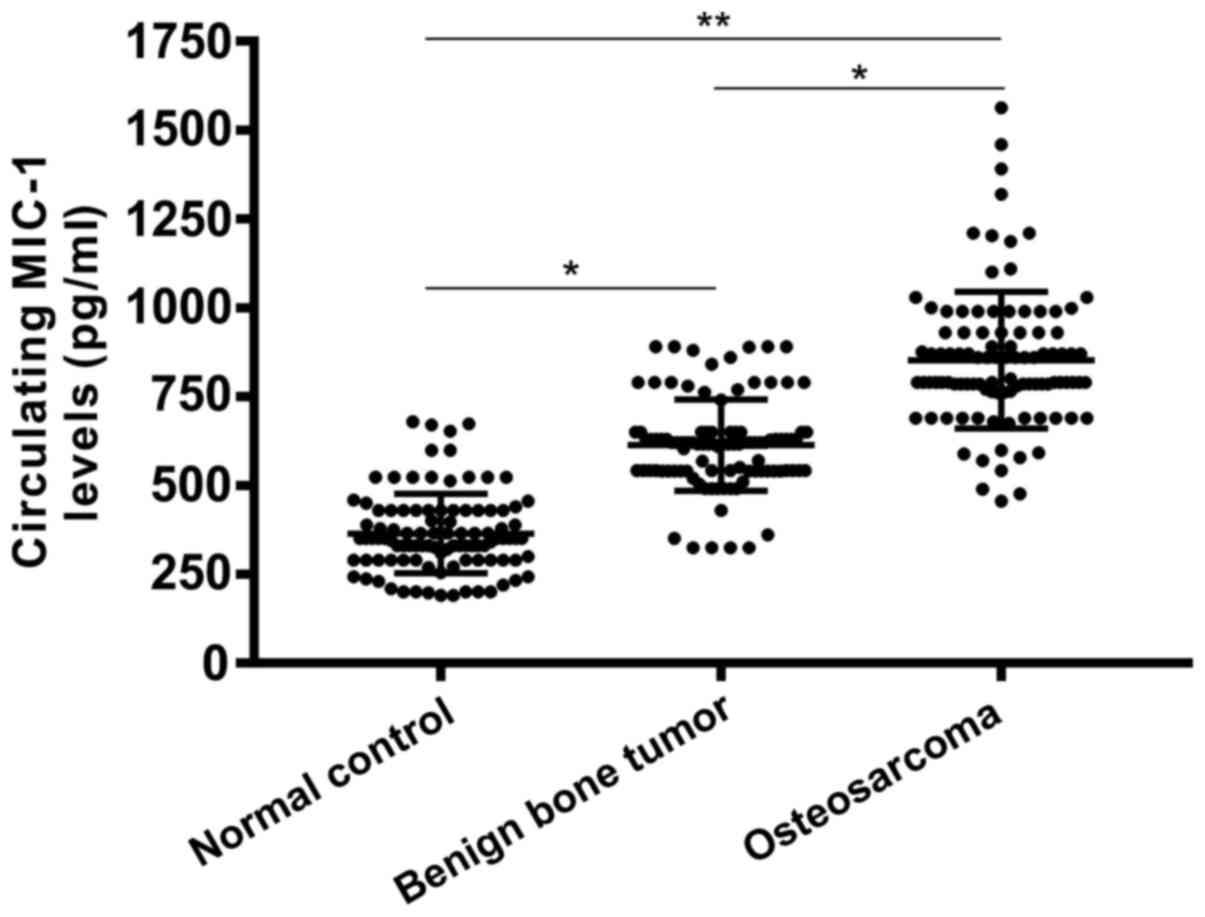
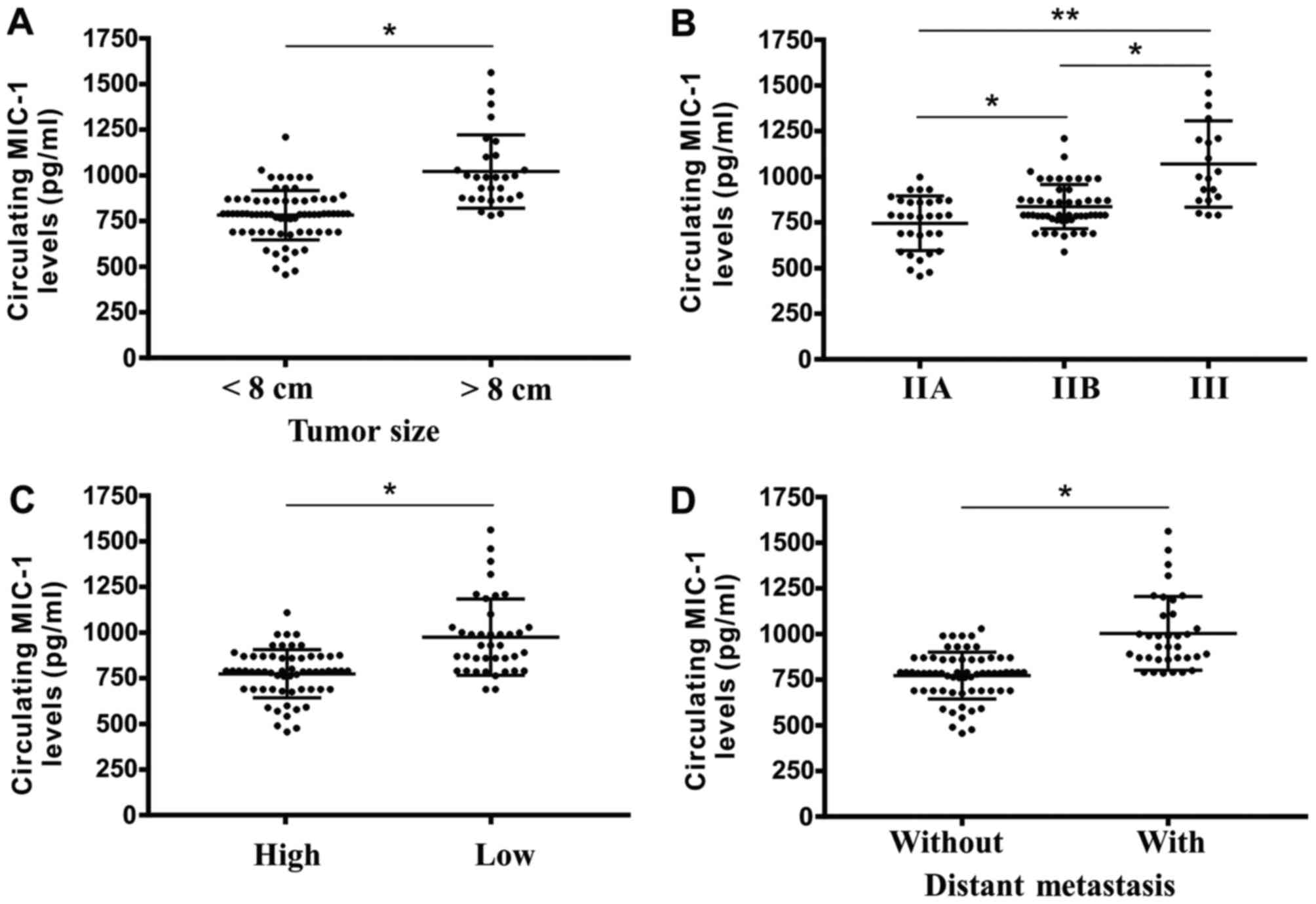
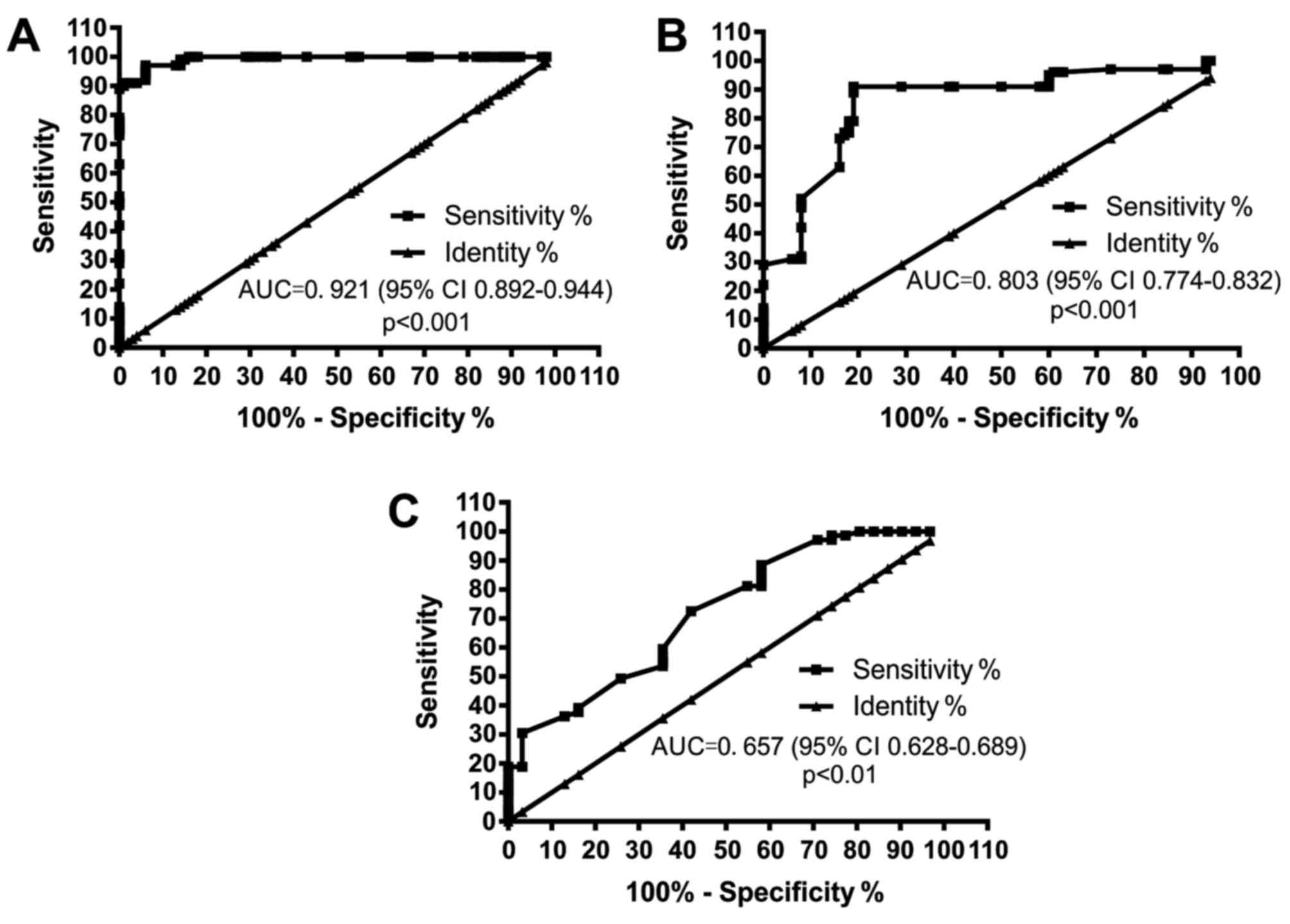
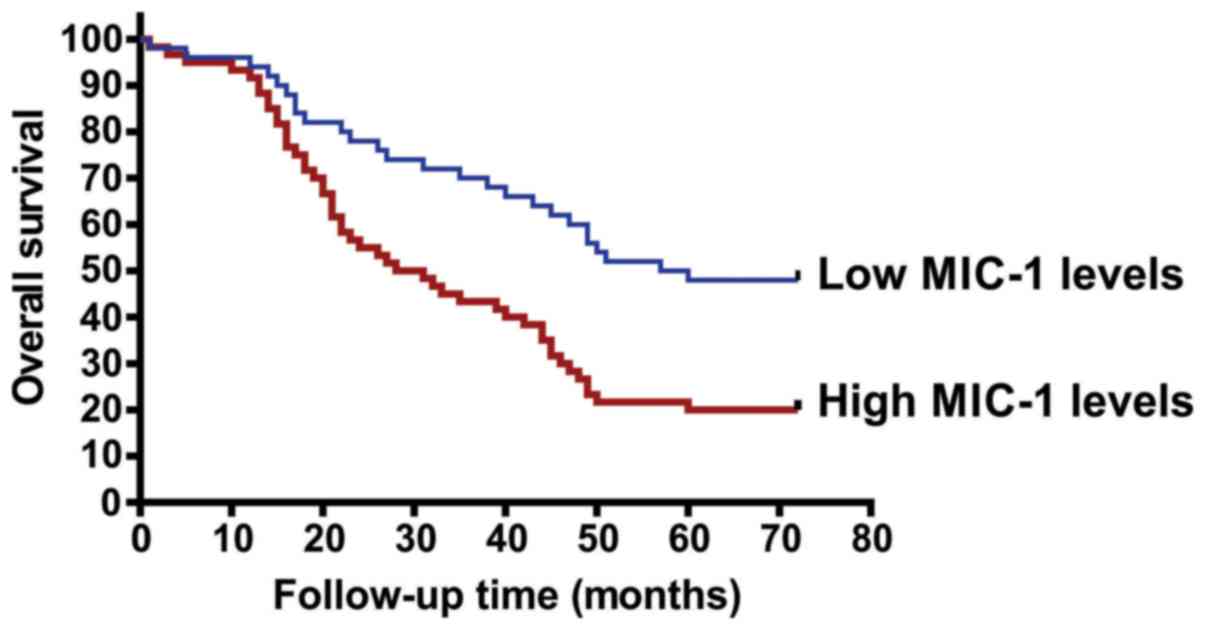
|
1
|
Geller DS and Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: A
review of diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies. Clin Adv
Hematol Oncol. 8:705–718. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Taran SJ, Taran R and Malipatil NB:
Pediatric osteosarcoma: An updated review. Indian J Med Paediatr
Oncol. 38:33–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davis AM, Bell RS and Goodwin PJ:
Prognostic factors in osteosarcoma: A critical review. J Clin
Oncol. 12:423–431. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shankar GM, Clarke MJ, Ailon T, Rhines LD,
Patel SR, Sahgal A, Laufer I, Chou D, Bilsky MH, Sciubba DM, et al:
The role of revision surgery and adjuvant therapy following
subtotal resection of osteosarcoma of the spine: A systematic
review with meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 27:97–104. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bishop MW, Janeway KA and Gorlick R:
Future directions in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Curr Opin
Pediatr. 28:26–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wan J and Zhang X, Liu T and Zhang X:
Strategies and developments of immunotherapies in osteosarcoma.
