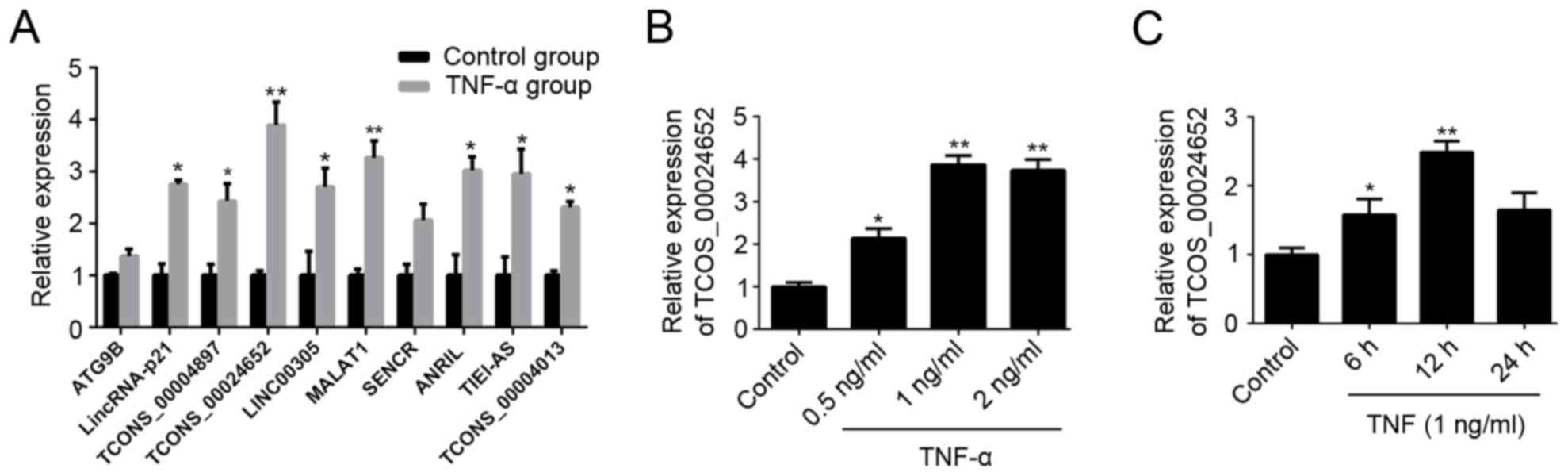
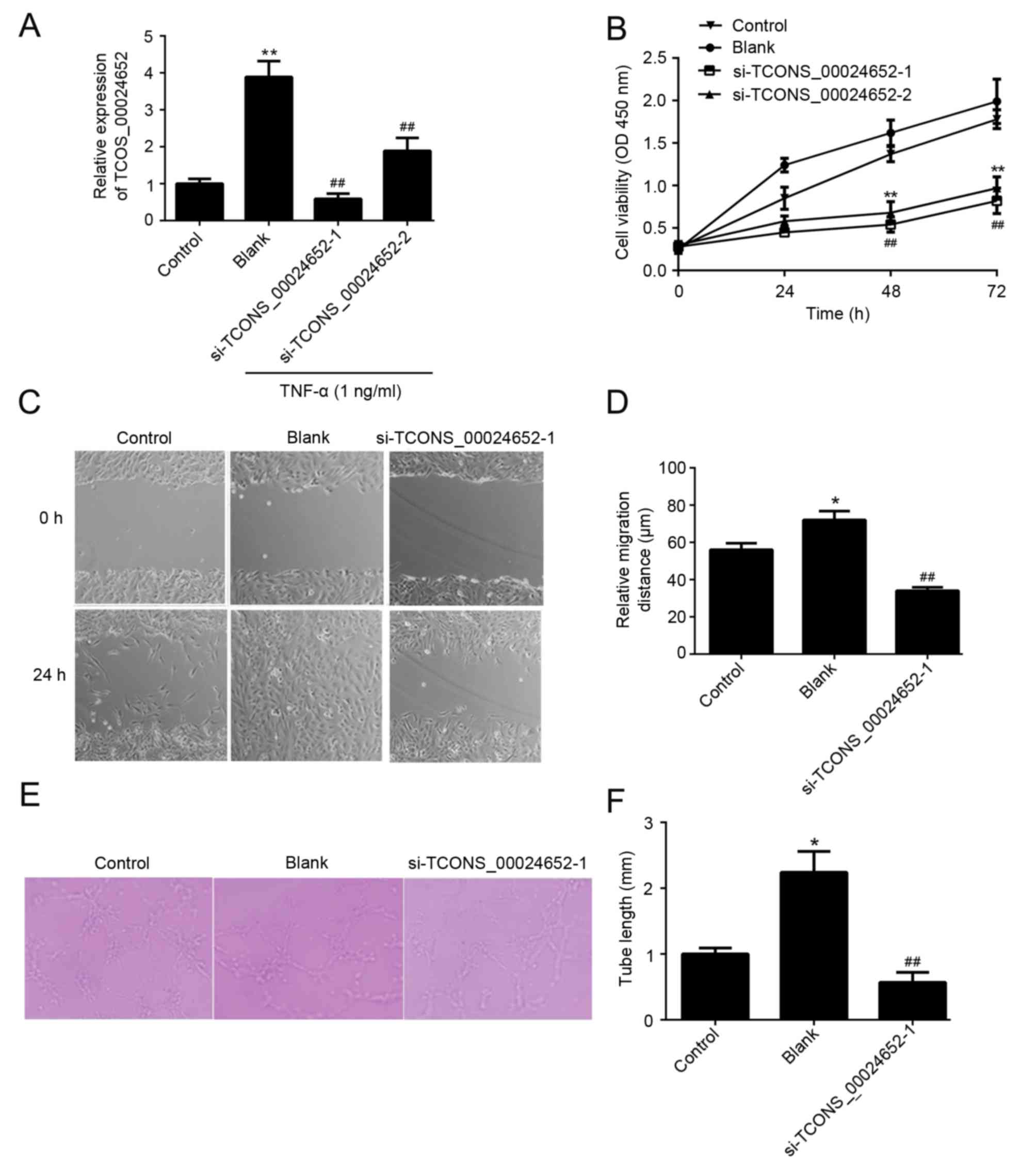
