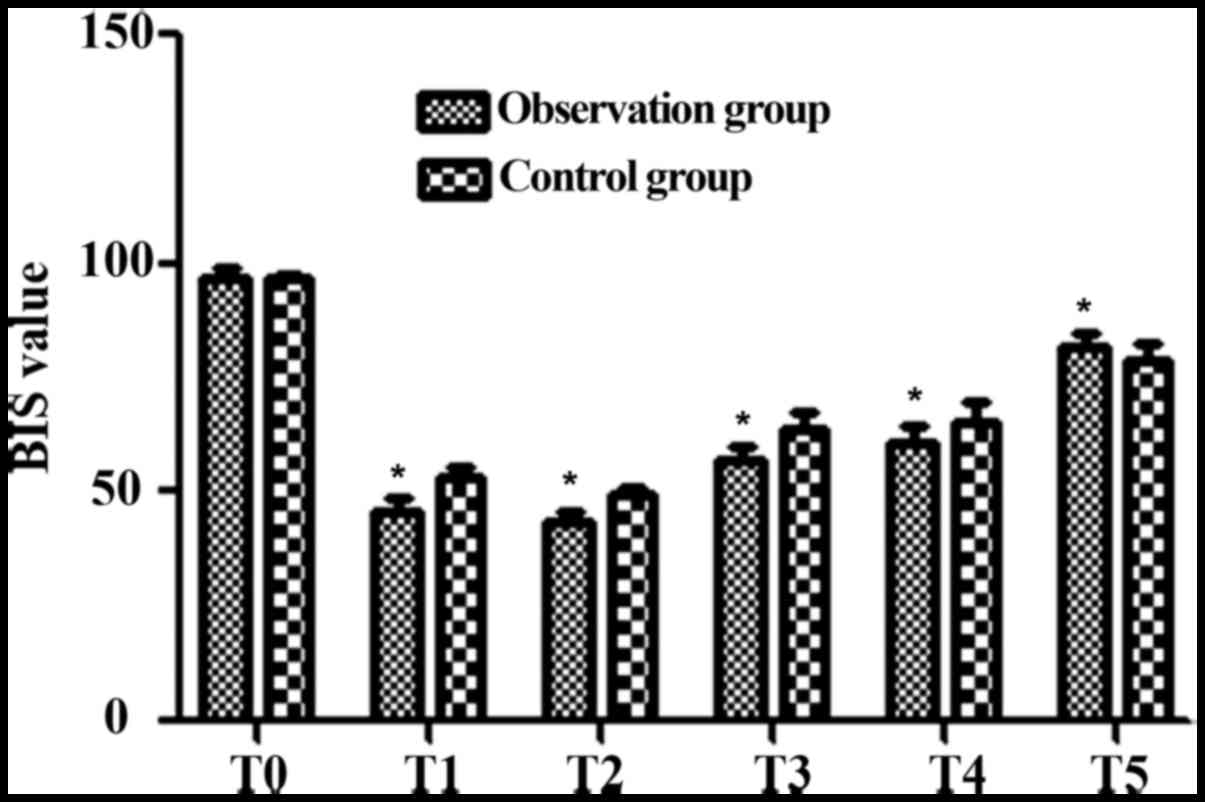
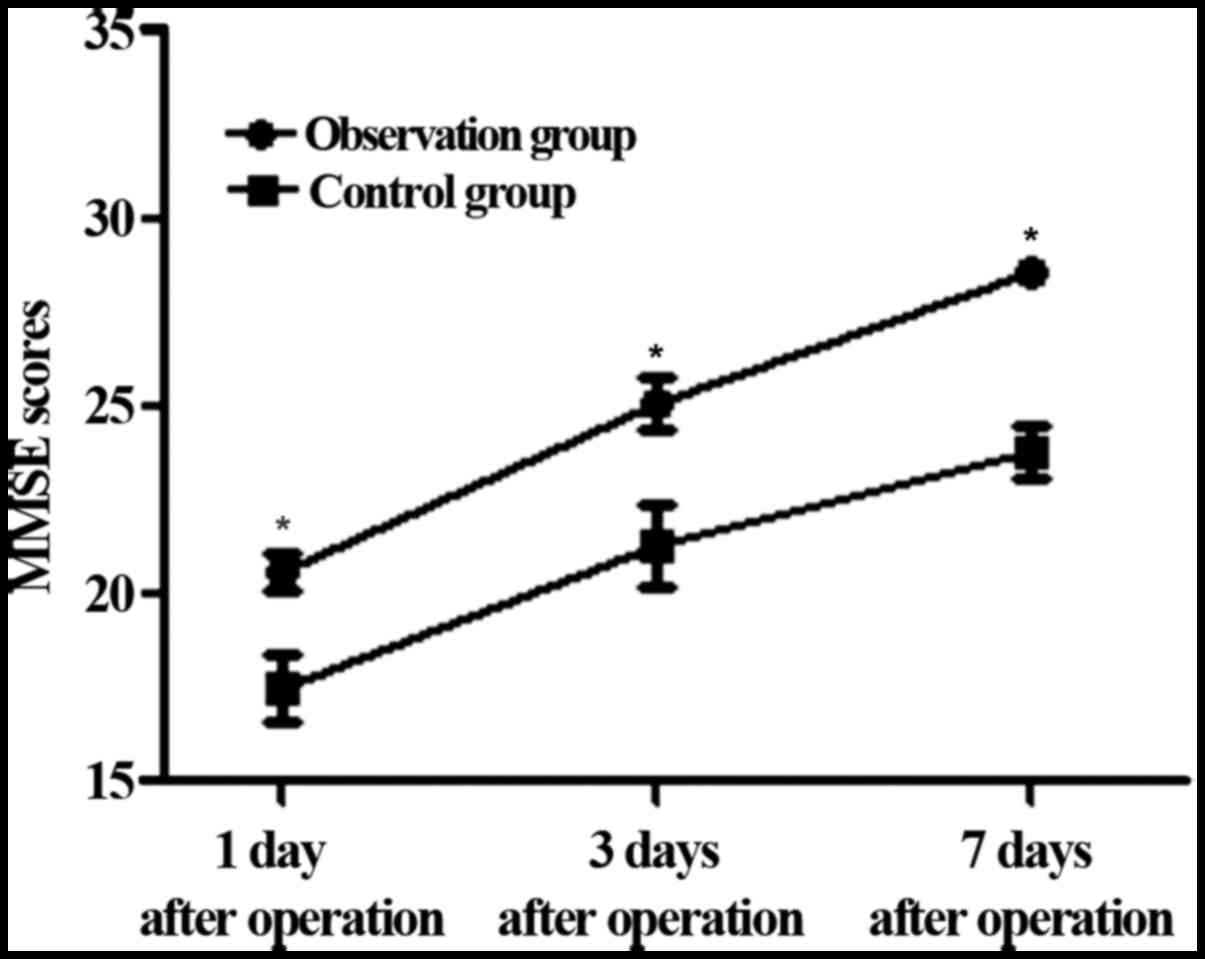
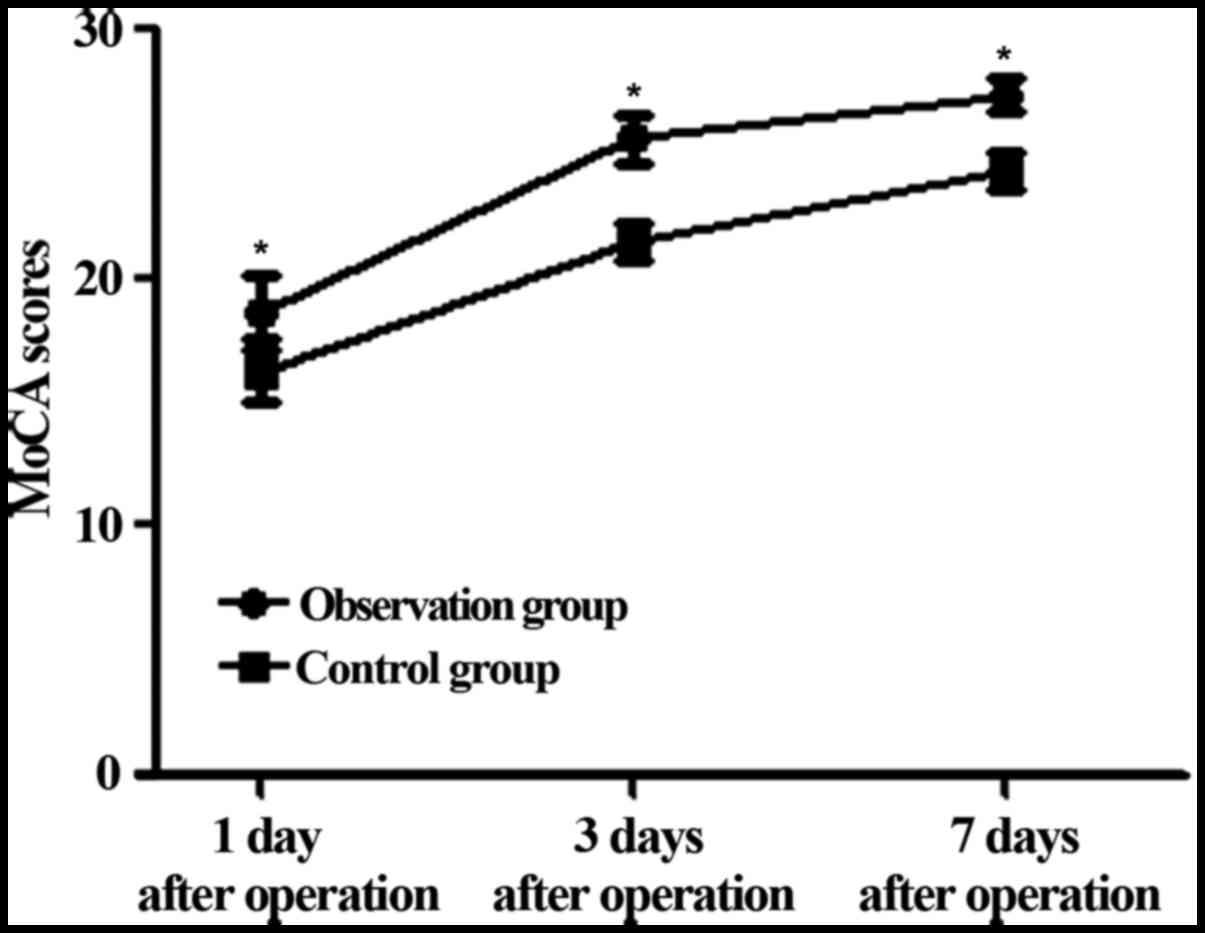
|
1
|
Jo YY, Kim JY, Lee JY, Choi CH, Chang YJ
and Kwak HJ: The effect of intraoperative dexmedetomidine on acute
kidney injury after pediatric congenital heart surgery: A
prospective randomized trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e74802017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anton-Martin P, Modem V, Taylor D, Potter
D and Darnell-Bowens C: A retrospective study of sedation and
analgesic requirements of pediatric patients on extracorporeal
membrane oxygenation (ECMO) from a single-center experience.
