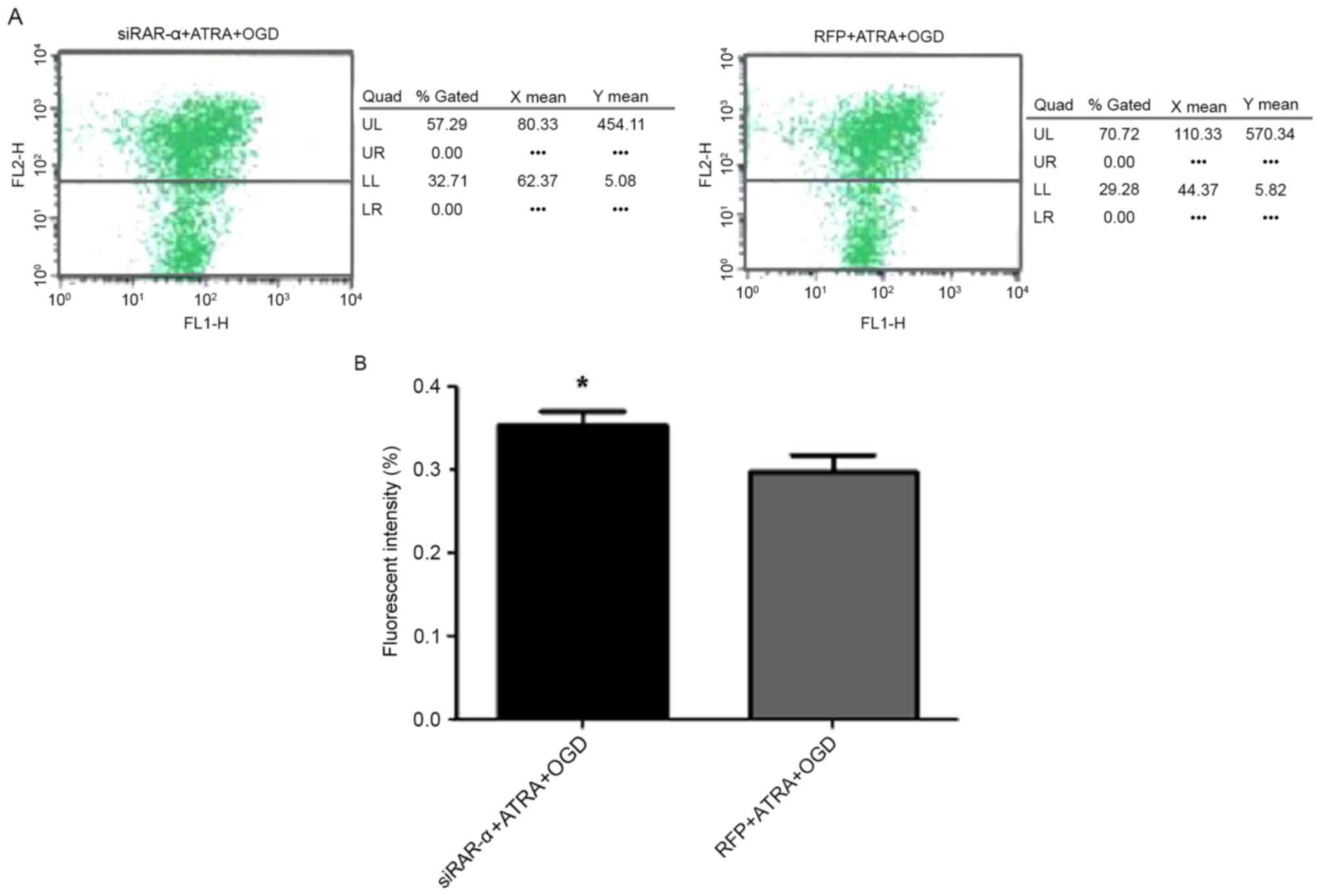
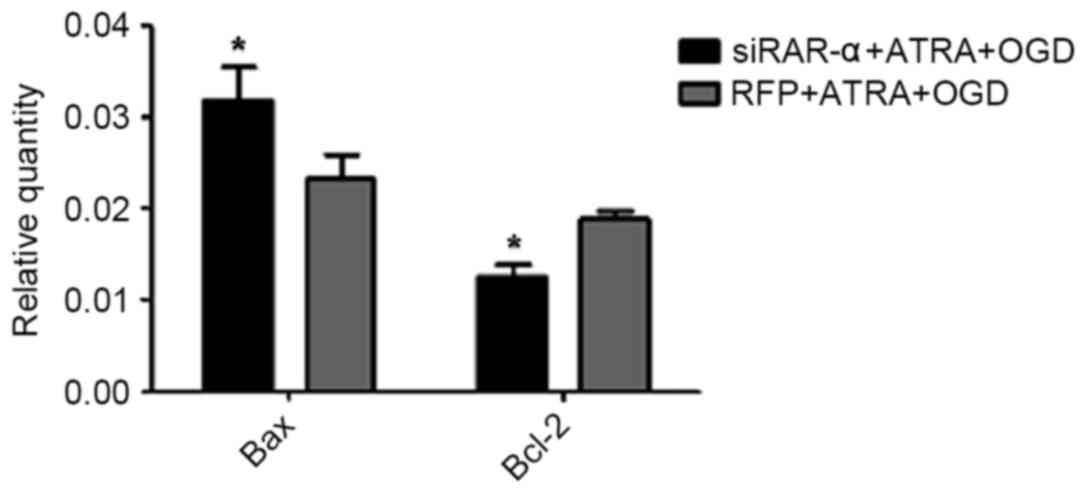
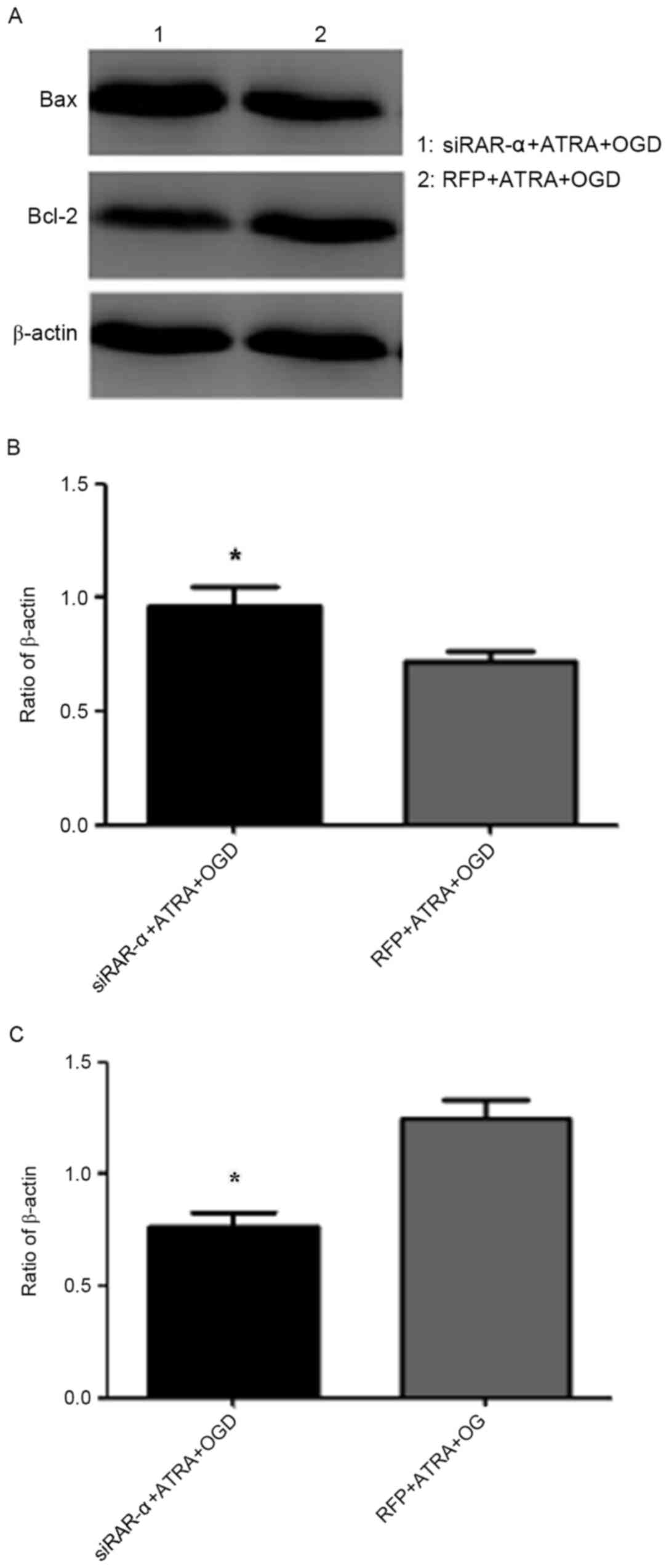
|
1
|
Xue BP: Advance in the treatment of
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Yi Xue Xin Xi. 24:25712011.