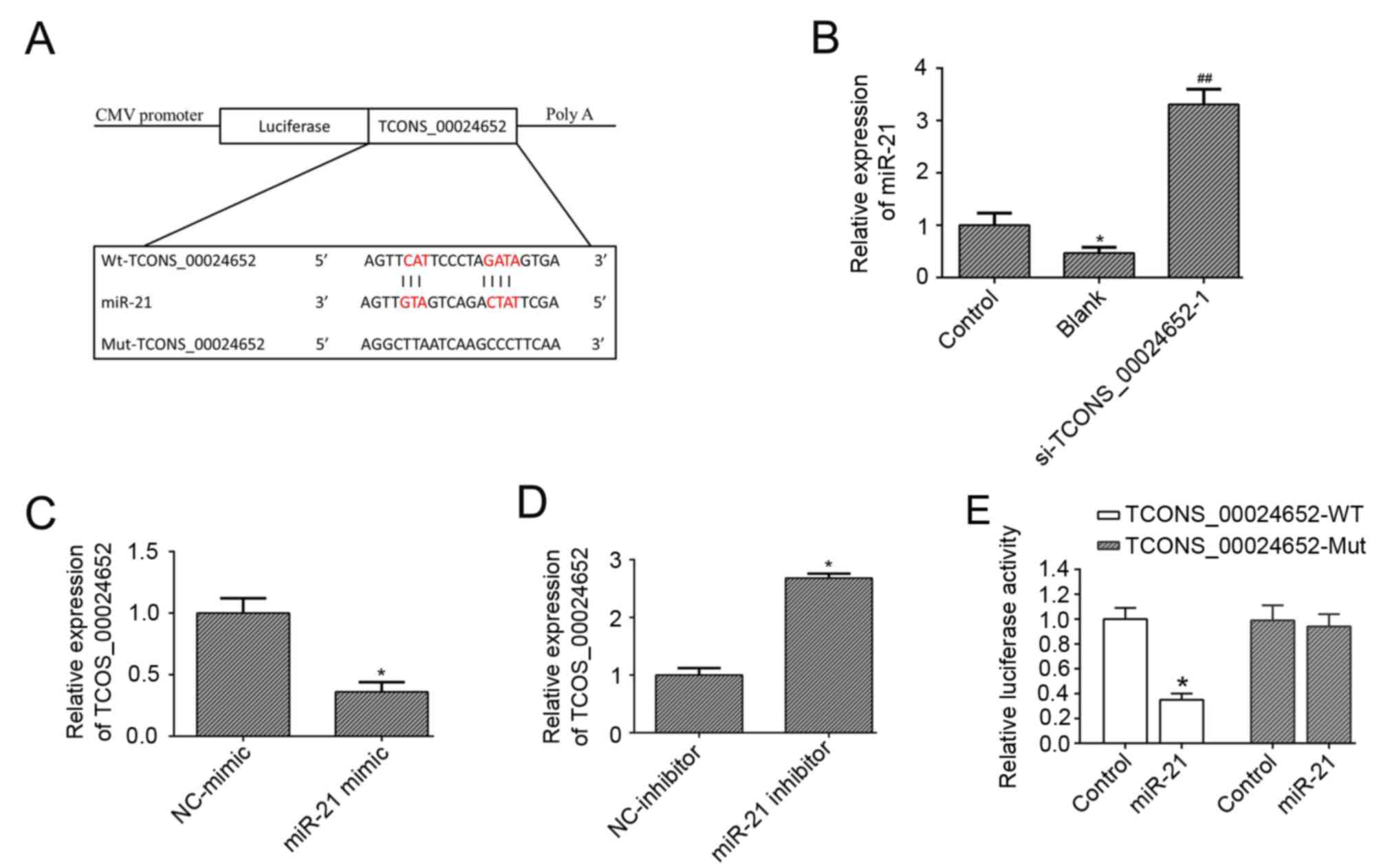
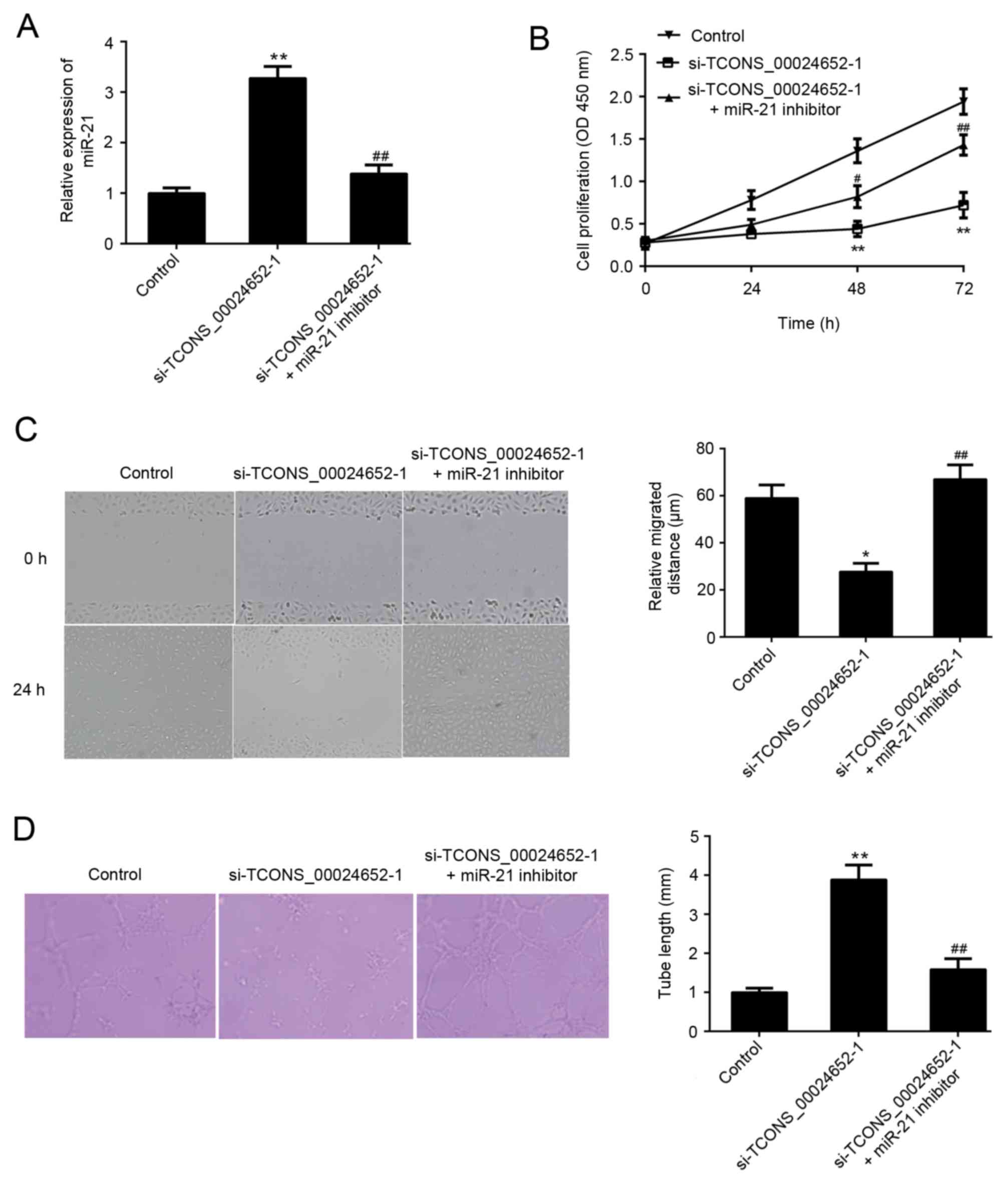
|
1
|
Camaré C, Pucelle M, Nègre-Salvayre A and
Salvayre R: Angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque. Redox Biol.