Perfusion. 32:183–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bulow NMH, Colpo E, Pereira RP, Correa
EFM, Waczuk EP, Duarte MF and Rocha JBT: Dexmedetomidine decreases
the inflammatory response to myocardial surgery under
mini-cardiopulmonary bypass. Braz J Med Biol Res. 49:e46462016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng X, Zuo Y, Zhao Q, Gu E and Huang Y:
Comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine and propofol on
hemodynamics and oxygen balance in children with complex congenital
heart disease undergoing cardiac surgery. Congenit Heart Dis.
10:E123–E130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klamt JG, Vicente WV, Garcia LV and
Ferreira CA: Hemodynamic effects of the combination of
dexmedetomidine-fentanyl versus midazolam-fentanyl in children
undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Rev Bras
Anestesiol. 60:350–362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tang W, Wang J, Fu GQ and Yuan L: Effect
of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on respiration and circulation
functions in patients undergoing open heart surgery under
acupuncture-assisted general anesthesia. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
39:216–221. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ueki M, Kawasaki T, Habe K, Hamada K,
Kawasaki C and Sata T: The effects of dexmedetomidine on
inflammatory mediators after cardiopulmonary bypass. Anaesthesia.
69:693–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ji F, Li Z, Young JN, Yeranossian A and
Liu H: Post-bypass dexmedetomidine use and postoperative acute
kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with
cardiopulmonary bypass. PLoS One. 8:e774462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu JG, Pensiero A, Aponte-Patel L, de
Villa Velez B, Rusanov A, Cheng B, Cabreriza SE and Spotnitz HM:
Short-term reduction in intrinsic heart rate during biventricular
pacing after cardiac surgery: A substudy of a randomized clinical
trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 146:1494–1500. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Curtis JA, Hollinger MK and Jain HB:
Propofol-based versus dexmedetomidine-based sedation in cardiac
surgery patients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 27:1289–1294. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bhaskar P, John J, Sivamurthy SK, Lone RA,
Tysarowski PA, Riyas MK, Syed SA, Bhat AN and Sallehuddin A:
Anesthetic management of an infant with Joubert syndrome for
cardiac surgery. J Clin Anesth. 25:488–490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Naguib AN, Tobias JD, Hall MW, Cismowski
MJ, Miao Y, Barry N, Preston T, Galantowicz M and Hoffman TM: The
role of different anesthetic techniques in altering the stress
response during cardiac surgery in children: A prospective,
double-blinded, and randomized study. Pediatr Crit Care Med.
14:481–490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wagner D, Pasko D, Phillips K, Waldvogel J
and Annich G: In vitro clearance of dexmedetomidine in
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Perfusion. 28:40–46. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Neema PK: Dexmedetomidine in pediatric
cardiac anesthesia. Ann Card Anaesth. 15:177–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoshitomi O, Cho S, Hara T, Shibata I,
Maekawa T, Ureshino H and Sumikawa K: Direct protective effects of
dexmedetomidine against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in
anesthetized pigs. Shock. 38:92–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kunisawa T, Ueno M, Kurosawa A, Nagashima
M, Hayashi D, Sasakawa T, Suzuki A, Takahata O and Iwasaki H:
Dexmedeto-midine can stabilize hemodynamics and spare anesthetics
before cardiopulmonary bypass. J Anesth. 25:818–822. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang J, Dinh M, Kuchle N and Zhou J:
Anesthetic management for combined mitral valve replacement and
aortic valve repair in a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Ann
Card Anaesth. 14:115–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leino K, Hynynen M, Jalonen J, Salmenperä
M, Scheinin H and Aantaa R; Dexmedetomidine in Cardiac Surgery
Study Group, : Renal effects of dexmedetomidine during coronary
artery bypass surgery: A randomized placebo-controlled study. BMC
Anesthesiol. 11:92011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Butt WW: Minimize stress and maximize
clinical outcome! Pediatr Crit Care Med. 14:1–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maldonado JR, Wysong A, van der Starre PJ,
Block T, Miller C and Reitz BA: Dexmedetomidine and the reduction
of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery. Psychosomatics.
50:206–217. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|