Oncol Lett. 11:511–520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hansen MF, Seton M and Merchant A:
Osteosarcoma in Paget's disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 21 Suppl
2:P58–P63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chakravarty K, Saeed IT and Fowler RW: A
fatal case of pleural osteosarcoma mimicking mesothelioma in
Paget's disease of bone. Rheumatology (Oxford). 42:1578–1579. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khaled YS, Elkord E and Ammori BJ:
Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1: A review of its pleiotropic
actions in cancer. Cancer Biomark. 11:183–190. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang J, Wen W and Sachdev PS: Macrophage
inhibitory cytokine-1/growth differentiation factor 15 as a marker
of cognitive ageing and dementia. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 29:181–186.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fuchs T, Trollor JN, Crawford J, Brown DA,
Baune BT, Samaras K, Campbell L, Breit SN, Brodaty H, Sachdev P, et
al: Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 is associated with cognitive
impairment and predicts cognitive decline-the Sydney memory and
aging study. Aging Cell. 12:882–889. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang H, Choi HJ, Park SH, Kim JS and Moon
Y: Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) and subsequent
urokinase-type plasminogen activator mediate cell death responses
by ribotoxic anisomycin in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 78:1205–1213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brown DA, Hance KW, Rogers CJ, Sansbury
LB, Albert PS, Murphy G, Laiyemo AO, Wang Z, Cross AJ, Schatzkin A,
et al: Serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1/GDF15): A
potential screening tool for the prevention of colon cancer? Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 21:337–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Broadhead ML, Clark JC, Myers DE, Dass CR
and Choong PF: The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: A
review. Sarcoma. 2011:9592482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He JP, Hao Y, Wang XL, Yang XJ, Shao JF,
Guo FJ and Feng JX: Review of the molecular pathogenesis of
osteosarcoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:5967–5976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P and
Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: Current treatment and a collaborative
pathway to success. J Clin Oncol. 33:3029–3035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Marino-Enriquez A and Bovée JV: Molecular
pathogenesis and diagnostic, prognostic and predictive molecular
markers in sarcoma. Surg Pathol Clin. 9:457–473. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Durfee RA, Mohammed M and Luu HH: Review
of osteosarcoma and current management. Rheumatol Ther. 3:221–243.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Unsicker K, Spittau B and Krieglstein K:
The multiple facets of the TGF-β family cytokine
growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:373–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Divergent
molecular mechanisms underlying the pleiotropic functions of
macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in cancer. J Cell Physiol.
224:626–635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mohamed AA, Soliman H, Ismail M, Ziada D,
Farid TM, Aref AM, Al Daly ME and Elmageed Abd ZY: Evaluation of
circulating ADH and MIC-1 as diagnostic markers in Egyptian
patients with pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 15:34–39. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Li Y, Tian H, Qi J, Li M, Fu C, Wu
F, Wang Y, Cheng D, Zhao W, et al: Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1
(MIC-1/GDF15) as a novel diagnostic serum biomarker in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:5782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu YN, Wang XB, Wang T, Zhang C, Zhang
KP, Zhi XY, Zhang W and Sun KL: Macrophage inhibitory Cytokine-1 as
a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in stage I and II
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:2026–2032. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou F, Xu X, Wu S, Cui X, Fan L and Pan
W: Protein array identification of protein markers for
serodiagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Sci Rep.
5:153492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Anderson KS, Sibani S, Wallstrom G, Qiu J,
Mendoza EA, Raphael J, Hainsworth E, Montor WR, Wong J, Park JG, et
al: Protein microarray signature of autoantibody biomarkers for the
early detection of breast cancer. J Proteome Res. 10:85–96. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aziz N: Measurement of circulating
cytokines and immune-activation markers by multiplex technology in
the clinical setting: What are we really measuring? For
Immunopathol Dis Therap. 6:19–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|