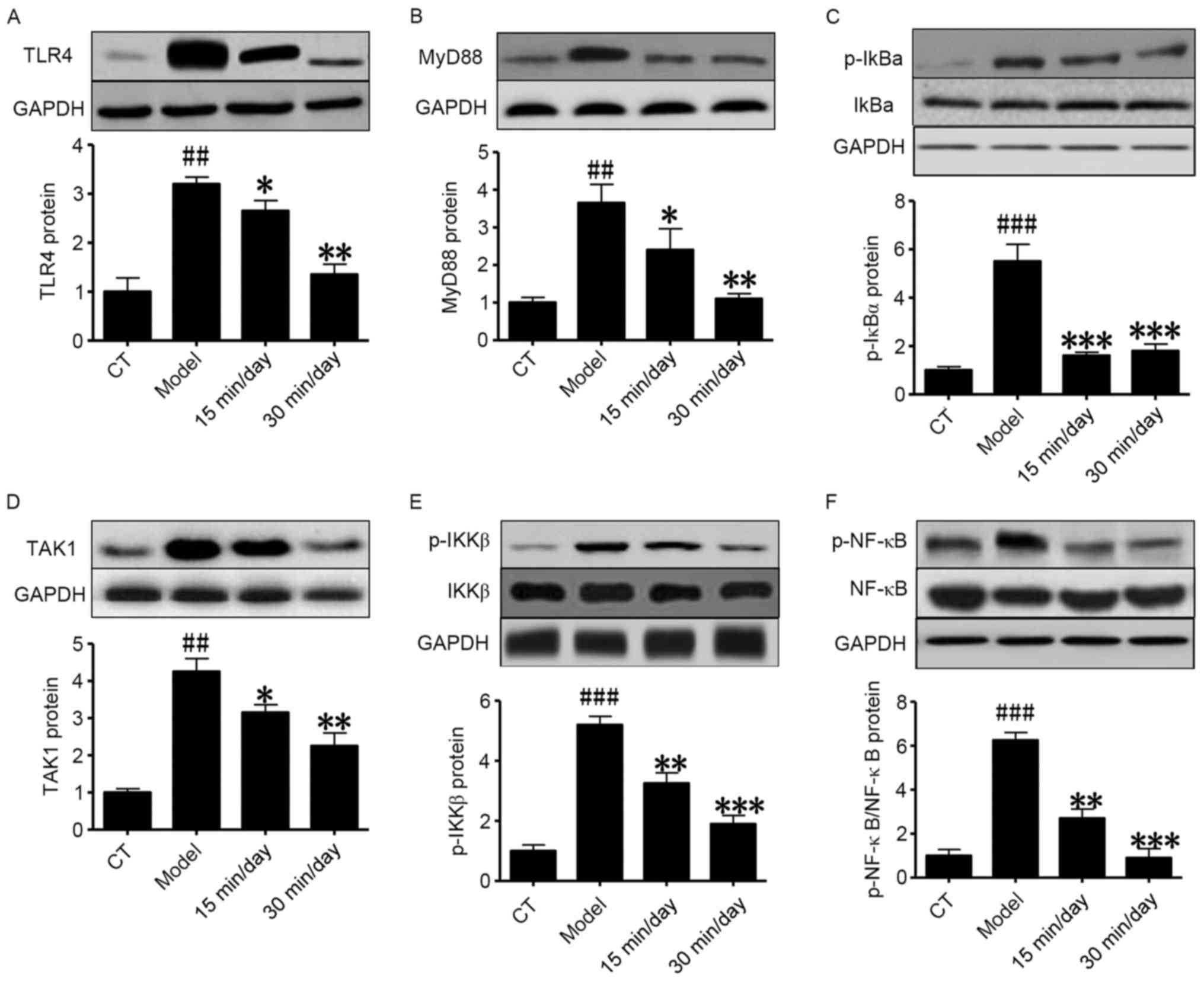
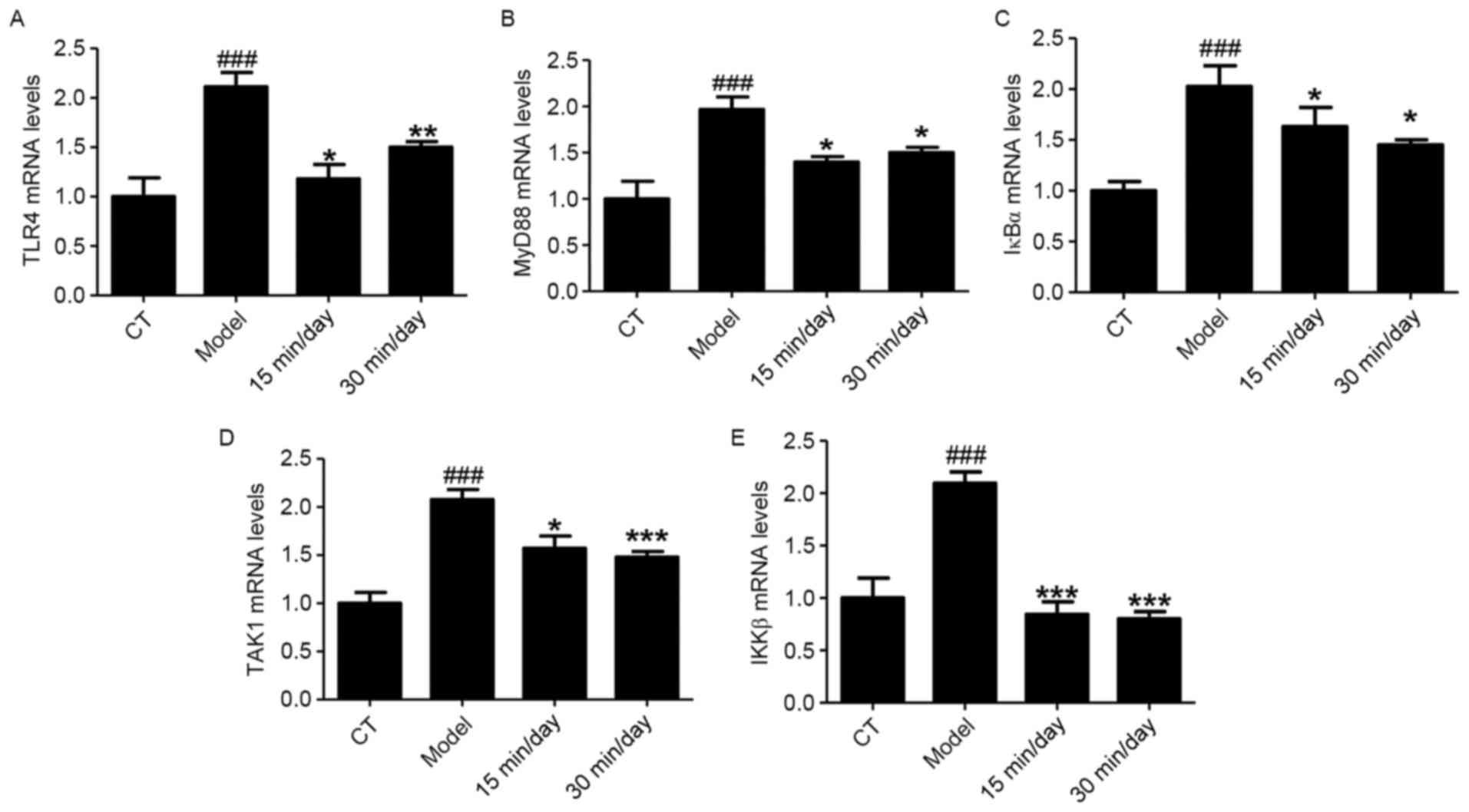
|
1
|
Siriphorn A, Dunham KA, Chompoopong S and
Floyd CL: Postinjury administration of 17β-estradiol induces
protection in the gray and white matter with associated functional
recovery after cervical spinal cord injury in male rats. J Comp
Neurol. 520:2630–2646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petrinovic MM, Hourez R, Aloy EM, Dewarrat
G, Gall D, Weinmann O, Gaudias J, Bachmann LC, Schiffmann SN, Vogt
KE and Schwab ME: Neuronal Nogo-A negatively regulates dendritic
morphology and synaptic transmission in the cerebellum. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:1083–1088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang F, Xing S, He M, Hou Q, Chen S, Zou
X, Pei Z and Zeng J: Nogo-A is associated with secondary
degeneration of substantia nigra in hypertensive rats with focal
cortical infarction. Brain Res. 1469:153–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu WW, Ma XL, Guo AL, Zhao HY and Luo HH:
Neuroprotective effects of NEP1-40 and fasudil on Nogo-A expression
in neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Genet Mol Res.