12:18–34. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weng J: Activation of CD137 signaling
promotes angiogenesis in atherosclerosis via modulating endothelial
Smad1/5-NFATc1 pathway. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:234–247. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sun Z: Atherosclerosis and Atheroma Plaque
Rupture: Imaging Modalities in the Visualization of Vasa Vasorum
and Atherosclerotic Plaques. Sci World J. 23:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mulligan-Kehoe MJ: The vasa vasorum in
diseased and nondiseased arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
298:H295–H305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moguillansky D, Leng X, Carson A, Lavery
L, Schwartz A, Chen X and Villanueva FS: Quantification of plaque
neovascularization using contrast ultrasound: A histologic
validation. Eur Heart J. 32:646–653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu MY and Li CJ: New insights into the
role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:E20342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pirillo A, Bonacina F, Norata GD and
Catapano AL: The interplay of lipids, lipoproteins and immunity in
atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 20:122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sedding DG, Boyle EC, Demandt JAF, Sluimer
JC, Dutzmann J, Haverich A and Bauersachs J: Vasa vasorum
angiogenesis: Key player in the initiation and progression of
atherosclerosis and potential target for the treatment of
cardiovascular disease. Front Immunol. 9:7062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N,
Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E and Chang HY: Long Noncoding RNA as
modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science.
329:689–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmitz SU, Grote P and Herrmann BG:
Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2491–2509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taylor DH, Chu ETJ, Spektor R and Soloway
PD: Long non-coding RNA regulation of reproduction and development.
Mol Reprod Dev. 82:932–956. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hecht PM, Ballesteros-Yanez I, Grepo N,
Knowles JA and Campbell DB: Noncoding RNA in the transcriptional
landscape of human neural progenitor cell differentiation. Front
Neurosci. 9:3922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu G, Cai J, Han Y, Chen J, Huang ZP, Chen
C, Cai Y, Huang H, Yang Y, Liu Y, et al: LincRNA-p21 regulates
neointima formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation,
apoptosis and atherosclerosis by enhancing p53 activity.
Circulation. 130:1452–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Puthanveetil P, Chen S, Feng B, Gautam A
and Chakrabarti S: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates
hyperglycaemia induced inflammatory process in the endothelial
cells. J Cell Mol Med. 19:1418–1425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leung A, Trac C, Jin W, Lanting L, Akbany
A, Sætrom P, Schones DE and Natarajan R: Novel long non-coding RNAs
are regulated by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Circ Res. 113:266–278. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leisegang MS, Fork C, Josipovic I, Richter
FM, Preussner J, Hu J, Miller MJ, Epah J, Hofmann P, Günther S, et
al: Long noncoding RNA MANTIS facilitates endothelial angiogenic
function. Circulation. 136:65–79. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhaskaran M and Mohan M: MicroRNAs:
History, biogenesis and their evolving role in animal development
and disease. Vet Pathol. 51:759–774. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen LJ, Lim SH, Yeh YT, Lien SC and Chiu
JJ: Roles of microRNAs in atherosclerosis and restenosis. J Biomed
Sci. 19:79–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN and
Bobryshev YV: Human miR-221/222 in physiological and
atherosclerotic vascular remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 15:1216–1229.
2015.
|
|
20
|
Landskroner-Eiger S, Qiu C, Perrotta P,
Siragusa M, Lee MY, Ulrich V, Luciano AK, Zhuang ZW, Corti F,
Simons M, et al: Endothelial miR-17~92 cluster negatively regulates
arteriogenesis via miRNA-19 repression of WNT signaling. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:12812–12817. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haque R, Iuvone PM, He L, Choi KSC, Ngo A,
Gokhale S, Aseem M and Park D: The MicroRNA-21 signaling pathway is
involved in prorenin receptor (PRR)-induced VEGF expression in
ARPE-19 cells under a hyperglycemic condition. Mol Vision.
