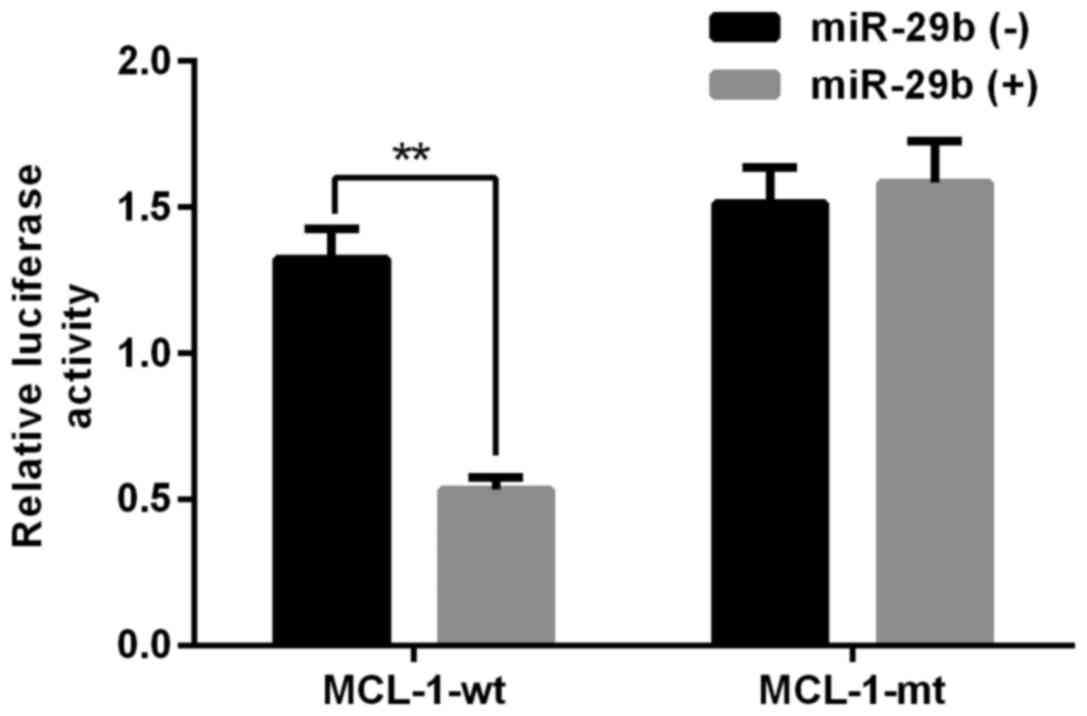
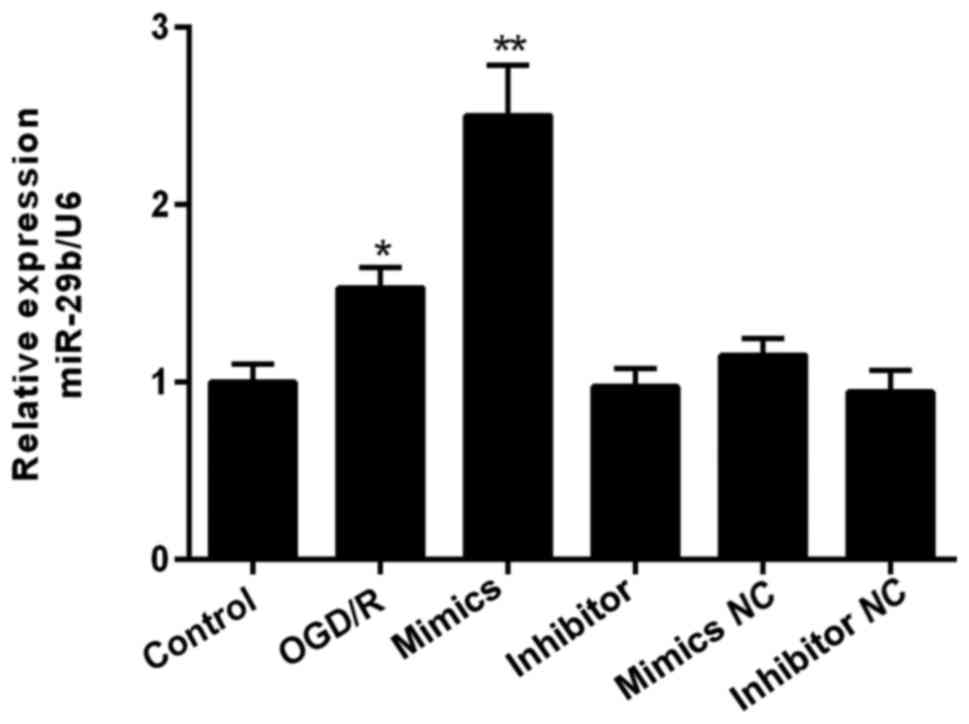
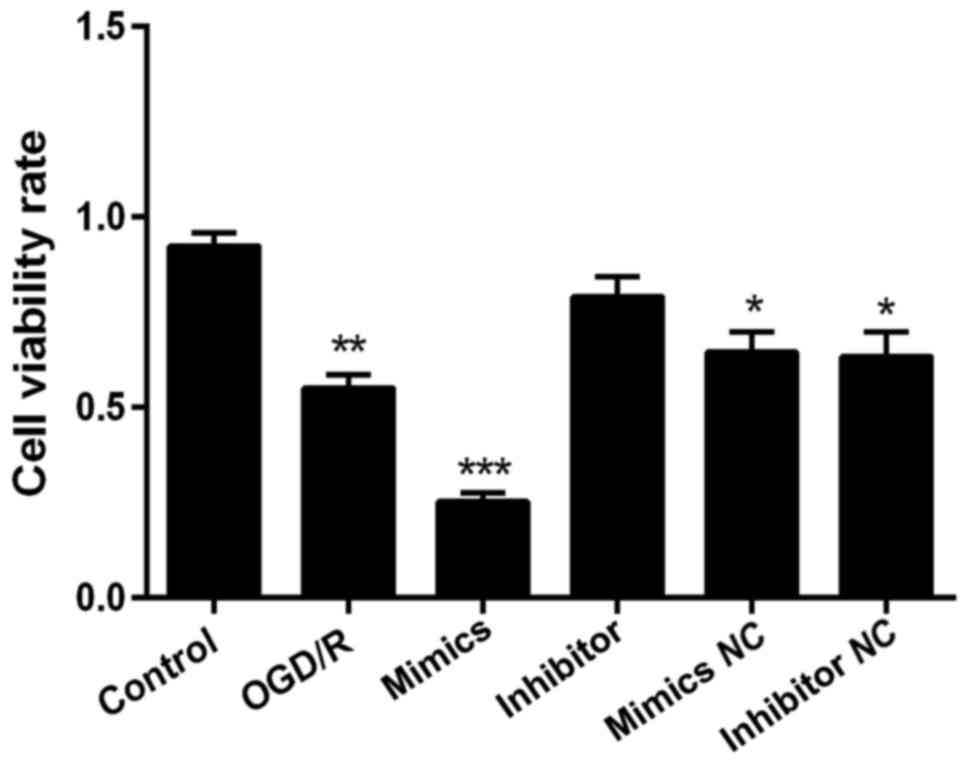
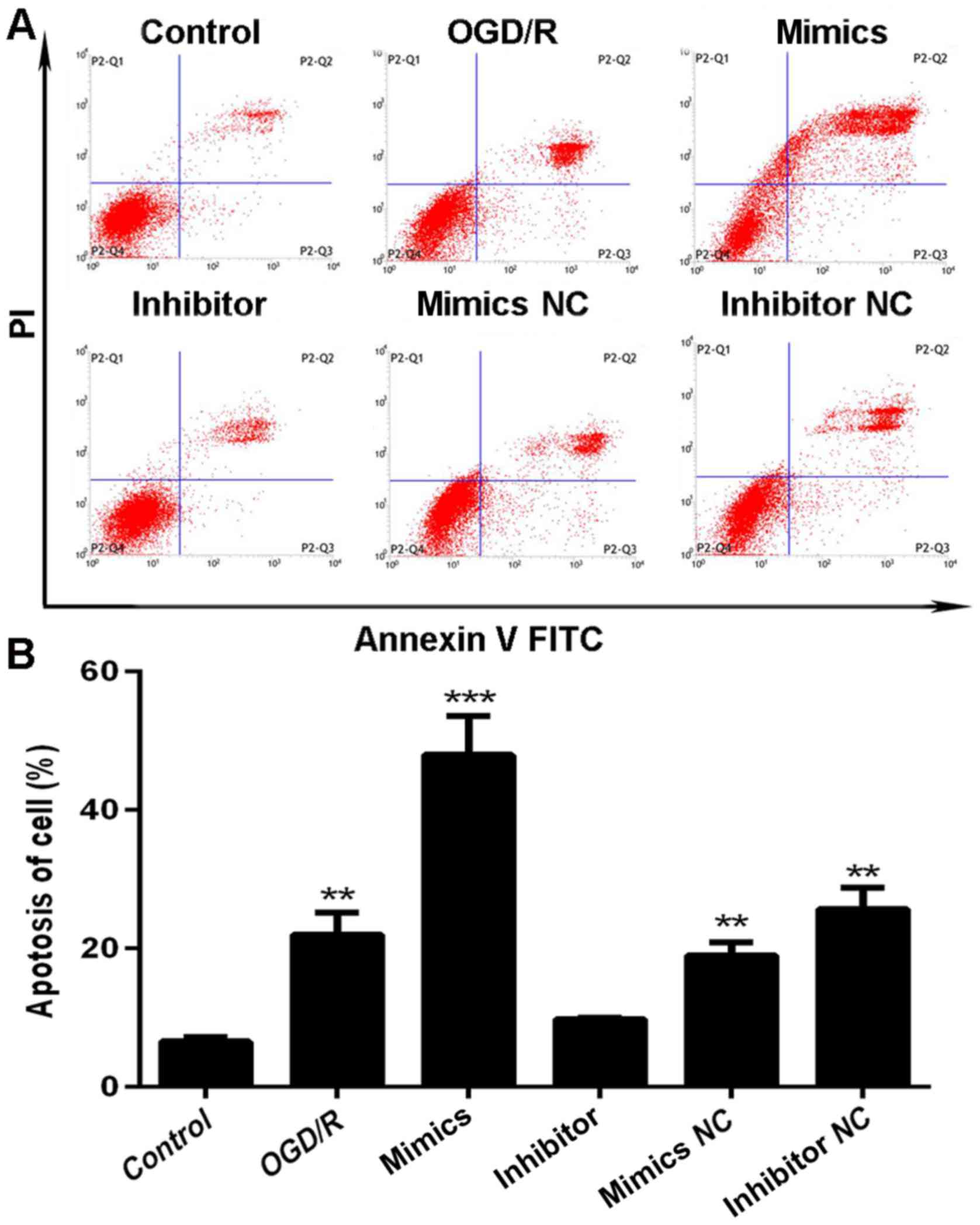
|
1
|
Zhai WW, Sun L, Yu ZQ and Chen G:
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in experimental and clinical stroke. Med
Gas Res. 6:111–118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang W, Zhao L, Bai F, Zhang T, Dong H and
Liu L: The protective effect of dopamine against OGD/R
injury-induced cell death in HT22 mouse hippocampal cells. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 42:176–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fluri F, Schuhmann MK and Kleinschnitz C:
Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical
research. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:3445–3454. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ni J, Wang X, Chen S, Liu H, Wang Y, Xu X,
Cheng J, Jia J and Zhen X: MicroRNA let-7c-5p protects against
cerebral ischemia injury via mechanisms involving the inhibition of
microglia activation. Brain Behav Immun. 49:75–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zuo XL, Deng HL, Wu P and Xu E: Do
different reperfusion methods affect the outcomes of stroke induced
by MCAO in adult rats? Int J Neurosci. 126:850–855. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li F, Shi W, Zhao EY, Geng X, Li X, Peng
C, Shen J, Wang S and Ding Y: Enhanced apoptosis from early
physical exercise rehabilitation following ischemic stroke. J
Neurosci Res. 95:1017–1024. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Gasperi R, Graham ZA, Harlow LM, Bauman
WA, Qin W and Cardozo CP: The signature of microRNA dysregulation
in muscle paralyzed by spinal cord injury includes downregulation
of microRNAs that target myostatin signaling. PLoS One.