10:2987–2995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim JH, Choi KH, Jang YJ, Bae SS, Shin BC,
Choi BT and Shin HK: Electroacupuncture acutely improves cerebral
blood flow and attenuates moderate ischemic injury via an
endothelial mechanism in mice. PLoS One. 8:e567362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim MW, Chung YC, Jung HC, Park MS, Han
YM, Chung YA, Maeng LS, Park SI, Lim J, Im WS, et al:
Electroacupuncture enhances motor recovery performance with
brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rats with cerebral
infarction. Acupunct Med. 30:222–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tan F, Wan S, Wu H, Huo Q, Wang J, Chen W,
Fang M, Liu X, Wang X and Sun J: Expression of neurocan mRNA and
ultrastructure of brain tissue after cerebral ischemia and
reperfusion in stroke-prone renovascular hypertensive rats treated
by electroacupuncture. Neural Regen Res. 6:2834–2838. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Hwang L, Choi IY, Kim SE, Ko IG, Shin MS,
Kim CJ, Kim SH, Jin JJ, Chung JY and Yi JW: Dexmedetomidine
ameliorates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced memory impairment by
inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic
factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Int J Mol Med.
31:1047–1056. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sung YH, Kim SC, Hong HP, Park CY, Shin
MS, Kim CJ, Seo JH, Kim DY, Kim DJ and Cho HJ: Treadmill exercise
ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal loss through suppressing
microglial activation in Parkinson's disease mice. Life Sci.
91:1309–1316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Donnelly DJ and Popovich PG: Inflammation
and its role in neuroprotection, axonal regeneration and functional
recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 209:378–388. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anwar MA, Al Shehabi TS and Eid AH:
Inflammogenesis of secondary spinal cord injury. Front Cell
Neurosci. 10:982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dominguez E, Mauborgne A, Mallet J,
Desclaux M and Pohl M: SOCS3-mediated blockade of JAK/STAT3
signaling pathway reveals its major contribution to spinal cord
neuroinflammation and mechanical allodynia after peripheral nerve
injury. J Neurosci. 30:5754–5766. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Swift DL, Johannsen NM, Lavie CJ, Earnest
CP and Church TS: The role of exercise and physical activity in
weight loss and maintenance. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 56:441–447. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Foster-Schubert KE, Alfano CM, Duggan CR,
Xiao L, Campbell KL, Kong A, Bain CE, Wang CY, Blackburn GL and
McTiernan A: Effect of diet and exercise, alone or combined, on
weight and body composition in overweight-to-obese postmenopausal
women. Obesity (Silver Spring). 20:1–1638. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kujala UM: Benefits of exercise therapy
for chronic diseases. Br J Sports Med. 40:3–4. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu Y, Xu J, Zhao W and Han HR: Measuring
self-care in persons with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review.
Eval Health Prof. 39:131–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tajiria N, Yasuharaa T, Shingo T, Kondo A,
Yuan W, Kadota T, Wang F, Baba T, Tayra JT, Morimoto T, et al:
Exercise exerts neuroprotective effects on Parkinson's disease
model of rats. Brain Res. 1310:200–207. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hutchinson KJ1, Gómez-Pinilla F, Crowe MJ,
Ying Z and Basso DM: Three exercise paradigms differentially
improve sensory recovery after spinal cord contusion in rats.