23:251–262. 2017.
|
|
22
|
Luo M, Tan X, Mu L, Luo Y, Li R, Deng X,
Chen N, Ren M, Li Y, Wang L, et al: MiRNA-21 mediates the
antiangiogenic activity of metformin through targeting PTEN and
SMAD7 expression and PI3K/AKT pathway. Sci Rep. 7:4521–4534.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Uchida S and Dimmeler S: Long noncoding
RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 116:737–750. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang BY, Jin Z and Zhao Z: Long
intergenic noncoding RNA 00305 sponges miR-136 to regulate the
hypoxia induced apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 94:238–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Zhu H and Ge J: Long noncoding RNA:
Recent updates in atherosclerosis. Int J Biol Sci. 12:898–910.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu L, Wu Z, Chen Y, Zhu Q, Hamidi S and
Navab R: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation,
invasion, migration and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2
in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One.
9:5324–5337. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Sabatel C, Malvaux L, Bovy N, Deroanne C,
Lambert V, Gonzalez ML, Colige A, Rakic JM, Noël A, Martial JA and
Struman I: MicroRNA-21 exhibits antiangiogenic function by
targeting rhob expression in endothelial cells. PLoS One.
6:6548–6560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Osborn EA and Jaffer FA: Imaging
inflammation and neovascularization in atherosclerosis: Clinical
and translational molecular and structural imaging targets. Curr
Opin Cardiol. 30:671–680. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
De León H, Boué S, Schlage WK, Boukharov
N, Westra JW, Gebel S, Van Hooser A, Talikka M, Fields RB,
Veljkovic E, et al: A vascular biology network model focused on
inflammatory processes to investigate atherogenesis and plaque
instability. J Transl Med. 12:1852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luo D, Luo Y, He Y, Zhang H, Zhang R, Li
X, Dobrucki WL, Sinusas AJ, Sessa WC and Min W: Differential
functions of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 signaling in
ischemia-mediated arteriogenesis and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol.
169:1886–1898. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ulitsky I and Bartel DP: lincRNAs:
Genomics, evolution and mechanisms. Cell. 154:26–46. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Di Gesualdo F, Capaccioli S and Lulli M: A
pathophysiological view of the long non-coding RNA world.
Oncotarget. 5:10976–10996. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gomes CPC, Spencer H, Ford KL, Michel LYM,
Baker AH, Emanueli C, Balligand JL and Devaux Y: Cardiolinc
network: The function and therapeutic potential of long Non-coding
RNAs in cardiovascular development and disease. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 8:494–507. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boulberdaa M, Scott E, Ballantyne M,
Garcia R, Descamps B, Angelini GD, Brittan M, Hunter A, McBride M,
McClure J, et al: A role for the Long Noncoding RNA SENCR in
commitment and function of endothelial cells. Mol Ther. 24:978–990.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yan B, Yao J, Liu JY, Li XM, Wang XQ, Li
YJ, Tao ZF, Song YC, Chen Q and Jiang Q: lncRNA-MIAT regulates
microvascular dysfunction by functioning as a competing endogenous
RNA. Circ Res. 116:1143–1156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li K, Blum Y, Verma A, Liu Z, Pramanik K,
Leigh NR, Chun CZ, Samant GV, Zhao B, Garnaas MK, et al: A
noncoding antisense RNA in tie-1 locus regulates tie-1 function in
vivo. Blood. 115:133–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu W, Huang SY, Su L, Zhao BX and Miao JY:
Long Noncoding RNA LOC100129973 suppresses apoptosis by targeting
miR-4707-5p and miR-4767 in vascular endothelial cells. Sci Rep.
6:9533–9547. 2016.
|
|
40
|
Yang R, Li P, Zhang G, Lu C, Wang H and
Zhao G: Long non-coding RNA XLOC_008466 functions as an oncogene in
human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-874. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:126–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cerezo AB, Hornedo-Ortega R,
Alvarez-Fernandez MA, Troncoso AM and Garcia-Parrilla MC:
Inhibition of VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 activation and HUVEC migration
by melatonin and other bioactive indolic compounds. Nutrients.
9:E2492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|