|
|
2
|
Fatemi A, Wilson MA and Johnston MV:
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the term infant. Clin Perinatol.
36:835–858, vii. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang XL, Zhao YS, Yang YJ, Xie M and Yu
XH: Therapeutic window of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in new-borne rats. Brain Res.
1222:87–94. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo P, Lin M, Lin M, Chen Y, Yang B and He
Q: Function of retinoic acid receptor alpha and p21 in
all-trans-retinoic acid-induced acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia
apoptosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 50:1183–1189. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Westerink RH and Ewing AG: The PC12 cell
as model for neurosecretion. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 192:273–285. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun B, Taing A, Liu H, Nie G, Wang J, Fang
Y, Liu L, Xue Y, Shi J, Liao YP, Ku J, Xia T and Liu Y: Nerve
growth factor-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles promote
neuron-like PC12 Cell proliferation and neurite growth. J Nanosci
Nanotechnol. 16:2390–2393. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li X, Zhang J, Zhu X, Wang P, Wang X and
Li D: Progesterone reduces inflammation and apoptosis in neonatal
rats with hypoxic ischemic brain damage through the PI3K/Akt
pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:8197–8203. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu RR and Li YD: Research progress of
interaction between Bcl-2 family and mitochondrial apoptosis
pathway. Journal of Zhong Guo Lao Nian Xue. 33:2977–2979. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Jiang W, Wen EY, Gong M, Shi Y, Chen L, Bi
Y, Zhang Y, Liu YF, Chen J, Qu P, et al: The pattern of retinoic
acid receptor expression and subcellular, anatomic and functional
area translocation during the postnatal development of the rat
cerebral cortex and white matter. Brain Res. 1382:77–87. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Yu Q, Jiang W, Bi Y, Zhang Y,
Gong M, Wei X, Li T and Chen J: All-trans retinoic acid suppresses
apoptosis in PC12 cells injured by oxygen and glucose deprivation
via the retinoic acid receptor α signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
10:2549–2555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang FF, Huang W, Li YF and Gao ZH:
Research status of siRNA non-viral delivery vector. Yao Xue Xue
Bao. 46:1436–1443. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan JC, Wang H, Xu C, Luo Z and Wu J: The
influence of centrifugal speed and time on TEM sample preparation
of culture cell. J Chongqing Med Univ. 34:1008–1010. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Henry-Mowatt J, Dive C, Martinou JC and
James D: Role of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in
apoptosis and cancer. Oncogene. 23:2850–2860. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chinopoulos C, Tretter L and Adam-Vizi V:
Depolarization of in situ mitochondria due to hydrogen
peroxide-induced oxidative stress in nerve terminals: Inhibition of
alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. J Neurochem. 73:220–228. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Maden M: Retinoic acid in the development,
regeneration and maintenance of the nervous system. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 8:755–765. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Le Doze F, Debruyne D, Albessard F, Barre
L and Defer GL: Pharmacokinetics of all-trans retinoic acid, 13-cis
retinoic acid, and fenretinide in plasma and brain of Rat. Drug
Metab Dispos. 28:205–208. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
di Masi A, Leboffe L, De Marinis E, Pagano
F, Cicconi L, Rochette-Egly C, Lo-Coco F, Ascenzi P and Nervi C:
Retinoic acid receptors: From molecular mechanisms to cancer
therapy. Mol Aspects Med. 41:1–115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo T, Wagner E, Crandall JE and Dräger
UC: A retinoic-acid critical period in the early postnatal mouse
brain. Biol Psychiatry. 56:971–980. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thompson Haskell G, Maynard TM,
Shatzmiller RA and Lamantia AS: Retinoic acid signaling at sites of
plasticity in the mature central nervous system. J Comp Neurol.