Brain. 127:1403–1414. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perot PL Jr, Lee WA, Hsu CY, Hogan EL, Cox
RD and Gross AJ: Therapeutic model for experimental spinal cord
injury in the rat: I. Mortality and motor deficit. Cent Nerv Syst
Trauma. 4:149–159. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC,
Anderson DK, Faden AI, Gruner JA, Holford TR, Hsu CY, Noble LJ,
Nockels R, et al: MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores:
Effects of experience and teamwork on reliability. Multicenter
Animal Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurotrauma. 13:343–359. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gaudet AD and Popovich PG: Extracellular
matrix regulation of inflammation in the healthy and injured spinal
cord. Exp Neurol. 258:24–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhuang ZY, Kawasaki Y, Tan PH, Wen YR,
Huang J and Ji RR: Role of the CX3CR1/p38 MAPK pathway in spinal
microglia for the development of neuropathic pain following nerve
injury-induced cleavage of fractalkine. Brain Behav Immun.
21:642–651. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guerrero AR, Uchida K, Nakajima H,
Watanabe S, Nakamura M, Johnson WE and Baba H: Blockade of
interleukin-6 signaling inhibits the classic pathway and promotes
an alternative pathway of macrophage activation after spinal cord
injury in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 9:402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Einstein O and Ben-Hur T: The changing
face of neural stem cell therapy in neurological diseases. Arch
Neurol. 65:452–456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kuh SU, Cho YE, Yoon DH, Kim KN and Ha Y:
Functional recovery after human umbilical cord blood cells
transplantation with brain-derived neutrophic factor into the
spinal cord injured rat. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 147:985–992. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carlson NG, Wieggel WA, Chen J, Bacchi A,
Rogers SW and Gahring LC: Inflammatory cytokines IL-1 alpha, IL-1
beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha impart neuroprotection to an excitotoxin
through distinct pathways. J Immunol. 163:3963–3968.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jones TB, McDaniel EE and Popovich PG:
Inflammatory-mediated injury and repair in the traumatically
injured spinal cord. Curr Pharm Des. 11:1223–1236. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
López-Vales R, Forés J, Verdú E and
Navarro X: Acute and delayed transplantation of olfactory
ensheathing cells promote partial recovery after complete
transection of the spinal cord. Neurobiol Dis. 21:57–68. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao ZM, Li HJ, Liu HY, Lu SH, Yang RC,
Zhang QJ and Han ZC: Intraspinal transplantation of CD34+ human
umbilical cord blood cells after spinal cord hemisection injury
improves functional recovery in adult rats. Cell Transplant.
13:113–122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mansilla E, Marin GH, Sturla F, Drago HE,
Gil MA, Salas E, Gardiner MC, Piccinelli G, Bossi S, Salas E, et
al: Human mesenchymal stem cells are tolerized by mice and improve
skin and spinal cord injuries. Transplant Proc. 37:292–294. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pal R, Gopinath C, Rao NM, Banerjee P,
Krishnamoorthy V, Venkataramana NK and Totey S: Functional recovery
after transplantation of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal
stromal cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Cytotherapy.
12:792–806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen HY and Boore JRP: Considering the
physiological and psychological consequences of spinal cord injury.
Br J Neuroscie. 1:225–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Driver HS and Taylorb SR: Exercise and
sleep. Sleep Med Rev. 4:387–402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gorman PH, Scott W, York H, Theyagaraj M,
Price-Miller N, McQuaid J, Eyvazzadeh M, Ivey FM and Macko RF:
Robotically assisted treadmill exercise training for improving peak
fitness in chronic motor incomplete spinal cord injury: A
randomized controlled trial. J Spinal Cord Med. 39:32–44. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Waris G and Ahsan H: Reactive oxygen
species: Role in the development of cancer and various chronic
conditions. J Carcinog. 5:142006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li QT and Verma IM: NF-kappaB regulation
in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Janssen-Heininger YM, Poynter ME and
Baeuerle PA: Recent advances towards understanding redox mechanisms
in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Free Radic Biol Med.
28:1317–1327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zandi E, Rothwarf DM, Delhase M, Hayakawa
M and Karin M: The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase
subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for IkappaB
phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. Cell. 19:243–252. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|