11:e01661892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia HF, Jin XH, Cao ZF, Hu Y and Ma X:
MicroRNA expression and regulation in the uterus during embryo
implantation in rat. FEBS J. 281:1872–1891. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Floris I, Kraft JD and Altosaar I: Roles
of MicroRNA across prenatal and postnatal periods. Int J Mol Sci.
17:E19942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W and
Xuming M: MicroRNAs expression and function in cerebral ischemia
reperfusion injury. J Mol Neurosci. 53:242–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jafarinejad-Farsangi S, Farazmand A,
Mahmoudi M, Gharibdoost F, Karimizadeh E, Noorbakhsh F, Faridani H
and Jamshidi AR: MicroRNA-29a induces apoptosis via increasing the
Bax: Bcl-2 ratio in dermal fibroblasts of patients with systemic
sclerosis. Autoimmunity. 48:369–378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu L, Xu Y, Jing Z, Wang X, Zha X, Zeng C,
Chen S, Yang L, Luo G, Li B and Li Y: Altered expression pattern of
miR-29a, miR-29b and the target genes in myeloid leukemia. Exp
Hematol Oncol. 3:172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF and Gores
GJ: mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 26:6133–6140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang YK, Wang H, Leng Y, Li ZL, Yang YF,
Xiao FJ, Li QF, Chen XQ and Wang LS: Overexpression of microRNA-29b
induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells through down regulating
Mcl-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 414:233–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Altintas O, Ozgen Altintas M, Kumas M and
Asil T: Neuroprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning via
modulating the expression of cerebral miRNAs against transient
cerebral ischemia in diabetic rats. Neurol Res. 38:1003–1011. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Annis RP, Swahari V, Nakamura A, Xie AX,
Hammond SM and Deshmukh M: Mature neurons dynamically restrict
apoptosis via redundant premitochondrial brakes. Febs J.
283:4569–4582. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Delgado-Soler L, Del Mar Orzaez M and
Rubio-Martinez J: Structure-based approach to the design of BakBH3
mimetic peptides with increased helical propensity. J Mol Model.
19:4305–4318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Santiveri CM, Sborgi L and de Alba E:
Nuclear magnetic resonance study of protein-protein interactions
involving apoptosis regulator Diva (Boo) and the BH3 domain of
proapoptotic Bcl-2 members. J Mol Recognit. 25:665–673. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Smits C, Czabotar PE, Hinds MG and Day CL:
Structural plasticity underpins promiscuous binding of the
prosurvival protein A1. Structure. 16:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dewson G: Characterizing Bcl-2 family
protein conformation and oligomerization using cross-linking and
antibody gel-shift in conjunction with native PAGE. Methods Mol
Biol. 1419:185–196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi H, Sun BL, Zhang J, Lu S, Zhang P,
Wang H, Yu Q, Stetler RA, Vosler PS, Chen J and Gao Y: miR-15b
suppression of Bcl-2 contributes to cerebral ischemic injury and is
reversed by sevoflurane preconditioning. CNS Neurol Disord Drug
Targets. 12:381–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Denoyelle C, Lambert B, Meryet-Figuière M,
Vigneron N, Brotin E, Lecerf C, Abeilard E, Giffard F, Louis MH,
Gauduchon P, et al: miR-491-5p-induced apoptosis in ovarian
carcinoma depends on the direct inhibition of both BCL-XL and EGFR
leading to BIM activation. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|