452:228–241. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goncalves MB, Boyle J, Webber DJ, Hall S,
Minger SL and Corcoran JP: Timing of the retinoid-signalling
pathway determines the expression of neuronal markers in neural
progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 278:60–70. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gottlieb DI and Huettner JE: An in vitro
pathway from embryonic stem cells to neurons and glia. Cells
Tissues Organs. 165:165–172. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Siegenthaler JA, Ashique AM, Zarbalis K,
Patterson KP, Hecht JH, Kane MA, Folias AE, Choe Y, May SR, Kume T,
et al: Retinoic acid from the meninges regulates cortical neuron
generation. Cell. 139:597–609. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mao CT, Li TY, Qu P, Zhao Y, Wang R and
Liu YX: Effects of early intervention on learning and memory in
young rats of marginal vitamin A deficiency and it's mechanism.
Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 44:15–20. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mao CT, Li TY, Liu YX and Qu P: Effects of
marginal vitamin A deficiency and intervention on learning and
memory in young rats. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 43:526–530. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shinozaki Y, Sato Y, Koizumi S, Ohno Y,
Nagao T and Inoue K: Retinoic acids acting through retinoid
receptors protect hippocampal neurons from oxygen-glucose
deprivation-mediated cell death by inhibition of c-jun-N-terminal
kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Neuroscience.
147:153–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Agudo M, Yip P, Davies M, Bradbury E,
Doherty P, McMahon S, Maden M and Corcoran JP: Aretinoic acid
receptorbeta agonist (CD2019 overcomes inhibition of axonal
outgrowth via phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in the injured
adult spinal cord. Neurobiol Dis. 37:147–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gomes MJ, Martins S and Sarmento B: siRNA
as a tool to improve the treatment of brain diseases: Mechanism,
targets and delivery. Ageing Res Rev. 21:43–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Katsuki H, Kurimoto E, Takemori S,
Kurauchi Y, Hisatsune A, Isohama Y, Izumi Y, Kume T, Shudo K and
Akaike A: Retinoic acid receptor stimulation protects midbrain
dopaminergic neurons from inflammatory degeneration via
BDNF-mediated signaling. J Neurochem. 110:707–718. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cotten CM and Shankaran S: Hypothermia for
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Expert Rev Obstet Gynecol.
5:227–239. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang ZQ and Yu H: Clinical virology. BJ:
China Medical Science Press. China; pp. 1–153. 2005
|
|
32
|
Vento M, Asensi M, Sastre J, Lloret A,
García-Sala F and Viña J: Oxidative stress in asphyxiated term
infants resuscitated with 100% oxygen. J Pediatr. 142:240–246.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park JR, Robertson K, Hickstein DD, Tsai
S, Hockenbery DM and Collins SJ: Dysregulated bcl-2 expression
inhibits apoptosis but not differentiation of retinoic acid-induced
HL-60 granulocytes. Blood. 84:440–445. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Karmakar S, Banik NL and Ray SK:
Combination of all-traps retinoic acid and pacfitaxel-induced
differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma U87MG
xenografts in nude mice. Cancer. 112:596–607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Keedwell RG, Zhao Y, Hammond LA, Qin S,
Tsang KY, Reitmair A, Molina Y, Okawa Y, Atangan LI, Shurland DL,
et al: A retinoid-related molecule that does not bind to classical
retinoid receptors potently induces apoptosis in human prostate
cancer cells through rapid caspase activation. Cancer Res.
64:3302–3312. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thin TH, Li L, Chung TK, Sun H and Taneja
R: Stra13 is induced by genotoxic stress and regulates
ionizing-radiation-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 8:401–407. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li J, Orr B, White K, Belogortseva N,
Niles R, Boskovic C, Nguyen H, Dykes A and Park M: Chmp 1 A is
amediator of the anti-proliferative effects of All-traps retinoic
acid in human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 8:72009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|